1.3 Environmental Factors in Disease
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
the six environmental diseases addressed
enviro toxins
tobacco
alcohol
non-therapeutic drugs
therapeutic drugs
physical agents
the types of enviro toxins:
carbon monoxide
lead
mercury
what is carbon monoxide?
colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-irritating gas
chronic poisoning may develop working in confined enviro
most common direct chemical cause of death
how does carbon monoxide work?
hemoglobin replaced by carboxyhemoglobin which limits capacity to carry oxygen
acute: cheery/vibrant red skin and oral mucosa
result: irreversible impairment of memory, vision, hearing, speech
lead as enviro toxin
pipes, gas, paint
absorption: 80-85% uptake teeth, bone 5-10% in blood, rest in soft tissues
Flint: switch to Detroit river as water source but lead pipes
more than 25% of homes greater than acceptable limit of 15 ppb
some house up to 13, 000 ppb
how does lead toxicity affect people?
children:
generally irreversible
low IQ
hyperactive
poor organizational skilla
adult: peripheral neuropathies
what is Burton’s line?
along gingival margin, result of heavy metal toxicity: lead
on hard tissue of teeth and soft tissue of gingiva
mercury as enviro toxin
mercuric chloride
source: seafood, mad hatter textile industry
result: acute GI ulcers ad severe renal damage
mercury toxicity can cause:
tongue tremor
gingivitis
bruxism
excessive salivation
trichotillomania: pull one’s hair
best recognized traditional risk factor for oral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
tobacco (and heavy alcohol consumption)
other risk factors: HPV, h/o cancer, immunosuporession
clinical presentations of oral and oropharyngeal cancer
leukoplakia: white
erythroplakia: red
non-healing ulcer
exophytic mass
high risk location of oral and oropharyngeal cancer
ventro-lateral tongue
floor of mouth
tonsillar pillars
oral and oropharyngeal cancer 5-year survival rate:
67%
Dna damage to epithelial cells of vaper vs non-vapers
2.6 times the damage
one drink is how many g of pure alcohol
1.5 oz distilled liquor
5 oz wine
12 oz beer
moderate vs heavy drinker
men | women | |
moderate | 2/day | 1/day |
heavy | 15/wk or 4/day | 8/wk or 3/day |
three drugs of abuse
cocaine
heroin
marijuana
1.5 mil users, 15-20% crack
smoked (w tobacco), ingested, injected, snorted
among most addictive of all drugs ‘no physical dependence
cardiovascular, CNS, teratogenic effects
vasoconstrictive, ischemia, palatal perforations
cocaine
from poppy plant
sequelae: a condition which is the consequence of a previous disease or injury
sudden death
pulmonary disease
infections
skin lesion
renal disease
heroin
increases heart rate and bp
3-fold increase in tar inhaled and retained in lungs compared to tobacco
in MA: indiv 1oz on person and 10oz in home but use prohibited in public
marijuana
therapeutic drugs addressed
aspirin, acetaminophen, hormonal replacement therapy, oral contraceptives, immunosuppressive, cancer chemotherapy
chronic toxicity → gastroduodenal bleeding
reye syndrome: encephalopathy following acute, febrile, viral illness in child
aspirin
large dose lead to hepatic necrosis
toxicity starts with nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
in suicide attempts
acteaminophen
Aspirin and acetaminophen are both
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) that inhibit cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes in stomach lining = irritation
hormonal replacement therapy adverse effects
thrombosis: blood clots
breast cancer
endometrial carcinoma
oral contraceptives adverse effects
thrombosis: blood clots
increase cervical cancer risk
no increase risk of breast cancer
protective against endometrial cancer
immunosuppressive adverse effects
opportunistic infections
cancer chemotherapy adverse effects
alopecia
GI erosion/ulceration
bone marrow failure
acute leukemia
other malignancies
two types of injury by physical agents
mechanical and radiation injury
physical injury type causes of death:
hemorrhage into body cavities
fat embolism from bone fractures
ruptured viscera
secondary infection
renal failure
mechanical: abrasions, contusions, lacerations incised wounds, puncture wounds
effects of (BLANK) trauma:
chronic low-grade trauma: prolif of tissue by stimulating fibroblasts and collagen
ex: poor fitting dentures can cause damage in vestibule
what type of physical injury leads to
DNA damage and carcinogenesis
damage to organ systems
fibrosis
(Ionizing) radiation: electron release cascade
(vs non-ionizing moves but does not displace electrons)
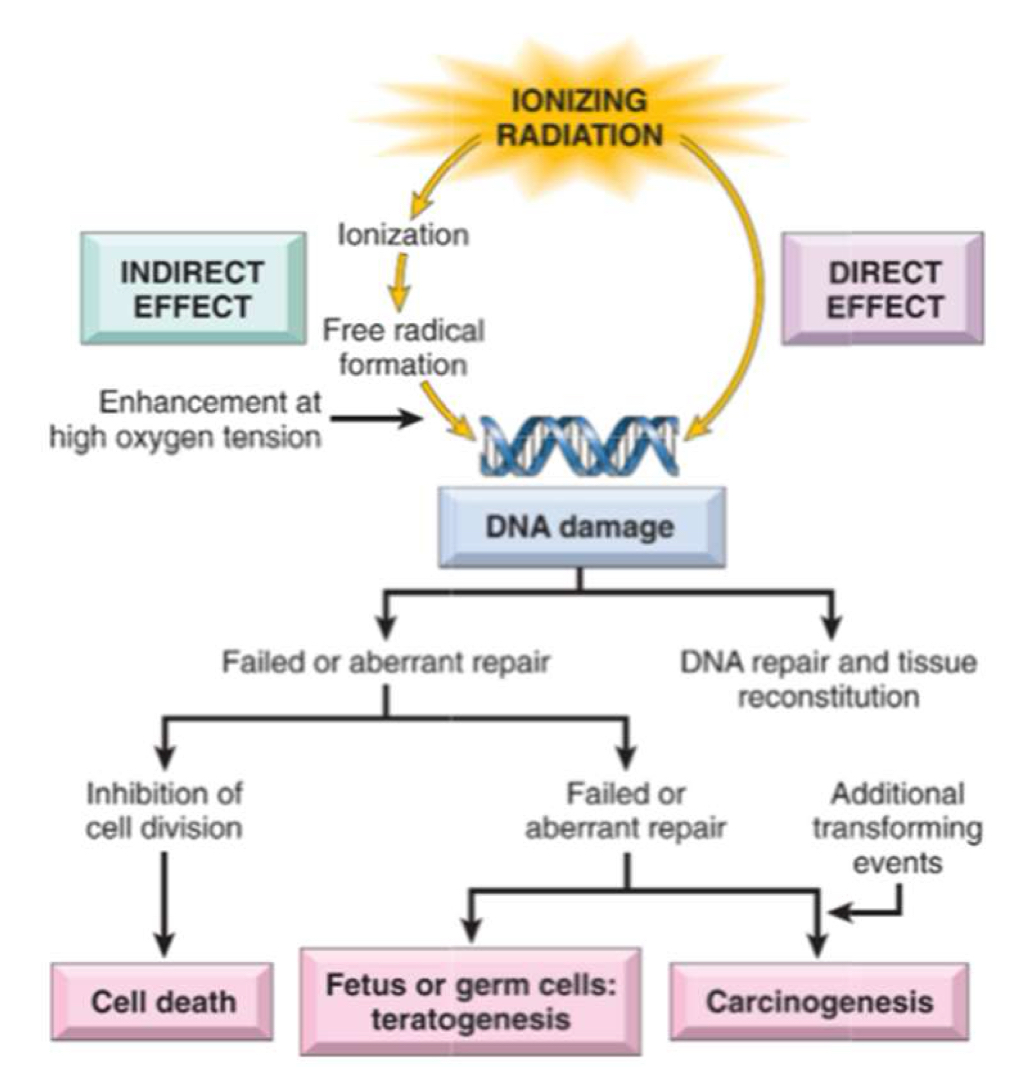
radiosensitivity of
bone
teeth
cartilage
muscle
CNS
kidney
liver
most endocrine glands
low sensitivity
radiosensitivity of
lymphoid
hematopoetic
germ
GI mucosa
rapidly dividing tumor cells
high sensitivity
radiosensitivity of
fibroblasts
endothelial cells
elastic tissue
salivary glands
eye
intermediate sensitivity
how does ionizing radiation injury work?
50 Gy (5,000) to any one body region: no severe or lethal consequences, but possible minor changes
what amount of ionizing radiation injury is deadly?
3 Gy to whole body 20-50% death
10 Gy to whole body 100% death
ionizing radiation sequelae
neoplasia: leukemias, cancers of bone, skin, thyroid, lung, breast
severe CNS injury
mucosal ulcers
acute bone marrow failure