Midterm Exam
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
phosphodiesterase (PDE)
Transducin activates _________
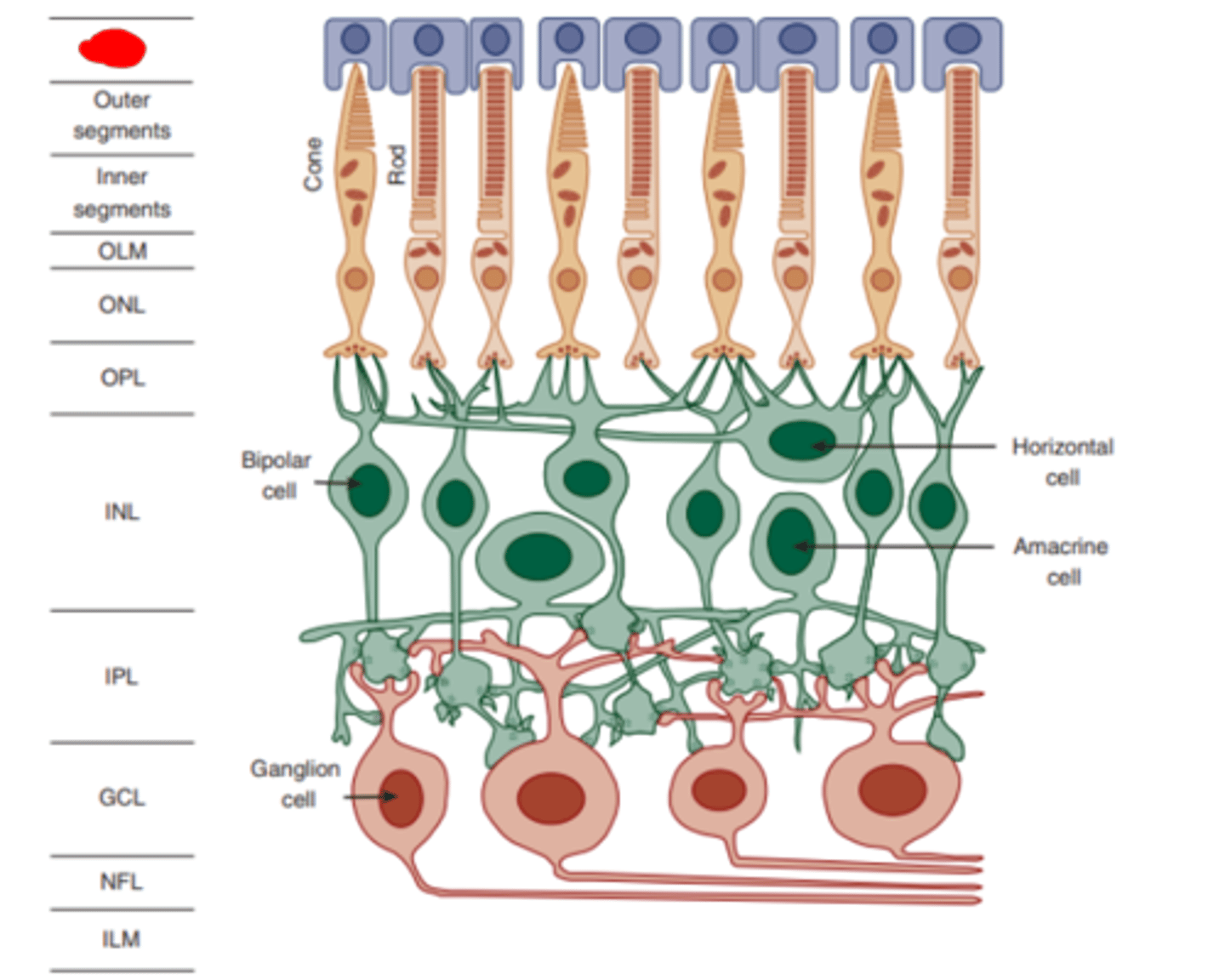
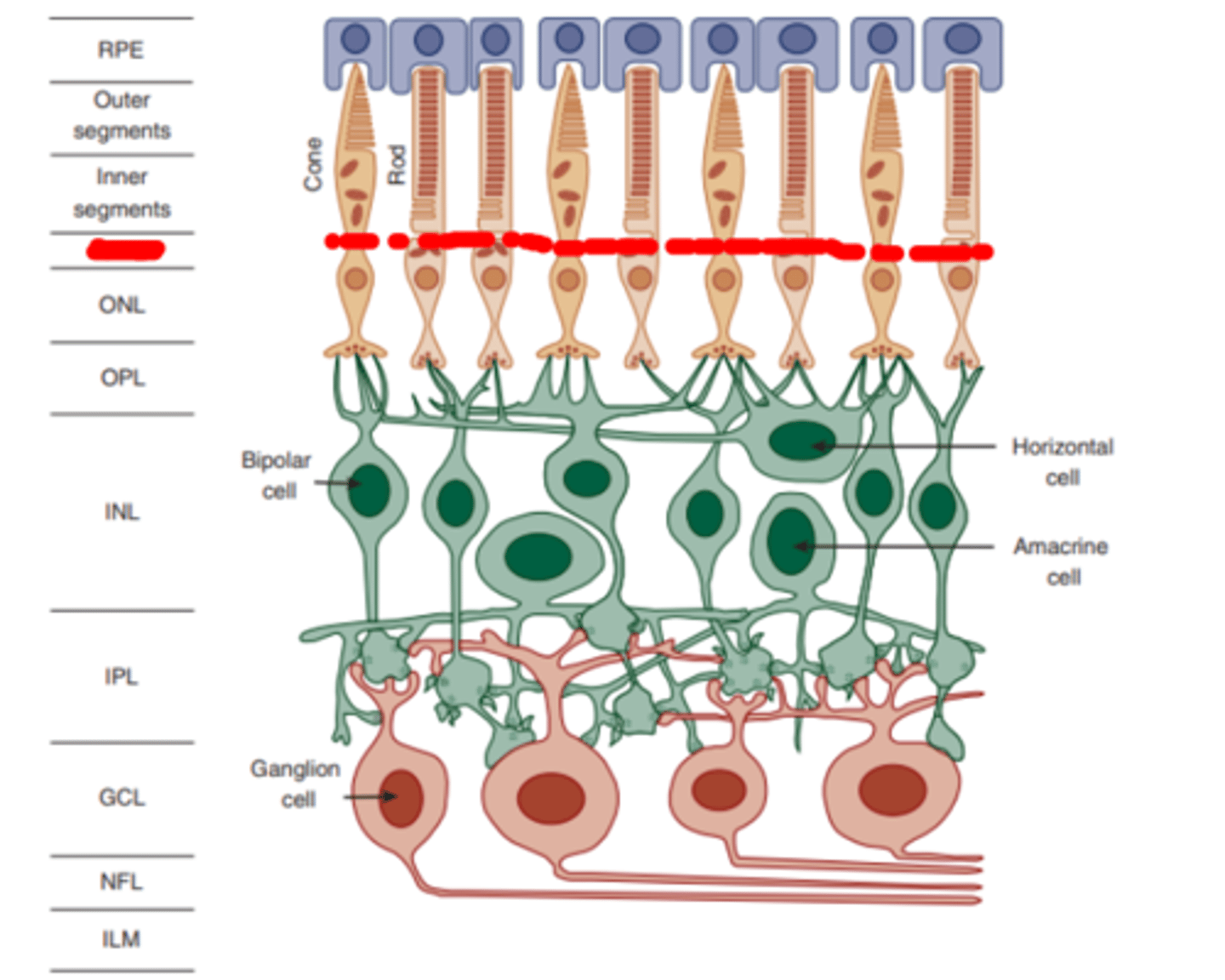
Retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE)
the outermost layer of the retina (most proximal to the choroid) which is not responsive to radiant energy, but provides crucial metabolic support including the phagocytosis of the photoreceptor outer segments. This structure also functions to reduce light scatter.
Retinitis pigmentosa
a rod-cone degenerative disease which occurs due to ineffective phagocytosis by the RPE and an accumulation of metabolic waste products.
Photoreceptors
cells that absorb light via photopigment and transform light energy into electrical activity and transmit this signal to retinal bipolar cells. They are highly metabolically active and therefore lie in the outer retina proximal to the RPE and choroid for metabolic support.
Rods
photoreceptors which are responsible for scotopic vision with no color discrimination.
Scotopic vision
vision mediated by rods occurring under dim lighting conditions. Where there is no color discrimination and poor vision acuity, but high sensitivity to dim lights.
Spherule
synaptic ending of a rod photoreceptor
rods
Outer segment discs in which photoreceptors are free floating?
Rhodopsin
the rod photopigment which can be excited by just a single photon of light. It is most sensitive to wavelengths of 507 nm
Opsin
the variable portion of the rhodopsin photopigment which determines the absorption profile.
Chromophore
portion of rhodopsin which is an altered form of retinol (vitamin A)
Univariance
principle that states once a quantum of light is absorbed by rhodopsin, all information regarding its wavelength is lost.
10, 10
___ rods must be activated by ____ quanta (total) in order to activate a single ganglion cell
507 nm
the scotopic system is most sensitive to this wavelength
Cones
photoreceptors which are responsible for photopic vision and are color sensitive.
Photopic vision
vision mediated by cones occurring under bright lighting conditions. Where there is poor sensitivity to dim lights, but great visual acuity and color discrimination.
Pedicle
synaptic ending of a cone photoreceptor.
cones
Outer segment disc in which photoreceptor are membrane bound?
Cyanolabe
S cone photopigment that is most sensitive to wavelengths of 426 nm
Chlorolabe
M cone photopigment that is most sensitive to wavelengths of 530 nm
Erythrolabe
L cone photopigment that is most sensitive to wavelengths of 557 nm
555 nm
the photopic system is most sensitive to this wavelength.
Mesopic vision
vision mediated by cones and rods occurring under intermediate lighting conditions.
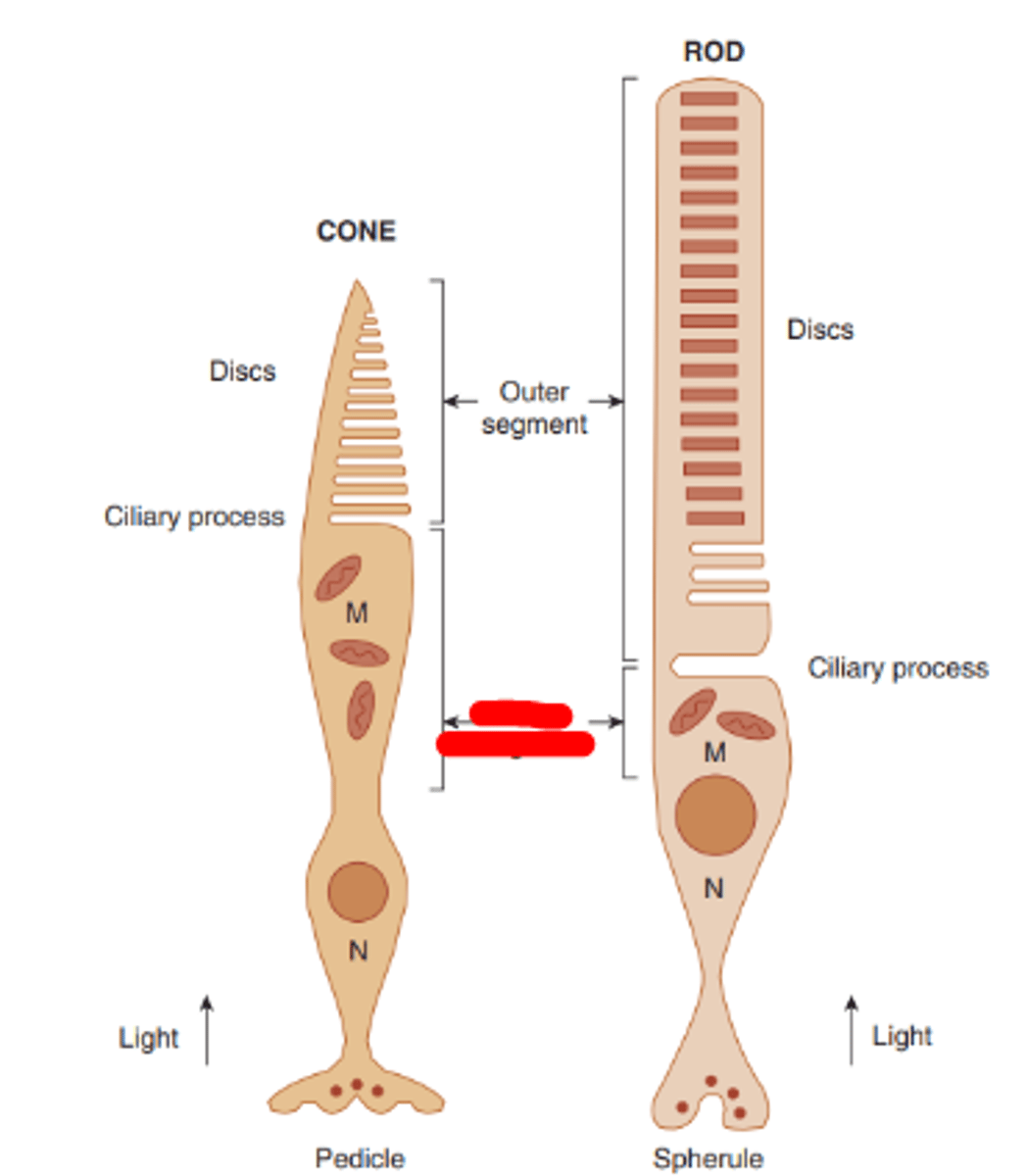
Outer segment
portion of the photoreceptor which contains photopigment that absorbs light.
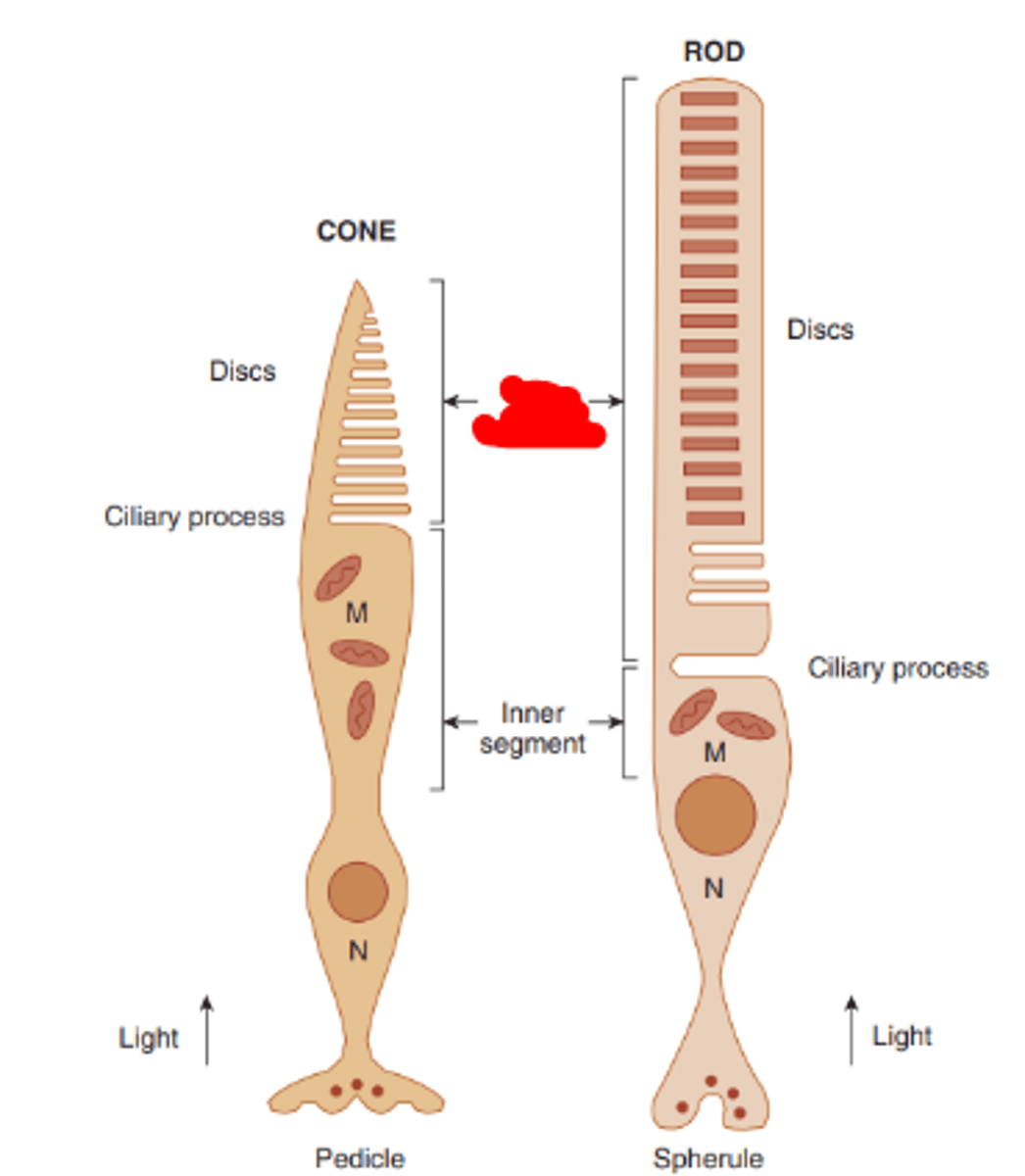
Inner segment
portion of the photoreceptor which contains all of the cell's organelles, excluding their nuclei.
Outer limiting membrane
layer of the retina formed by the interconnecting processes of Muller cells separating the inner segments of the photoreceptors from their nuclei.
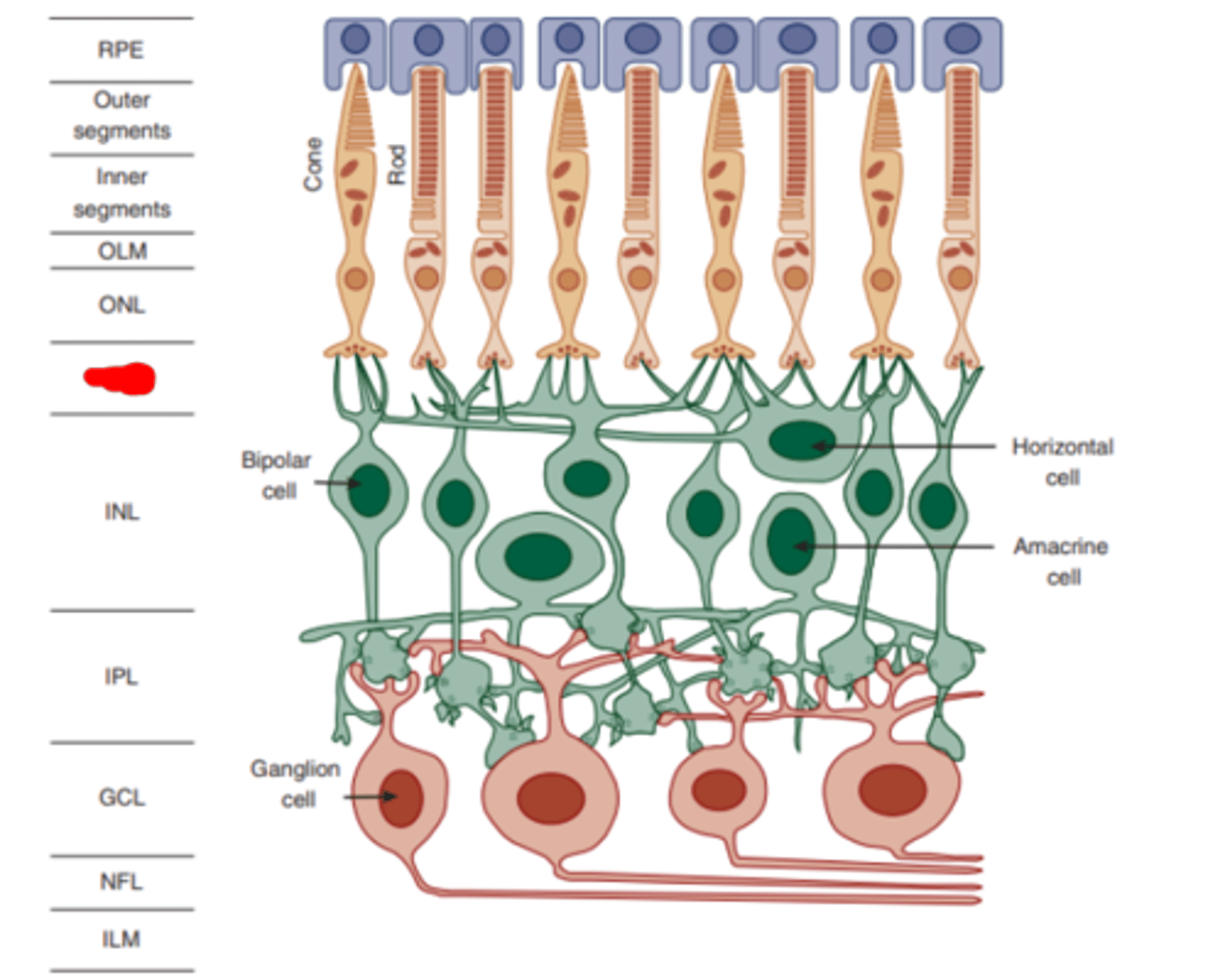
Outer nuclear layer
layer of the retina made up of photoreceptor nuclei.
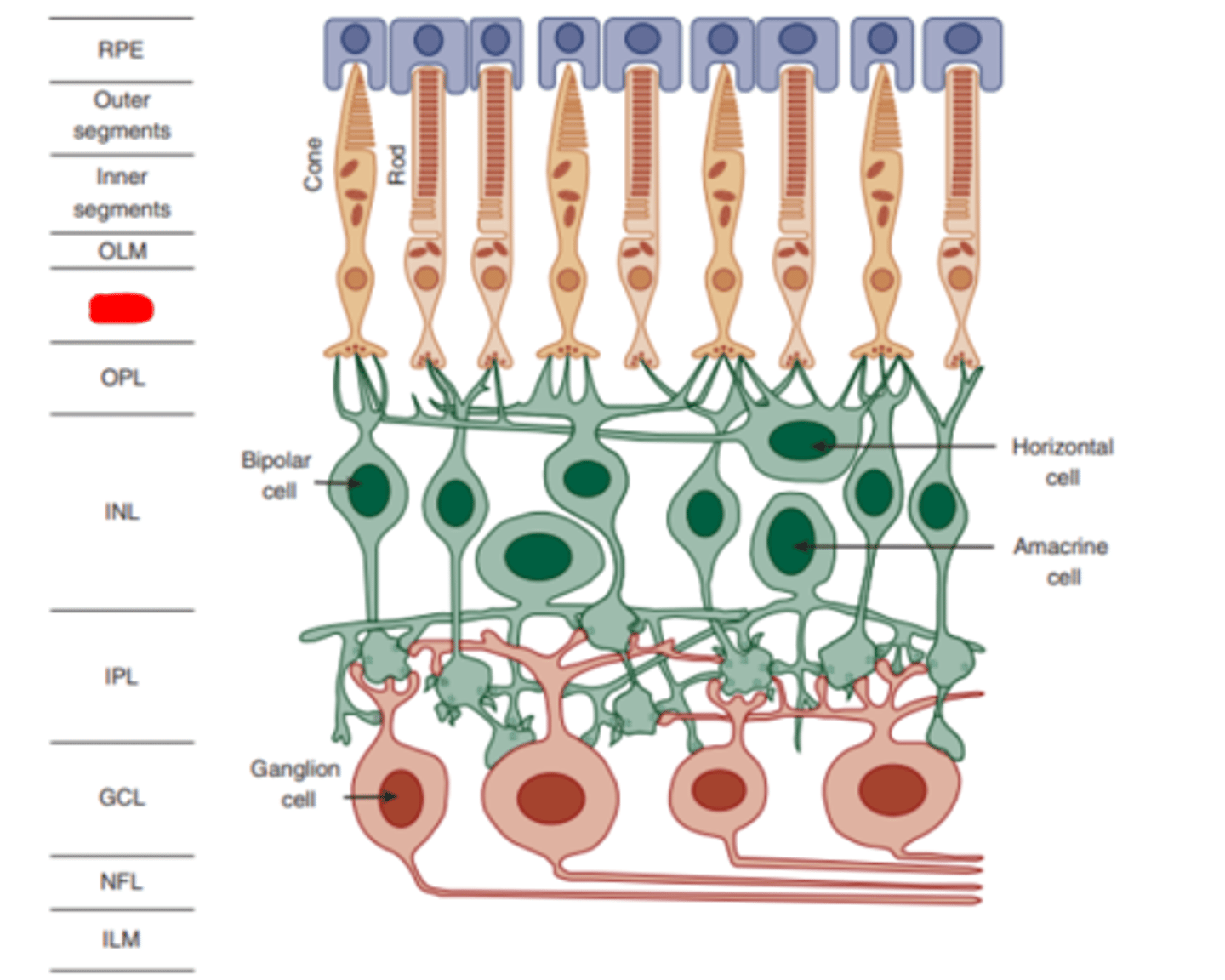
Outer plexiform layer
layer of the retina which consists of the synapses formed between the synaptic endings of the photoreceptors and the dendrites of the bipolar and horizontal cells.
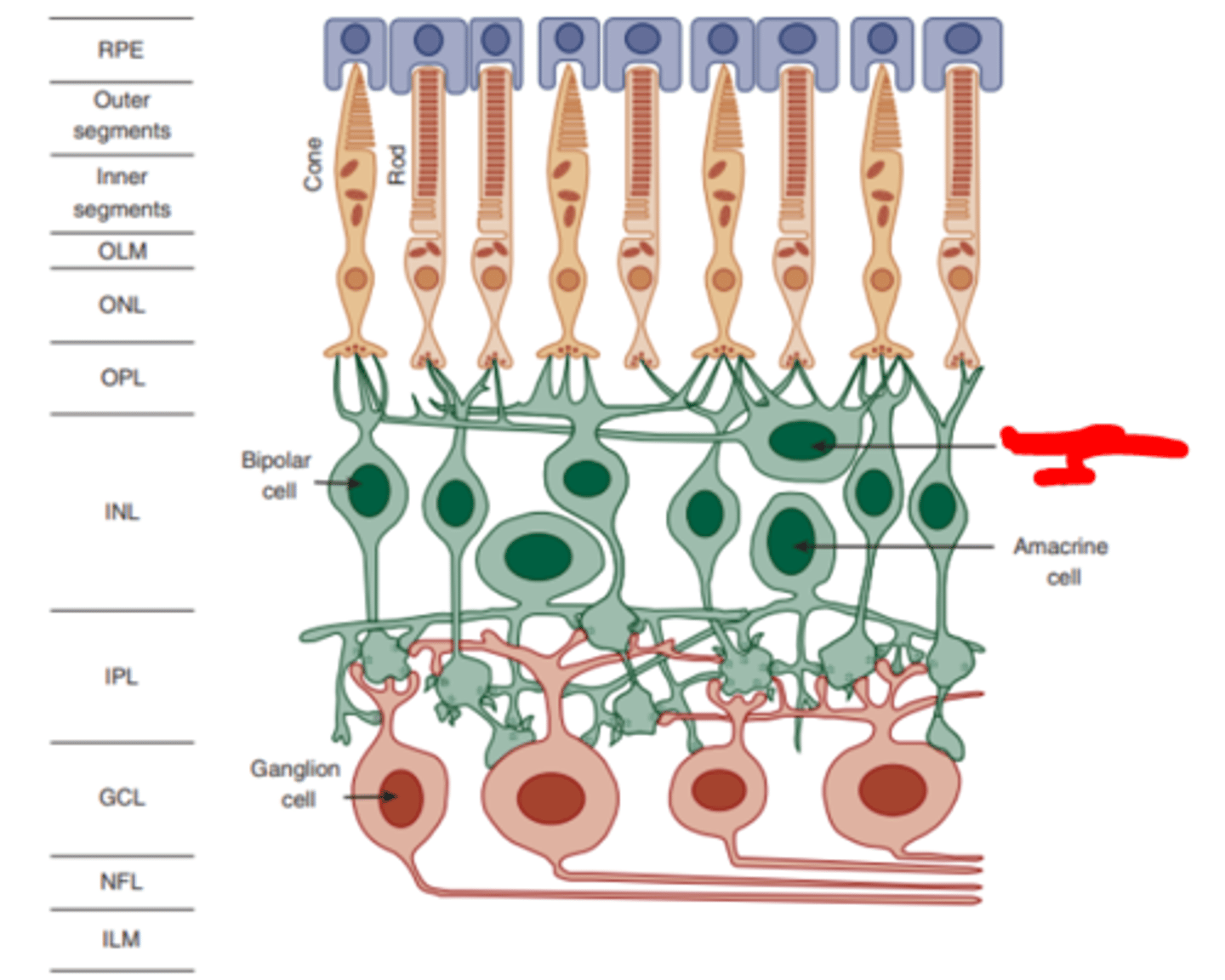
Horizontal cells
dendritic trees of these cells synapse with a large number of photoreceptors laterally manifesting substantial spatial summation. Also feed forward to bipolar cells.
H1 cells
horizontal cells the receive input primarily from M and L cones, and little input from S cones
H2 cells
horizontal cells that receive input from M and L cones, but have very strong connections with S cones as well.
Bipolar cells
cells that synapse onto ganglion cells. THE FIRST RETINAL CELLS TO DISPLAY SPATIAL ANTAGONISM (RECEPTIVE FIELDS).
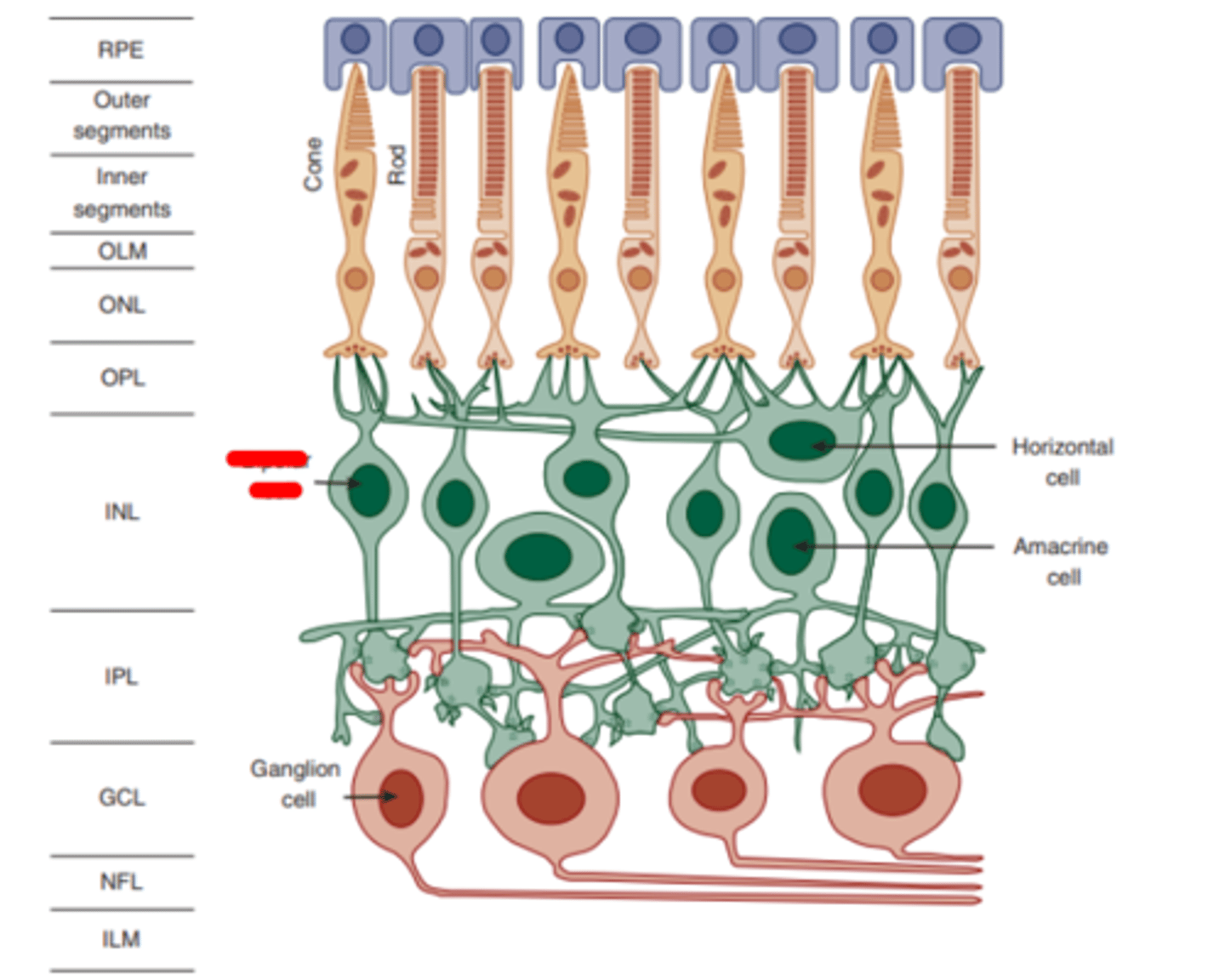
Midget bipolar cells
Bipolar cells that are smaller and synapse with midget ganglion cells.
Diffuse bipolar cells
bipolar cells that are larger and synapse with parasol ganglion cells.
S cone bipolar cells
bipolar cells that synapse with small bistratified ganglion cells.
Rod bipolar cells
bipolar cells that exclusively contact about 15-30 rods/bipolar cell.
Amacrine cells
cells of the retina that synapse laterally with bipolar cells and forward to ganglion cells. They are thought to play a critical role in coding movement because they respond transiently to a the signals they receive.
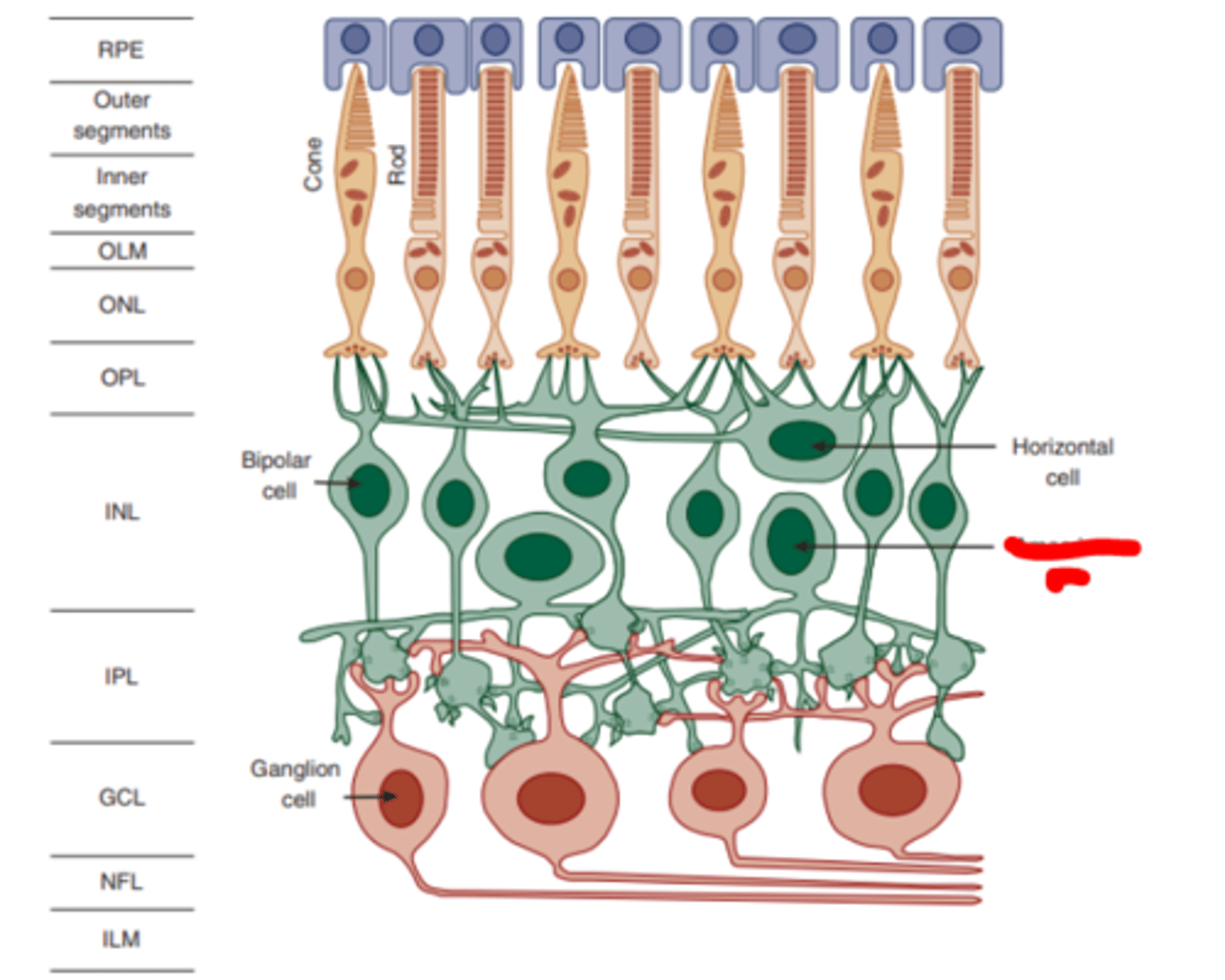
Inner nuclear layer
layer of the retina consisting of the cell bodies of the bipolar, horizontal, and amacrine cells.
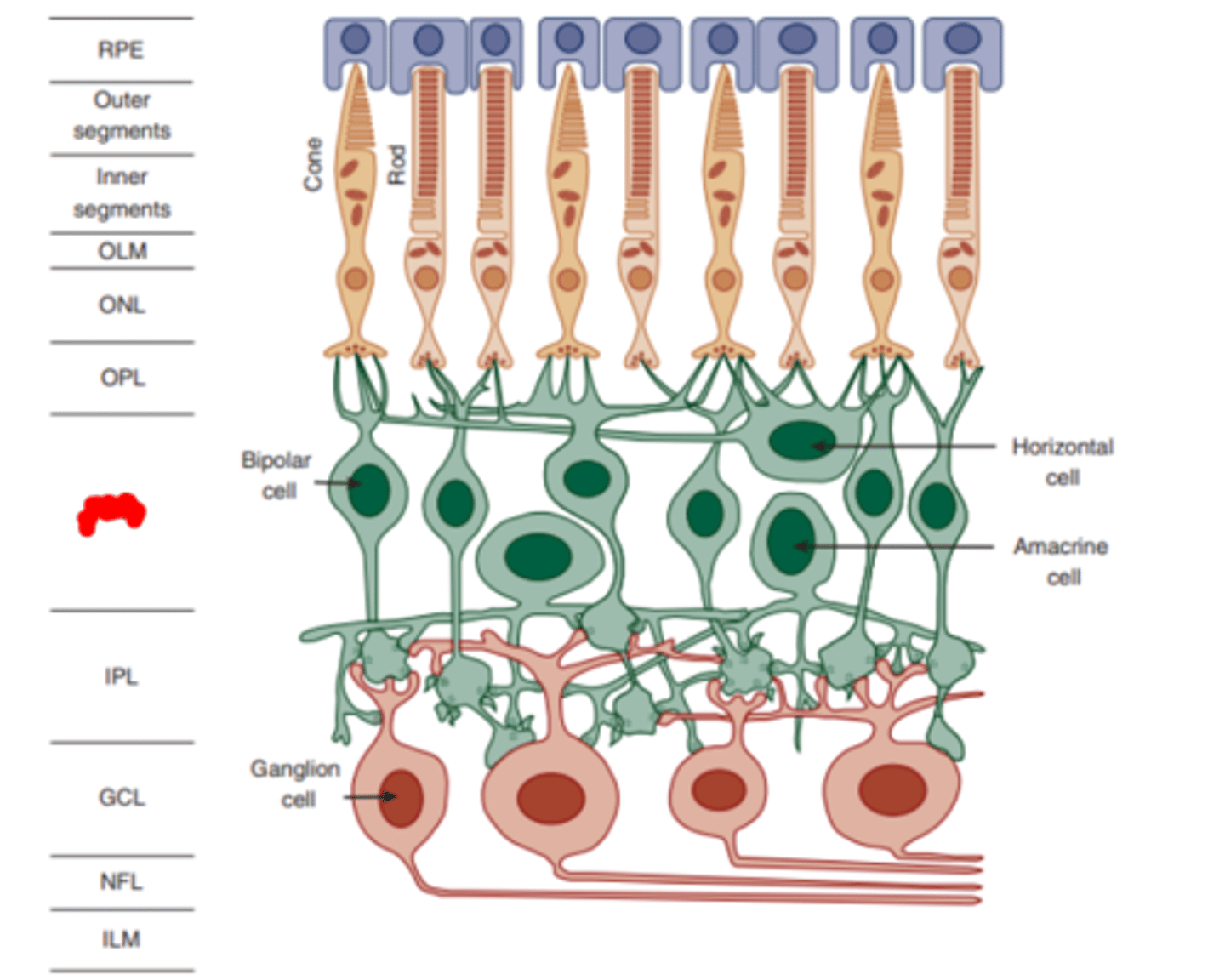
Inner plexiform layer
layer of the retina containing synapses between the synaptic endings of bipolar and amacrine cells and the dendrites of ganglion cells.
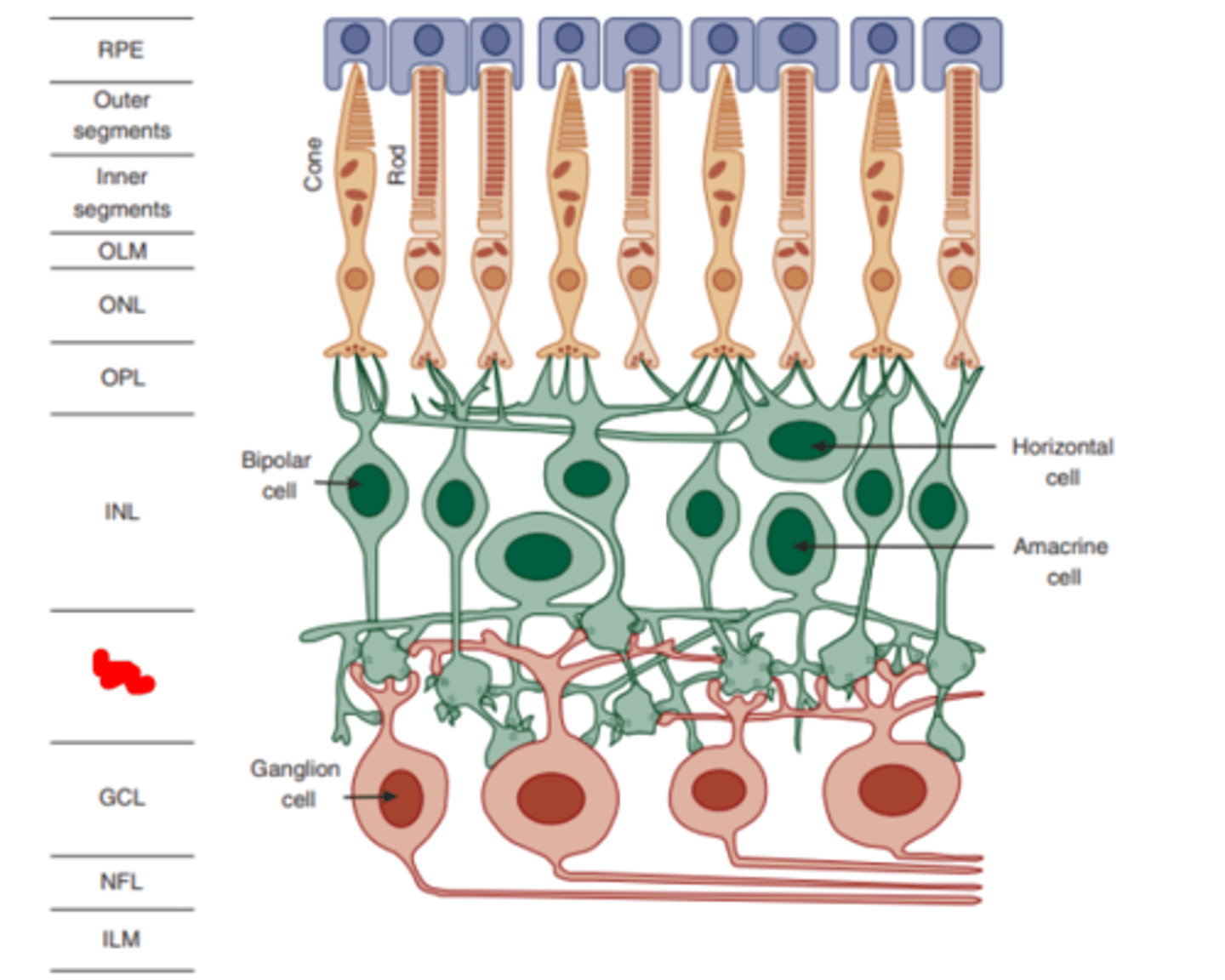
Ganglion cells
cells who receive input from bipolar and amacrine cells and whose long axons leave the eye to form the optic nerve and synapse in the LGN. Their fundamental role is in edge detection. THE FIRST RETINAL CELLS TO GENERATE ACTION POTENTIALS.
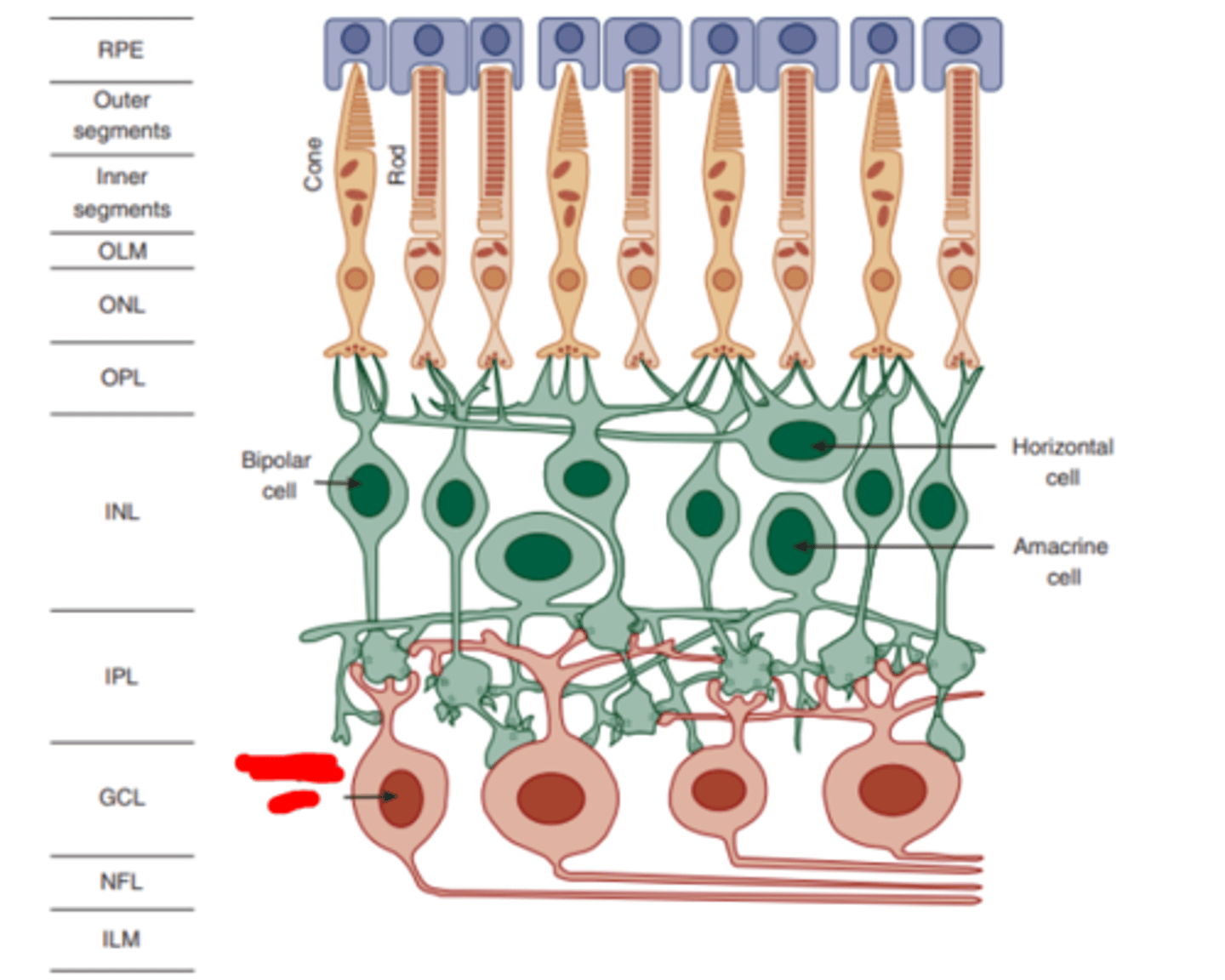
Midget ganglion cells
smaller ganglion cells compromising about 80% of ganglion cell population. Synapse on parvo cells in the LGN to form the parvo retinogeniculate pathway.
80%
what percent of the ganglion cell population is midget ganglion cells?
10%
what percent of the ganglion cell population is parasol ganglion cells?
Parasol ganglion cells
larger ganglion cells compromising about 10% of the ganglion cell population. Synapse on the magno cells in the LGN to form the magno retinogeniculate pathway.
10%
what percent of the ganglion cell population is small bistratified ganglion cells?
Small bistratified ganglion cells
the least studied group of ganglion cells. Receive input from S cone bipolar cells and synapse on the konio cells in the LGN to form the konio retinogeniculate pathway.
melanopsin, circadian rhythm
Recent studies have resulted in the discovery of specialized ganglion cells that contain the photopigment _____ which is sensitive to 483 nm blue light. These cells project to the suprachiasmic nucleus of the hypothalamus and are involved in the development of _____
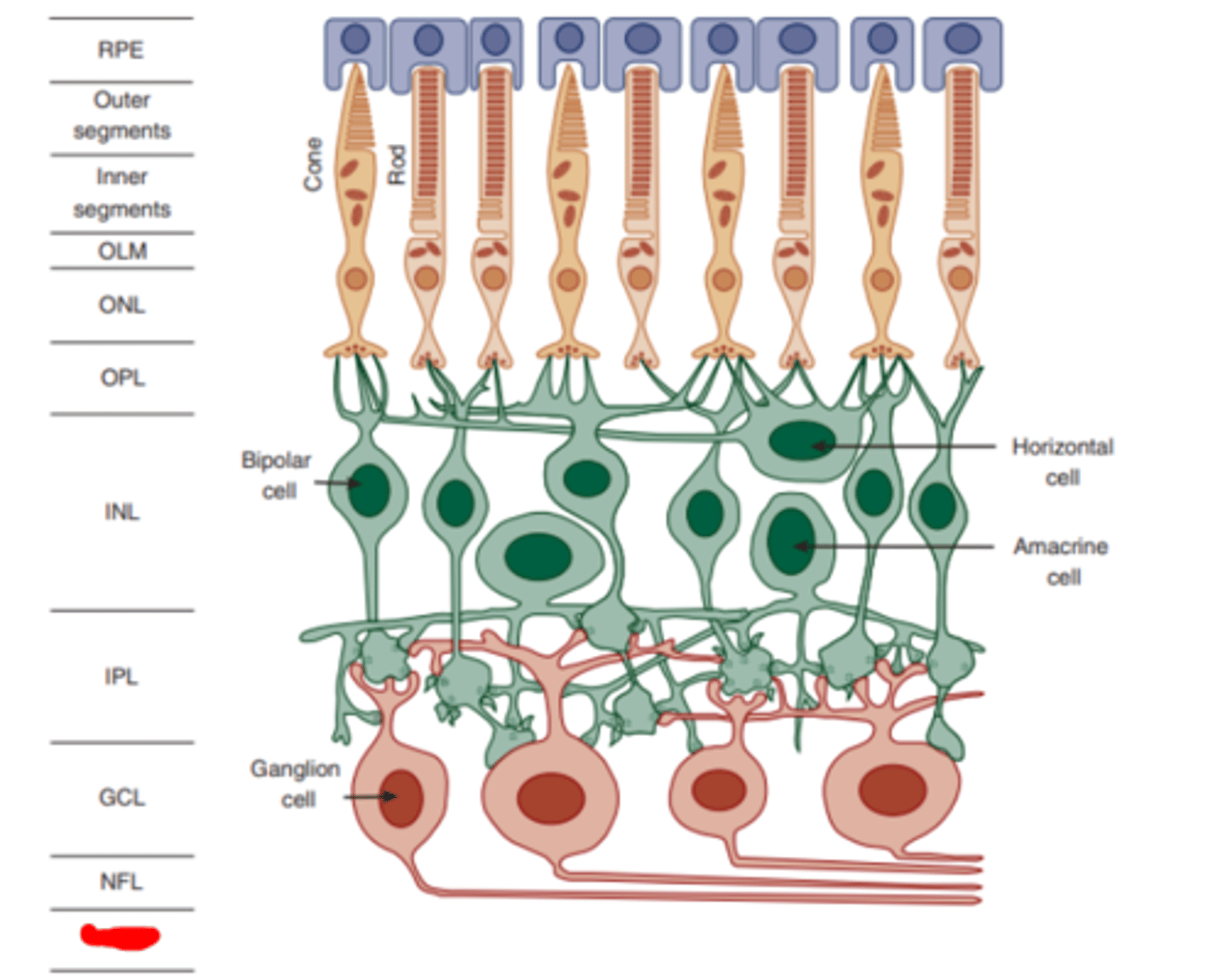
Nerve fiber layer
layer of the retina made up of the axons of ganglion cells.
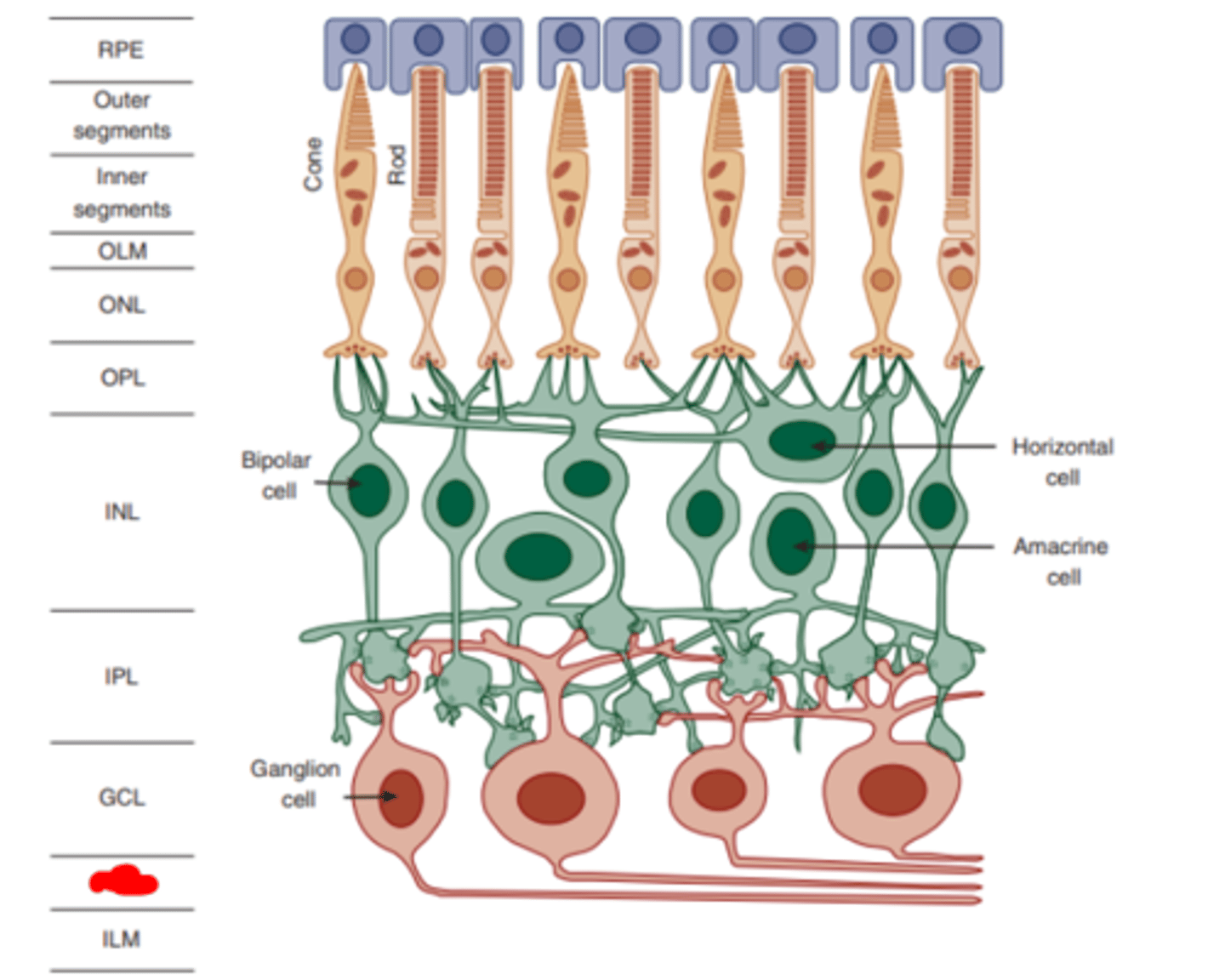
Internal limiting membrane
the innermost layer of the retina acting as an interface between the retina and the vitreous humor.
Graded (slow) potentials
changes in membrane potential that vary in size and travel over a short distance. The neural signal is mediated by a change in magnitude, not temporal frequency of the membrane potential. Represents the type of neurotransmission mediated by several classes of retinal cells. Ie) the amount of hyperpolarization of a photoreceptor is dependent on the stimulus intensity
Action potential
a momentary spike of current recorded from a neuron. Strength of the neural signal is mediated by a change in temporal frequency (change/time), not magnitude of the membrane potential.
Depolarization
change in membrane potential where the potential value becomes smaller, closer to zero than resting potential (less negative)
Hyperpolarization
change in membrane potential where the potential value becomes larger, further from zero than resting potential (more negative)
Repolarization
a restoration of resting membrane potential after depolarization mediated via sodium potassium pumps.
Dark current
slight depolarization caused by a small influx of sodium ions into the rod outer segment while in the dark. This represents the rod resting state where no stimulus is present.
hyperpolarized, sodium
When exposed to light, photoreceptors become ______. Going from a resting membrane potential of –50 mV to –70 mV. This occurs due to the closing of _____ channels.
cis, trans, opsin
Light incident on the rod causes the conversion of all ____ retinol to all ____ retinol and allows for the dissociation of _____
Transducin
_____ activates phosphodiesterase (PDE)
Transducin
Opsin activates _____
Phosphodiesterase
____ breaks down cGMP into GMP
cGMP, GMP
Phosphodiesterase breaks down ____ into ____
Opsin
____ activates Transducin
decrease
(increase or decrease) in cGMP levels leads to the closing of sodium channels in the rod outer segment
cGMP
Decrease in ____ levels leads to the closing of sodium channels in the rod outer segment
sodium
Decrease in cGMP levels leads to the closing of _____ channels in the rod outer segment
sodium
Closing of ____ channels results in hyperpolarization
hyperpolarization
Closing of sodium channels results in _____
Optic disc
a prominent clinical landmark of the retina. It is constituted of the ganglion cell axons as they leave the eye to form the optic nerve.
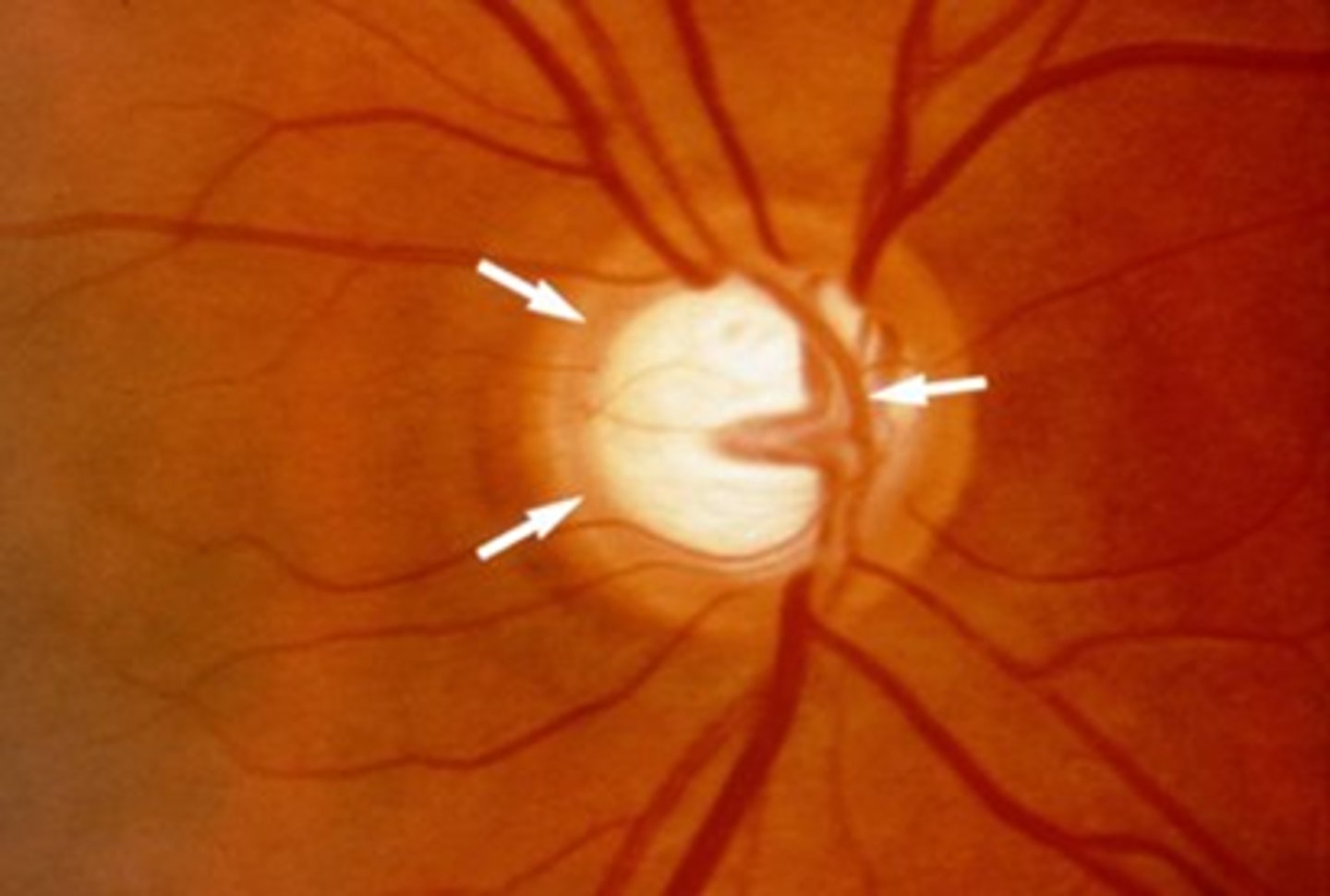
Physiological blind spot
temporal blind spot which occurs due to the fact that there are no photoreceptors in the optic disc located on the nasal retina.
Fovea
a specialized retinal region of highly developed visual acuity found temporal to the optic disc. A disproportionate area of the striate visual cortex is devoted to the processing of information from this highly specialized region.
Foveola
pit found within the fovea containing only cone photoreceptors, which are arranged to allow light to fall directly on the photopigment containing outer segments.
Foveal avascular zone
area larger than the foveola, but smaller than the fovea, which is avascular. This adaptation prevents the scattering of light by retinal vessels.
Optic nerve
cranial nerve formed by the axons of retinal ganglion cells as they leave the eye.
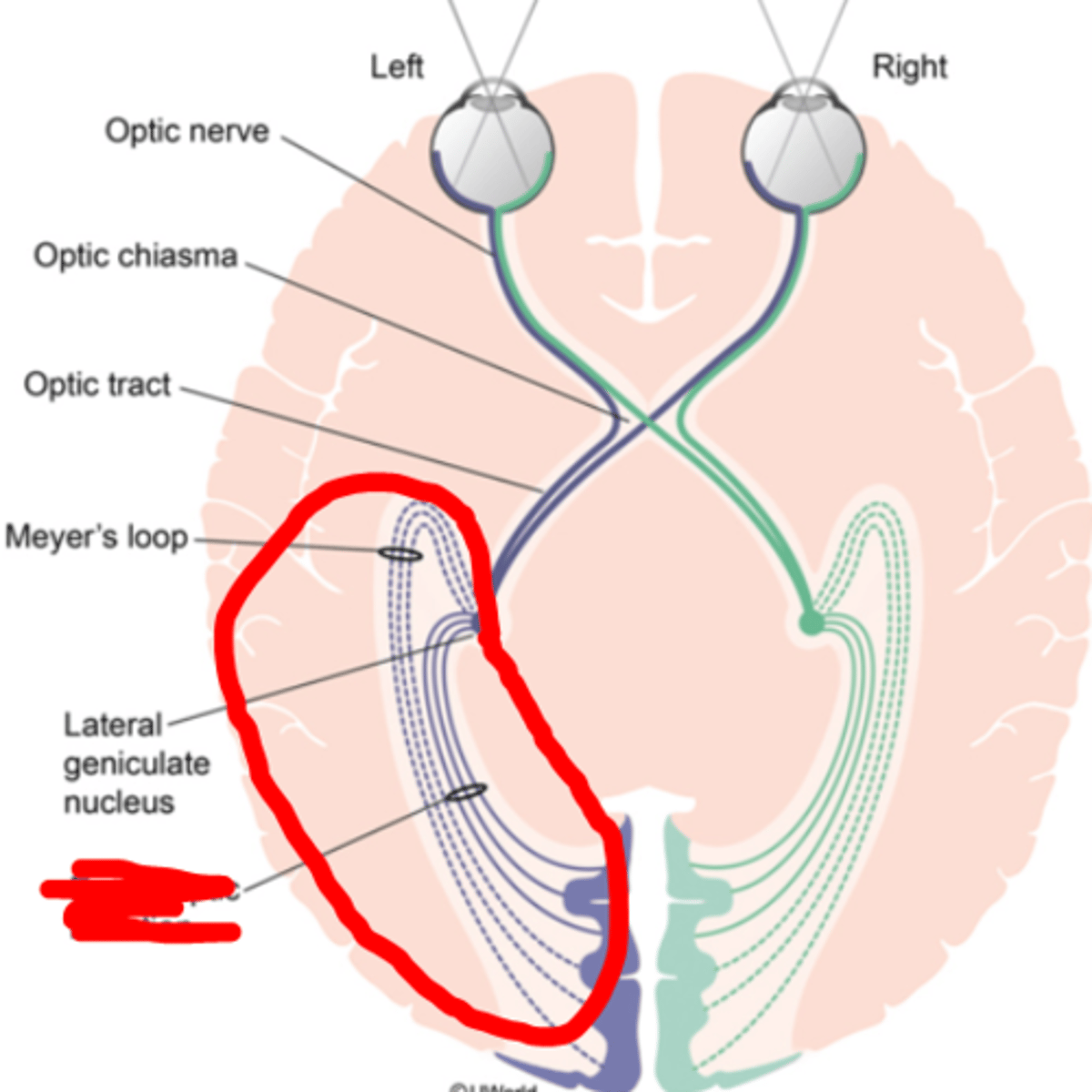
Optic chiasm
location where crossing over of the ganglion cell fibers from the nasal retina of each eye occurs
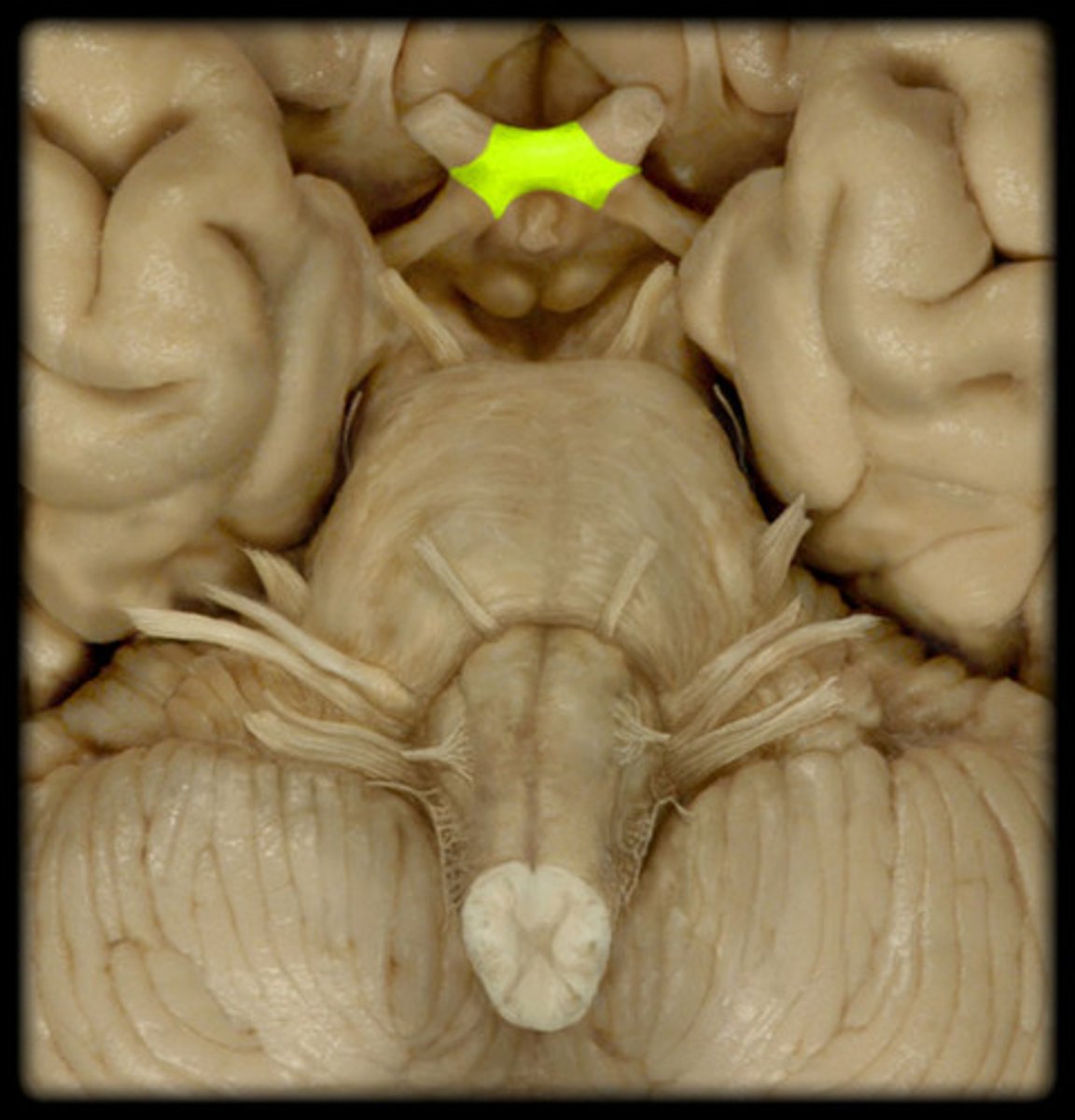
Optic tract
formed by the joining of the nasal fibers of one eye and the temporal fibers of the other. Results in the right visual field and the left visual field being transported to the brain via separate routes.
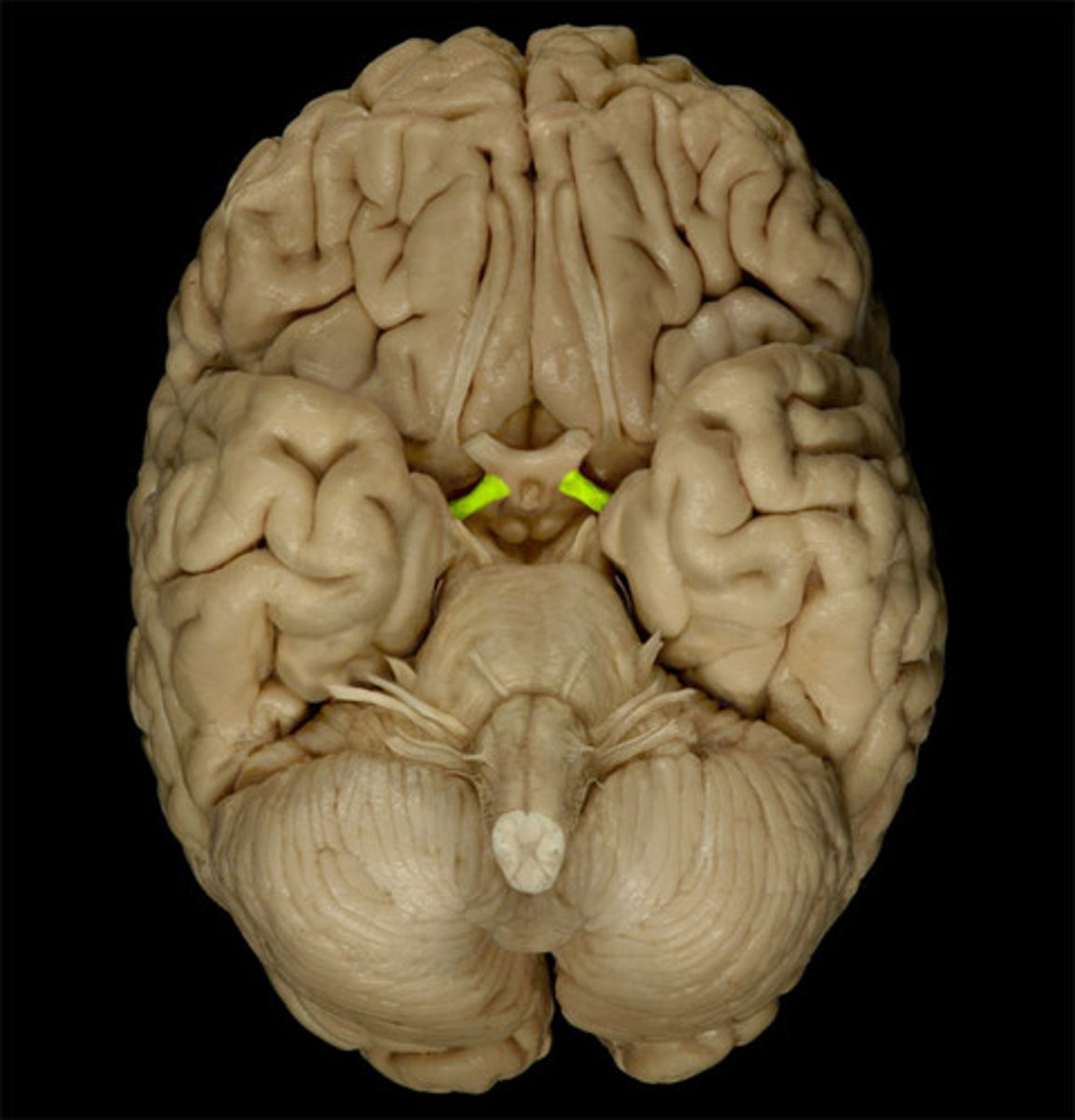
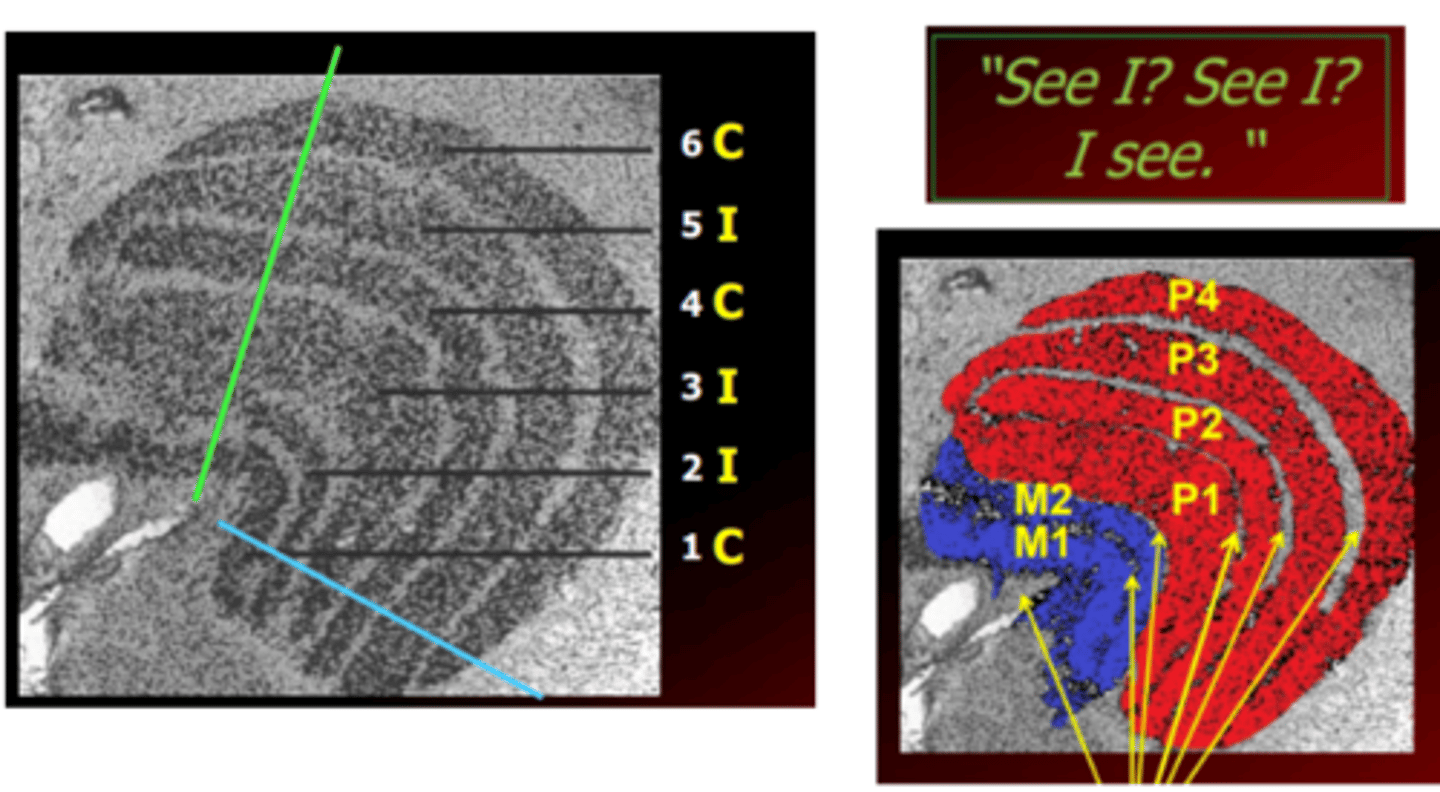
Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN)
a six layered thalamic nucleus where most of the retinal ganglion cells synapse (85%). Serves as a neural relay station from the retina to the visual cortex. Functions to organize parvocellular and magnocellular pathways for output to the visual cortex and subcortical structures.
85%
what percent of ganglion cells synapse at the LGN?
Optic radiations
fibers running from the LGN to the cortex
10%
percentage of input to the LGN that comes from the retina
90%
percentage of input to the LGN that comes from the cortex and brainstem
80%
percentage of output from the LGN that feeds into the primary visual cortex
20%
percentage of output from the LGN that feeds into midbrain centers
1, 4, 6
LGN layers corresponding to the nasal hemifield of the contralateral eye
2, 3, 5
LGN layers corresponding to the temporal hemifield of the ipsilateral eye
1, 2
LGN layers that are magnocellular
3-6
LGN layers that are parvocellular
Magnocellular layers
layers of the LGN containing large neurons called magno cells. Receive input from parasol ganglion cells to form the magno retinogeniculate pathway.
Magno retinogeniculate pathway
pathway formed by magnocellular layers of the LGN that encodes non-color and is sensitive to fast movement.
Frequency doubling technology (FDT)
testing used to evaluate the function of the magnocellular system in the early development of glaucoma using flickering grating stimuli. It is fast, but not very sensitive. Shown to be useful in pediatrics because it is shorter and easier than VF testing.
Octopus 600 (Pulsar stimulation)
testing used to evaluate the function of the magnocellular system in the early development of glaucoma. Very fast making it useful for the elderly, peds, and developmentally delayed patients.
Parvocellular layers
layers of the LGN containing small neurons called parvo cells. Receive input from the midget ganglion cells to form the parvo retinogeniculate pathway.
Parvo retinogeniculate pathway
pathway formed by the parvocellular layers of the LGN that encodes high detail, red-green color information.
Koniocellular layers
layers of the LGN found between magnocellular and parvocellular layers containing small neurons called konio cells. Receive input from the small bistratified ganglion cells to form the konio retinogeniculate pathway.
Konio retinogeniculate pathway
pathway formed by the koniocellular layers of the LGN that encodes blue-yellow color vision, visual proprioception, and extrastriate communication.
Striate visual cortex
the cortical region of the brain in which most of the LGN axons synapse. It is mostly dominated by foveal input.
Extrastriate visual cortex
visual cortical areas outside of the striate cortex which receive axons from the striate cortex.
Superior colliculus
midbrain structure involved in the control of visually guided saccadic eye movements
Pulvinar region
thalamic nucleus that plays a role in visual attention, motion processing, and visually guided movements. Eye hand control integration and also feeds back to the visual cortex.
Pretectal olivary nucleus and EWN
two nuclei involved in afferent pupil reflexes
Accessory optic system
extracortical region involve in OKN and pursuit eye movements