Bio 120 Lab practical 3
1/181
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
182 Terms
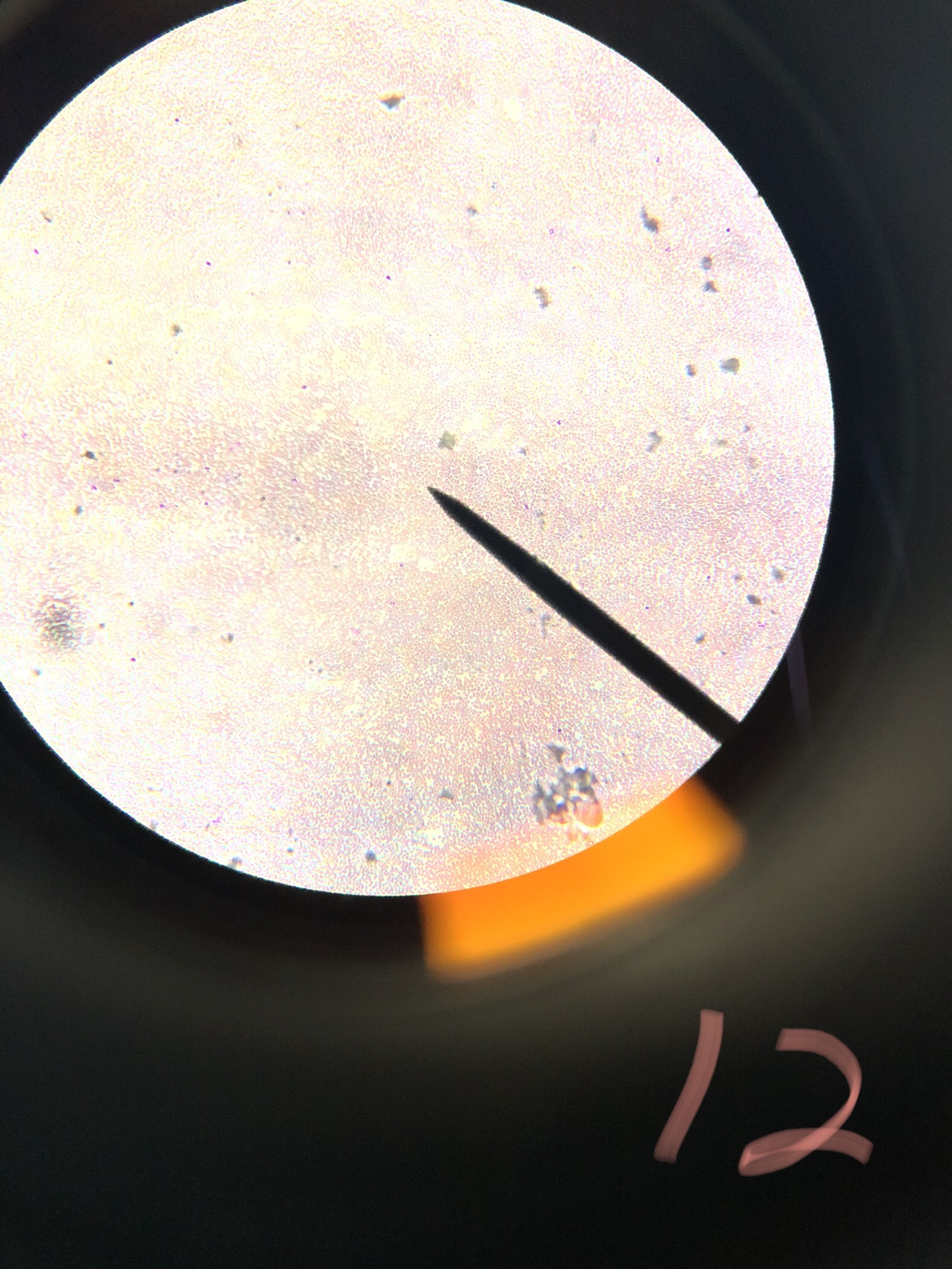
Human Cuboidal Epithelium
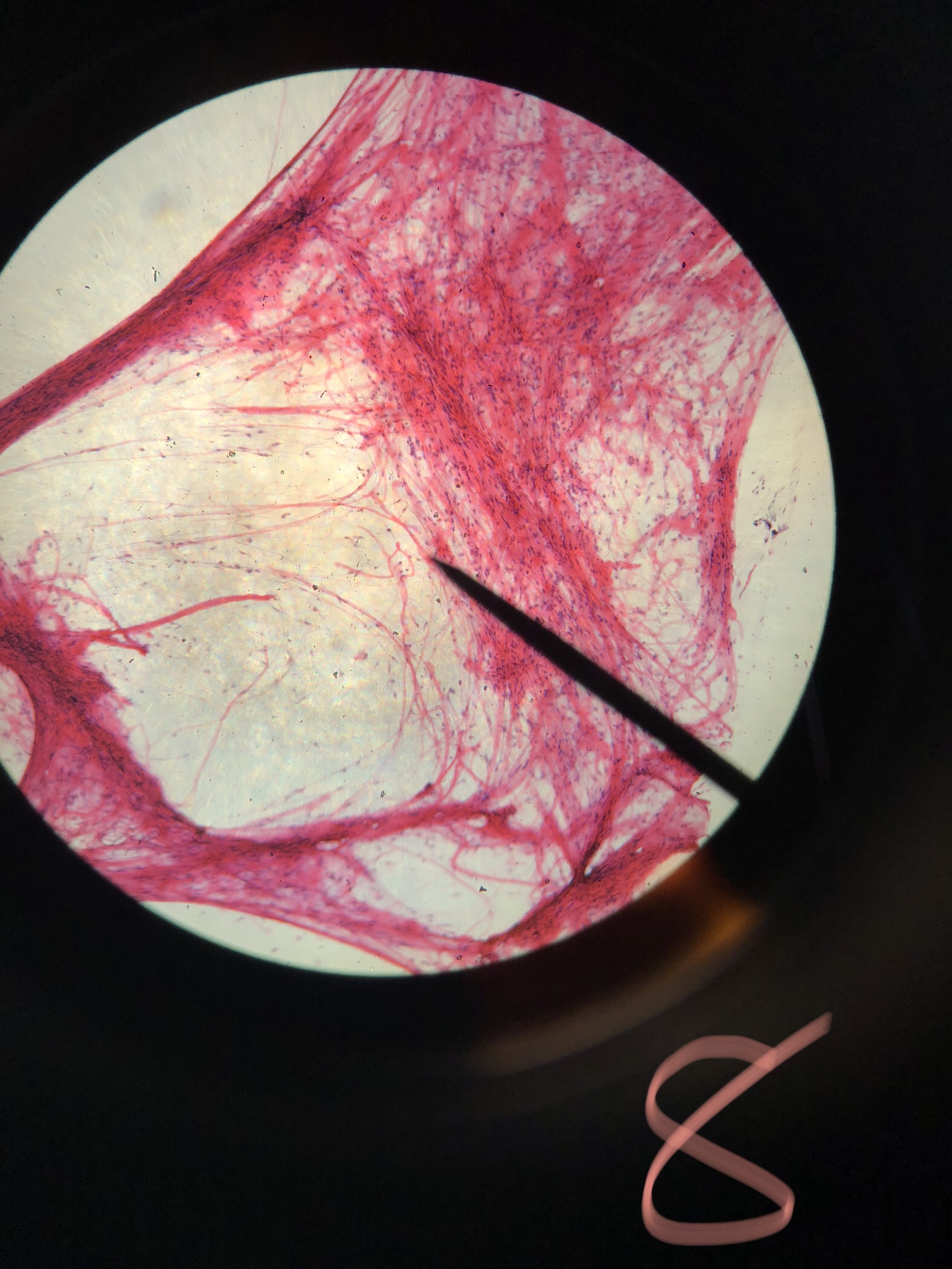
Mammal Areolar tissue Spread
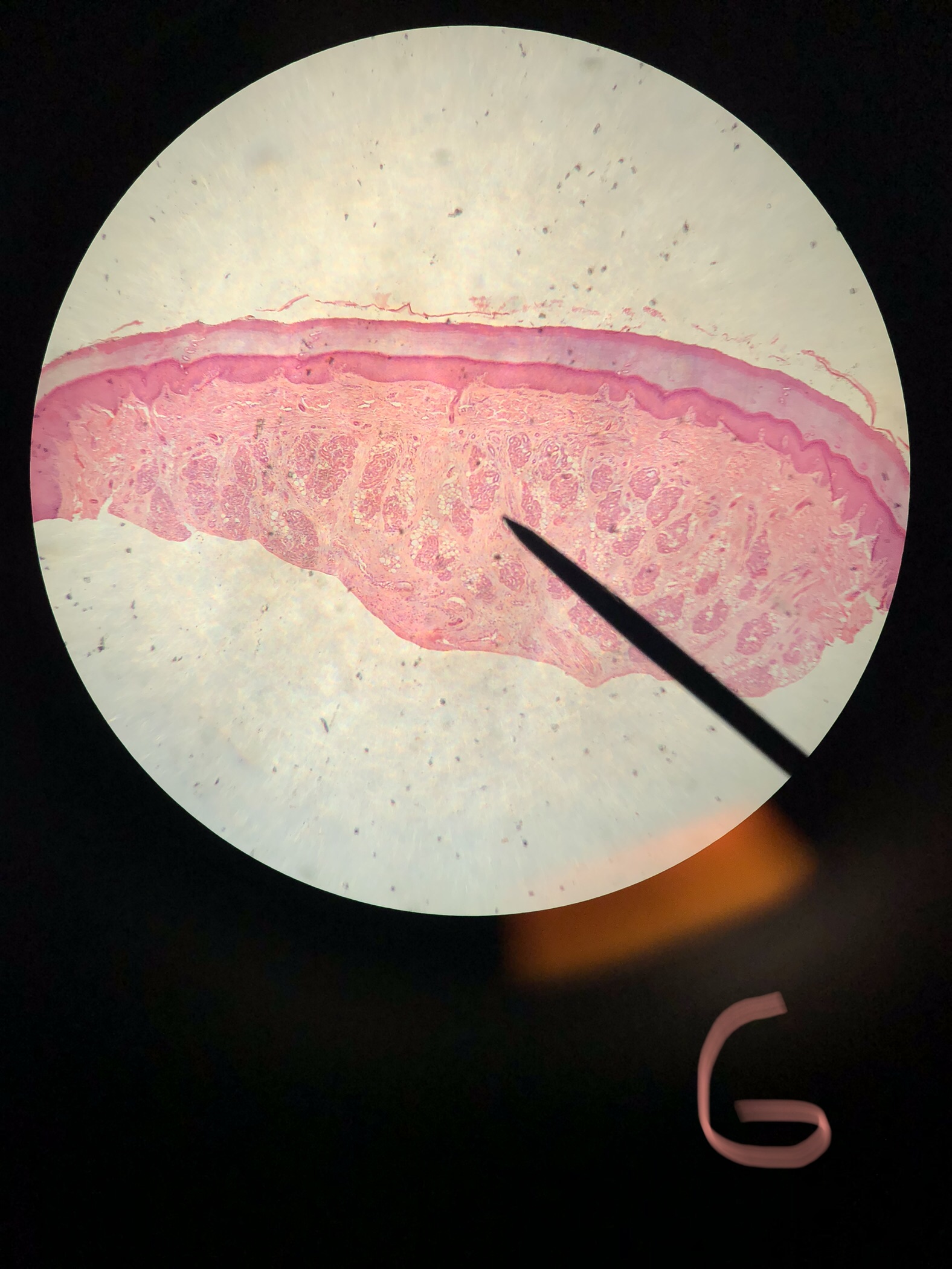
Stratified squamous epithelium
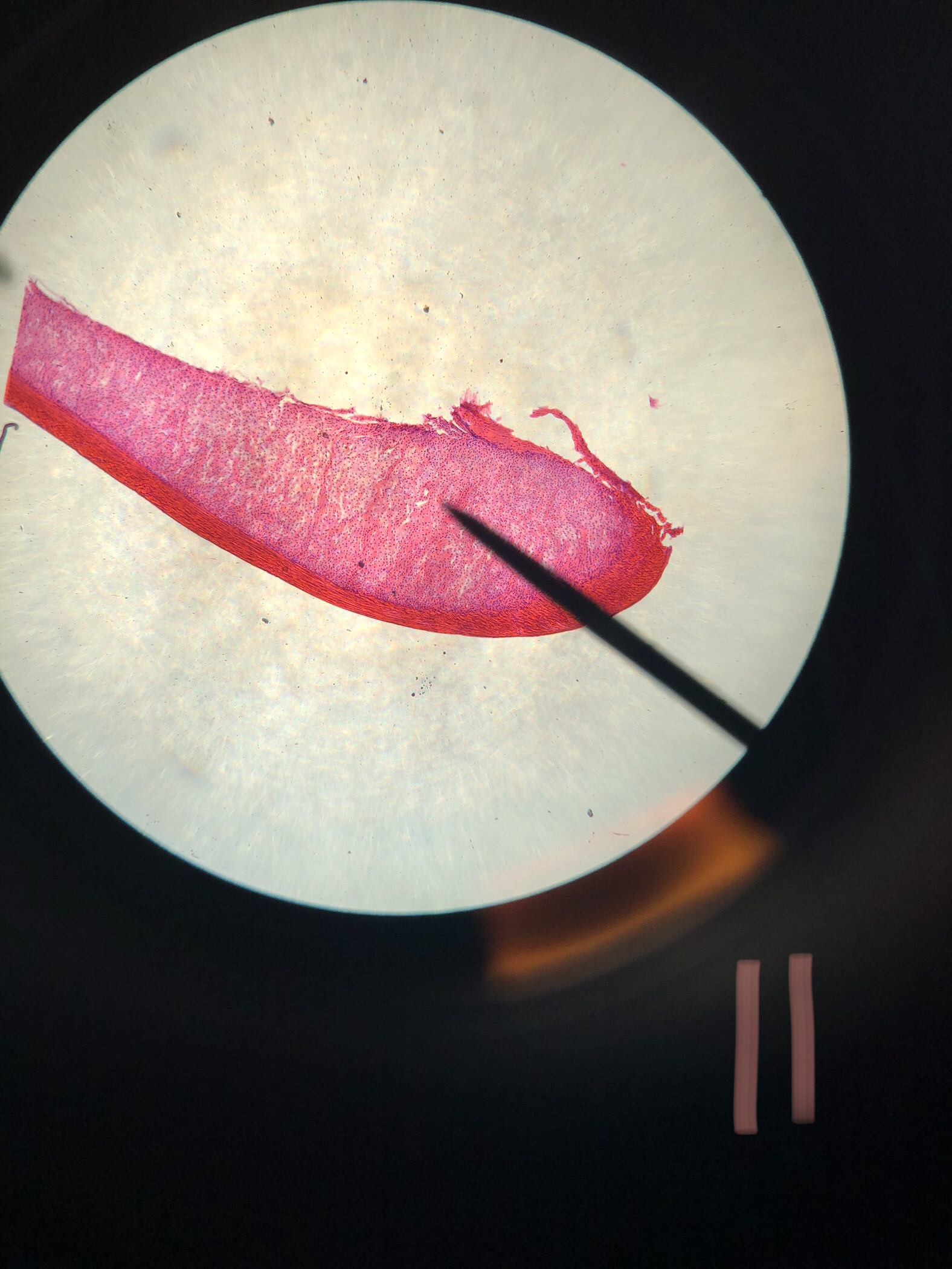
Mammal Tendon
Human Blood smears wright
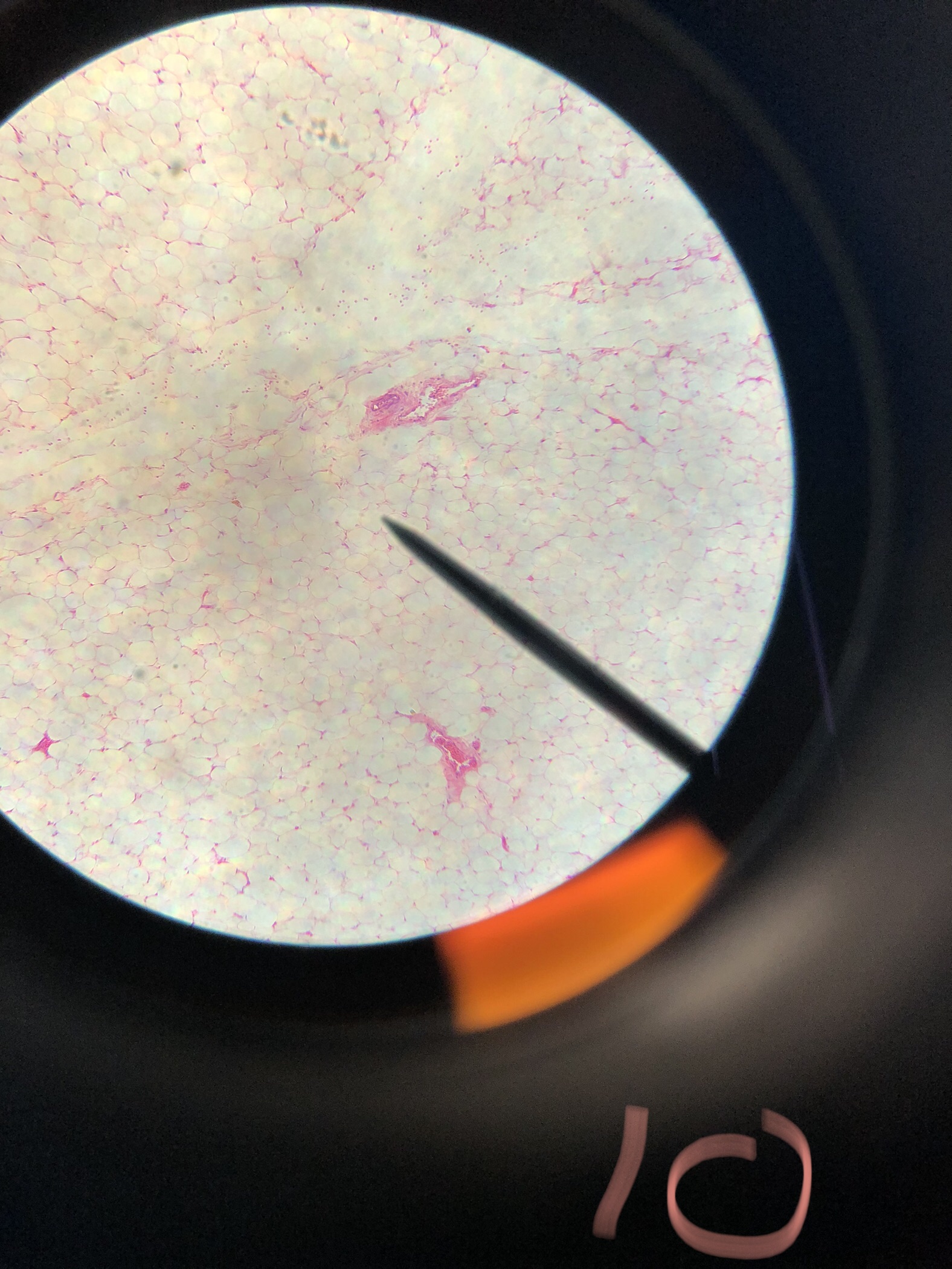
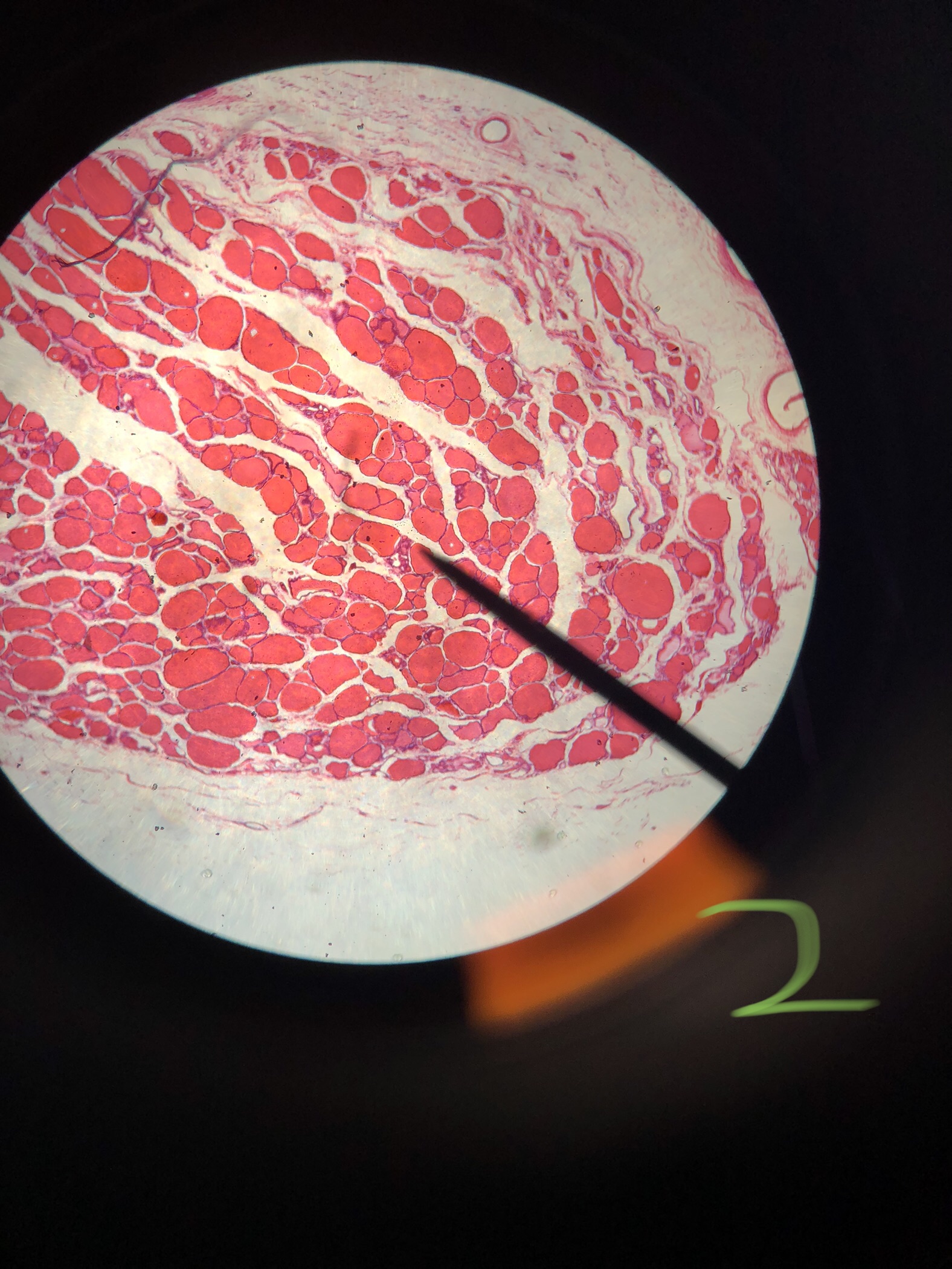
Human Adipose tissue
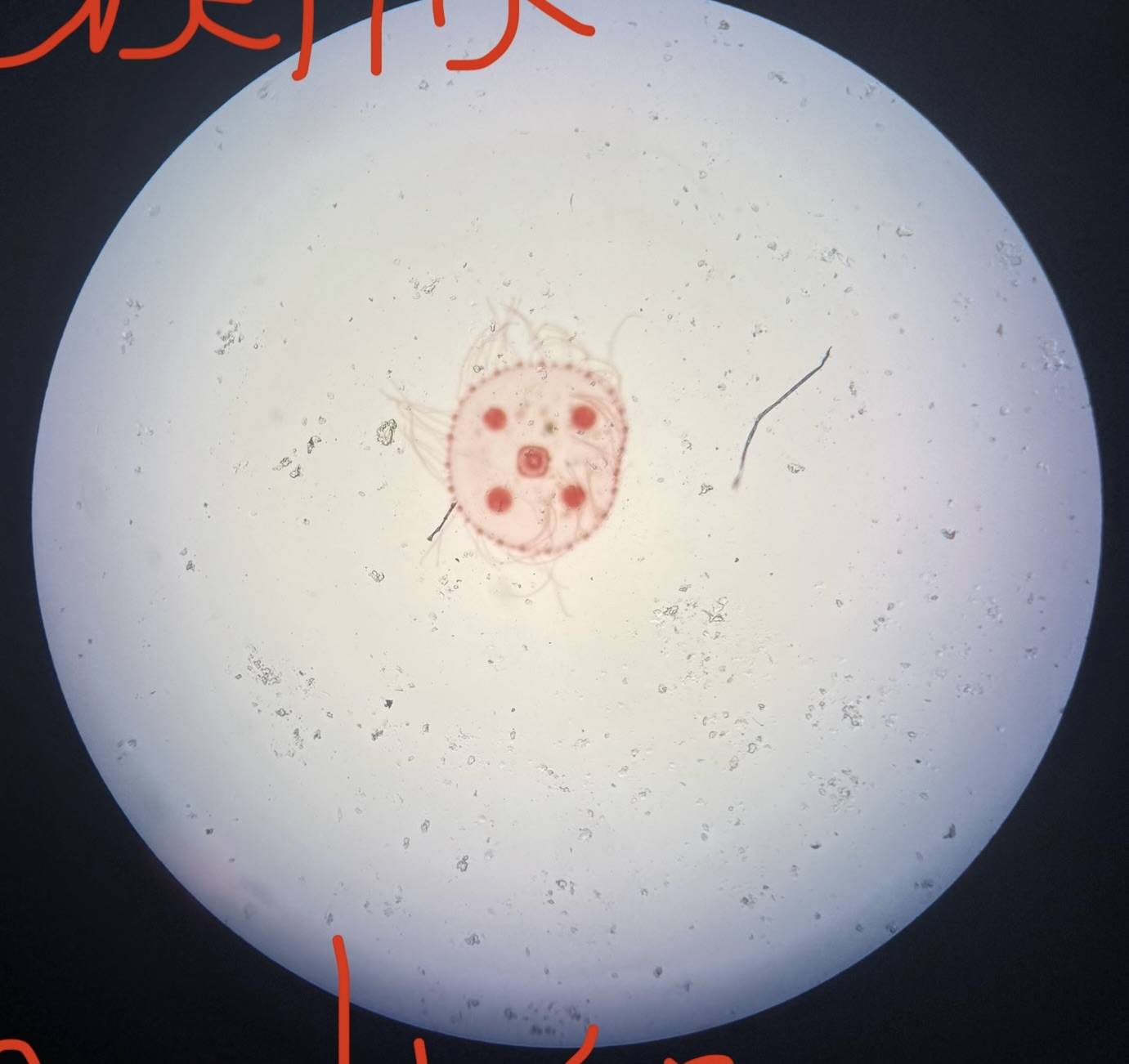
Obelia Medusa
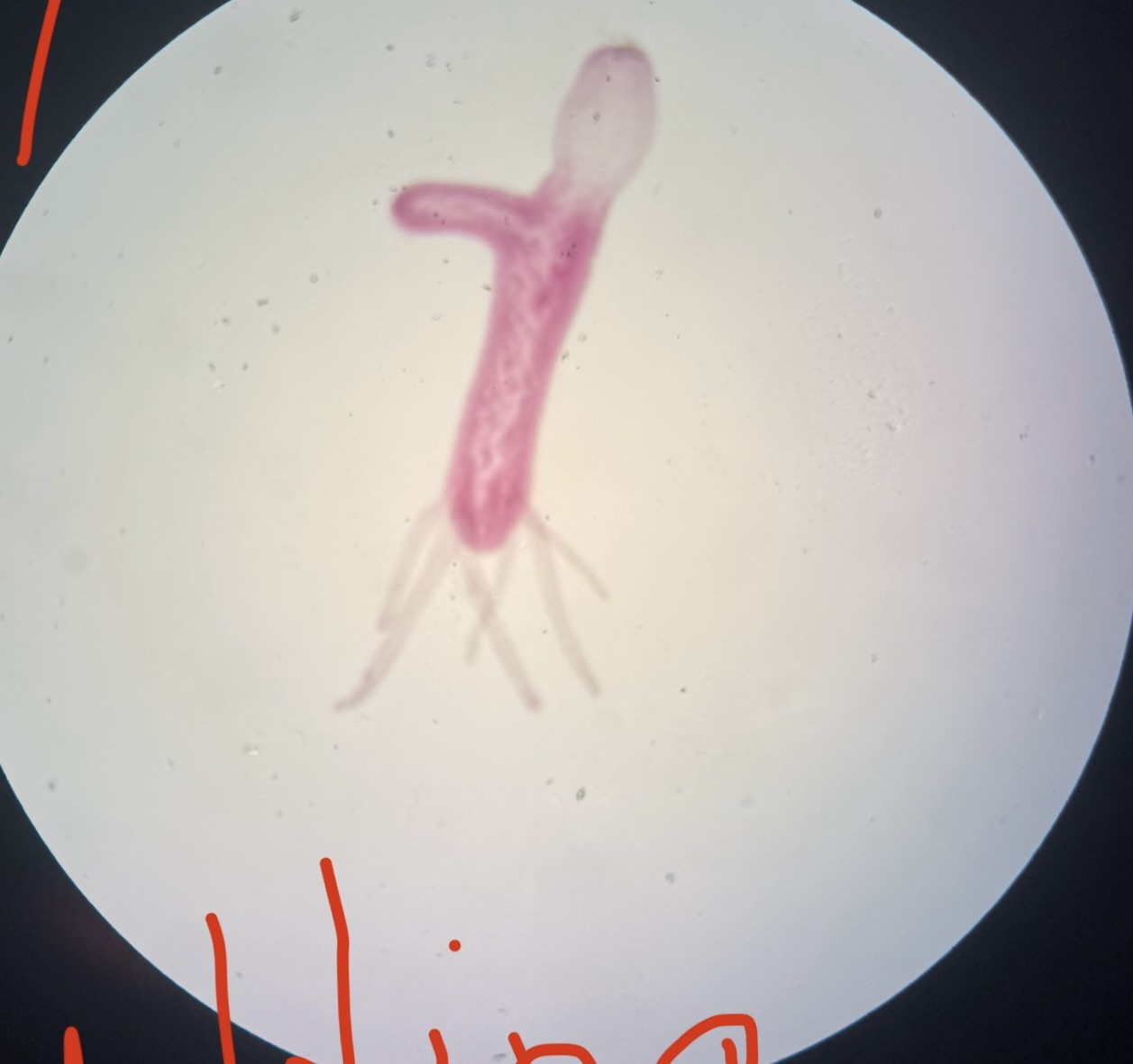
Hydra Budding
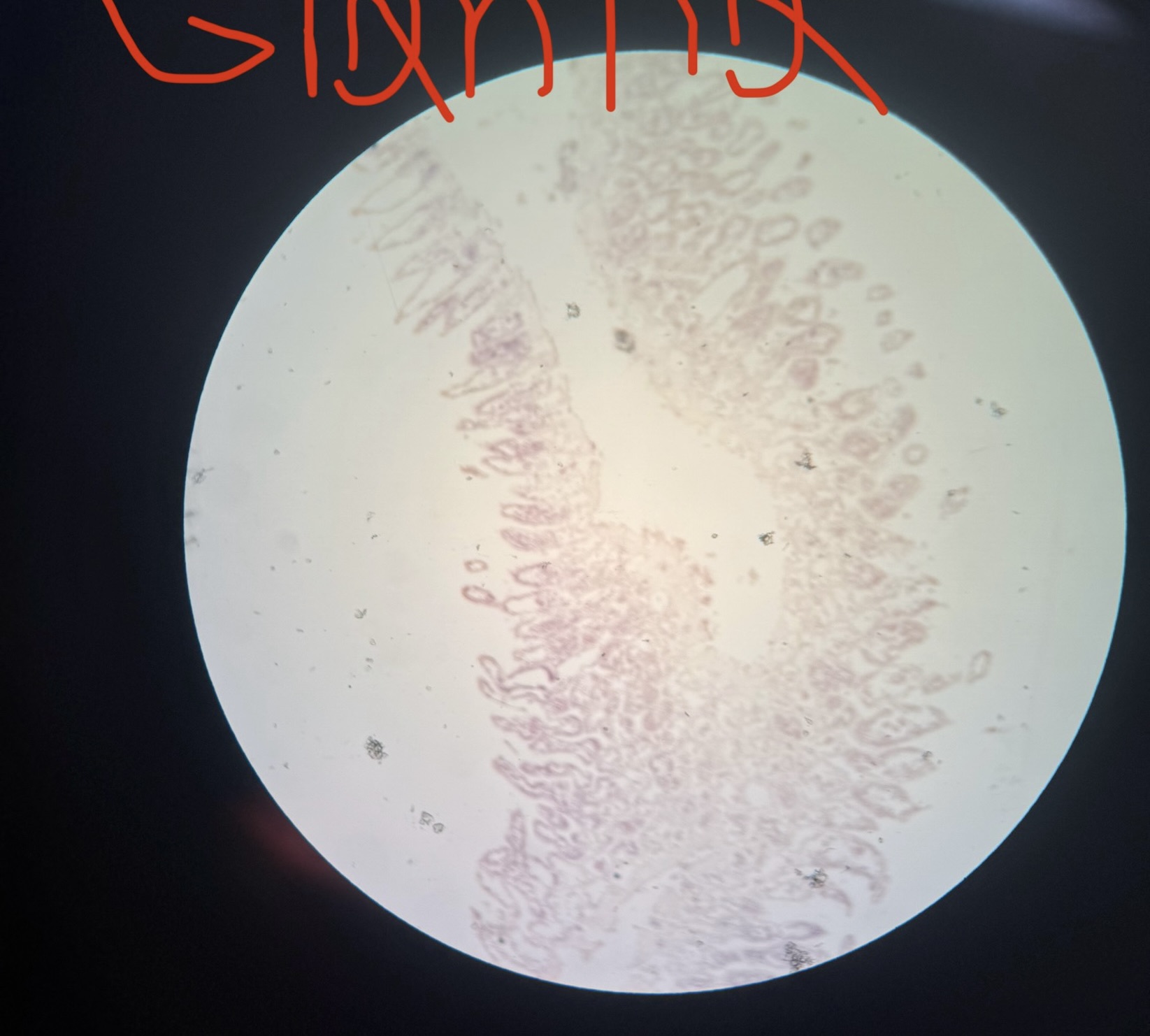
Grantia
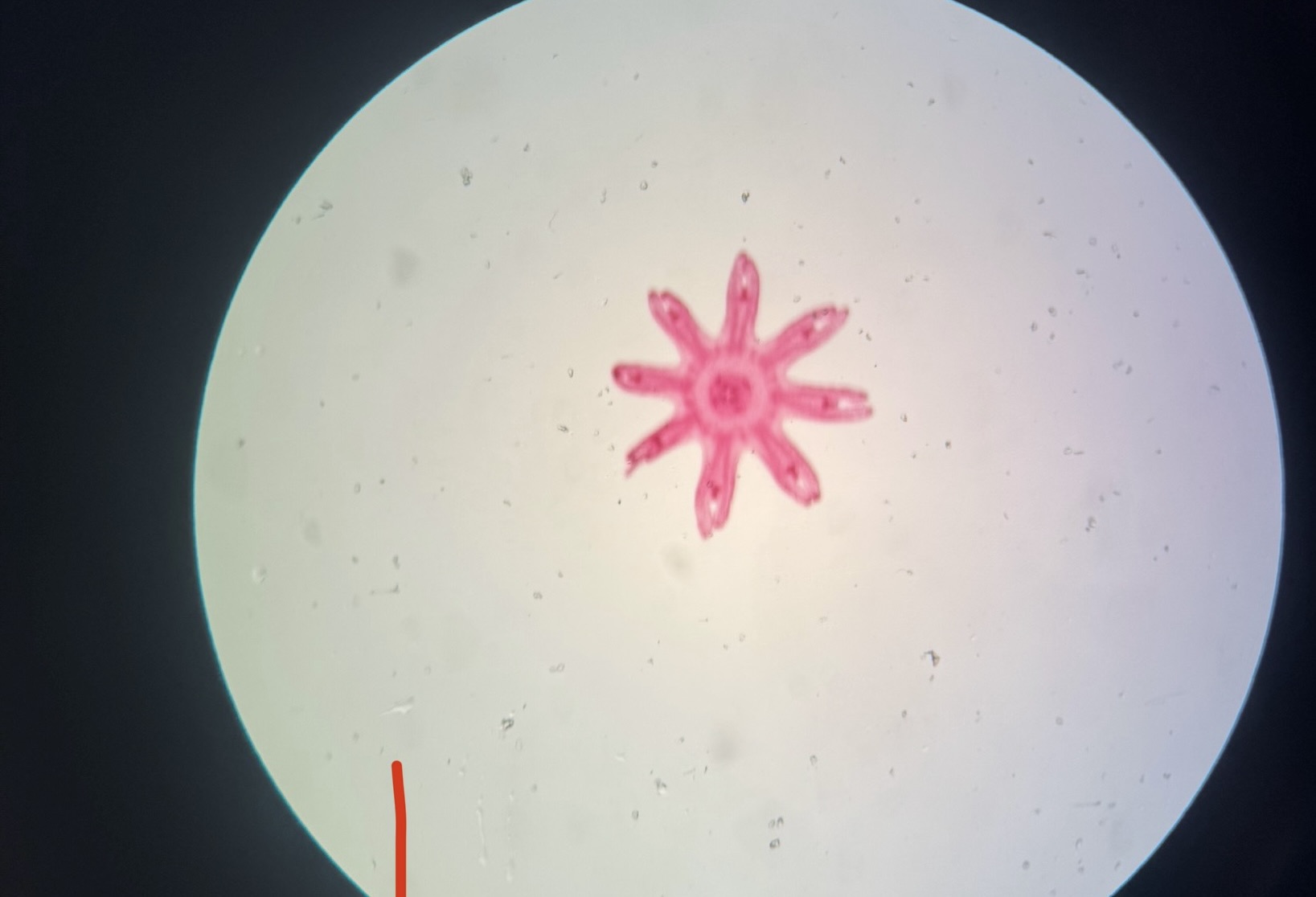
Aurelia Ephyra
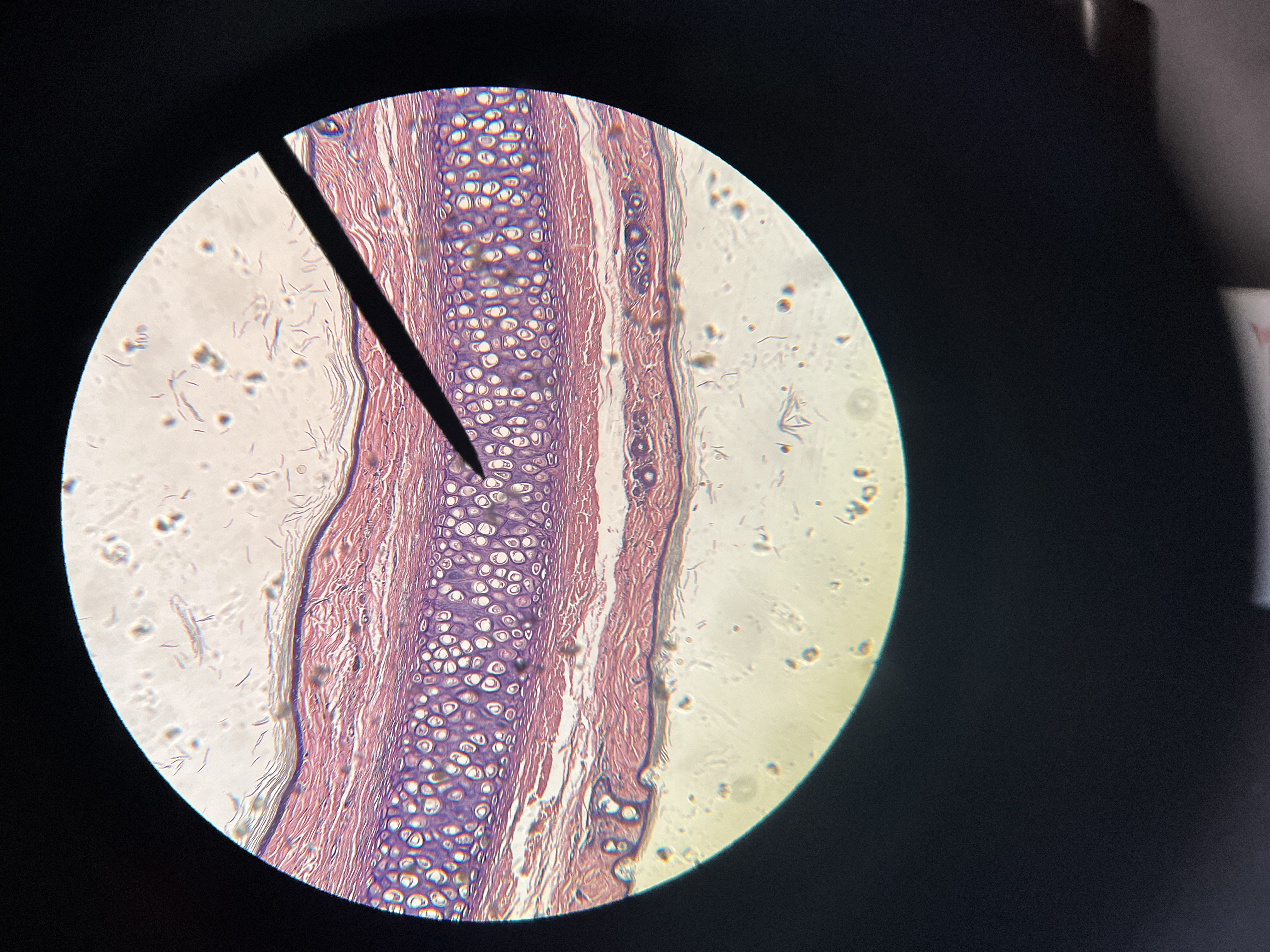
Mammal elastic cartilage
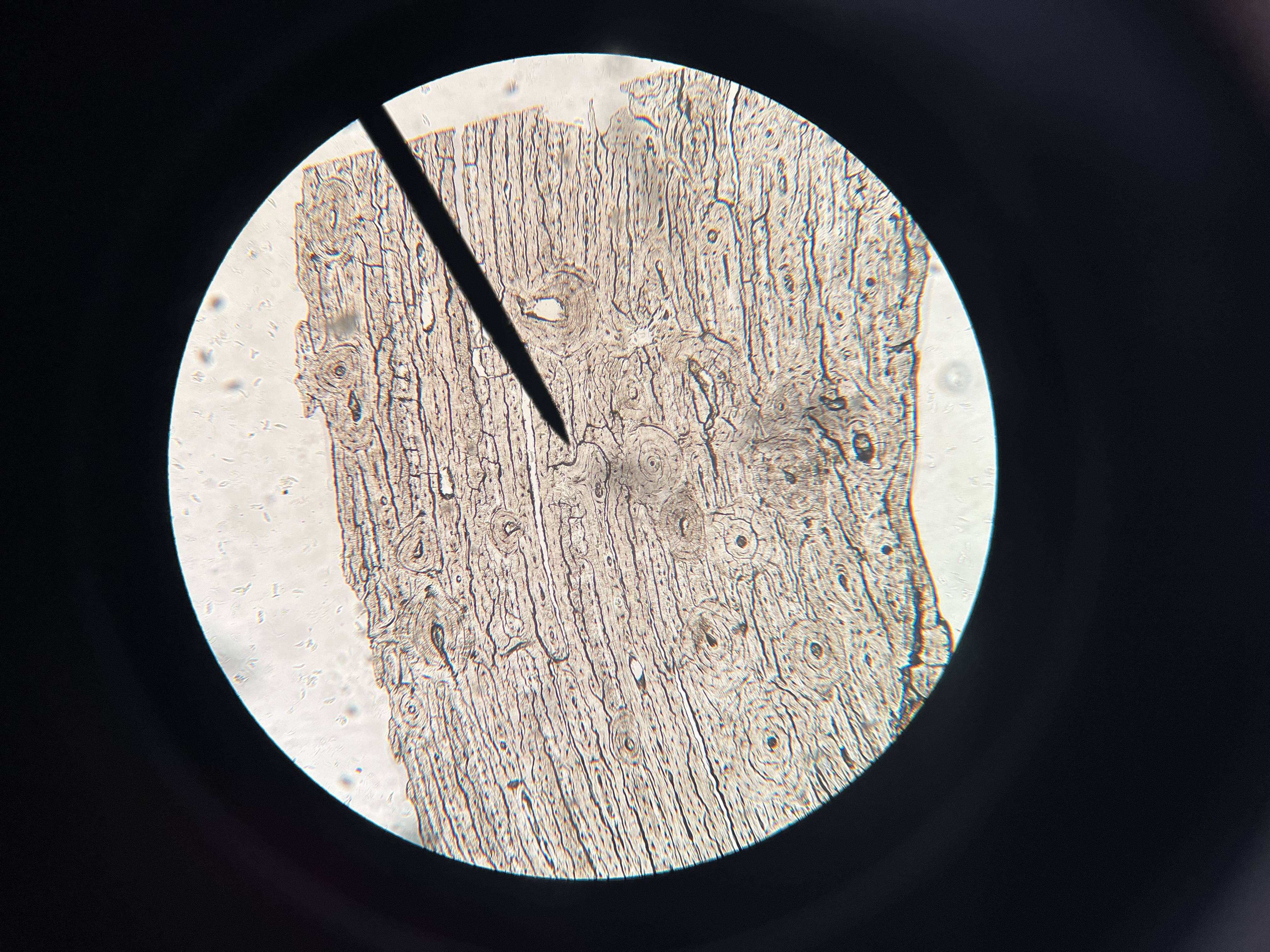
Mammal bone ground
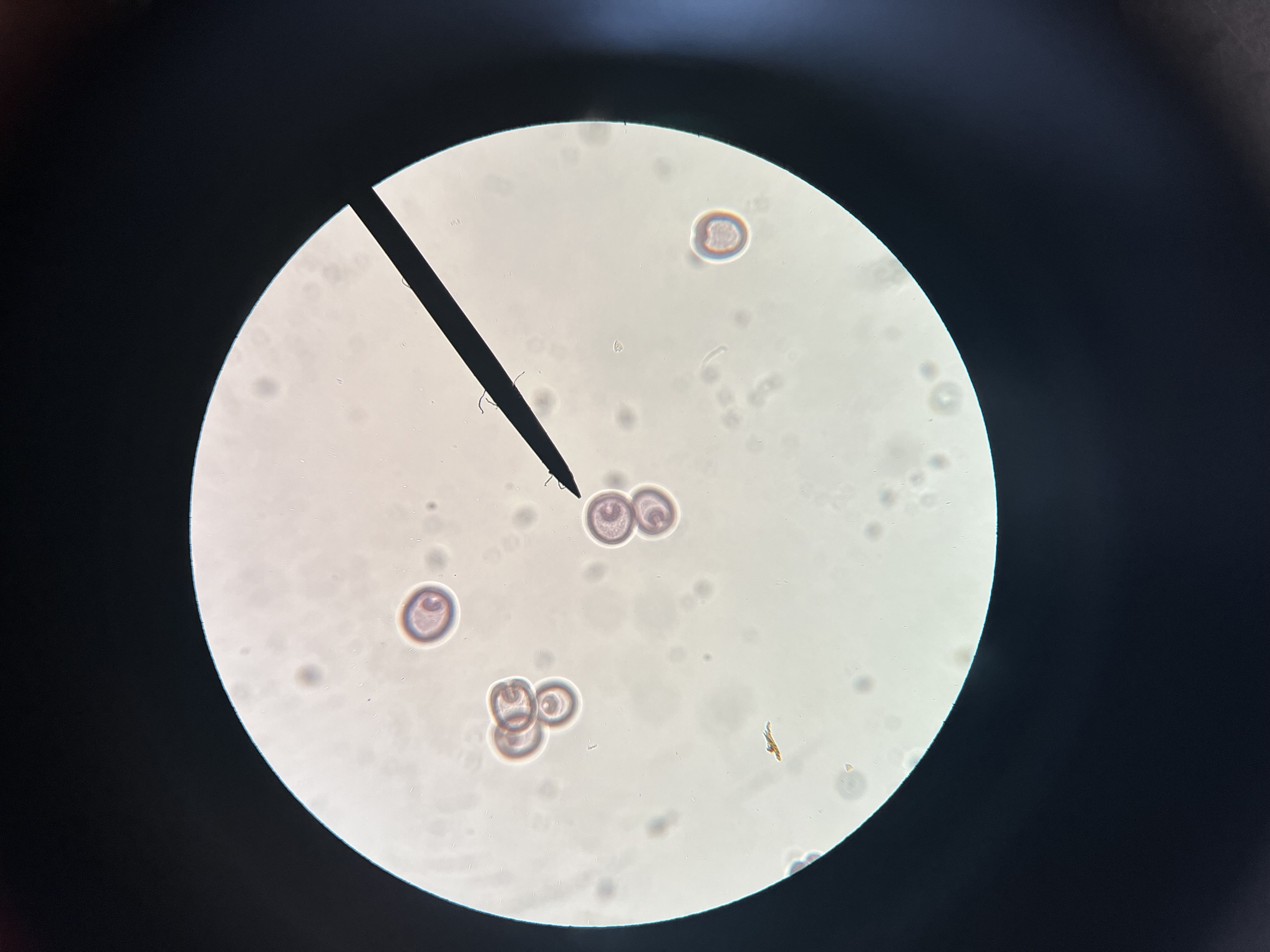
starfish development
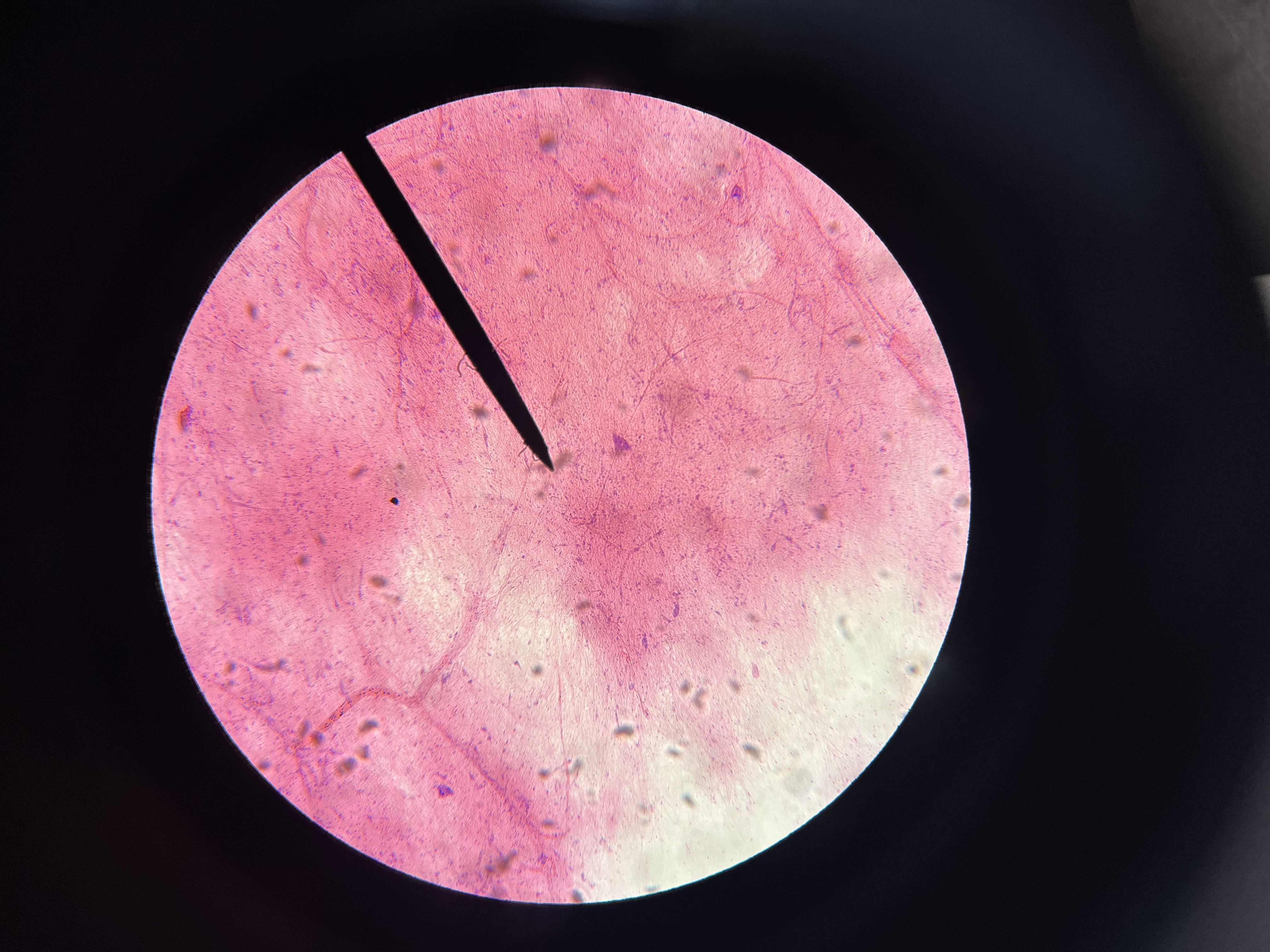
Nerve cells spinal cord
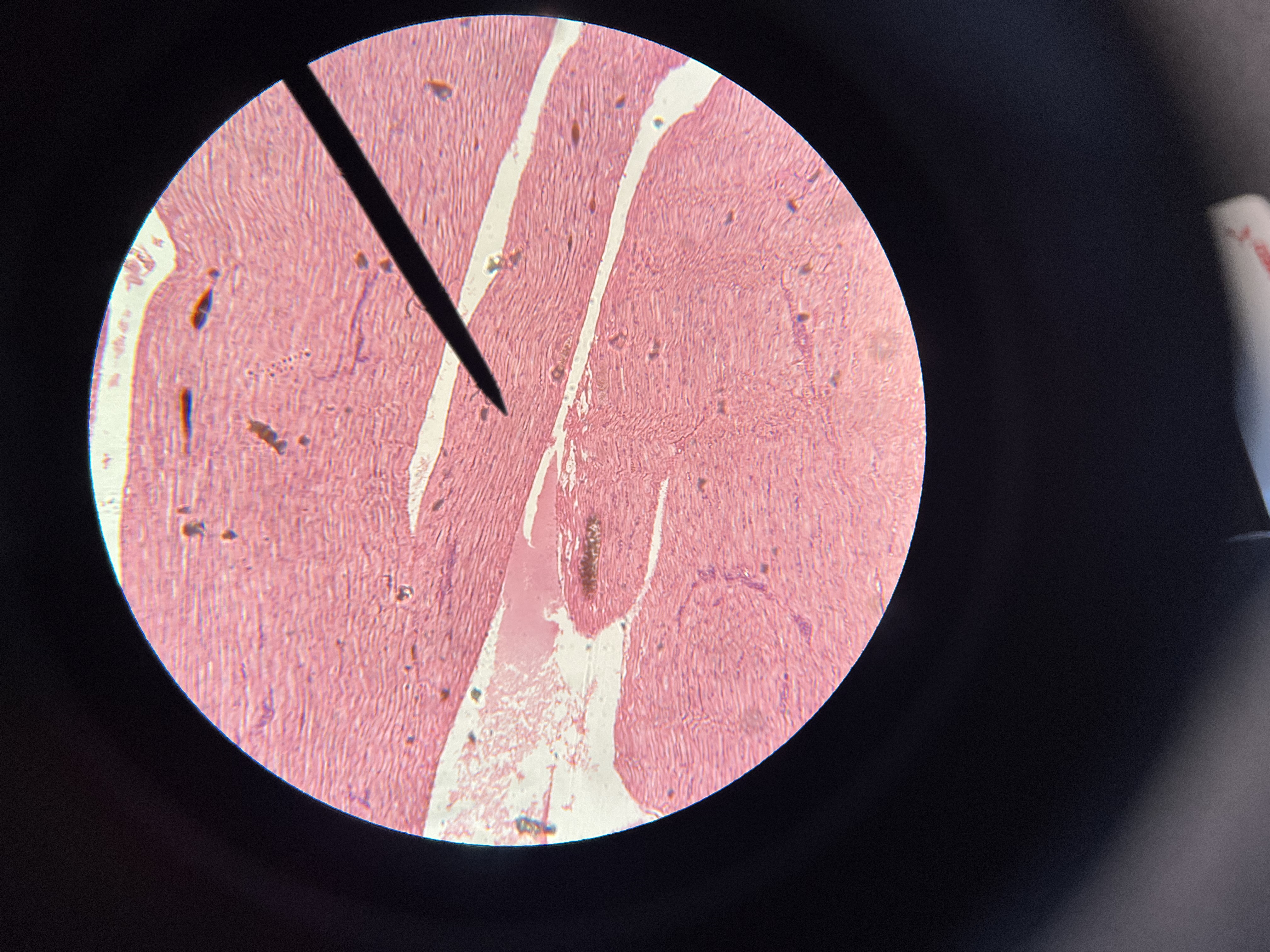
Cardiac Muscle intercalated discs
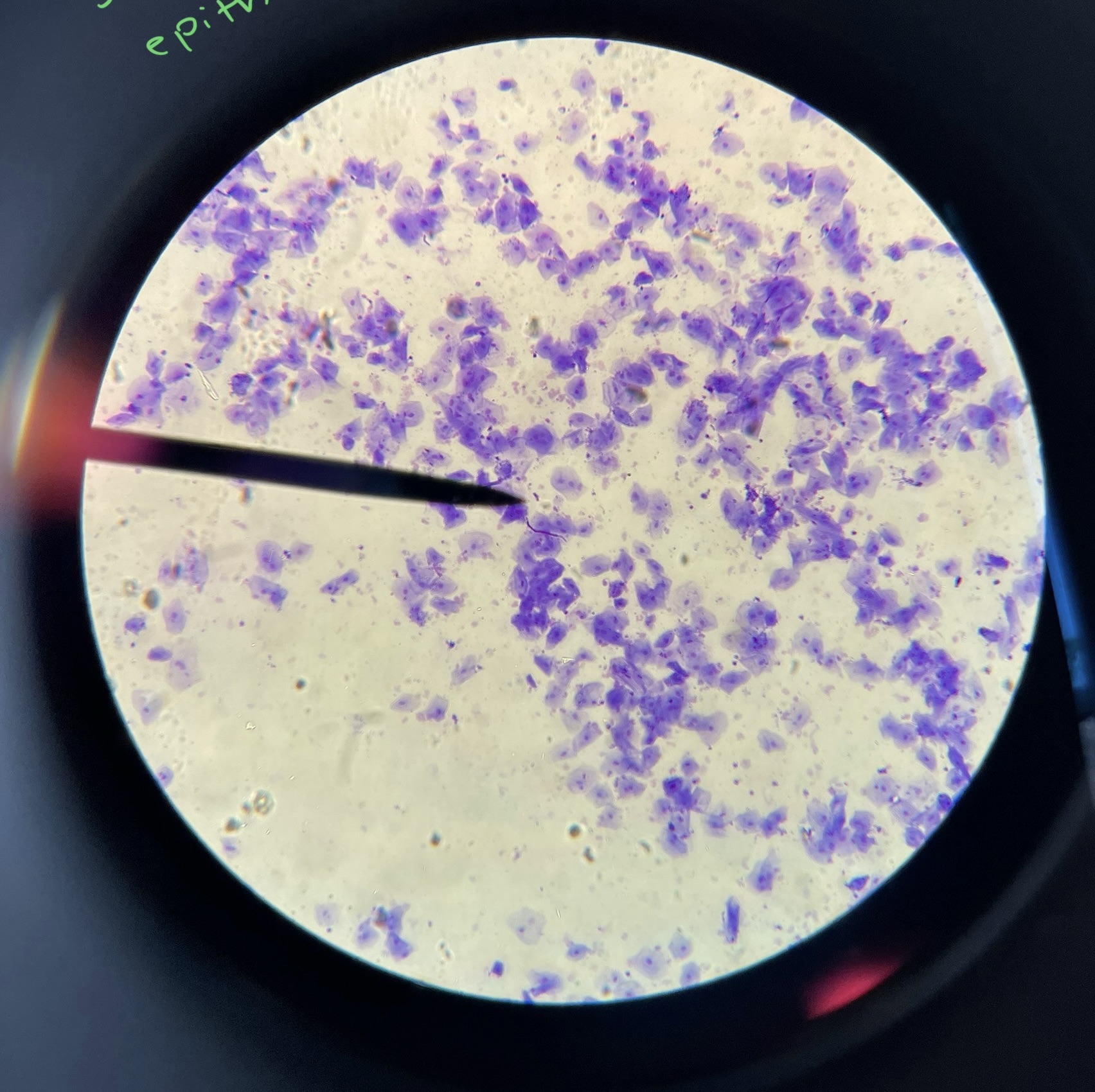
Simple squamous Epithelium
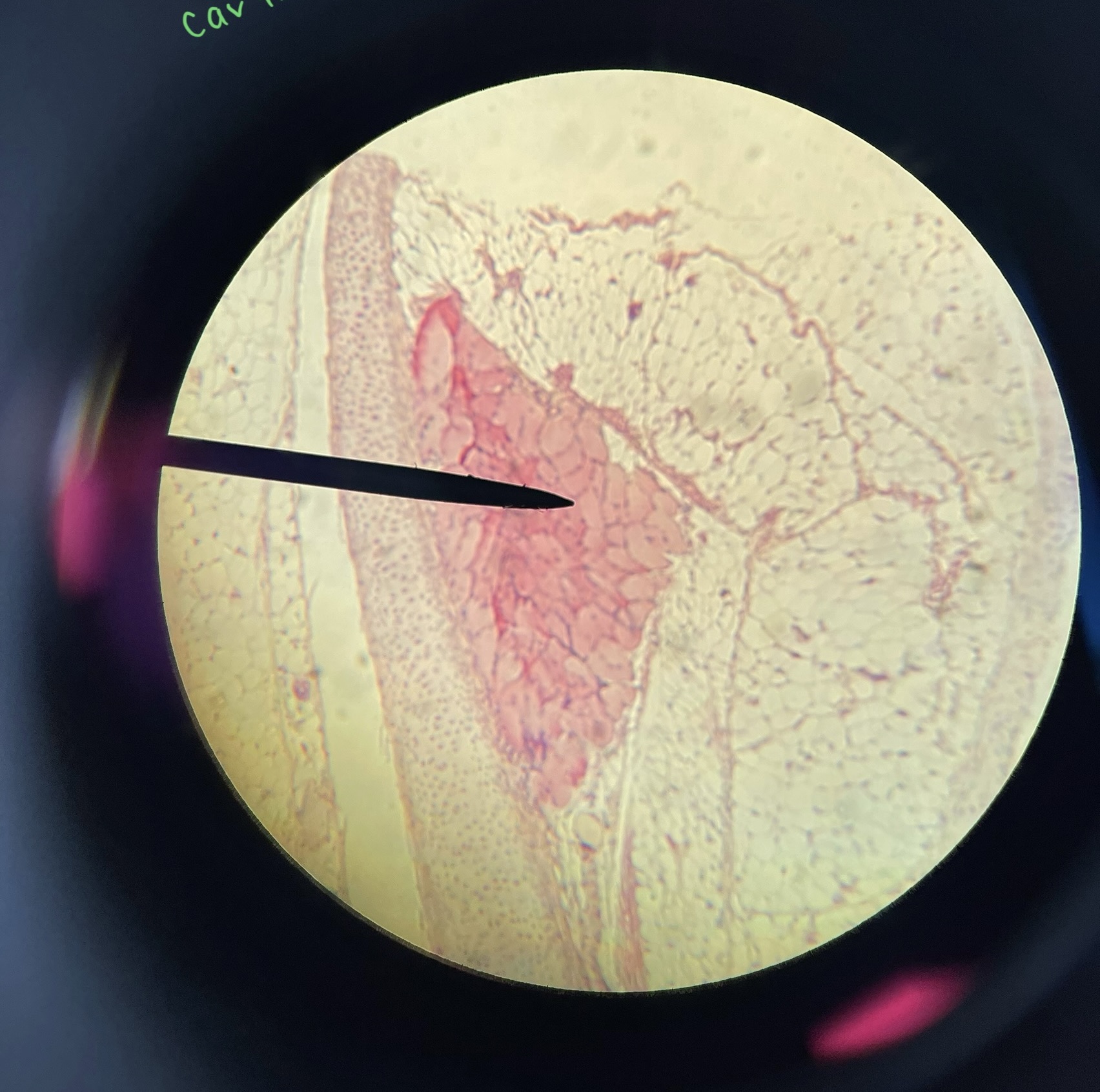
Hyaline Cartilage
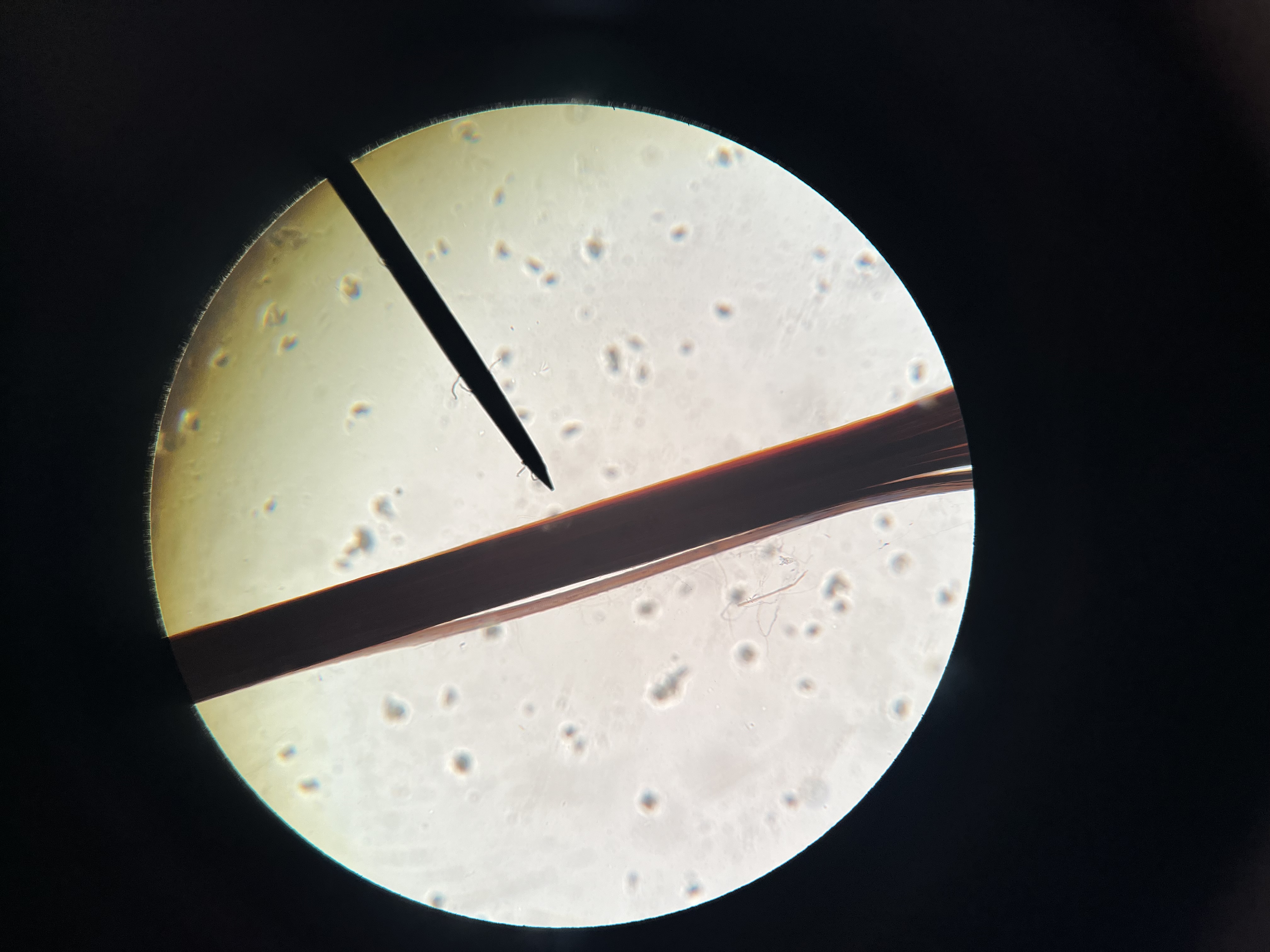
Skeletal Muscle teased
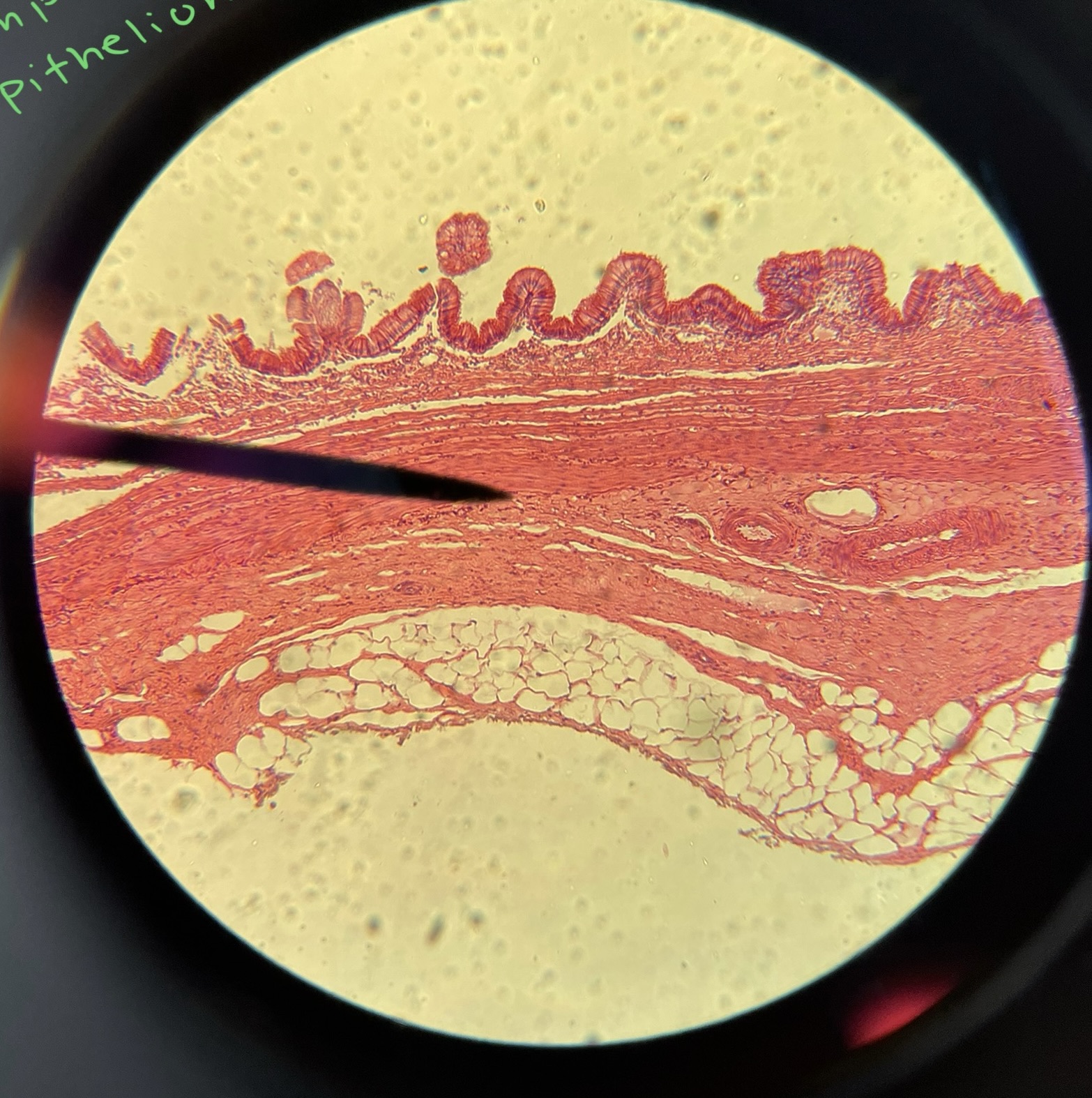
Human simple columnar epithelium
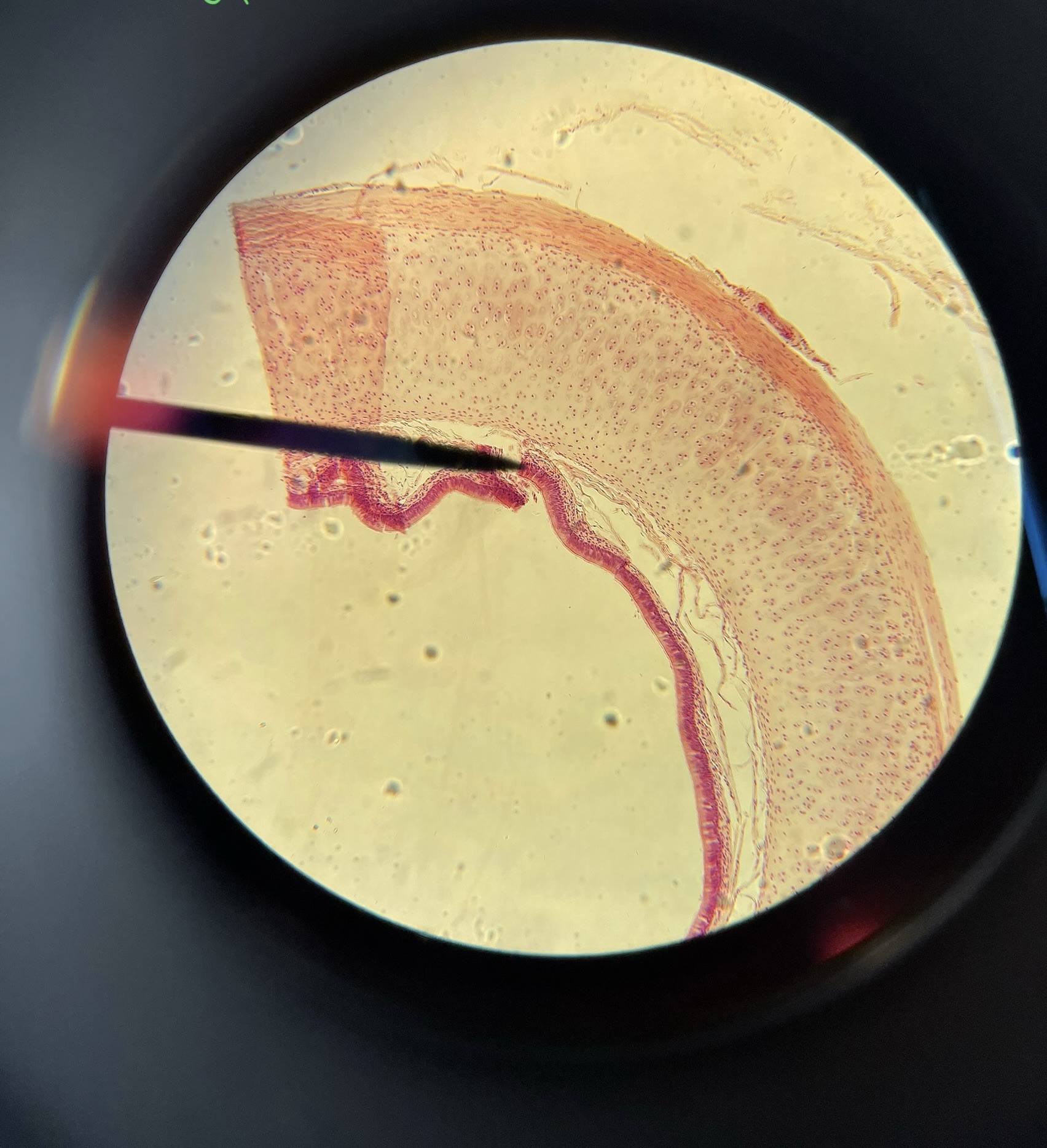
Ciliated columnar epithelium
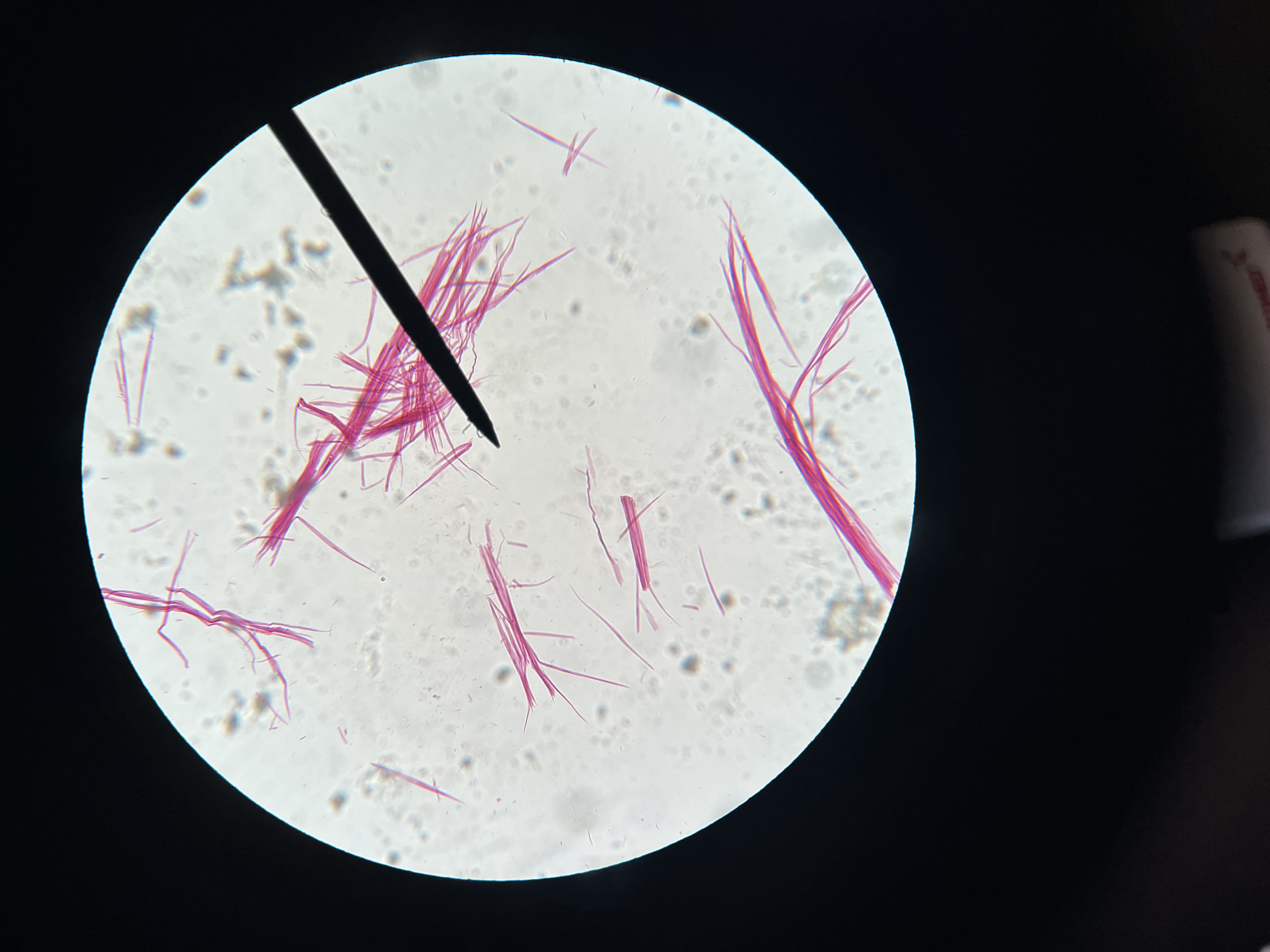
Smooth Muscle teased
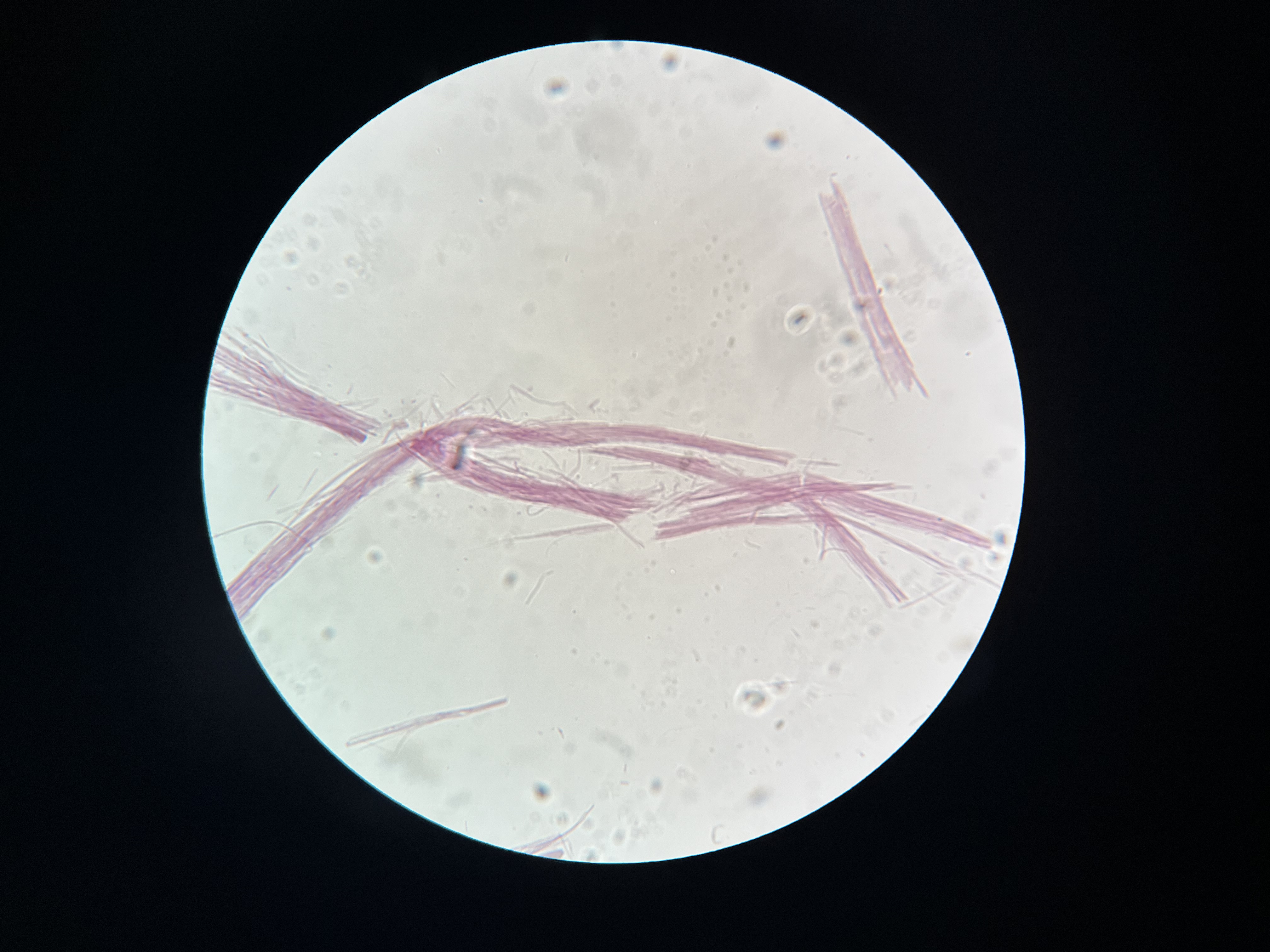
Heart muscle teased
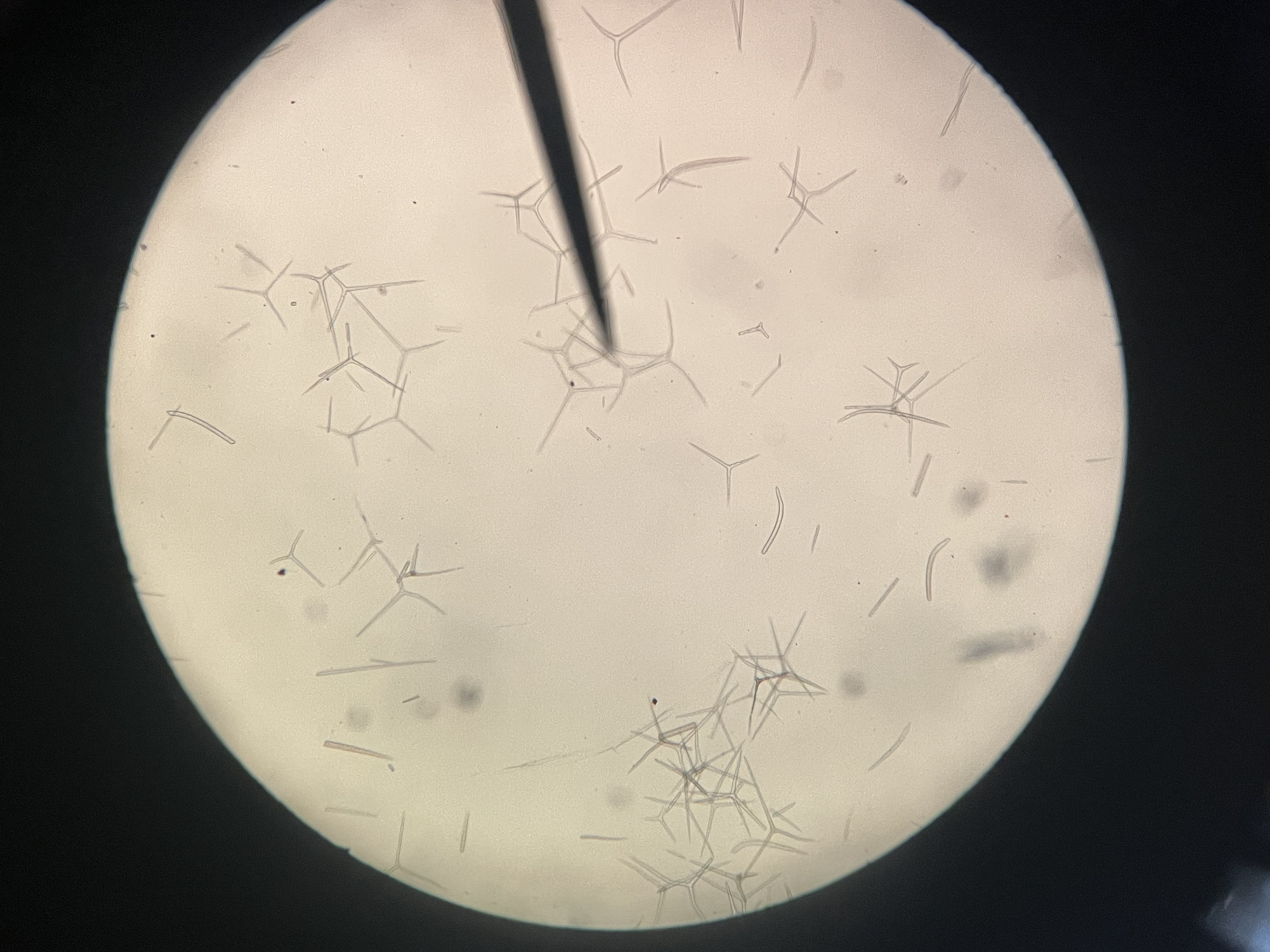
Sponge Spicules
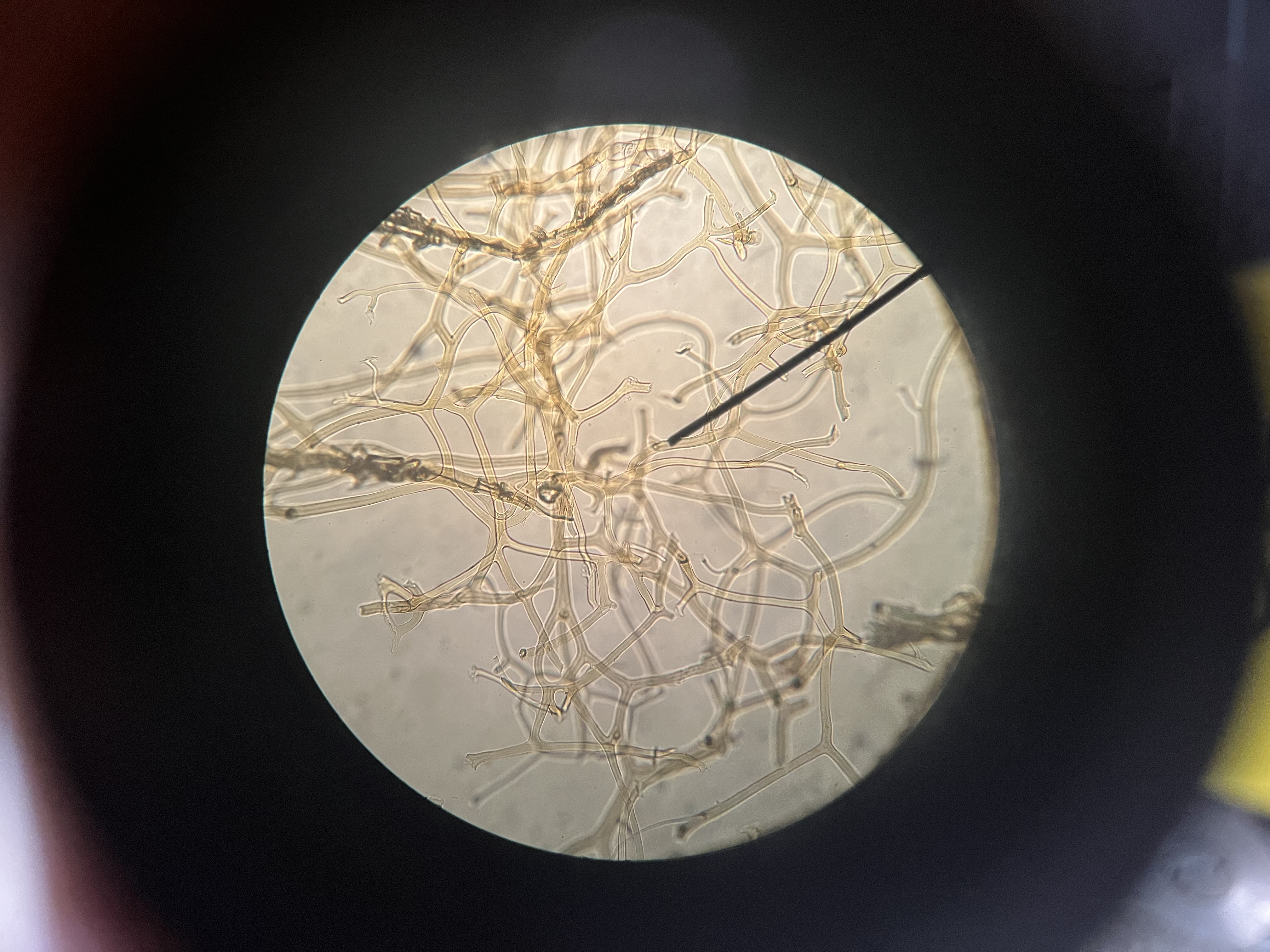
Commercial sponge fibers
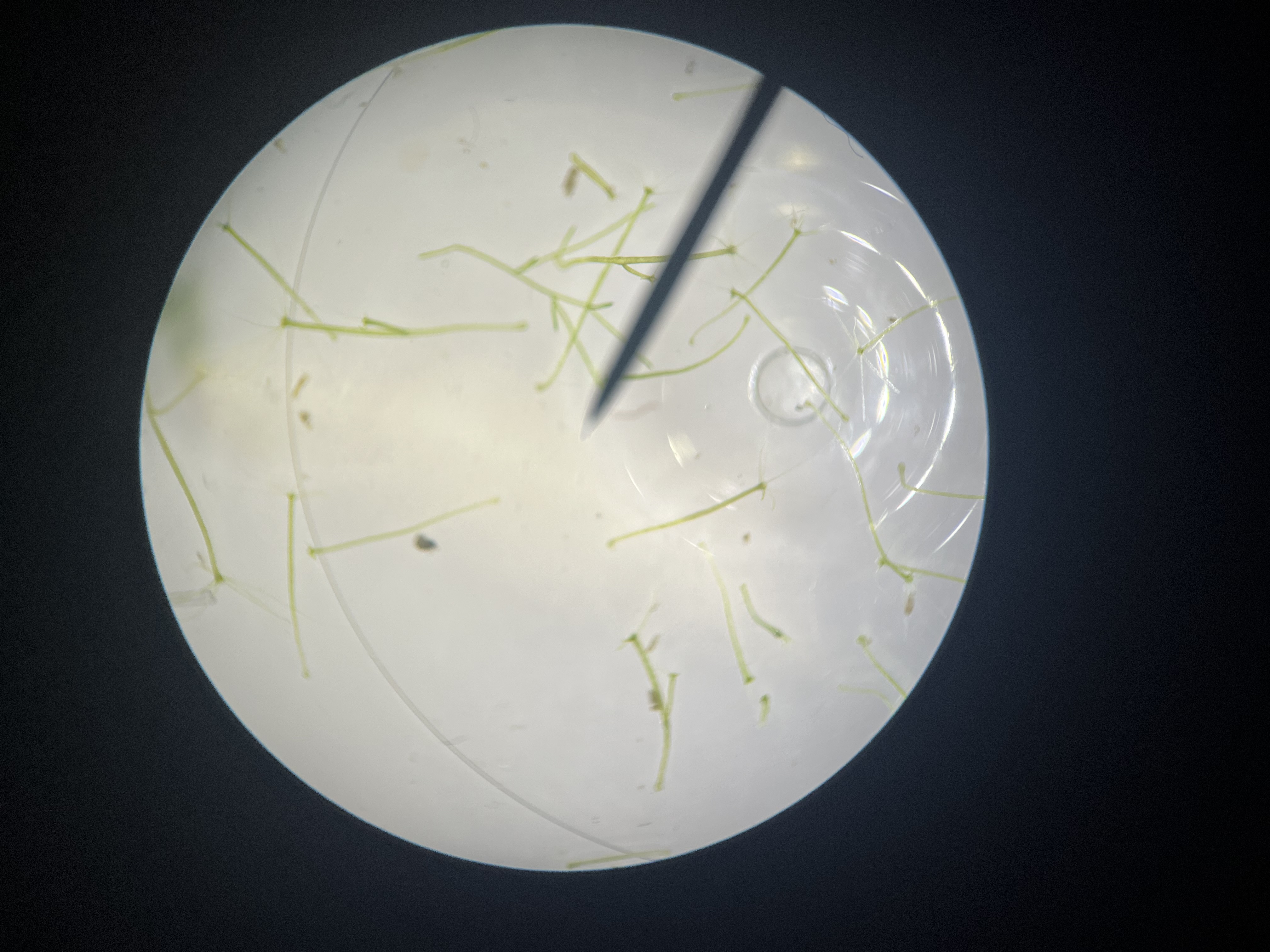
PHYLUM: CNIDARIA
CLASS: HYDROZOA
GENUS: Hydra
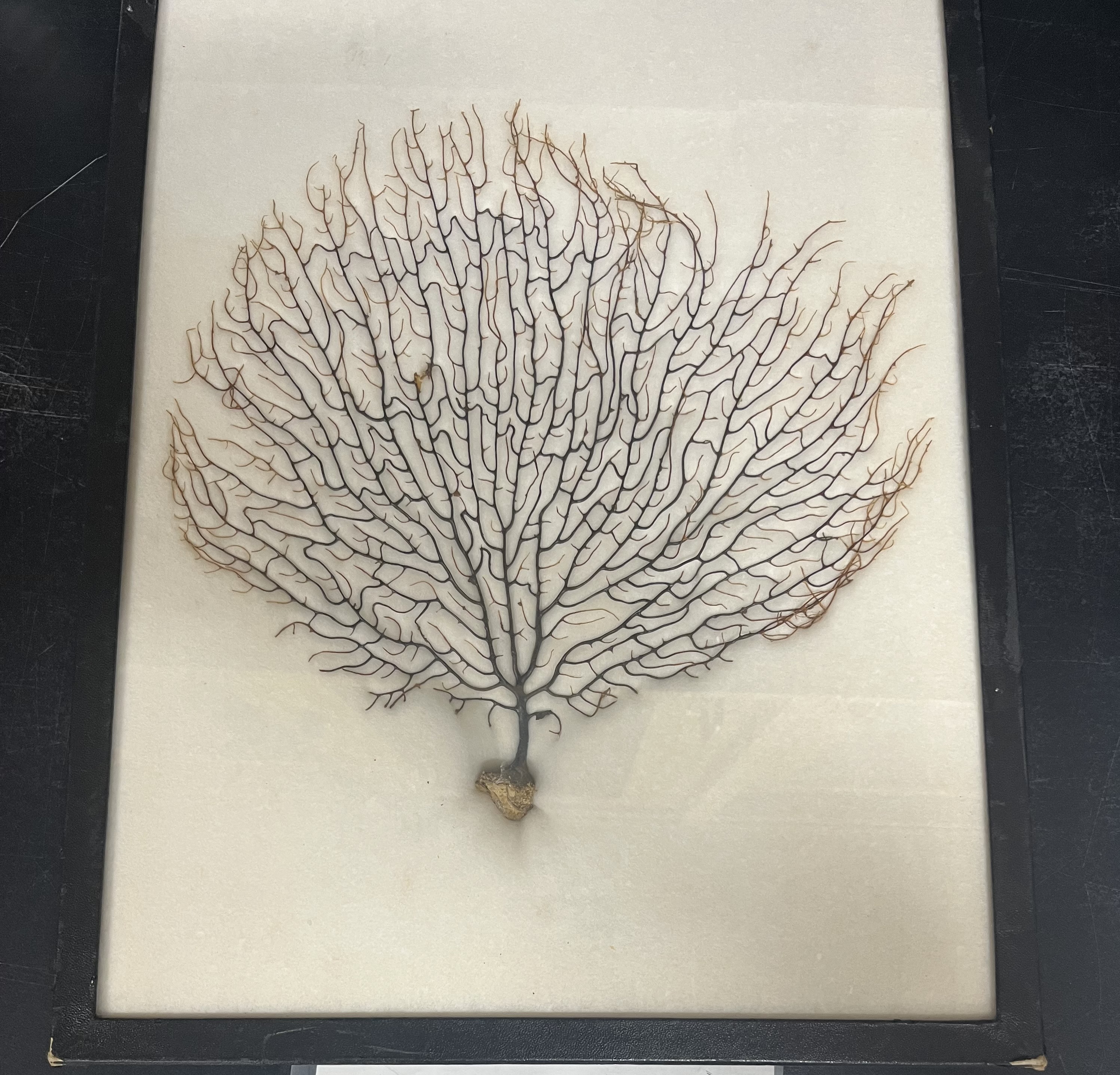

PHYLUM: CNIDARIA
CLASS: ANTHOZOA
NAME: SEA PANSY

PHYLUM: CNIDARIA CLASS: ANTHOZOA
GENUS: Metridium
NAME: SEA ANEMONE
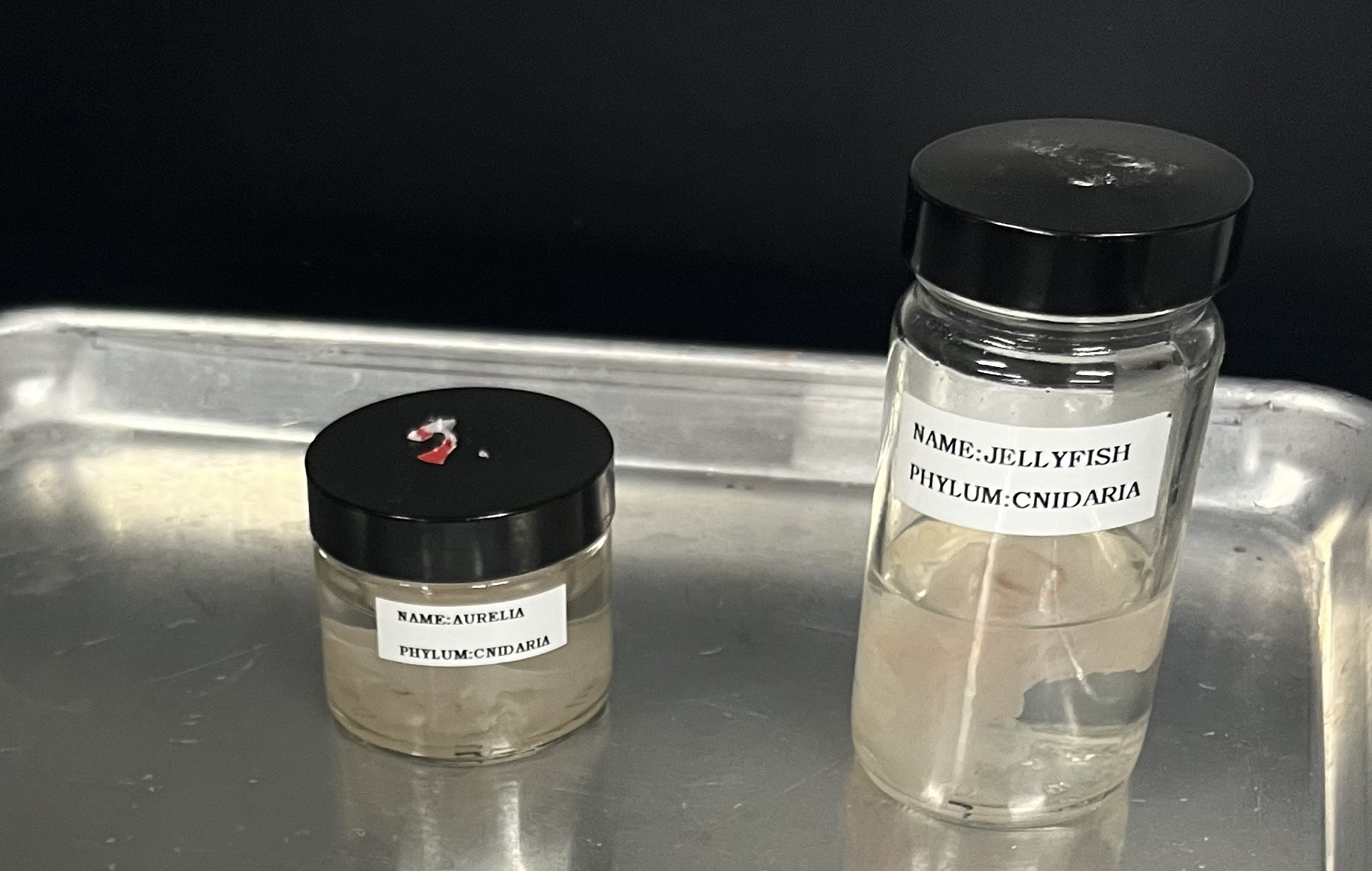

PHYLUM: CNIDARIA
CLASS: SCYPHOZOA
GENUS: Aurella
NAME: SEA JELLIES