OSPE, Parasitology
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MV
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
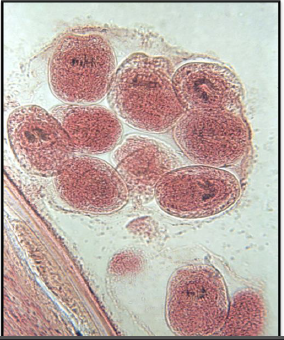
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used.
Mention the diagnostic methods used for ocular infection caused by this parasite.
Identify the parasitic stage.
Acanthamoeba castellanii cyst.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
About 15–20 µm in size.
Has a polygonal double wall with many pores.
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used.
Samples: CSF, brain tissue, corneal tissue, and skin biopsy.
Culture medium: Non-nutrient agar (1.5%) enriched with Escherichia coli.
Mention the diagnostic methods used for ocular infection caused by this parasite.
Corneal scrapings or sections examined by direct microscopy and staining, or by cultivation.
Laser confocal microscopy can visualize both trophozoites and cysts.
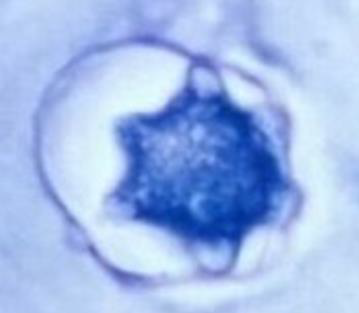
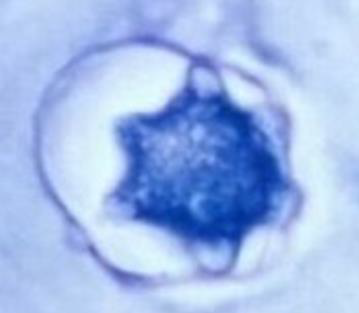
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention the contents of this stage.
State the best method for diagnosing this disease?
Hydatid sand
Detached scolices, brood capsules, and daughter cysts that fall in hydatid fluid.
Fluid aspirated from surgically removed cyst.
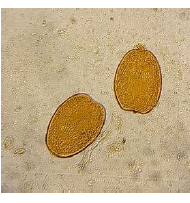
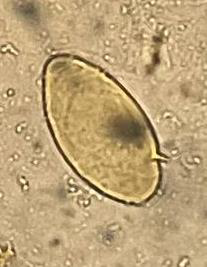
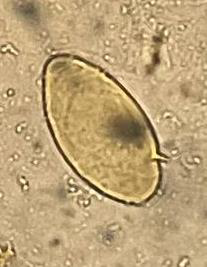
Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
Mention two characteristic features of this stage.
Mention the direct methods used for diagnosing the neurological form of this disease.
Specify CSF characteristics in case of neurological affection.
Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
Schistosoma mansoni egg
Mention two characteristic features of this stage.
About 140 × 70 µm, colourless, contains mature miracidium
Thin shell with a lateral spine
Mention the direct methods used for diagnosing the neurological form of this disease.
Confirmation of schistosomal infection by a direct method
Histopathological examination of the nervous tissue
Specify CSF characteristics in case of neurological affection.
Increased total protein
Presence of eosinophils and antibodies
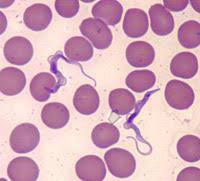
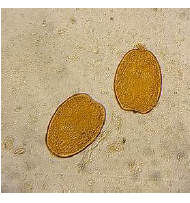
1. Identify the parasitic stage, and mention the disease caused by this parasite.
2. Mention the stain used in this blood smear.
3. Mention two diagnostic samples for detecting this parasite.
4. List haematological findings in this infection.
5. Mention the pathognomonic immune cell in CSF in this infection.
1. Identify the parasitic stage, and mention the disease caused by this parasite.
→ Polymorphic trypomastigotes
→ Disease: African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)
2. Mention the stain used in this blood smear.
→ Giemsa stain
3. Mention two diagnostic samples for detecting this parasite.
→ - Chancre aspirate for Thick blood or buffy coat smears
→ - Lymph node aspirate, bone marrow, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
4. List haematological findings in this infection.
→ - Anaemia and thrombocytopenia
→ - Moderate leukocytosis
→ - High levels of immunoglobulins, mainly IgM
5. Mention the pathognomonic immune cell in CSF in this infection.
→ Morula cell of Mott
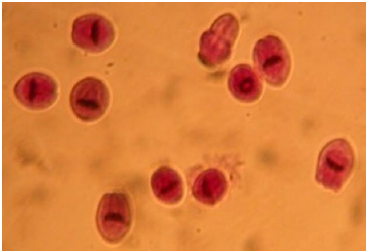
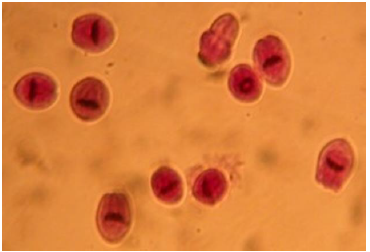
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention the contents of this stage.
State the best method for diagnosing this disease?
Hydatid sand
Detached scolices, brood capsules, and daughter cysts that fall in hydatid fluid.
Fluid aspirated from surgically removed cyst.
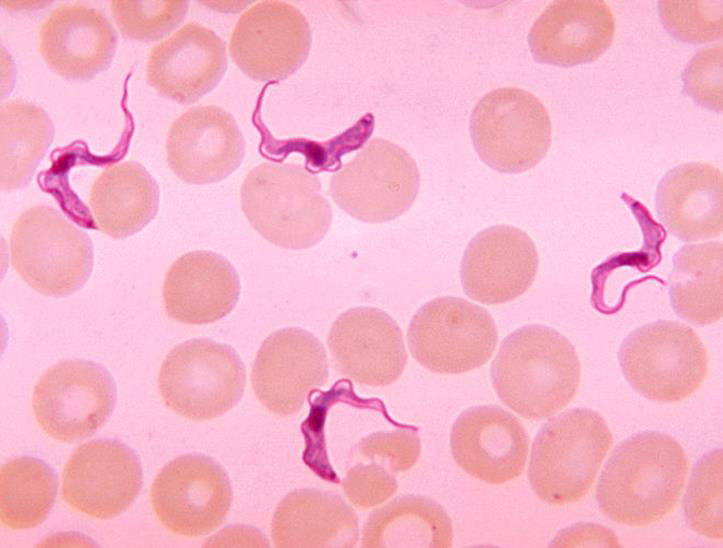
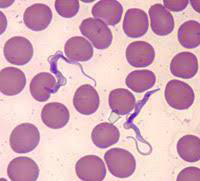
Mention two direct methods for detection of this parasite.
How to differentiate between the two species of this parasite? And which antibody can be elevated?
Which parasite species has available card agglutination test?
Mention two characteristics of CSF in this disease.
Mention two direct methods for detection of this parasite.
Microscopy:
a. Wet mount smears examination to detect trypanosomes’ motility.
b. Examination of Giemsa-stained smears to detect the morphological characteristics of polymorphic trypomastigotes.Culture
Animal inoculation
How to differentiate between the two species of this parasite? And which antibody can be elevated?
The card-agglutination test is used for detection of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense only.
High levels of specific antibodies (IgM) are elevated.
Which parasite species has available card agglutination test?
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
Mention two characteristics of CSF in this disease.
Raised pressure
Increased cell count (mainly lymphocytes) and protein levels
Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
Mention the resting form of this parasite.
Mention two other stages of this parasite.
Mention two morphological characters of this stage.
Identify samples used for detection of this parasitic stage.
List two stains used for detecting this parasite.
1. Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
→ Toxoplasma gondii trophozoite
2. Mention the resting form of this parasite.
→ Toxoplasma true tissue cyst
3. Mention two other stages of this parasite.
→ True tissue cyst and pseudocyst in humans; oocyst in cats
4. Mention two morphological characters of this stage.
→ - Crescent-shaped, measuring about 3–7 µm
→ - Has a pointed anterior end with granules and a rounded posterior end containing the nucleus
5. Identify samples used for detection of this parasitic stage.
→ Blood, lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and other body fluids
6. List two stains used for detecting this parasite.
→ Giemsa stain, Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E), or Immunofluorescent Antibody (IFA) stain
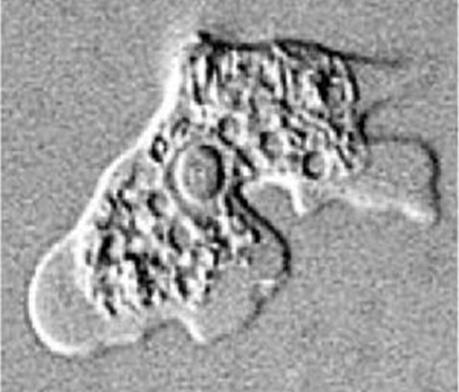
Identify parasite/stage, mention the examined sample, and name the disease induced by this parasite in the CNS.
Mention the culture media you can use to confirm the diagnosis.
Mention the stain used and two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Identify another sample that can be used to detect this stage.
Identify parasite/stage, mention the examined sample, and name the disease induced by this parasite in the CNS.
Naegleria fowleri trophozoite, CSF.
Causes Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAME).
Mention the culture media you can use to confirm the diagnosis.
Non-nutrient agar (1.5%) enriched with Escherichia coli.
Mention the stain used and two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Wright–Giemsa stain.
About 10–15 µm, has a single nucleus with a large central karyosome, blunt pseudopodia, food vacuoles, and a contractile vacuole.
Identify another sample that can be used to detect this stage.
Brain tissue biopsy
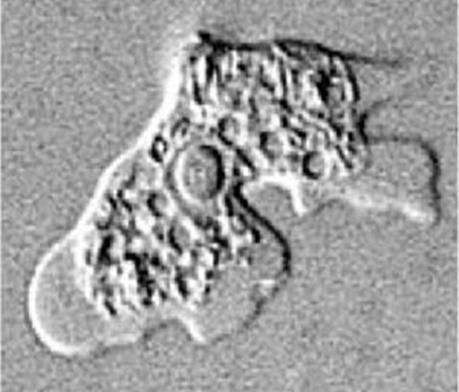
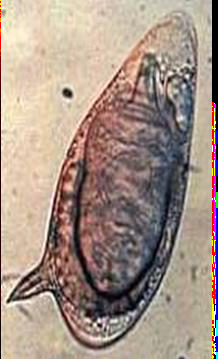
Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
Mention two characteristic features of this stage.
Mention the direct methods used for diagnosing the neurological form of this disease.
Specify CSF characteristics in case of neurological affection.
Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
Schistosoma mansoni egg
Mention two characteristic features of this stage.
About 140 × 70 µm, colourless, contains mature miracidium
Thin shell with a lateral spine
Mention the direct methods used for diagnosing the neurological form of this disease.
Confirmation of schistosomal infection by a direct method
Histopathological examination of the nervous tissue
Specify CSF characteristics in case of neurological affection.
Increased total protein
Presence of eosinophils and antibodies

This is a CSF sample withdrawn from a suspected case of Naegleria fowleri infection:
Comment on its physical appearance.
Comment on the CSF diagnostic criteria in this infection, and identify the diagnostic stage.
Name two stains used to stain CSF smears in this infection.
Identify blood examination findings in this infection.
This is a CSF sample withdrawn from a suspected case of Naegleria fowleri infection:
Comment on its physical appearance.
Turbid.
Comment on the CSF diagnostic criteria in this infection, and identify the diagnostic stage.
CSF is purulent, bloody, and neutrophilic, with high protein content and reduced glucose concentration.
Motile trophozoites are the diagnostic stage.
Name two stains used to stain CSF smears in this infection.
Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS)
Giemsa, Wright, or Wright–Giemsa stain
Identify blood examination findings in this infection.
Polymorphonuclear leukocytosis up to 25,000 cells/mm³ with a predominance of neutrophils.

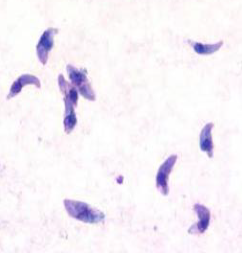
Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
Mention the resting form of this parasite.
Mention two other stages of this parasite.
Mention two morphological characters of this stage.
Identify samples used for detection of this parasitic stage.
List two stains used for detecting this parasite.
1. Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
→ Toxoplasma gondii trophozoite
2. Mention the resting form of this parasite.
→ Toxoplasma true tissue cyst
3. Mention two other stages of this parasite.
→ True tissue cyst and pseudocyst in humans; oocyst in cats
4. Mention two morphological characters of this stage.
→ - Crescent-shaped, measuring about 3–7 µm
→ - Has a pointed anterior end with granules and a rounded posterior end containing the nucleus
5. Identify samples used for detection of this parasitic stage.
→ Blood, lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, and other body fluids
6. List two stains used for detecting this parasite.
→ Giemsa stain, Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E), or Immunofluorescent Antibody (IFA) stain
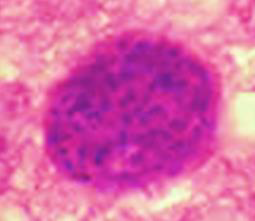
Identify this parasitic stage and its adult parasite.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Identify this parasitic stage and its adult parasite.
Coenurus cerebralis
Adult parasite: Taenia serialis (or Multiceps multiceps)
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Small translucent cyst, about 2 cm in diameter, filled with fluid
Formed of germinal layer containing multiple macroscopic invaginated scolices (no brood capsule, no daughter cyst)
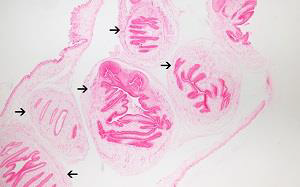
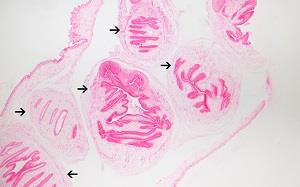
1. Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
2. Mention two morphological characters of this stage.
3. Mention the active form of this parasite.
4. Identify the types of antibodies detected in serological diagnosis of this disease and their significance.
5. Mention two immunological tests to augment diagnosis.
1. Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
→ Toxoplasma gondii true cyst
2. Mention two morphological characters of this stage.
→ - Resting form that contains slowly multiplying bradyzoites
→ - Has a true cyst wall
3. Mention the active form of this parasite.
→ Toxoplasma pseudocyst
4. Identify the types of antibodies detected in serological diagnosis of this disease and their significance.
→ - Rising IgG titer and presence of IgM signify active infection
→ - IgM detected in a baby’s blood is fetal in origin (maternal IgM does not cross the placenta)
→ - IgG antibodies signify chronic (latent) infection
5. Mention two immunological tests to augment diagnosis.
→ - ELISA for detection of anti-Toxoplasma antibodies
→ - Immunochromatographic Test (ICT) / Toxo Rapid Test
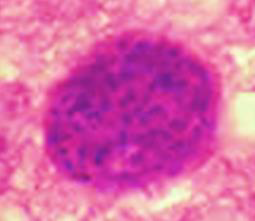
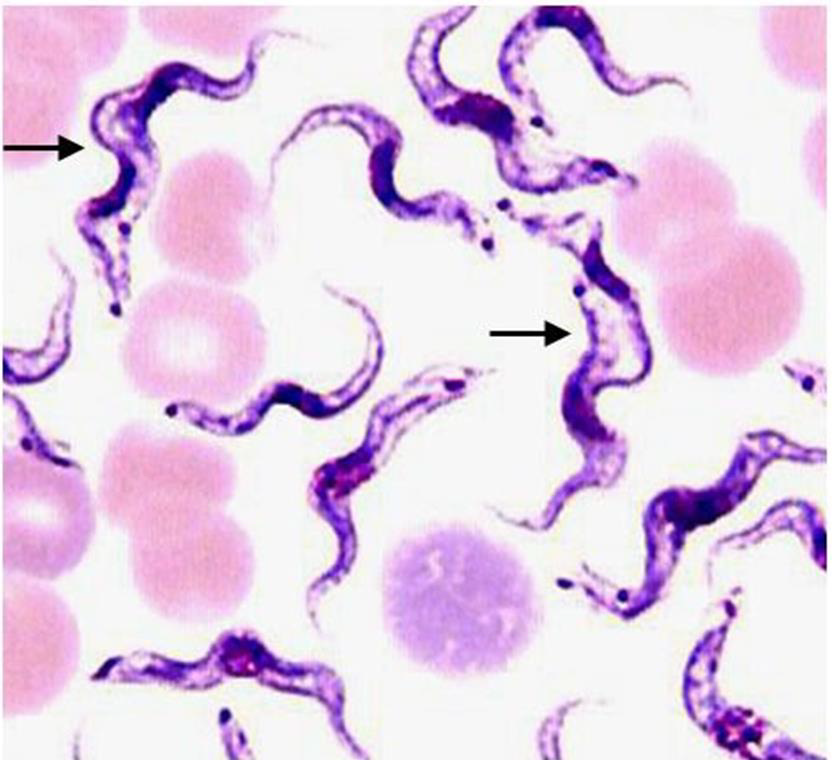
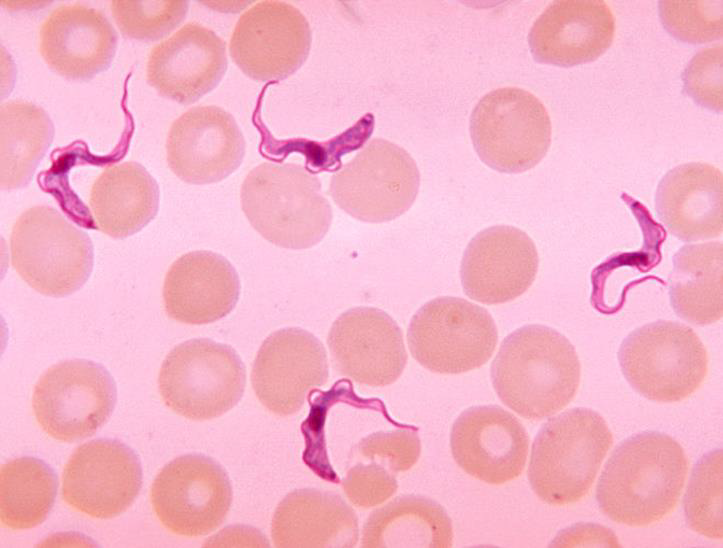
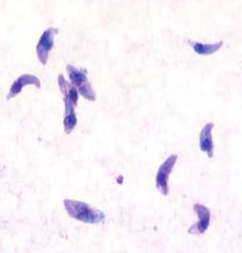
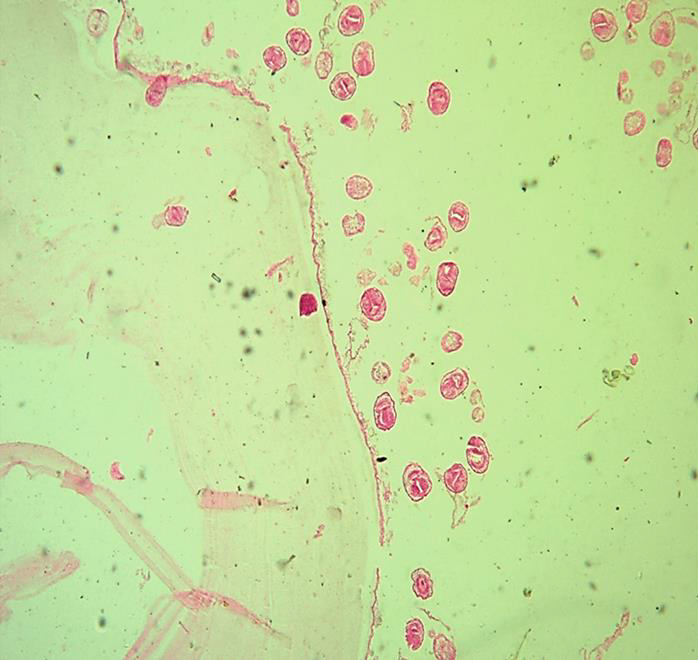
1. Identify the parasitic stage, and mention the disease caused by this parasite.
2. Mention the stain used in this blood smear.
3. Mention two diagnostic samples for detecting this parasite.
4. List haematological findings in this infection.
5. Mention the pathognomonic immune cell in CSF in this infection.
1. Identify the parasitic stage, and mention the disease caused by this parasite.
→ Polymorphic trypomastigotes
→ Disease: African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)
2. Mention the stain used in this blood smear.
→ Giemsa stain
3. Mention two diagnostic samples for detecting this parasite.
→ - Chancre aspirate for Thick blood or buffy coat smears
→ - Lymph node aspirate, bone marrow, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
4. List haematological findings in this infection.
→ - Anaemia and thrombocytopenia
→ - Moderate leukocytosis
→ - High levels of immunoglobulins, mainly IgM
5. Mention the pathognomonic immune cell in CSF in this infection.
→ Morula cell of Mott
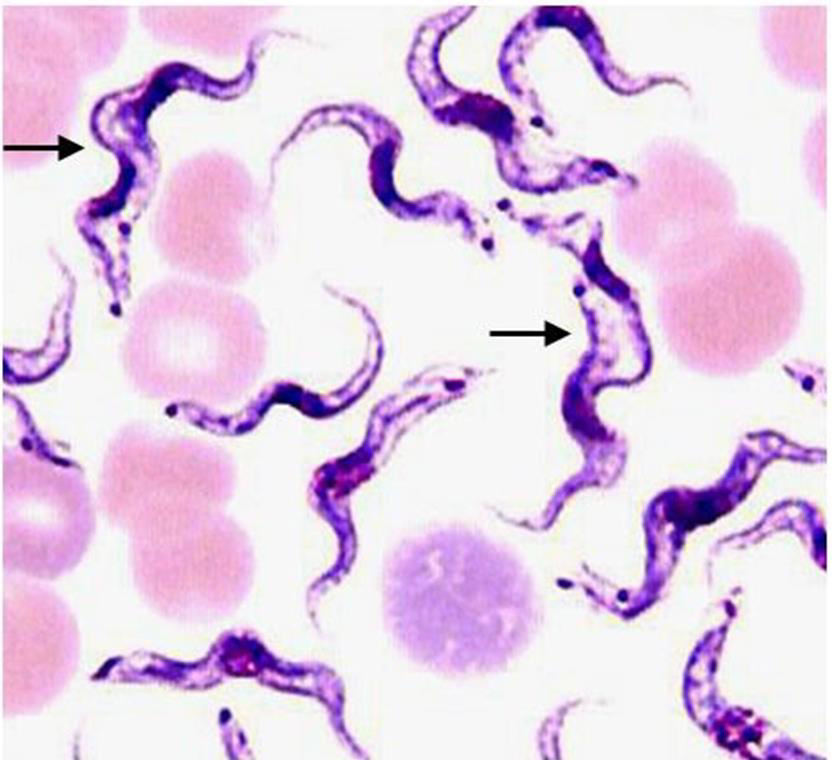
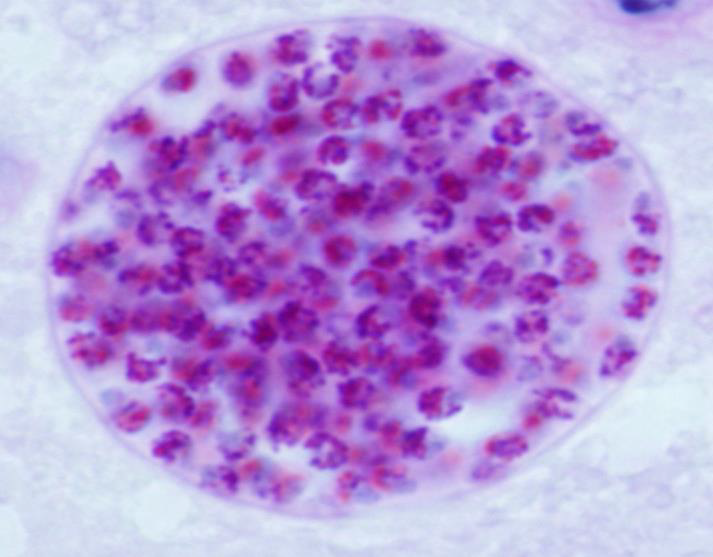
1. Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
2. Mention two morphological characters of this stage.
3. Mention the active form of this parasite.
4. Identify the types of antibodies detected in serological diagnosis of this disease and their significance.
5. Mention two immunological tests to augment diagnosis.
1. Identify the parasite (Genus, species, and stage).
→ Toxoplasma gondii true cyst
2. Mention two morphological characters of this stage.
→ - Resting form that contains slowly multiplying bradyzoites
→ - Has a true cyst wall
3. Mention the active form of this parasite.
→ Toxoplasma pseudocyst
4. Identify the types of antibodies detected in serological diagnosis of this disease and their significance.
→ - Rising IgG titer and presence of IgM signify active infection
→ - IgM detected in a baby’s blood is fetal in origin (maternal IgM does not cross the placenta)
→ - IgG antibodies signify chronic (latent) infection
5. Mention two immunological tests to augment diagnosis.
→ - ELISA for detection of anti-Toxoplasma antibodies
→ - Immunochromatographic Test (ICT) / Toxo Rapid Test
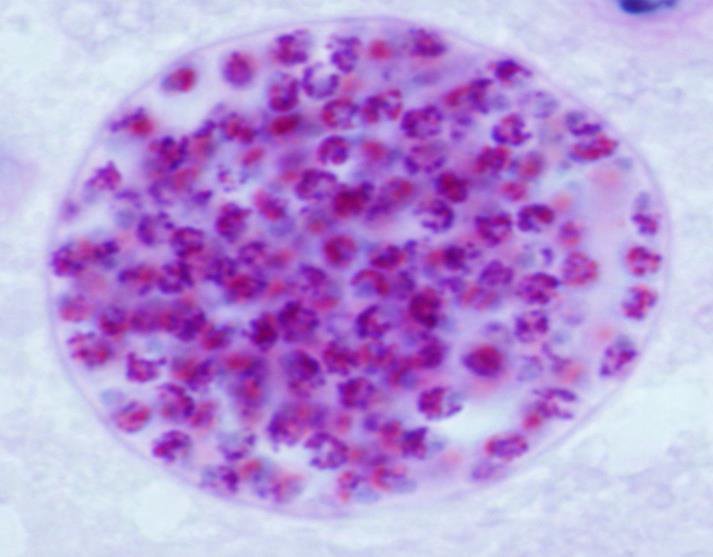
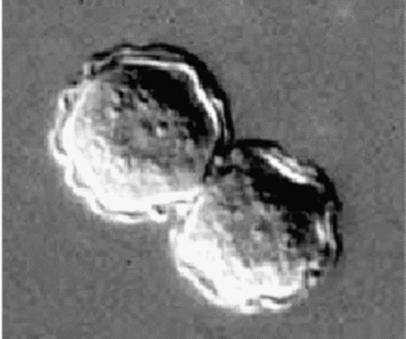
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used.
Mention the diagnostic methods used for ocular infection caused by this parasite
Identify the parasitic stage.
Acanthamoeba castellanii cyst.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
About 15–20 µm in size.
Has a polygonal double wall with many pores.
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used.
Samples: CSF, brain tissue, corneal tissue, and skin biopsy.
Culture medium: Non-nutrient agar (1.5%) enriched with Escherichia coli.
Mention the diagnostic methods used for ocular infection caused by this parasite.
Corneal scrapings or sections examined by direct microscopy and staining, or by cultivation.
Laser confocal microscopy can visualize both trophozoites and cysts.
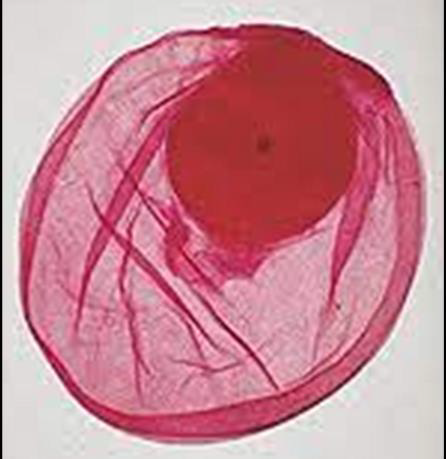
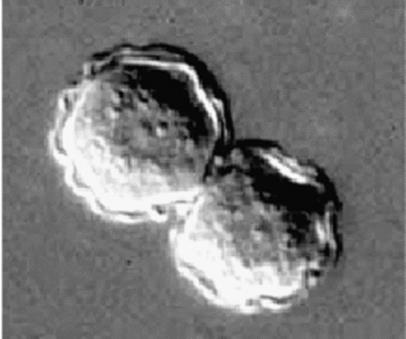

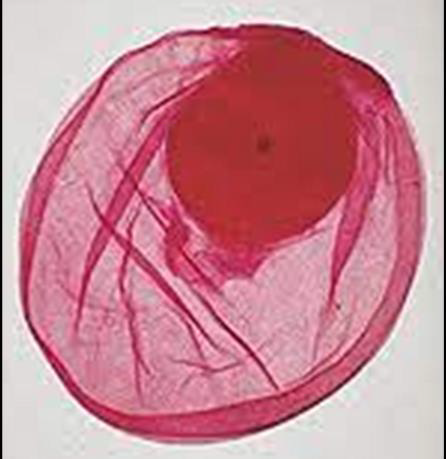
Identify this parasitic stage, its adult parasite, and mention the type of brain lesion it produces.
What is the definitive diagnostic technique?
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Identify this parasitic stage, its adult parasite, and mention the type of brain lesion it produces.
Cysticercus cellulosae
Adult parasite: Taenia solium
Brain lesion: Cystic lesion (cysticercosis)
What is the definitive diagnostic technique?
Excision biopsy
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
About 5 × 10 mm, bladder-like (contains fluid)
Scolex invaginated with 4 suckers and double rows of hooks

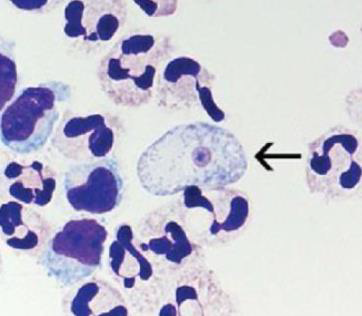
Identify parasite/stage, mention the examined sample, and name the disease induced by this parasite in the CNS.
Mention the culture media you can use to confirm the diagnosis.
Mention the stain used and two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Identify another sample that can be used to detect this stage.
Identify parasite/stage, mention the examined sample, and name the disease induced by this parasite in the CNS.
Naegleria fowleri trophozoite, CSF.
Causes Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis (PAME).
Mention the culture media you can use to confirm the diagnosis.
Non-nutrient agar (1.5%) enriched with Escherichia coli.
Mention the stain used and two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Wright–Giemsa stain.
About 10–15 µm, has a single nucleus with a large central karyosome, blunt pseudopodia, food vacuoles, and a contractile vacuole.
Identify another sample that can be used to detect this stage.
Brain tissue biopsy
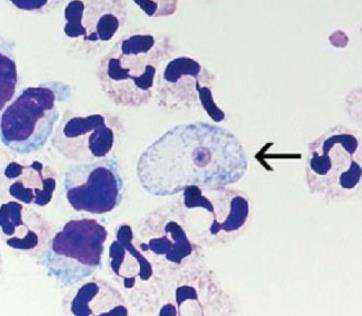
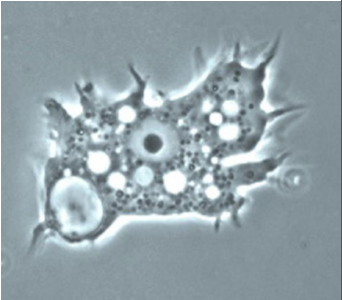
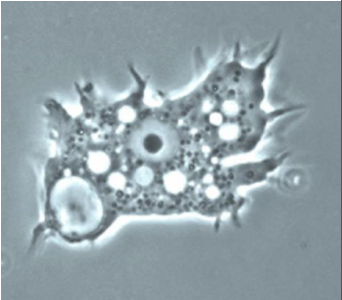
Identify the parasite/stage, and name the disease induced by this parasite in the CNS.
Mention direct diagnosis for this infection (techniques and detected stages).
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Mention the culture media you can use to confirm the diagnosis.
List human tissue/parts affected by this parasite.
Identify the parasite/stage, and name the disease induced by this parasite in the CNS.
Acanthamoeba castellanii trophozoite
Causes Granulomatous Amoebic Encephalitis (GAE).
Mention direct diagnosis for this infection (techniques and detected stages).
Direct microscopy and staining, or culture for detection of trophozoites and cysts in tissues or CSF.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
About 20–40 µm, with multiple spiky pseudopodia.
Mention the culture media you can use to confirm the diagnosis.
Non-nutrient agar (1.5%) enriched with Escherichia coli.
List human tissue/parts affected by this parasite.
Brain, eye, and skin.
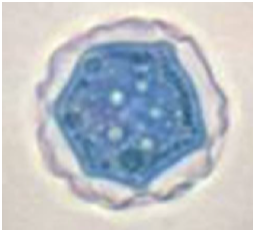
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used.
Mention the diagnostic methods used for ocular infection caused by this parasite
Identify the parasitic stage.
Acanthamoeba castellanii cyst.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
About 15–20 µm in size.
Has a polygonal double wall with many pores.
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used.
Samples: CSF, brain tissue, corneal tissue, and skin biopsy.
Culture medium: Non-nutrient agar (1.5%) enriched with Escherichia coli.
Mention the diagnostic methods used for ocular infection caused by this parasite.
Corneal scrapings or sections examined by direct microscopy and staining, or by cultivation.
Laser confocal microscopy can visualize both trophozoites and cysts.
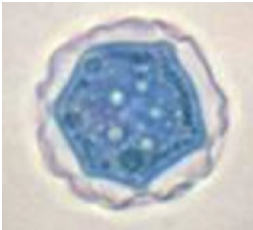
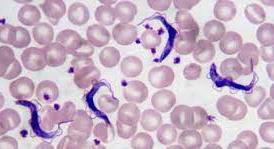
Mention two direct methods for detection of this parasite.
How to differentiate between the two species of this parasite? And which antibody can be elevated?
Which parasite species has available card agglutination test?
Mention two characteristics of CSF in this disease.
Mention two direct methods for detection of this parasite.
Microscopy:
a. Wet mount smears examination to detect trypanosomes’ motility.
b. Examination of Giemsa-stained smears to detect the morphological characteristics of polymorphic trypomastigotes.Culture
Animal inoculation
How to differentiate between the two species of this parasite? And which antibody can be elevated?
The card-agglutination test is used for detection of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense only.
High levels of specific antibodies (IgM) are elevated.
Which parasite species has available card agglutination test?
Trypanosoma brucei gambiense
Mention two characteristics of CSF in this disease.
Raised pressure
Increased cell count (mainly lymphocytes) and protein levels
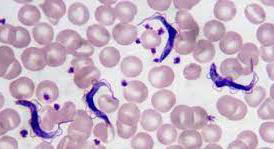
Identify this parasitic stage, its adult parasite, and mention the type of brain lesion it produces.
What is the definitive diagnostic technique?
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Identify this parasitic stage, its adult parasite, and mention the type of brain lesion it produces.
Cysticercus cellulosae
Adult parasite: Taenia solium
Brain lesion: Cystic lesion (cysticercosis)
What is the definitive diagnostic technique?
Excision biopsy
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
About 5 × 10 mm, bladder-like (contains fluid)
Scolex invaginated with 4 suckers and double rows of hooks
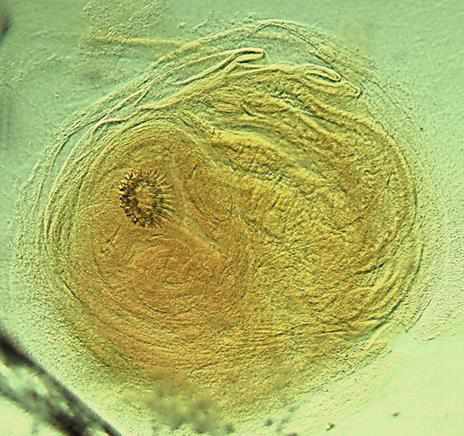
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention the contents of this stage.
State the best method for diagnosing this disease.
Hydatid sand
Detached scolices, brood capsules, and daughter cysts that fall in hydatid fluid
Fluid aspirated from surgically removed cyst
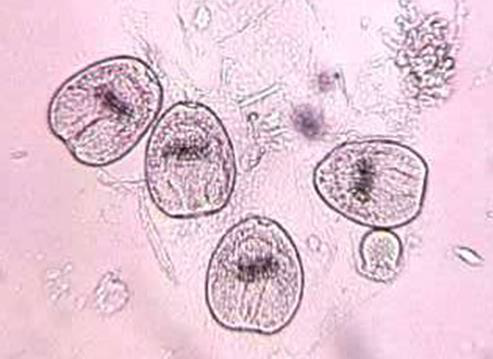
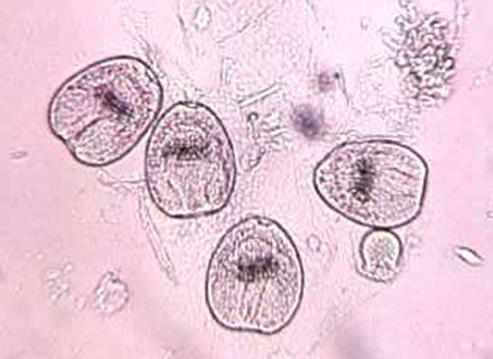
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used
Identify the parasitic stage.
Balamuthia mandrillaris trophozoite
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Pleomorphic, large (12–60 µm)
Actively motile by broad or finger-like pseudopodia
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used.
Samples: CSF, brain tissue, and skin biopsy
Culture medium: Non-nutrient agar (1.5%) enriched with Escherichia coli
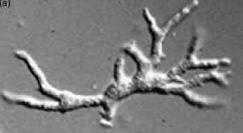
Identify this parasitic stage, its adult parasite, and mention the type of brain lesion it produces.
What is the definitive diagnostic technique?
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Identify this parasitic stage, its adult parasite, and mention the type of brain lesion it produces.
Cysticercus cellulosae
Adult parasite: Taenia solium
Brain lesion: Cystic lesion (cysticercosis)
What is the definitive diagnostic technique?
Excision biopsy
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
About 5 × 10 mm, bladder-like (contains fluid)
Scolex invaginated with 4 suckers and double rows of hooks
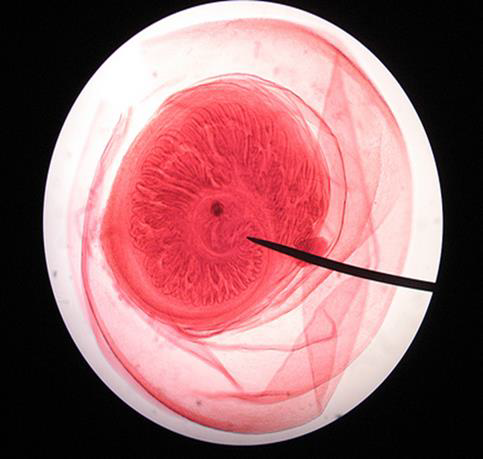
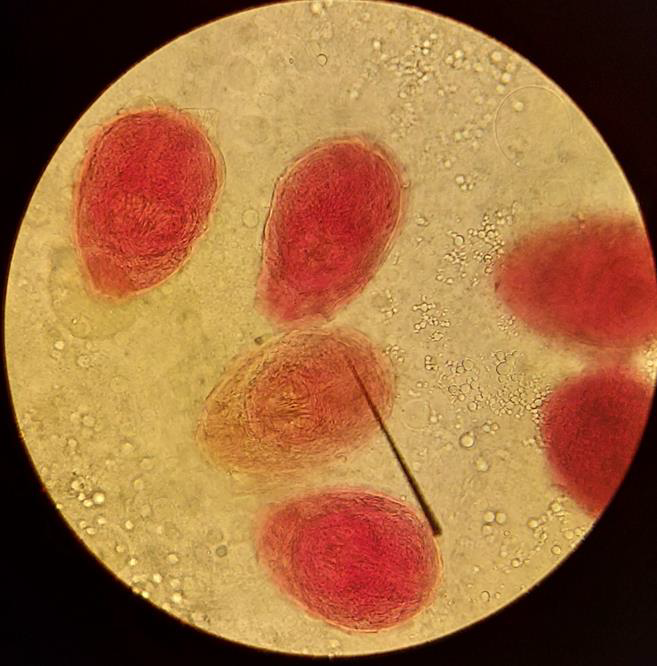
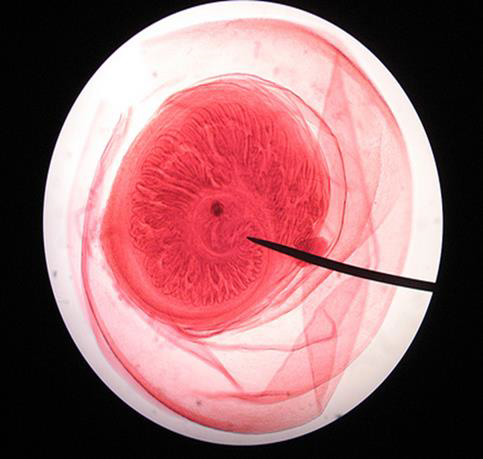
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention the contents of this stage.
State the best method for diagnosing this disease.
Hydatid sand
Detached scolices, brood capsules, and daughter cysts that fall in hydatid fluid
Fluid aspirated from surgically removed cyst
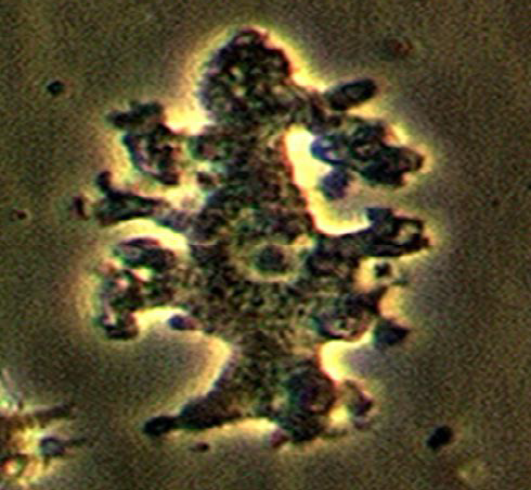
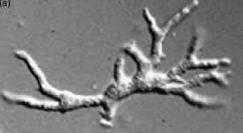
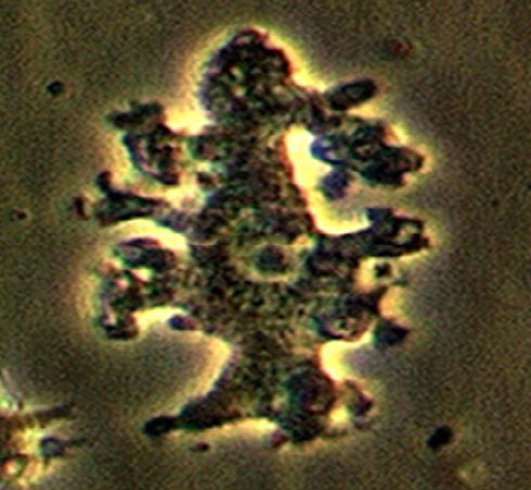
Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used
Identify the parasitic stage.
Balamuthia mandrillaris trophozoite
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Pleomorphic, large (12–60 µm)
Actively motile by broad or finger-like pseudopodia
Mention the possible human samples used for diagnosis, and the culture medium used.
Samples: CSF, brain tissue, and skin biopsy
Culture medium: Non-nutrient agar (1.5%) enriched with Escherichia coli
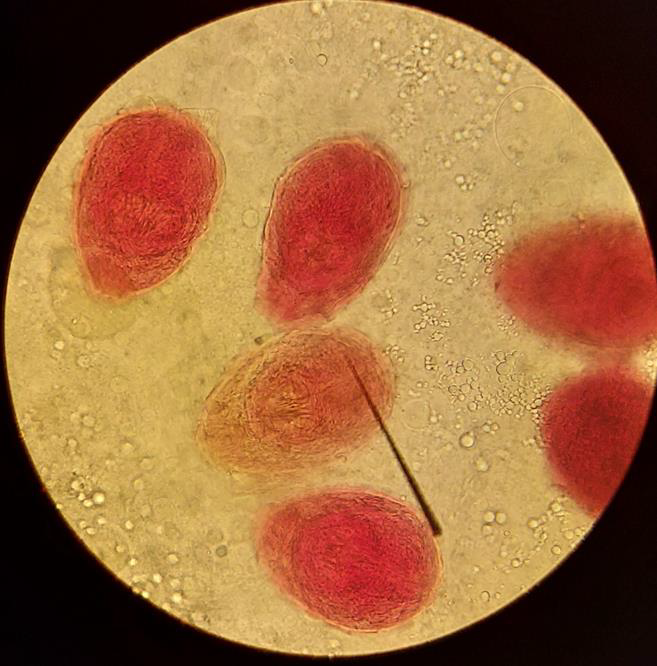
Name the parasitic stage.
Mention special characteristics of the stage.
Name the intradermal test used for diagnosis of this disease.
What is the definitive diagnostic method?
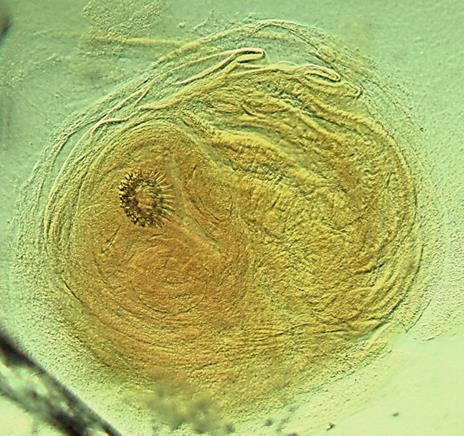
Name the parasitic stage.
Hydatid cyst
Mention special characteristics of the stage.
Wall has two layers: outer laminated non-cellular layer and inner cellular germinal layer
Contents include individual scolices, brood capsules, daughter cysts, hydatid fluid, and hydatid sand
Name the intradermal test used for diagnosis of this disease.
Casoni test
What is the definitive diagnostic method?
Surgical removal of the cyst and confirmation of its structure and contents histologically
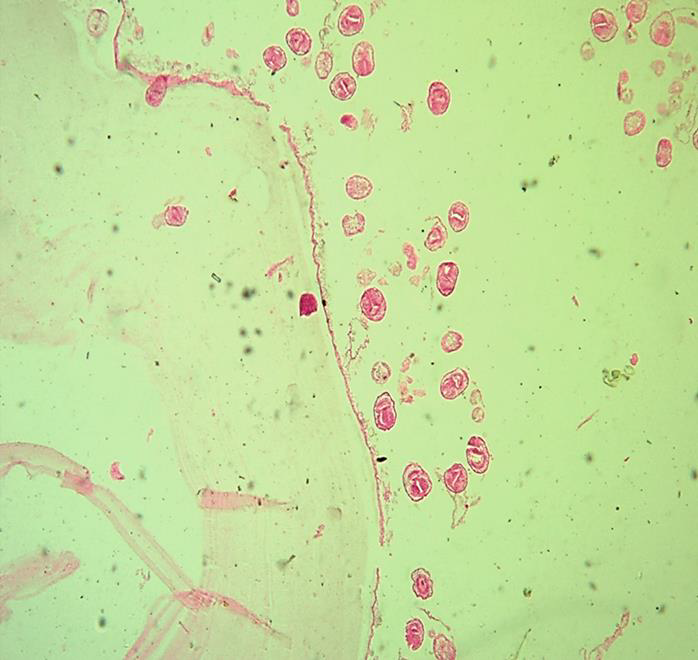

Identify the parasitic stage.
Mention the contents of this stage.
State the best method for diagnosing this disease.
Hydatid sand
Detached scolices, brood capsules, and daughter cysts that fall in hydatid fluid
Fluid aspirated from surgically removed cyst

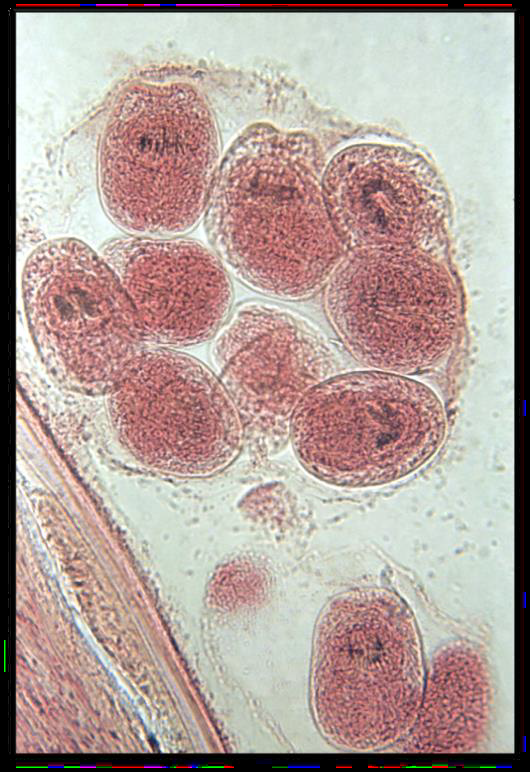
Identify this parasitic stage, its adult parasite, and mention the type of brain lesion it produces.
What is the definitive diagnostic technique?
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
Identify this parasitic stage, its adult parasite, and mention the type of brain lesion it produces.
Cysticercus cellulosae
Adult parasite: Taenia solium
Brain lesion: Cystic lesion (cysticercosis)
What is the definitive diagnostic technique?
Excision biopsy
Mention two morphological characteristics of this stage.
About 5 × 10 mm, bladder-like (contains fluid)
Scolex invaginated with 4 suckers and double rows of hooks
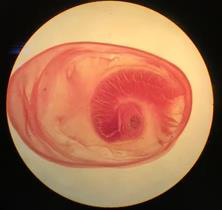
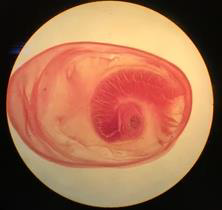
Name the parasitic stage.
Mention special characteristics of the stage.
Name the intradermal test used for diagnosis of this disease.
What is the definitive diagnostic method?
Name the parasitic stage.
Hydatid cyst
Mention special characteristics of the stage.
Wall has two layers: outer laminated non-cellular layer and inner cellular germinal layer
Contents include individual scolices, brood capsules, daughter cysts, hydatid fluid, and hydatid sand
Name the intradermal test used for diagnosis of this disease.
Casoni test
What is the definitive diagnostic method?
Surgical removal of the cyst and confirmation of its structure and contents histologically