General Psychology Quiz 1 - University of Florida
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
119 Terms
What are the 6 "levels of analysis” in psychology
Molecular 2. Neurochemical 3. Neurological/physiological 4. Mental 5. Behavioral 6. Social
What are the 5 factors that distinguish psychology from other sciences
"Multiply determined" behavior
Interdependence of behavioral influences
Individual differences
Social influence (reciprocal determinism)
Culture
What is reciprocal determinism
A feedback loop of your behavior both influencing and being influenced by your surrounding environment
What are the cognitive biases in science
Confirmation bias
Tunnel Vision
Belief perseverance
Naive realism
What is confirmation bias
A preconceived notion that results in applying different standards to incoming evidence that doesn’t “confirm” that notion
What is tunnel vision
Being blind to everything except what the researcher considers to be “true”
What is belief perserverance
Maintaining initial beliefs even when presented with contradictory evidence, can be overcome with long-term exposure to clear and consistent evidence
What is naive realism
The idea that “seeing is believing” and that one’s own perception of the world is objective and everyone else is biased
What are the key indicators of possible pseudoscience
Ad hoc immunizing hypotheses
Lack of self-correction
Over reliance on anecdotes
Absence of connectivity
Exaggerated claims
Lack of peer review
Psychobabble
Claims of “proof”
What are Ad Hoc immunizing hypotheses
An indicator of possible pseudoscience, a technique that allows a presenting party to always have a way to explain away null results (eg: vibes were wrong, you don’t “believe” enough)
What is a lack of connectivity in pseudoscience
A warning sign when results come out with no connection to past studies or peer reviewed content. “Out of the blue” findings
What is psychobabble
A technique in pseudoscience that employs technical jargon to intentionally misguide consumers into a false level of credibility
Why are claims of proof indicative of pseudoscience?
You can never absolutely prove something to be true, only that evidence fails to support or supports a hypothesis
Why might someone fall for pseudoscientific claims?
Terror management theory and patternicity
What is terror management theory
A coping mechanism in response to our fear of mortality, often weaponized by those making pseudoscientific claims
What is patternicity
The tendency of humans to find patterns in meaningless data, leading to conspiracy theories and reasoning to for believing in pseudoscience
What is the difference between pseudoscience and metaphysical claims
Pseudoscience claims to be scientific and utilizing scientific methods incorrectly and manipulatively, while metaphysical claims - a branch of philosophy - never pretend to be scientific, they deal with questions about existence and reality that are inherently beyond empirical testing.
What are the 6 principles of scientific thinking
Ruling out rival hypotheses
Differentiating correlation and causation
Falsifiability
Replicability
Generalizability
Identifying extraordinary evidence for extraordinary claims
What are the 5 theoretical frameworks that shaped psychology
Structuralism, Functionalism, Behavioralism, Cognitivism, and Psychoanalysis
What is structuralism?
aimed to look at and identify the basic structures of psychology and map consciousness
Who founded structuralism
E.B. Titchener
Why did structuralism fail?
Infighting and disagreements over subjective reports and “imageless thought”
What is functionalism
Wanted to understand the adaptive purposes of characteristics like thought or behavior
Who founded functionalism
William James who was inspired by Charles Darwin
what is behaviorism?
Focuses on discovering the principles of learning through looking at observable behaviors. No subjective reports of the consciousness.
Who founded behaviorism
John B. Watson
Cognitivism. what is it?
Believe that thinking does affect behavior, interpretations of rewards and punishments is important
Psychoanalysis
Internal and subconscious psychological processes that are driven by sexuality and aggression, emphasis on childhood experience as a root for psychological conflicts
Who founded psychoanalysis
Sigmund Freud
Who founded cognitivism
Jean Piaget
Basic Research vs. Applied Research
How the mind works and using basic research to solve real-life problems
Intuitive thinking is which system
System 1
What is intuitive thinking
Quick and reflexive gut feeling, can be important survival instincts but can also prompt heuristics
What system is analytical thinking
System 2
What is analytical thinking
Slow and requires more mental effort, but capable of overriding conclusions from intuitive thinking
What is important when applying the scientific method to studying psychology
random selection, reliability vs. validity, and replicability
Types of variables
Independent, dependent, confounding
Random selection
Participants selected randomly to be most representative of a population
What are the 5 types of research design
Naturalistic observation, case study, correlational design, questionnaires, experimental design
Naturalistic observation
Observing peoples behavior without interference or manipulation. High external validity because it directly translates to real world, but low internal validity because of a lack of control over variables.
Case studies
Follows a single person or small group over an extended period of time. Good for existence proofs but not for testing hypothesis because of a lack of generalizability and that a plural of an anecdote does not equate to a fact
Questionnaires (Surveys and Self-reports)
Cheap, efficient, and easy to administer. Can be prone to participant bias like social desirability and malingering.
What is a rating data questionnaire
Someone other than subject to rate subject in a questionnaire, avoids personal bias but can have halo and horns effect
What is halo effect and horns effect
A positive/negative judgement about a single aspect of a person that overtakes their character
Correlational designs
To what extent two variables are related. Scatterplot and correlation coefficient. CORRELATION VS. CAUSATION, only experimental studies can infer causation.
Experimental Designs
Characterized by random assignment and independent variables. Random participants are in either experimental or control groups, IV manipulated, DV is those results. only research design to be able to prove causation
CT (Computed tomography)
MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging)
PET (positron emission technology)
FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
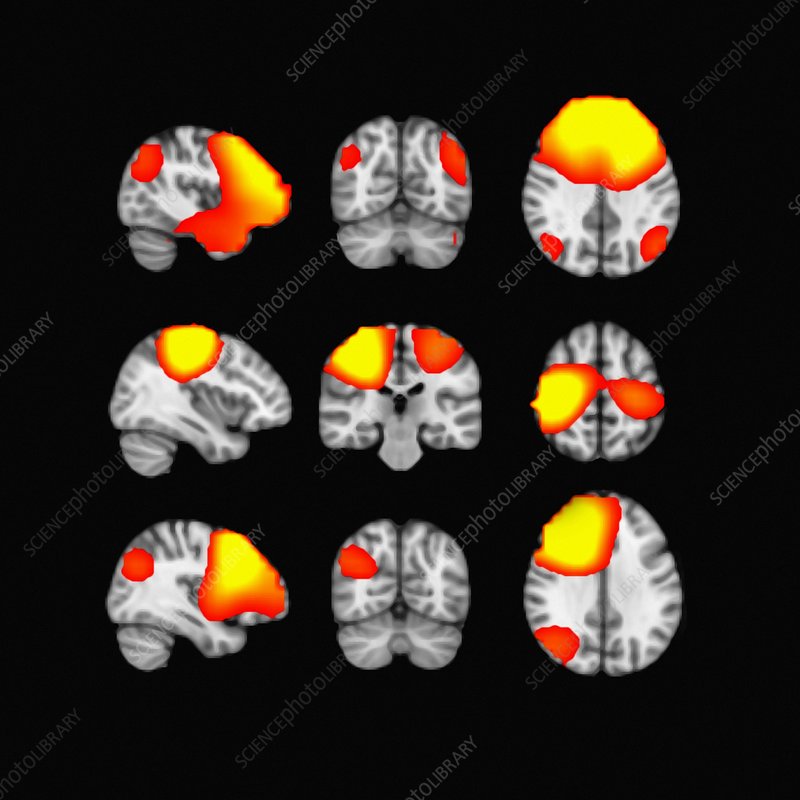
MEG
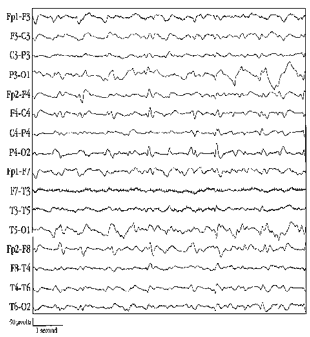
EEG (Electroencephalograph).
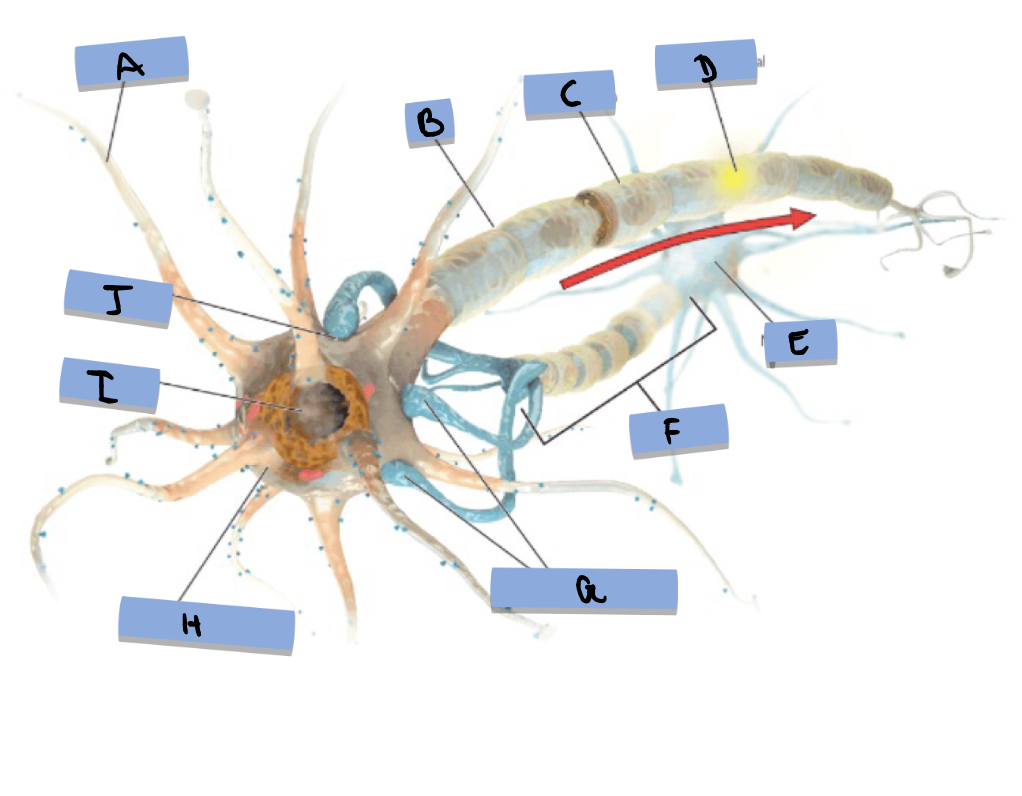
A: dendrite, B: node, C: Myelin sheath, D: Action potential, E: Neuron, F: Axon, G: Axon terminals, H: Soma (cell body), I: Nucleus, J: Synapse
What is the soma
The soma is the cell body of a neuron
What are dendrites
They are the structures that receive information from other neurons
What is the axon
The tail-like extension that sends messages to neighboring neurons via action potential
What are axon terminals
Knob-like structures at the end of the axon that contain synaptic vessels and hold neurotransmitters
Name the steps of intraneuron activity
Resting potential, threshold of excitation, action potential, and the absolute refractory period
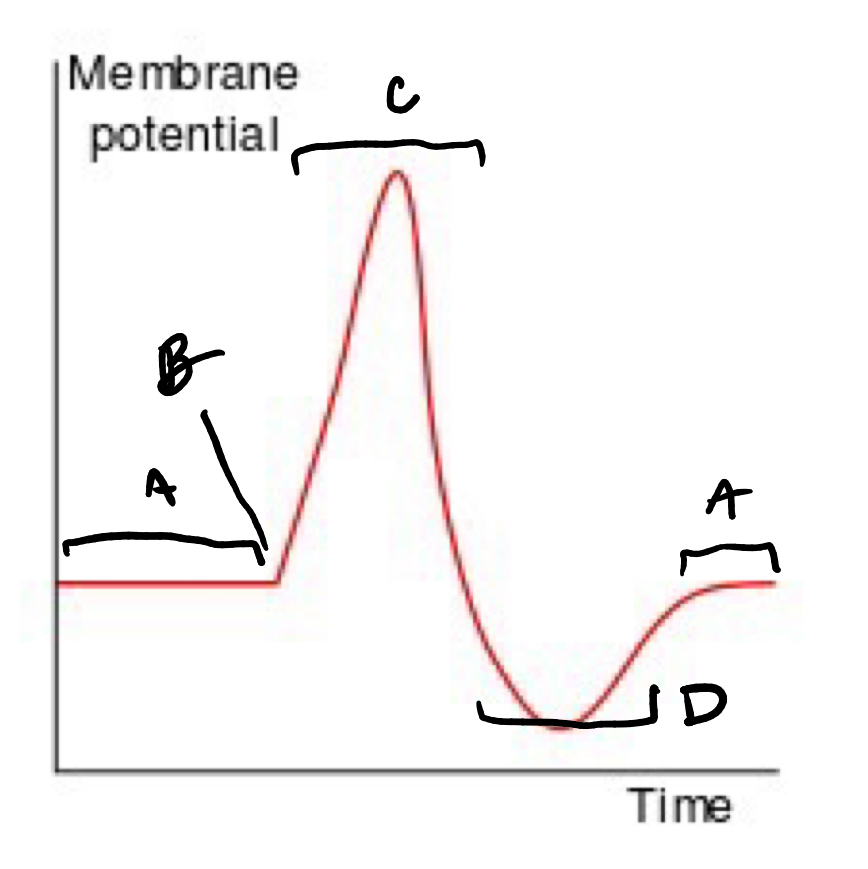
A: resting potential
B: threshold of excitation
C: Action potential
D: absolute refractory period
What is a synapse
The interface between two neurons, aka the point of info exchange
What is a synaptic cleft
The gap between cells that is crossed by neurotransmitters during an action potential
What is reuptake
Stops neurotransmission and reabsorbs the unused neurotransmitters
What are the two types of glial cells
Astrocytes and Oligodendrocytes
What are the major functions of an astrocyte
Neuron message transmission, the blood-brain barrier the brain’s “security system”
What are the functions of an oligodendrocyte
To promote new connections, heal cell damage, and produce myelin sheath
What is the basic function of Acetylcholine
The learning neurotransmitter
What is the basic function of GABA
The calming neurotransmitter
What this the basic function of dopamine
The pleasure neurotransmitter
What is the basic function of endorphins
The euphoria neurotransmitter
Basic function of serotonin
The mood neurotransmitter
What is neural plasticity
The nervous system’s ability to change over time
Types of neural plasticity
Growth of dendrites/axons, synaptogenesis (new connections, and synaptic pruning (eliminating connections), myelination, potentiation (increase in strength of common neural pathways), and neurogenesis.
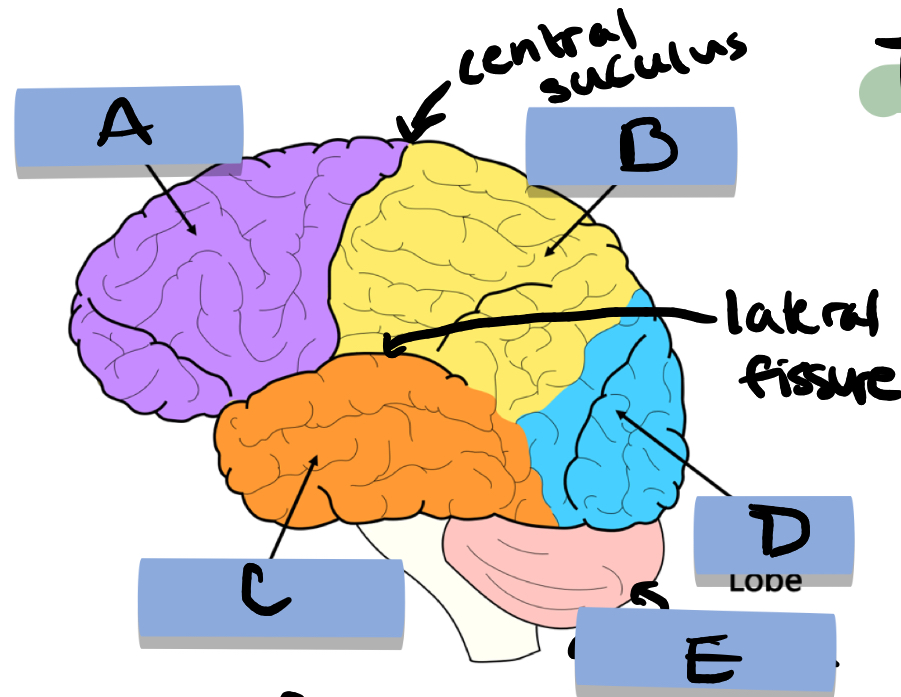
A: frontal lobe
B: parietal lobe
c: temporal lobe
D: occipital lobe
E: cerebellum
Functions of the frontal lobe
Decision making, personality, self-awareness (prefrontal), speech production (Brock’s), and the motor control cortex
Functions of the Cerebellum
Balance and coordination, learning motor skills
Functions of the temporal lobe
Auditory cortex, language comprehension (Wernicke’s), and object recognition
Functions of the parietal lobe
Somatosensory cortex (pain, pressure, temperature), and spatial awareness
Functions of the occipital lobe
Vision (color differentiation, form, motion, and depth perception)
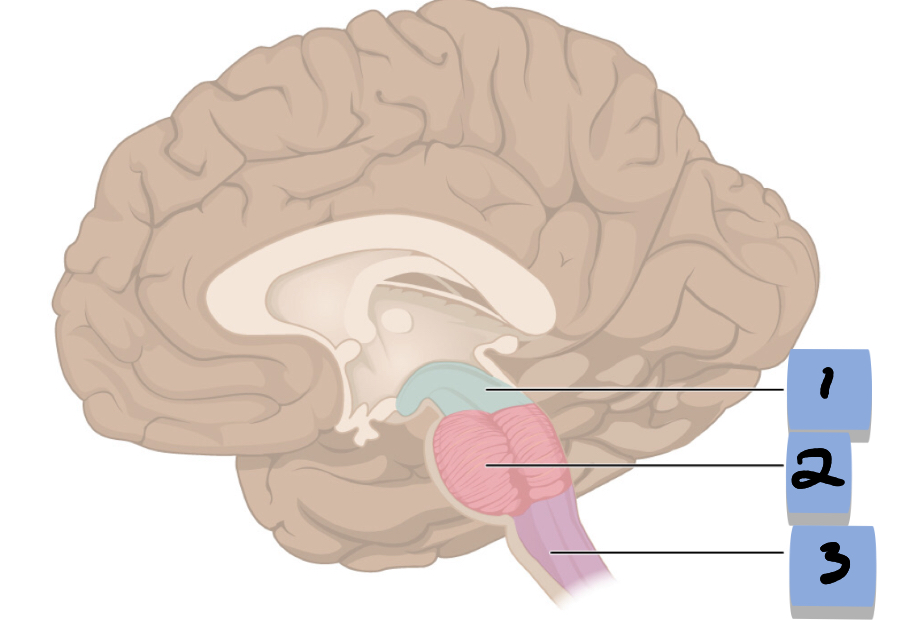
midbrain
Pons
Medulla
What is the CNS
Central nervous system; brain and spinal cord
What is the PNS
The peripheral nervous system; Somatic and Autonomic nervous system
What is the Somatic nervous system
Intentional action via musculature like stabilization, movement of joints, and posture