Human Development
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Developmental Psychology
Study of normal changes in behavior that occur across the life-span.
Shaped by a continuous interaction between hereditary (nature) and environment (nurture).
Helps to understand human growth, identify potential problems and develop interventions to support individuals
Nature vs Nurture
Explores the extent to which an individual’s development is shaped by genetics (nature) or environment
Nature: Biological genetic transmission, via genes, of physical and psychological transmissions from parents to their children. unique characteristics, hair.
Nurture: Sum of all external conditions that affect a person, especially effect of learning. Childhood experiences, surrounding cultures.
Nurture
Sensitive period: Phase when children are more susceptible to some types of environmental influences.
Deprivation: Lack of certain stimulation. Ex: only child.
Enrichment: Environment is stimulating, complex.
Teratogens; eg. nicotine, alcohol; may lead to congenital conditions.
Physical Development
Concerned how bodies change and grow.
Newborns have reflexes, physical and mental capacities.
Physical: Muscle mass, weight, height.
Follow an orderly pattern of development.
Social Development
Affectional needs: care, love, relationships are as important as basic needs for water, food etc.
Early social development: rooted in emotional attachment to primary caregivers and the need for physical contact.
Emotional attachment: close emotional bonds that infants form with parents, caregivers or other.
Separation anxiety to show emotional attachment.
Attachment Quality
Emotional bonding that results from infants’ feelings of security in times of stress or uncertainty.
Secure attachment: Stable & positive emotional bond, seeks mother out when she returns.
Insecure-Avoidant attachment: Turns away from mother when she returns.
Insecure-Ambivalent attachment: Seeks to be near mother but resists contact with her.
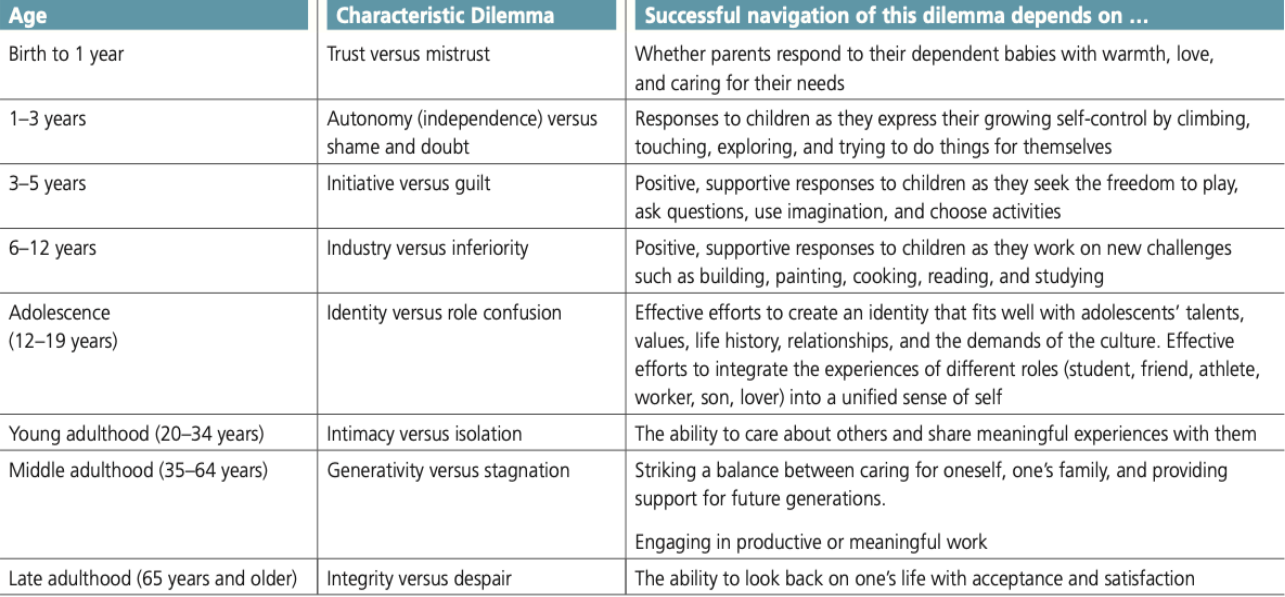
PsychoSocial Theory
Erik Erikson:
8 development staged with development tasks that must be overcome for optimal development.
Developmental Tasks: Any skill that must be mastered or personal change that must take place for optimal development.
Psychosocial Dilemma: Conflict between personal impulses & social world to create balance.
Erikson’s Model:
Cognitive Development:
Jean Piaget:
Believe children pass through a set of 4 stages during cognitive development, where the schema forms & improves with experiences.
Stages: Sensorimotor, Pre-operational, Concrete Operational, Formal Operational.
Sensorimotor Stage:
Age: 0-2 years
Sensory input and motor responses become increasingly coordinated, most intellectual development is non-verbal.
Children get to know the world through senses and movements.
Develop object permanence.
Pre-Operational Stage
Age: 2-7 years
Children begin to develop mental images but cannot transform them.
Transformation: Mentally changing the shape or form of a mental image.
Able to think symbolically and engage in symbolic play.
Their thinking is centered, intuitive and egocentric.
Concrete Operational
Age: 7-11 years
Children learn logic and concrete concepts such as time, space, volume but simplified.
Children become able to carry out mental operations such as reversibility.
Formal Operation
Age: 11+ years
Thinking now includes more complex, abstract, hypothetical ideas and rely less on concrete objects.
Abstract principles/concepts and are able to use metaphors and analogies.
SocioCultural theory
Vygotsky: Believed children actively seek to discover new principles & expand their knowledge.
It is cultural & contextual.
Zone of Proximal Development: Range of tasks that a child is able to master only with the guidance of a more capable partner.
Scaffolding: Framework or temporary support for a beginner to understand a problem or gain skills.
Moral Development
Kohlberg’s Moral Development:
Moral development: Acquiring feelings, values & beliefs that guide behavior.
Preconventional moral reasoning: Moral thinking based on consequences based on consequences of one’s actions or choices (punishment, reward).
Conventional moral reasoning: reasoning based on a desire to please others or to follow accepted rules and values.
Postconventional moral reasoning: Follows self-chosen moral principles, not those supplied by outside authorities.
Later Adulthood
Personal developments are complicated by physical capabilities.
Midlife crisis: Reworking old identities, rediscover values and preparing for old age.
Ageism: discrimination or prejudice against a person’s age.
Gerontology: study of ageing and its effects.
Death & Dying
Elizabeth Ross: Describes 5 basic reaction to death.
Denial & isolation: Denying death’s reality and isolating oneself from information confirming death.
Anger: Asking “Why me?”; anger may be projected onto the living.
Bargaining: Terminally ill with bargain with God or themselves.
Depression: Feelings of futility, exhaustion and deep sadness.
Acceptance: Many will accept death calmly.