3.6 Biology - Exchange
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Features of Specialised Exchange ?
Large SA:Vol ratio → increases diffusion rate
Thin walls → shortens diffusion pathway
Extensive blood supply → maintains concentration gradient
Selectively Permeable → controls what is exchanged
How does gas exchange occur in insects
Air enters the tracheal system through open spiracles in the exoskeleton.
Air moves into tracheae and diffuses into tracheoles.
Oxygen dissolves in water in tracheal fluid and diffuses from tracheoles into body cells.
Carbon dioxide diffuses out of body cells into the tracheoles.
Air is then carried back to the spiracles via the tracheae and released from the body.
Describe how the structure of the insect gas exchange system:
provides cells with sufficient oxygen
limits water loss
Explain your answers. (5)
spiracles, trachea and tracheoles form gas exchange system
spiracles close to reduce water loss
endoskeleton is impermeable
spiracles allow diffusion of oxygen
tracheoles are thin to decrease diffusion pathway
tracheoles are highly branched which increases SA
Components of digestion
Salivary Glands → Contain amylase → (Starch to maltose)
Oesophagus
Stomach → digests foods (esp proteins), produces acid to destroy pathogens & has muscular walls
Liver → produces bile salts → help digest lipids
Pancreas → contains enzymes (lipase, exo & endopeptidase, amylase)
Small Intestine (ileum) → microvilli increase SA & are thin to shorten diffusion pathway
Large Intestine → absorbs water
Rectum & Anus → Store and release faeces
Describe Inhalation
External intercostal muscles contract and ribcage is pulled up and out
Diaphragm contracts and flattens
Thorax volume increases and pressure decreases so air is drawn in down pressure gradient
Describe Exhalation
External intercostal muscles relax and ribcage moves down and out
Diaphragm relaxes and becomes dome shaped
Thorax volume decreases and pressure increases so air is forced out by elastic recoil in lungs
How do insects limit water loss?
Exoskeleton is covered in waxy cuticle to prevent water loss
Spiracles can close
What are the adaptations for gills?
Lamellae increase surface area
Lamellae are thin → decrease diffusion pathway
Gills have good blood supply → maintains conc. gradient
Describe counter-current flow system
Blood and water flow in opposite directions
So concentration gradient is maintained across whole length of lamellae
As there is always more oxygen in water than in blood
How can plants limit water loss ?
guard cells that open and close stomata (close at night when photosynthesis isnt occuring)
waxy cuticle
How do xerophytes limit water loss ?
thick waxy cuticle → increases diffusion pathway, reduces water loss
rolled leaves → maintain humid air around stomata so shallower concentration gradient
hairy leaves → maintain humid air around stomata so shallower concentration gradient
stomata in sunken pits → maintain humid air around stomata so shallower concentration gradient
fewer stomata → reduces water loss
small leaf surface area → reduces SA for evaporation
State the adaptations of the human gas exchange system
Trachea → rings of cartilage to prevent collapsing, muscle can contract to control airflow & elastic fibres can stretch out and spring back
Bronchi → produces mucus to trap dirt and cilia moves dirty mucus to throat + cartilage
Bronchioles → elastic fibres so can stretch out and recoil
Alveoli → elastic which allows recoil and prevents bursting, thin to decrease diffusion pathway, large surface area
Describe the role of micelles in the absorption of fats into the cells lining the ileum
Micelles include bile salts and fatty acids
They make the fatty acids more soluble
They carry fatty acids to epithelial cell lining
They maintain higher concentration of fatty acids than in cell
How is alveoli adapted for gas exchange?
(CO2 diffuses out of blood in capillaries to alveoli and O2 diffuses into blood from alveoli)
many alveoli in lungs increase SA
thin walls decrease diffusion pathway
surrounded by a network of capillaries which maintains conc. gradient
elastic so it can recoil and it prevents bursting
what is digestion
physical → large food molecules are broken down into smaller molecules which increases SA for chemical digestion
chemical → large insoluble molecules are hydrolysed into small soluble molecules by enzymes
how are carbohydrates digested
amylase (pancreas + salivary glands) hydrolyses starch into maltose
maltase (small intestine) hydrolyses maltose into glucose
(glucose passes into cytoplasm from lumen of gut via facilitated diffusion)
how are proteins digested
endopeptidase hydrolyses peptide bonds between amino acids in the middle of polypeptide
exopeptidase hydrolyses peptide bond between amino acids at the end of polypeptide
dipeptidase hydrolyses peptide bond between two amino acids
how are lipids digested
Lipids are emulsified by bile salts (produced in liver, stored in gall bladder)
Many droplets of lipids increase SA and allow fast hydrolysis by lipase
Lipase hydrolyses emulsified lipids into fatty acids and monoglycerides
describe the process of lipid absorption
Micelles contain bile salts and fatty acids/monoglycerides
Micelles make fatty acids/monoglycerides more soluble
Fatty acids/monoglycerides absorbed into ileum by diffusion
triglycerides reform in golgi and are packaged into chylomicrons for transport
chylomicrons exit epithelial cell via exocytosis and enter bloodstream via lacteals
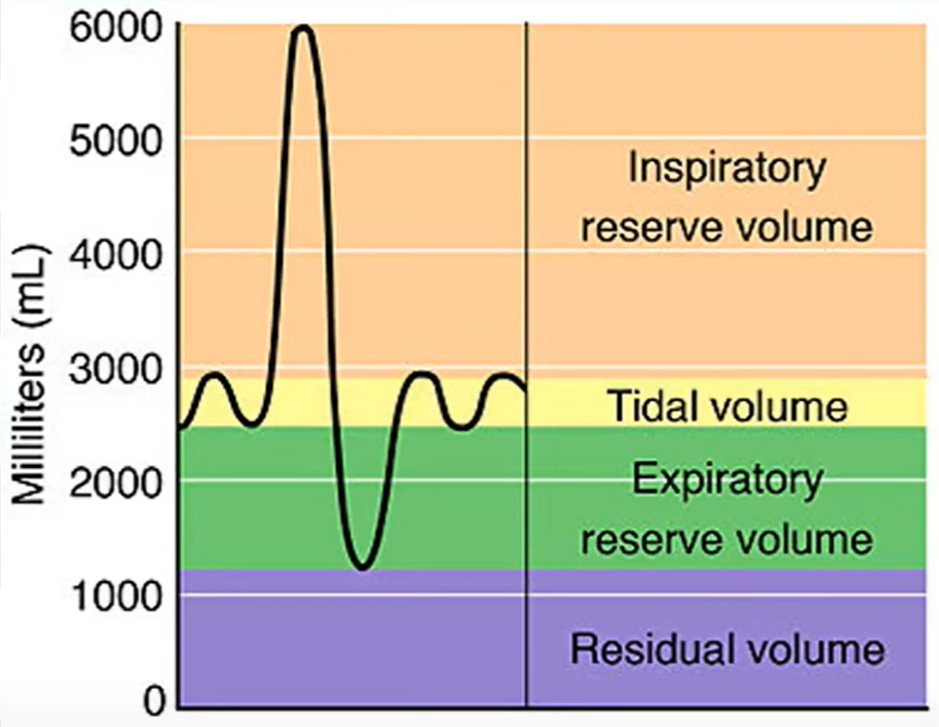
define tidal, vital, residual and total lung capacity
how do you calculate pulmonary ventilation rate (PVR)
tidal volume → resting breathing rate
vital capacity → the max volume you can inhale or exhale
residual volume → the minimum volume in the lungs
total lung capacity → max. volume of air u can fit in lungs
PVR = breathing rate x tidal volume
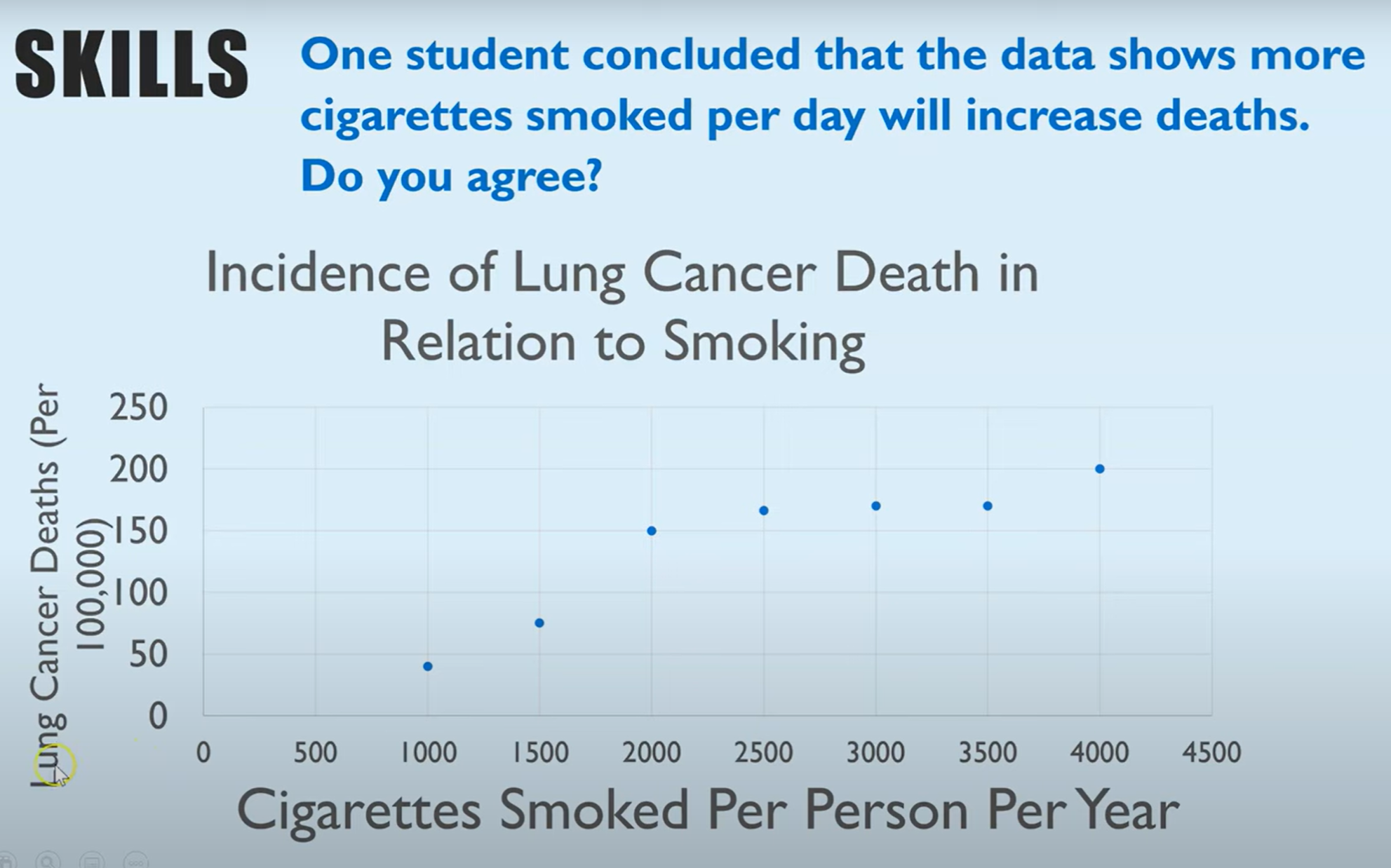
there is positive correlation between lung cancer deaths and cigarettes smoked per year
however correlation doesnt mean causation
data overlaps from 2500 to 3500 cigarettes smoked per year as lung cancer deaths doesnt increase
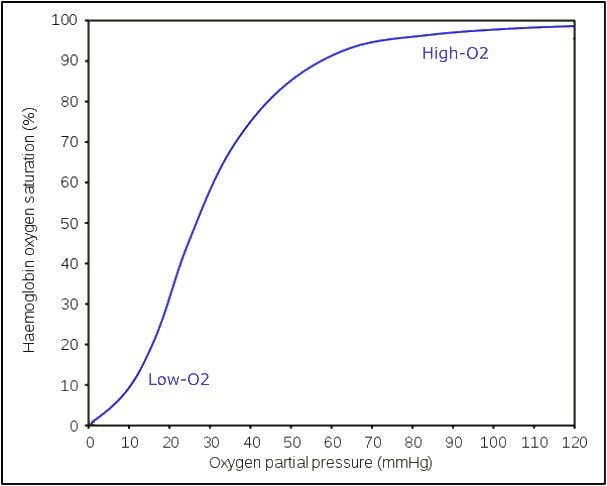
explain the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve
At low pO2 there is low affinity, e.g. in respiring cells where haemoglobin readily unloads oxygen
At high pO2 there is high affinity e.g. in lungs where haemoglobin loads to oxygen
Binding of first oxygen changes quaternary structure of Hb making binding of another oxygen easier as it uncovers haem group binding sites
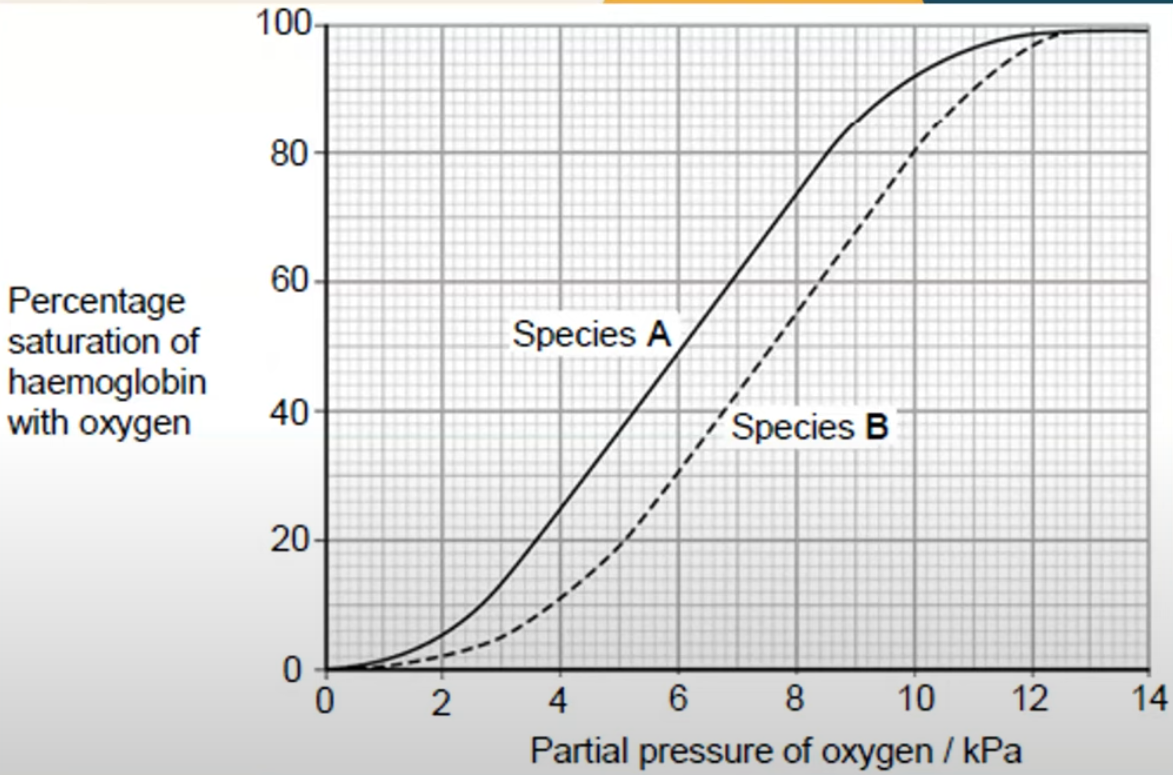
Species B, the rat, is more active than species A, the human. Use the graph to explain how the haemoglobin of the rats allows a greater level of activity. (4)
The curve for species B shifted to the right so Hb has a lower affinity for oxygen
So it unloads more readily
So more oxygen is delivered to cells
for more respiration
what is the bohr effect
when high CO2 causes the oxyhaemoglobin dissociation curve to shift to the right bc it decreases pH, meaning haemoglobin’s affinity for oxygen decreases as CO2 slightly changes the shape / quaternary structure of the Hb
(right=release)
Describe the role of haemoglobin (Hb) in the loading, transport and unloading of oxygen. (5)
At high partial pressure of oxygen, Hb loads readily to oxygen in lungs
At low partial pressure of oxygen, Hb unloads readily in respiring cells
Oxygen is transported as oxyhaemoglobin in RBC
First oxygen that binds to Hb changes quaternary structure of Hb so makes it easier for next oxygen to bind as it uncovers haem group binding sites
why is it referred to as a closed double circulatory system
closed = blood remains in vessels
double = two circuits, one from heart to lungs and other from heart to body
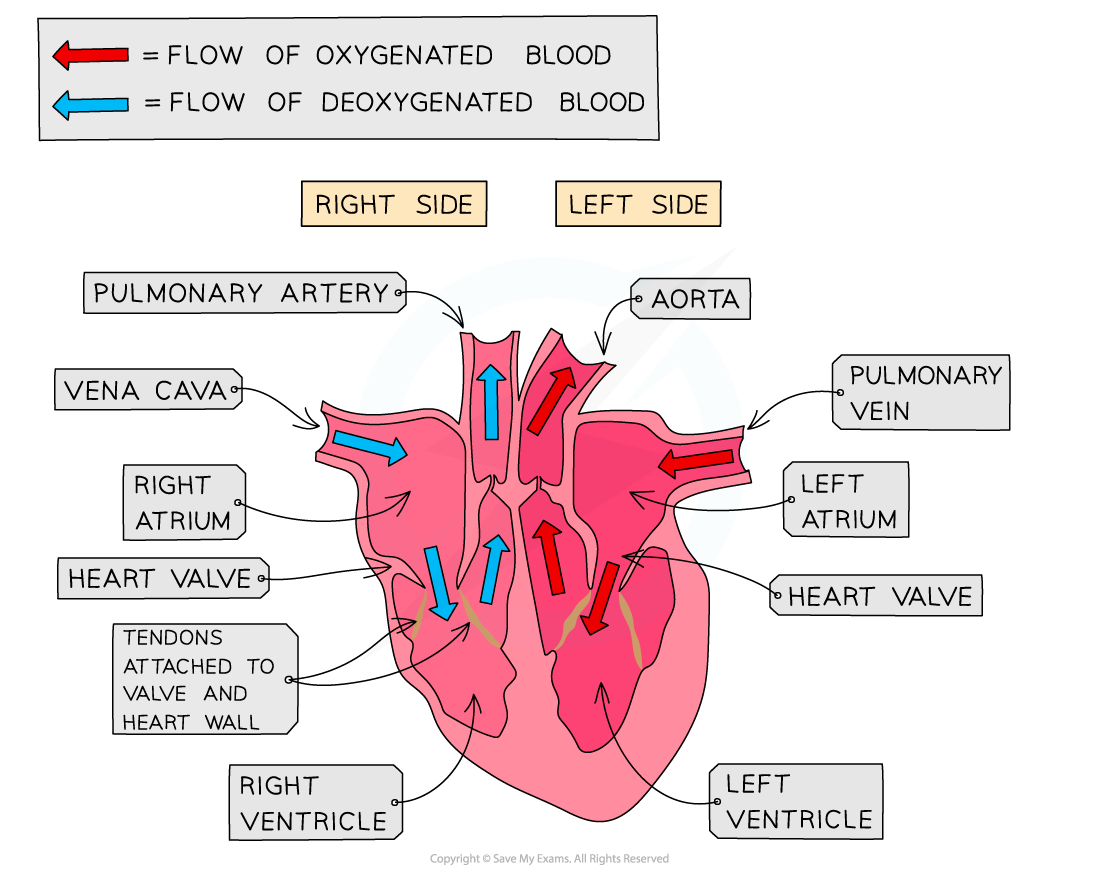
label heart
(atrioventricular valves are between atrium and ventricles and open when pressure in atrium is higher)
(semilunar valves are between ventricles and arteries and open when pressure in ventricles is higher)
what do coronary arteries do
supply heart muscles with oxygenated blood
chambers of the heart
atria → elastic and thin walls as they only contract to ventricles
ventricles → thicker walls ↑ contraction to further distances
right ventricle → blood to lungs, low pressure to prevent damage to capillaries, slow blood flow for gas exchange
left ventricle → thicker - blood to body
(septum seperates oxygentated and deoxygenated blood
describe the cardiac cycle
atria systole - atria contact, decreasing volume of chambers and increasing pressure in chambers so atrioventricular valves open as pressure in atria exceeds ventricles
ventricular systole - atria relax, blood enters ventricles and ventricles contract, increasing blood pressure more than atria’s so atrioventricular valves close and semilunar valves open so then blood enters aorta and pulmonary artery
diastole → semi lunar valves close
Describe the stages of the cardiac cycle in a healthy heart after it has been filled with blood. (5)
atria contract
this increases pressure and decreases volume so blood is forced into ventricles
atrioventricular valves open which prevents backflow into atria
ventricles contract
this increases pressure and decreases volume so blood leaves through aorta and pulmonary artery
semilunar valves prevent backflow of blood into heart
atria and ventricles relax so blood fills heart
what is the role of the heart in the formation of tissue fluid
the ventricles contract which creates a high hydrostatic pressure
which forces water out of the blood
Tissue fluid is formed from blood at the arteriole end of a capillary bed.
Explain how water from tissue fluid is returned to the circulatory system. (4)
Excess tissue fluid is returned through lymphatic system
Large plasma proteins remain in capillaries
Which decrease water potential
So tissue fluid enters capillaries via osmosis
Arteries structure and function
Thick walls → elastic layer stretches and recoils to maintain blood pressure
Smooth endothelium reduces friction
Narrow lumen to maintain high blood pressure
Structure and function of arterioles
Thick muscle layer → contract and constrict lumen to control blood flow
Structure and function of veins
Thin walls → carry blood under low pressure
Valves → prevent backflow
Wide lumen → carries high volume of blood
Structure and function of capillaries
One cell thick → decrease diffusion pathway
Small lumen → slows blood movement to increase diffusion
Highly branched → increase SA
(made up of flattened cells to decrease diffusion pathway)