Chapter 2: Bioenergetics and Carbohydrate Metabolism
1/82
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Midterm Part II
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Bioenergetics
the study of energy changes accompanying biochemical reactions in biological systems
field of biochemistry concerned with the transformation and use of energy by living cells
Catabolic Reactions
involve the breakdown of chemical molecules
Anabolic Reactions
involve the synthesis of compounds
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
the main energy currency for organisms
synthesize ATP and break down ATP
The goal of metabolic and catabolic processes are:
to _____________ from available starting materials
to _____________ into (ADP and Pi) by utilizing it in biological process
Free Energy
the energy actually available to do work (utilizable) is known as __________
Changes in Free Energy
are valuable in predicting the feasibility of chemical reactions
the reactions can occur spontaneously if they are accompanied decrease in free energy
during a chemical reaction, heat may be released or absorbed
Photosynthetic cells
acquire free energy from absorbed solar radiation
Heterotrophic cells
acquire free energy from nutrient molecules
First law of thermodynamics
principle of conservation of energy
for any physical/chemical change, the total amount of energy in closed system remains constant
First Law of Thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed - it can only be changed from one form to another
Second law of thermodynamics
universe tends toward increasing disorder
in all natural processes, the entropy of the universe increases (unless energy requiring processes counteract it)
Gibbs free energy (G)
which is equal to the total amount of energy capable of doing work during a process at constant temperature and pressure
Exergonic
if G is negative, then the process is spontaneous and termed ________
Endergonic
if G is positive then the process is non spontaneous and termed __________
Equilibrium
if G is equal to zero then the process has reached __________
Enthalpy (H)
the total heat energy in a system
the amount of heat energy transferred (absorbed/emitted) in a chemical process under constant pressure
Exothermic
when H is negative, the process produces heat and is termed ______
Endothermic
when H is positive, the process absorbs heat and is termed __________
Entropy (S)
quantitative expression of the degree of randomness or disorder of the system
measures the amount of heat dispersed or transferred during a chemical process
Increased
when S is positive, then the disorder of the system has _________
Decreased
when S is negative, then the disorder of the system has ________
G = H - T(S)
Relationship between the change in Free energy, Enthalpy and Entropy
Exergonic Reaction
implies the release of energy from a spontaneous chemical reaction without any concomitant utilization of energy
these reactions have an ability to perform work and include most of the catabolic reactions in cellular respiration
Exergonic Reaction
most of these reactions involve breaking of bonds during the formation of reaction intermediates
Endergonic Reaction
most anabolic reactions like photosynthesis and DNA and protein synthesis are ______ in nature
Endergonic Reaction
non-spontaneous reaction, energy should be provided from outside for the progression of the reaction
Nutrition
the science of how the body utilizes food to meet requirements for development, growth, repair and maintenance
Carbohydrate
most abundant organic molecule on earth
all carbohydrates have the general formula
are defined as aldehyde or keto derivatives of polyhydric alcohols
Aldose
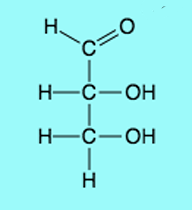
Ketose
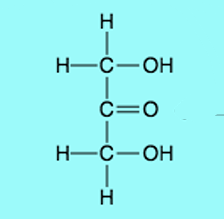
Triose
Classification of Carbohydrates by Number of Carbons:
What is the generic name for the carbohydrates with 3 carbons?
Tetrose
Classification of Carbohydrates by Number of Carbons:
What is the generic name for the carbohydrates with 4 carbons?
Pentose
Classification of Carbohydrates by Number of Carbons:
What is the generic name for the carbohydrates with 5 carbons?
Hexose
Classification of Carbohydrates by Number of Carbons:
What is the generic name for the carbohydrates with 6 carbons?
Monosaccharides
the smallest, most basic units of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides
Properties:
sweet-tasting
quickly absorbed
soluble in water
Disaccharides
made of two monosaccharides joined together
Disaccharides
Properties
still sweet
need to be broken down into monosaccharides before absorption
Oligosaccharides
made up of a few (typically 3-10) monosaccharide units linked together
Oligosccharides
Properties:
usually not very sweet
often partially/poorly digested by humans
Raffinose
Components:
Galactose + Glucose + Fructose
Stachyose
Components:
2 Galactose + Glucose + Fructose
Fructooligosaccharides (FOS)
Components:
Short chains of fructose
Galactooligisaccharides
Components:
chains of galactose
Raffinose
Found:
beans
cabbage
broccoli
Stachyose
Found:
soybeans
legumes
Fructooligosaccharides
Found:
onions
garlic
bananas
chicory
Galactooligosaccharides
Found:
human milk
legumes
Raffinose
Notes:
can cause gas
Stachyose
Notes:
harder to digest
Fructooligosaccharides
Notes:
prebiotic
Galactooligosaccharides
Notes:
also prebiotic
Polysaccharides
long chains of monosaccharides
Fischer Formula/Fischer Projection
is a two-dimensional way of representing the 3d structure of organic molecules, especially sugars and amino acids
Penultimate Carbons
Carbon atom that determines if a sugar is D or L
the chiral carbon farthest from the aldehyde or ketone functional group (2nd to the last C)
Haworth Projection Formula
cyclic structures of sugars
method used to show the 3d stereochemistry of cyclic sugars (or saccharides)
Anomers
differ only in the configuration at the hemiacetal carbon
a-OH
is pointing down
b-OH
is pointing up
Isomers
compounds that have the same chemical formula but have different structures
Epimers
are carbohydrates that differ in the location of the -OH group in one location
Energy Source
Functions of Carbohydrate:
main fuel for cells (especially brain & red blood cells)
Sparing Protein
Functions of Carbohydrate:
prevents protein breakdown for energy
fat metabolism
Functions of Carbohydrate:
needed for complete fat metabolism; otherwise, ketones form
Digestive Health
Functions of Carbohydrate:
fiber supports bowel health & regularity
Brain Function
Functions of Carbohydrate:
brain relies heavily on glucose (about 120g/day)
Metabolism
is the set of chemical reactions that occur in living organisms to maintain life
Convert food into energy, build and repair tissues, eliminate waste products and support all bodily functions
Metabolism allows the body to (4):
Catabolism
breaks down larger molecules into smaller ones
releases energy
ends with “lysis”/”oxidation”
Anabolism
builds up complex molecules from simpler ones
uses energy
ends with “genesis”/”synthesis”
Glucose in the bloodstream
after you eat carbohydrates, your body breaks them down into glucose which enters the bloodstream
Insulin release (in most cases)
the pancreas releases insulin (a hormone)
some tissues require insulin for glucose uptake, while others dont
Glucose Transporters (GLUT proteins)
these are membrane proteins that facilitate glucose entry into cells
Glucose entry via GLUT4 (muscle and fat)
in insulin-sensitive tissues like muscle and adipose (fat):
insulin binds to insulin receptors on the cell membrane
GLUT4 transporters are moved to the cell membrane
glucose enters the cell through GLUT4
once inside, glucose can be:
used for energy (via glycolysis)
stored as glycogen (in muscle/liver), or;
converted into fat (in adipose tissue)
Glycolysis
Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas Pathway / E.M.P. Pathway
is the metabolic pathway that breaks down one molecule of glucose (6-carbon) into two molecules of pyruvate (3-carbon), producing small amounts of energy in the form of ATP and NADH
Citric Acid Cycle/ Kreb’s Cycle/ Tricarboxylic Acid/TCA Cycle
is a central metabolic pathway that:
takes place in the mitochondrial matrix
requires oxygen indirectly (aerobic conditions)
converts Acetyl-CoA into Co2, while producing high-energy electron carriers (NADH, FADH2) and ATP
Gluconeogenesis
is the metabolic process by which the body creates glucose from non-carbohydrate sources - mainly during fasting, starvation, or intense exercise
Lactate
Major Precursors:
from anaerobic glycolysis
Alanine (Amino Acids)
Major Precursors:
from protein breakdown
Glycerol
Major Precursors:
from fat breakdown (triglycerides)
Propionate
Major Precursors:
from odd-chain fatty acids (minors)
Glycogenesis
anabolic process of synthesizing glycogen from glucose
store excess glucose as glycogen for later use