COM - Theory - M4
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
The Self
Self-awareness processes : knowing yourself
Interactions with others
Agency and Self-Regulation
Self-Knowledge
everything you believe to be true about who you are, what you are and what is important
Self-Schema
Individual beliefs (trait & state)
Trait
stable and enduring characteristics or pattern of behaviour
State
Temporary way of being that changes per situation
Forming of self-knowledge
Introspection
Interactions with the self
Interactions with others
Self-concept motivators
Diagnosticity
Self-Enhancement
Consistency of self-verification
Diagnosticity
Preference for clearest information
Self-Enhancement
Preference for favourable information
Consistency of self-verification
Preference for confirmation
Self deception
believing what you want ; Self-serving attribution bias (take credit, blame others) ; Basking in reflected glory
Self Esteem
Evaluative part of self-concept
High = consistent belief
Self in interaction with others
Self emerges from interpersonal relations ; Self-presentation (impression management)
Social Identity Theory
We define our identity based on whom we interact with
Social Categorization
In-Group and Out-Group
In-Group
Group that one belongs to
Out-Group
Group one does not belong to
Social facilitation
Performing a task with an audience (know well → performance up / don’t know well → perfomance down)
Self Regulation
Self capacity to alter itself (internal & autonomous control / deliberate control)
Feedback loop
Comparing behaviour to standards
Monitoring: Keeping track of the behavior to be changed
Willpower: capacity to change the self
Agency
Need to assert oneself and make decisions based on personal interest and values
Frustration
Emotional outcome of a negative computing experience
High UX / High Usability
Important for participants
Provide easy form of leisure
Perform intended function w/o problems
Low UX / Low Usability
Causes frustration
Tasks users would rather not do
Products have problems that disturb use
High UX / Low Usability
Investment of time
Rewarding result
Meant for reaching a specific goal
Learning curve
Low UX / High Usability
Products with minor - severe issues
Easy to use, not enjoyable
Positive aspects of products
Utility ; Usability ; Likeability
Utility
Product works
Usability
User can work with the product
Likeability
Users feeling of suitability that leads to satisfaction
-
-
UX
Person’s perceptions and responses that result from the use or anticipated use of a product, system or service
Accessibility
Usability of a product/service/environment/facility by people with widest range of capabilities
Adoption
Longtidunial process leading to a decision for technology use
Acceptance
focuses more on the user’s perceptions of adopting a technological innovation
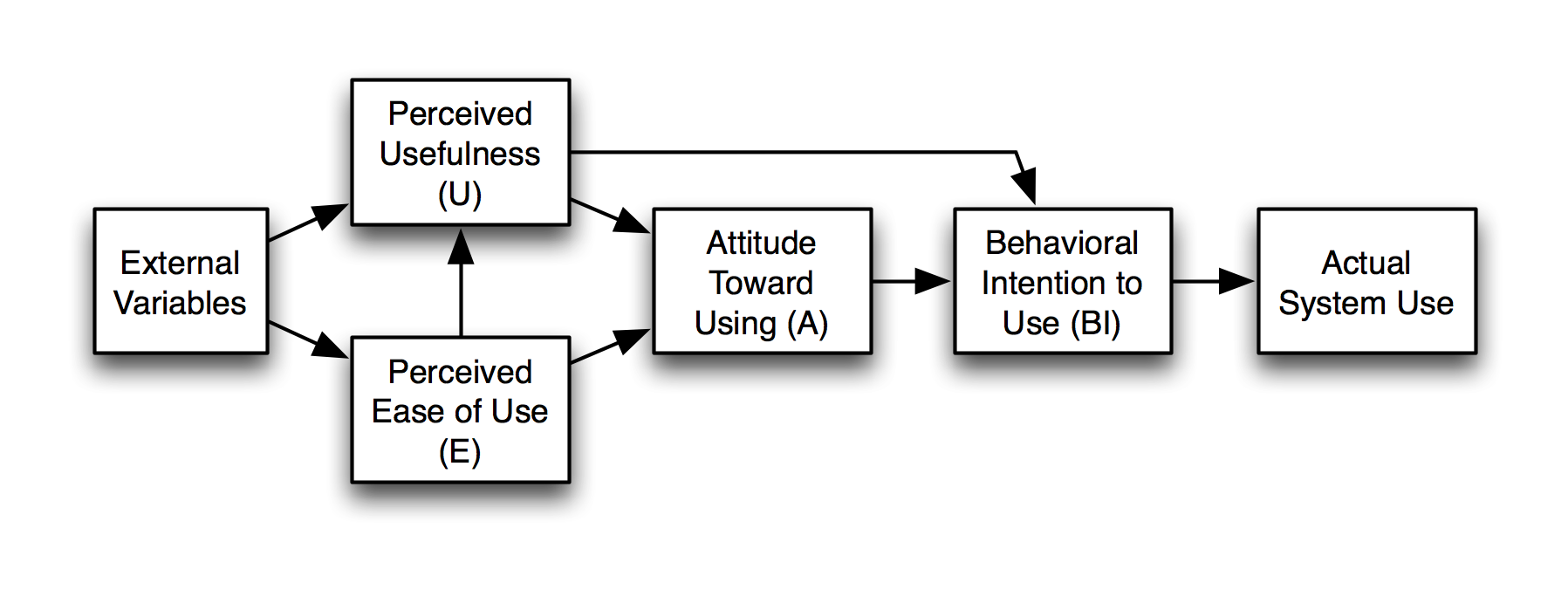
Technology Acceptance Model
Perceived Usefulness
Perceived Ease of Use
Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technologies
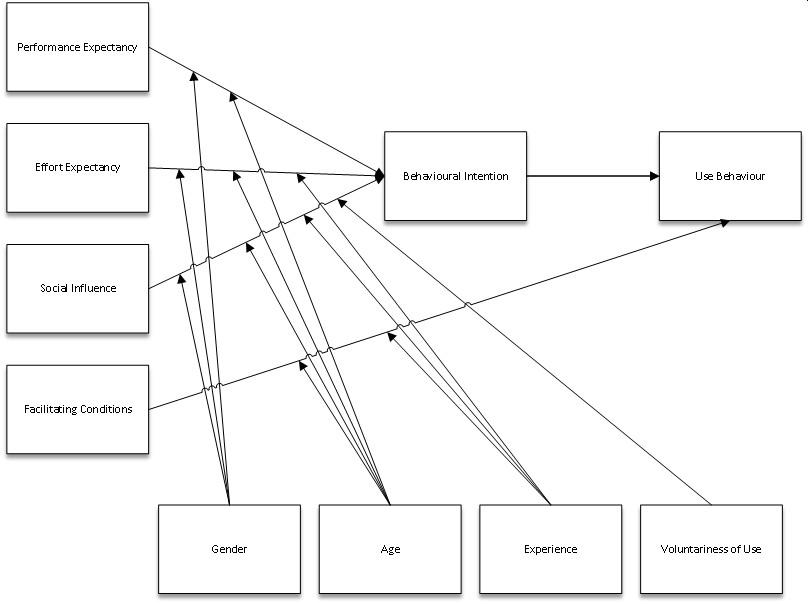
Integrates 8 seperate models
Bases includes elements on empirical results
Through psychological includes more of social environment and context
Focus on the determinants of perceived user friendliness and usefulness, social determinants of intended/actual use, and behavioral control/mental resources.
Appropriation
Technical and cognitive mastery of technology, which integrates practices into daily use in significant and creative manner
Processes for technology integration into users’ lives
Research focuses on quality, diversity, intensity, which influences impact
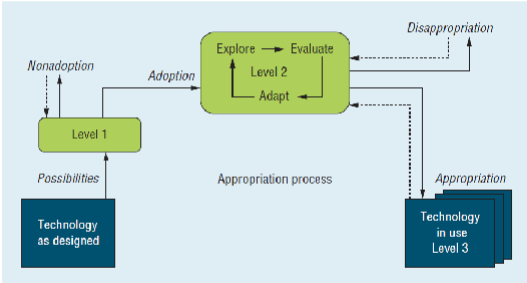
Model of Technology Appropriation
Model of Technology Appropriation - Levels
Initial Evaluation, weighing perceived features and value expectations
Getting to know technology through use. Constraints and functionalities are explored
Stable use of scenario of technology. Users know what they can use it for
Model of Technology Appropriation - Assumptions
Users shape technologies and users are shaped by technologies → constructivism
Teleological Perspective
Goal-drive change
Change driven by intentionality of users
Dialectical Perspective
Change is driven by opposing or contradictory forces
Evolutionary Perspective
Change occurs through continuous process of variation selection and retention
Domestication
Deals with cultural, social and technological networks of everyday life of households
Mutual shaping: technology and daily life affect each other
Technical properties might be less important than social negotiations and norms
Attitude
Good or bad evaluations we attach to objects
Valence (psychology)
the emotional value associated with a stimulus, event, or state.
Attitude structure
Valence and arousal
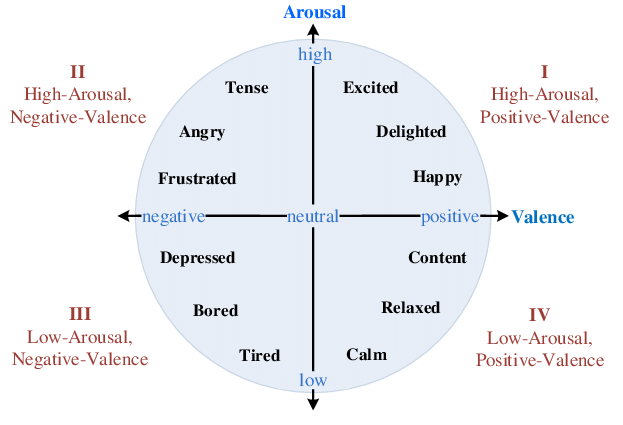
Attitude dimensions
Strength ; Extremity ; Importance ; Certainty ; Accessibility
Origins of attitude
Direct Exposure
Mere Exposure
Selective Exposure
Mere exposure
favourable attitude by increasing frequency
Selective exposure
avoiding / seeking information
Evaluative conditioning
valence of stimulus can be transferred to other stimuli when repeatedly represented together
Self-persuasion
Actively thinking about arguments in favor of a certain position
Advocating
Teaching yourself new positions theories
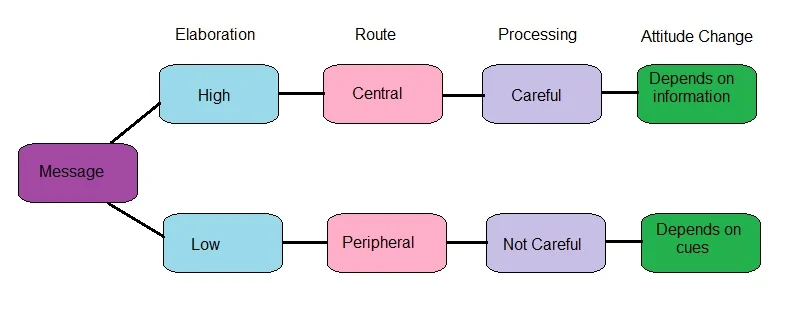
Elaboration Likelihood Model
Central vs Peripheral Route
The Six Principles of Persuasion
Reciprocity
Commitment
Social Proof
Liking
Authority
Scarcity
Unity
Reciprocity
Desire to give back when receiving an unexpected gift
Commitment
Desire to maintain consistency in what is said and done
Social Proof
Desire to follow lead of similar people
Liking
Desire to agree with people who share your values
Authority
Desire to agree with expert based on visual cues
Scarcity
Desire to get something that is limited or difficult to obtain
Unity
We’re likely to comply with requests from people in our group
Intention
Willingness to perform behaviour
Behaviour
Overt acts of an individual
Determinants of behaviour change
Self-Efficacy
Expected Outcome
Risk Perception
Goal setting & planning
Cognitive Dissonance
Two conflicting ideas
Try to rationalize dissonance
Change belief/action/perception of action
Biologically Primary Knowledge
We evolved to gain this knowledge
Modular knowledge, aquired independently
Acquired easily, automatically and unconsciously
Biologically Secondary Knowledge
Cultural knowledge
Types of knowledge that related and are acquired similarly
Acquired deliberately with conscious effect
Best acquired with explicit instruction
Information Processing Characteristics
Information store principle
Borrowing and reorganizing principle
Randomness as a genesis principle
Narrow limits of change principle
Environmental organizing and linking principle
Cognitive Load Theory
How we process information; germane, extraneous, intrinsic
Element interactivity
degree to which parts of knowledge have to be learned together to make sense
Germane
mental capacity for integrating old with new information
Extraneous
added load caused by bad instructions
Intrinsic
inate level of difficulty
Cognitive theory of multimedia learning
Dual channel
Limited Capacity
Active Processing
One channel is overloaded with learning demands
move essential processing to the other channel
Both channels are overloaded with learning demands
segmentation & pretraining
One or both channels are overloaded by combo of learning demands and distraction because extraneous material is included
Weeding & Signaling
One or both channels are overloaded by combo of learning demands and distraction because essential material is presented in a confusing way
Aligning words and pictures → spatial contiguity effect
Eliminating redundancy
One or both channels are overloaded by combo of learning demands and distraction and demands caused by intrinsic cognitive load
synchronising → temporal contiguity effect
individualising
Affordances
physical characteristics of a device or interface that allows it’s operation and characteristics in the appearance that give clues to proper functions
Cognitive Affordances
Helps to think or know about something
Physical Affordances
helps to physically do something
Sensory affordances
helps to perceive something
Hick-Hyman Law
the time that user needs to make a choice, based on the number of options
Fitt’s Law
The time required to mova a pointing device to a target is a function of the distance to the target and size