Mentalization-Based Treatment
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:36 AM on 6/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
Mentalizing
Capacity to understand ourselves and others in terms of intentional mental states
Thinking & feeling at the same time, having the mind in mind, the heart in mind
Recognising that what's inside us influences us in many different ways
Understanding misunderstanding
Fundamental and developmental part of people, and something you never fully "succeed in learning"
Thinking & feeling at the same time, having the mind in mind, the heart in mind
Recognising that what's inside us influences us in many different ways
Understanding misunderstanding
Fundamental and developmental part of people, and something you never fully "succeed in learning"
2
New cards
Why can humans live in such large social groups?
Because we have the ability to make a whole set of interpretations about the person's mental state, intentions etc, which allows us to collaborate with them
3
New cards
E**ffective Mentalizing**
Being open to alternative perspectives
Taking responsibility, forgiveness, humility
Doubt or curiosity, openness to alternative perspectives
Turn taking
Thinking about life story
Belief in changeability
Awareness of the impact of affect
Etc.
Taking responsibility, forgiveness, humility
Doubt or curiosity, openness to alternative perspectives
Turn taking
Thinking about life story
Belief in changeability
Awareness of the impact of affect
Etc.
4
New cards
Non-effective mentalizing
Being very certain about the mental states of others (I'm sure he's mad at me")
Rigidity
Apparent lack of interest in mental states
Overfocused
Not: Being highly emotionally aroused, because you can still mentalize (even though it's harder)
Rigidity
Apparent lack of interest in mental states
Overfocused
Not: Being highly emotionally aroused, because you can still mentalize (even though it's harder)
5
New cards
What is the theoretical framework of mentalization-based therapy?
Initially, improving the mentalizing capacity
Over the past 10-15 years, more of a complex understanding - concept of epistemic trust was developed
Over the past 10-15 years, more of a complex understanding - concept of epistemic trust was developed
6
New cards
What is the “Window of tolerance” with mentalizing?
The fact that you need to be in a certain state of arousal (not too low, not too high) in order to effectively mentalize. If arousal is too low, there is numbness and shutdown, if it’s too high, you cannot see the other person’s perspective
\
\
7
New cards
What is the ideal framework of mentalizing development?
Caregiver:
• Reflects accurately the intentions of the child (mirroring) • Marked (baby-talking is an example of this; establishes "I think you're feeling this") /contingent/congruent
\
Child develops:
• Affect regulation
• Notion of a mind by being in mind
• Agency and subjective sense of self - only in the presence of someone else they develop
Are prewired to develop mentalizing, but need someone else to develop
• Reflects accurately the intentions of the child (mirroring) • Marked (baby-talking is an example of this; establishes "I think you're feeling this") /contingent/congruent
\
Child develops:
• Affect regulation
• Notion of a mind by being in mind
• Agency and subjective sense of self - only in the presence of someone else they develop
Are prewired to develop mentalizing, but need someone else to develop
8
New cards
Attunement
If you mirror something wrong, you can tell that you were wrong and figure out what the correct answer is (together with the patient)
9
New cards
What are the three mentalizing modes, when do they show up and what happens if something goes wrong?
**Teleological** (0-1,5 years):
Object constancy (if I can't see it, it's not there, panic when they don't see caregiver).
Their understanding of the world is based on external actions and characteristics.
Internal mental states can only be affected by physical actions/impact.
In patients: Only know they're loved if they get reassurance through Whatsapp messages Sometimes overlaps with:
**Psychic equivalence (1,5-3 years):**
Own internal = external reality
Concrete understanding/suspension of doubt (I feel (that there's a monster under the bed), so there must be)
Rigid beliefs and thoughts "Knowing/reading" the minds of others
No room for alternative perspectives
In patients: I don't feel stuck, I am stuck. Need to join that perspective initially Flashbacks: Feeling that you are in the situation
\
**Pretend (3-4 years)**
Internal reality is disconnected from external reality i.e. Pretend play: chair is a train, if you dress up as a knight you are a knight
Feelings of emptiness / dissociation Have all kinds of insights that are not directly linked to actual mental states Circularity without confusion
Hyper-mentalizing
Dissociation
Object constancy (if I can't see it, it's not there, panic when they don't see caregiver).
Their understanding of the world is based on external actions and characteristics.
Internal mental states can only be affected by physical actions/impact.
In patients: Only know they're loved if they get reassurance through Whatsapp messages Sometimes overlaps with:
**Psychic equivalence (1,5-3 years):**
Own internal = external reality
Concrete understanding/suspension of doubt (I feel (that there's a monster under the bed), so there must be)
Rigid beliefs and thoughts "Knowing/reading" the minds of others
No room for alternative perspectives
In patients: I don't feel stuck, I am stuck. Need to join that perspective initially Flashbacks: Feeling that you are in the situation
\
**Pretend (3-4 years)**
Internal reality is disconnected from external reality i.e. Pretend play: chair is a train, if you dress up as a knight you are a knight
Feelings of emptiness / dissociation Have all kinds of insights that are not directly linked to actual mental states Circularity without confusion
Hyper-mentalizing
Dissociation
10
New cards
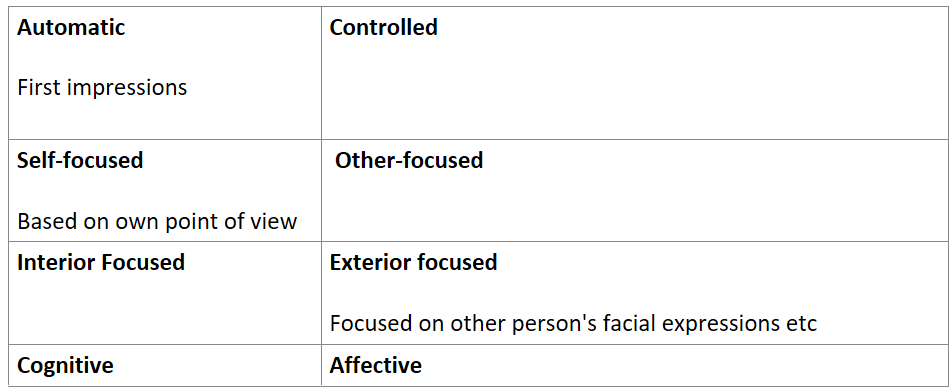
What are some dimensions of mentalizing?
Cognitive: capacity for perspective-taking and belief-desire reasoning (the capacity to understand people’s actions based on their beliefs and desires)
11
New cards
How do we know that epistemic trust is not innate?
Young children are very mistrustful of new information - first need to develop a good filter
12
New cards
What happened in the experiment where a child was asked to give an object to an experimenter?
1. Child is just asked to give one object to the experimenter (50%)
2. Experimenter expresses preference (70% of time child gives preferred object)
3. Other experimenter asks for the child to give the object (77% child gives object that first experimenter preferred -- generalizing)
4. Pay attention to the child (mentalizing and generalization happens). Don't pay attention to the child: Child doesn't generalize the preference to the second experimenter
13
New cards
What are the 3 mentalizing techniques that people learn about when they do mentalization-based therapy?
1. Teaching and learning content
1. Communication of therapeutic treatment model, group psychotherapy, think about therapy from a common perspective
1. The re-emergence of mentalizing
1. Reinstating mentalizing when it's lost, entering into a "not knowing" stance
1. Apply social learning in the wider environment
14
New cards
What is some evidence for mentalizing being an effective treatment?
Since 2017, lots of meta-analyses that show that MBT works for BPD
Symptomatic improvement: people can lose their diagnosing
Interpersonal improvement: less improvement
Less connection to the world around them
Evidence MBT is better for more severe cases or BPD in adolescents
Mentalizing: Now being broadened for use in other disorders as well
Symptomatic improvement: people can lose their diagnosing
Interpersonal improvement: less improvement
Less connection to the world around them
Evidence MBT is better for more severe cases or BPD in adolescents
Mentalizing: Now being broadened for use in other disorders as well
15
New cards
How does MBT work?
Not many techniques/exercises in MBT: more of a principle focused therapeutic model
Collaborative process: Client is expert on him/herself
Highly structured and clear focus in the treatment phases and sessional structure
Consistent, coherent, continuous
Acknowledge what the patient brings to the table, not assuming you know "more"
Interventions are focused on affective arousal level and mentalizing
Active not-knowing therapeutic stance
Collaborative process: Client is expert on him/herself
Highly structured and clear focus in the treatment phases and sessional structure
Consistent, coherent, continuous
Acknowledge what the patient brings to the table, not assuming you know "more"
Interventions are focused on affective arousal level and mentalizing
Active not-knowing therapeutic stance
16
New cards
How are people in MBT told to behave “Like a normal person”
Having a good time = mentalizing
Placing yourself in their shoes
What do I think/feel and how might that help the process
Model honesty, courage, but also humility
We all lose our mentalizing capacity sometimes, even if you're a professional
Placing yourself in their shoes
What do I think/feel and how might that help the process
Model honesty, courage, but also humility
We all lose our mentalizing capacity sometimes, even if you're a professional
17
New cards
What are the treatment plans for MBT?
* Dynamic formulation (case conceptualization): Linking mentalizing assessment
* Addressing 5 goals of MBT: Commitment, Reducing general psychiatric symptoms, improve interpersonal relationships, reduce destructive behaviours, improve societal functioning)
* Try to make SMART goals
* For example: Try to get them to consider what they're feeling just before something bad happens (when you feel misunderstood, you withdraw)
* Initial treatment phase: Individual psychotherapy and crisis management, psychiatric consultation
* Intensive treatment phase: Group therapy, individual psychotherapy and crisis management
* Final treatment phase: Lowering frequency of therapy
* Addressing 5 goals of MBT: Commitment, Reducing general psychiatric symptoms, improve interpersonal relationships, reduce destructive behaviours, improve societal functioning)
* Try to make SMART goals
* For example: Try to get them to consider what they're feeling just before something bad happens (when you feel misunderstood, you withdraw)
* Initial treatment phase: Individual psychotherapy and crisis management, psychiatric consultation
* Intensive treatment phase: Group therapy, individual psychotherapy and crisis management
* Final treatment phase: Lowering frequency of therapy
18
New cards
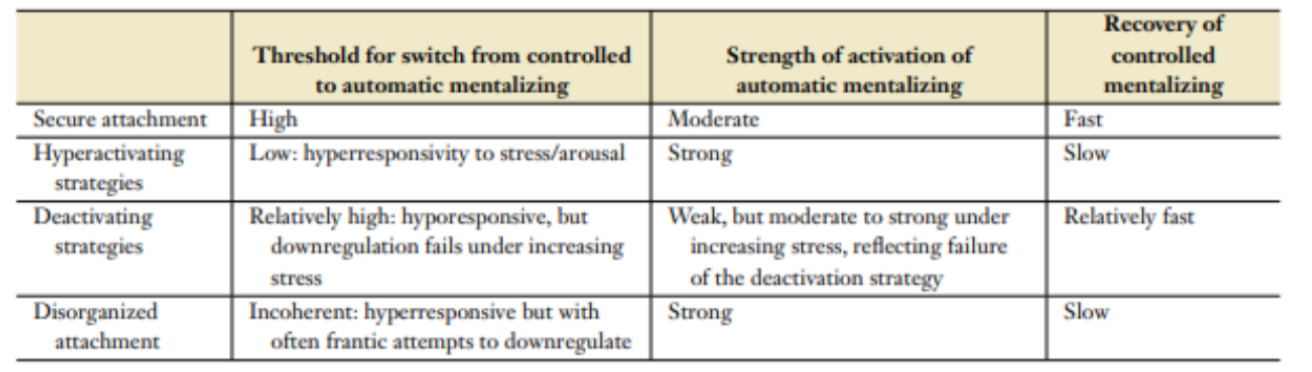
What are the way different aspects of mentalizing develop in different attachment styles?
19
New cards
What are some strengths of MBT?
Low dropout rates and better effectiveness with patients with more severe symptoms
20
New cards
What is the social commmunicative perspective?
A perspective that includes social and cultural context in developing mentalizing. It proposes that effective changes in mentalizing are due to one of 3 systems
\
\
21
New cards
What are the 3 communication systems as proposed by the social communicative perspective
Communication system 1: the treatment should contain effective and self-relevant models of the mind to the patient
Communication system 2: Reactivating the patient’s capacity for epistemic trust within a trusting therapeutic environment. The goal is to enhance mentalizing and foster the virtuous cycle of salutogenesis
Communication system 3: Reengagement with the social world by mentalizing. This frees the patient of isolation
Communication system 2: Reactivating the patient’s capacity for epistemic trust within a trusting therapeutic environment. The goal is to enhance mentalizing and foster the virtuous cycle of salutogenesis
Communication system 3: Reengagement with the social world by mentalizing. This frees the patient of isolation
22
New cards
What creates vulnerability for BPD according to MBT treatment?
Early neglect/ early environment incompatible with understanding oneself and others creates vulnerability for BPD
23
New cards
Therapeutic relationship in MBT
Very important, collaborative
Clinician tries to see things from patient’s perspective
Transference not to explain things, but to discuss client-therapist relationship for the benefit of the client
Clinician tries to see things from patient’s perspective
Transference not to explain things, but to discuss client-therapist relationship for the benefit of the client
24
New cards
What are the 5 goals of MBT?
Commitment, Reducing general psychiatric symptoms, improve interpersonal relationships, reduce destructive behaviours, improve societal functioning)