Patho ENT
1/108
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
109 Terms
Mastoidectomy: is used to treat mastoiditis which is a complecation of untreated acute otitis interna
False
The surgical removal of mastoid cells is known as a/an ____________________. This procedure is performed in this area to treat an infection that cannot be controlled with antibiotics.
mastoidectomy
A/An ____________________ is the surgical removal of part of the stapes and its replacement with a metal or plastic prosthesis.
stapedectomy
------- is a term describes the concavity on the tympanic membrane where the malleus is attached.
umbo
-----------: a common tumor that surrounds eighth cranial nerve; usually benign but may be recurrent
acoustic neuroma
--------- :Cyst of infected skin cells within middle ear that erodes the cavity and ossicles
cholesteatoma
The medical term for the substance commonly known as earwax is ____________________.
cerumen
The surgical removal of the stapes of the middle ear is a/an ____________________.
stapedectomy
Snail-shaped, spirally wound tube in the inner ear:
Cochlea
Most common hemostatic agent used in Otorhinolaryngology is Gelfoam and is mixed with epinephrine.
True
Myring/o means:
Tympanic membrane
Earwax is known as ________.
cerumen
Myringoplasty is performed to close a small nonhealing hole in the _____________.
tympanic membrane
A cochlear implant is used to transmit external sound directly into the _______________.
eighth cranial nerve
The accumulation of fluid in the middle ear, if left untreated, may cause ________.
mastoiditis
What is a cholesteatoma?
benign cyst in the mastoid cavity
Otosclerosis is the term used to describe ____.
fixation of the stapes
Which of the following is not a normal feature of the tympanic membrane?
convex
The footplate of the stapes rests upon the ____.
oval window
The stapes vibrates the fluid inside the --------- of the inner ear.
oval window
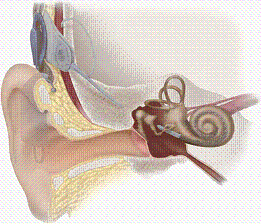
This Pictures shows
Cochlear Implant
The _______ contains mechanoreceptors that convert sound waves to nerve impulses.
inner ear
Which term means fusing together of the bones of the middle ear resulting in a conductive hearing loss?
otosclerosis
A chronic disease of the inner ear marked by a recurring syndrome of vertigo, tinnitus, progressive hearing loss, and a sensation of pressure in the ear is called
Ménière's disease.
Davis and McIvor are names of which type of instrument?
mouth gags
Colorado needle tip is loaded on :
ESU
in Caldwell-Luc procedure --------------- is used to enlarge the opening in the maxilla bone
Kerrison ronjeur
The ________ is used to suction the irrigation and wound fluids or debris during otological procedures.
Frazier
If acute otitis media is left untreated, it may lead to the condition known as ____.
mastoiditis
Walters, Caldwell, lateral, and submental radiographic views are used to establish diagnosis for which anatomical area?
sinus cavities
Which statement is correct concerning oral procedures?
Oral procedures are not considered sterile; use the best technique possible.
A/An ________ is typically done for cosmetic reasons.
rhinoplasty

This picture shows Cushing elevator.
False
What is a cholesteatoma?
benign cyst in the mastoid cavity
Cholesteatoma:It is a benign tumor of the middle ear
True
The portion of the jaw that surrounds and supports the tooth is the ____.
alveolar process
Which of the following involves the highest portion of the midface and presents the most extensive damage?
Le Fort III
Cochlear implants are contraindicated in children under the age of --------, A cochlear implant has ---components.
2 years , two
The Caldwell-Luc procedure is performed to remove diseased portions of the antral wall, evacuate the sinus contents, and establish drainage through the mouth.
False
Uncontrolled nasal hemorrhage may require the ligation of External Maxillary artery.
False
What is the name of the structure that divides the two chambers of the nasal cavity?
septum
____ is injected into the joint space to distend the capsule during a TMJ arthroscopy.
Lactated Ringer’s
Which surgical procedure would be performed for excision of a cholesteatoma?
mastoidectomy
What is the name of the narrow, double-angle retractor frequently used in oral procedures?
Minnesota
Another name for the malar bone is ____.
zygomatic
________ is performed to create a permanent opening in the tear duct for the drainage of tears.
Dacryocystorhinostomy
Turbinectomy or Turbinate Reduction nasal airflow Performed to ---------
improve nasal airflow
Otosclerosis is the term used to describe ____.
fixation of the stapes
Which of the following statements regarding arch bars is CORRECT?
They are thin, malleable bars with hooks facing up for maxilla and down for mandible.
Which tonsils are removed during the procedure called adenoidectomy?
pharyngeal
Baron, Frazier, House, and Rosen are names of which type of instrument?
suction
During Mastoidectomy the surgeon places the---------and then the -------is placed over it.
fascia graft , skin graft
Which procedure is performed for removal of impacted wisdom teeth?
odontectomy
What is the term that describes the side of teeth closest to the cheek?
buccal
the Paranasal sinuses include all of the following EXCEPT:
Zygomatic.
Myringoplasty is performed to close a small nonhealing hole in the _____________.
tympanic membrane
Which part of the tympanic membrane is fibrous, largest, and where drainage tubes are inserted?
pars tensa
Which bone contributes to the posterior and inferior portion of the nasal septum?
vomer
Before repair of frontal sinus fractures, the sinus mucosa must be removed and the duct occluded. The sinus is then often filled with a ___________.
fat graft
Name the three sections of the pharynx.
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
Glasscock dressing is used after ----------procedure
Ear
Crescent-shaped cartilage found in the TMJ and knee joints is the ____.
meniscus
What can be done to treat an intranasal dural tear?
cover with fat, fascia, or muscle graft
Which structure is often blocked with stones in the parotid gland, possibly necessitating surgical removal of the gland?
Steno’s duct
Why is nitrous oxide NOT used during reconstructive ear surgery?
It expands the middle ear.
most common Epistaxis occur in -------
Kiesselbach’s plexus
Which term is commonly referred to as the throat?
pharynx
Which of the following is the MOST commonly used autograft in otologic procedures?
temporalis fascia
Le Fort ____ is a horizontal fracture of the maxilla that causes the hard palate and alveolar process to become separated from the remainder of the maxilla. The fracture extends into the lower nasal septum, lateral maxillary sinus, and palatine bones.
I
Why is Gelfoam used in ENT surgical procedures?
achieve hemostasis
Uncontrolled nasal hemorrhage may require the ligation of ---------
Internal Maxillary artery
Which procedure is performed for treatment of sleep apnea?
UPPP
A rubber wedge placed between the upper and lower teeth of the unaffected side to maintain the patient’s mouth in an open position is called a(n) ____.
mouth prop
Which of the following procedures would require use of an operating microscope?
stapedectomy
In the Le Fort _____ fracture there is a separation of all the facial bones from their cranial base. It includes fracture of the zygoma, maxilla, and nasal bones. The fracture line extends through the ethmoid bone and bony orbit with severe facial flattening and swelling.
III
Which instrument is routinely used in ear procedures to pass a prothesis or a graft?
Alligator
Ménière's Disease :Chronic disease of the------
inner ear
the throat pack is moistened , 4x4 or raytecs. inserted in the throat prior to maxillofacial surgery to reduce risk of aspiration and preventing tooth or bone fragments from entering the throat, which instrument is Used to place the throat pack:
McGill Forceps
Which tonsils are removed during the procedure called tonsillectomy?
palatine
What is the term for bony overgrowth of the stapes?
otosclerosis
The purpose of arch bars is to stabilize the ____ bone(s)?
maxillary
Pectoralis Myocutaneous (PMC) and Deltopectoral (DP) :
Flaps tissue are created to provide coverage for soft tissue defect
The ________ transmits the vibrations of the tympanic membrane and the other ossicles to the inner ear via the oval window.
stapes
What are the Conchae (Turbinates)?
osseous ridges on the lateral walls of the nasal cavity
Which of the following is the MOST common type of midfacial fracture and is also known as a transmaxillary fracture?
Le Fort I
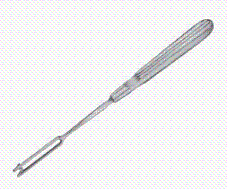
this picture shows
Ballenger swivel knife
What is the name of the long, thin, cupped, pistol-grip type handled forceps used in many nasal procedures?
Takahashi
How many craniofacial bones make up the orbit?
seven
The inner Ear is surrounded by ---------
Labyrinth bone
Care must be taken when preauricular and submandibular incisions are made to protect this nerve :
VII Facial . N
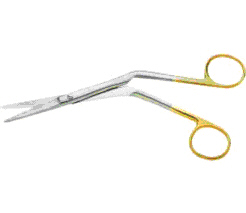
this picture shows
Knight scissors
LeFort II and III fractures can also be referred to as ____ fractures.
panfacial
Cholesteatoma
Cyst of infected skin cells within middle ear that erodes the cavity and ossicles
What structure attaches the tongue to the floor of the buccal cavity?
lingual frenulum
The Le Fort ______ fracture is pyramidal. It extends from the nasal bone, to the frontal processes of the maxilla, lacrimal bones, and inferior orbital floor, and may extend into the orbital foramen. Inferiorly, it extends into the anterior maxillary sinus, and into the pterygoid plates.
II
What term describes the concavity on the tympanic membrane where the malleus is attached?
umbo
The name of the radical antrostomy procedure to provide adequate visualization is known as a(n) ____.
Caldwell-Luc
What structures are removed during UPPP?
tonsils, adenoids, uvula, portion of the soft palate
Cholesteatoma :bengin Cyst or tumor that fills the mastoid cavity this process can also damage the ossicles.
True
During a tracheostomy, the ________ is sent with the patient to his or her room.
obturator