2.4 Meiosis creates haploid gametes and spores and chances genetic variation in species.
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Meiosis
The process of cell division in gametogenesis or sporogenesis during which the diploid number of chromosomes is reduced to the haploid number. Production of haploid gametes
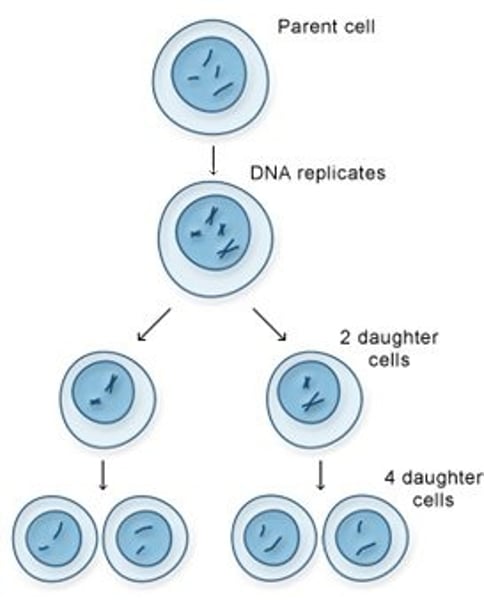
Fertilization
the fusion of haploid gametes
genetic variation
consequences of meiosis
Interphase, Meiosis I, Meiosis II
stages of meiosis
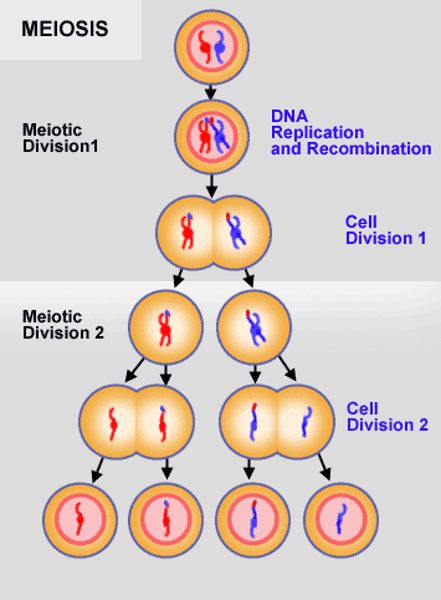
Interphase
DNA synthesis and chromosome replication phase occurs before meiosis 1
Meiosis 1
separation of homologous chromosome pairs.
and reduction of the chromosome number by half
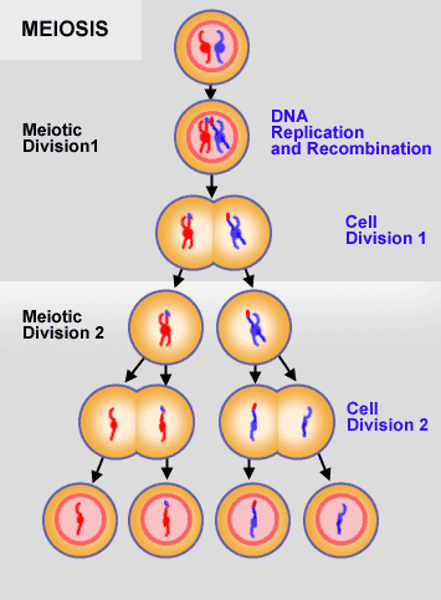
Meiosis 2
separation of sister chromatids, also known as equational division.
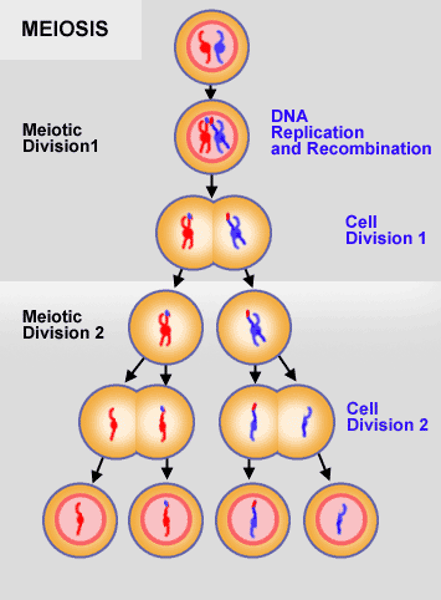
Metaphase 1, Anaphase1, and telophase 1
Homologous chromosomes separate and move towards poles. Sister chromatids remain attached at centromeres- number of dyads (sister pairs) is equal to the haploid number. Duplicated chromosomes reach poles. Each pole now has a haploid number of dyads. Cytokinesis. Nuclear envelope forms around chromosomes in some species.
Prophase 2, metaphase 2, anaphase 2, telophase 2
second meiotic division
prophase 2
each dyad is composed of one pair of sister chromatids attached by the common centromeric region
metaphase 2
the centromeres are positioned on the equatorial plate
anaphase 2
sister chromatids are separated to opposite poles
telophase 2
one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes present at each poles
4 cells new produced from original cell. New cells are haploid. new cells from meiosis are genetically different from parent cells.
Consequences of meiosis and genetic variation
Crossing over
The exchange of chromosomal material (parts of chromosomal arms) between homologous chromosomes by breakage and reunion. The exchange of material between non sister chromatids during meiosis is the basis of genetic recombination.