Ch 3: Prokaryotic Cells
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about prokaryotic cells.
- Most of a prokaryote's nutrients are obtained through diffusion
- All prokaryotes are unicellular organisms
- All prokaryotes lack a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
- Prokaryotes do not change shape or arrangement to enhance their survival
- Most of a prokaryote's nutrients are obtained through diffusion
- All prokaryotes are unicellular organisms
- All prokaryotes lack a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
Choose the statement which best defines a pleomorphic organism.
- Pleomorphic organisms can alter their size but not their shape
- Pleomorphic organisms can take on different forms, which enhances their survival and transmission to a human host
- Pleomorphic organisms lack the ability to take on different forms such as shape or arrangement
- Pleomorphic organisms do not impact an organism's ability to form a biofilm
Pleomorphic organisms can take on different forms, which enhances their survival and transmission to a human host
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about binary fission in prokaryotic cells.
- Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction that is simpler than mitosis
- Binary fission results in offspring, which are genetically identical to the parent cell
- Binary fission is a type of sexual reproduction which introduces genetic variation from parent to offspring
- Binary fission frequency differs between species and is affected by environmental conditions
- Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction that is simpler than mitosis
- Binary fission results in offspring, which are genetically identical to the parent cell
- Binary fission frequency differs between species and is affected by environmental conditions
Choose the FALSE statement regarding prokaryotic plasma membranes.
- Gases, water, and small non-charged substances can diffuse through the selectively permeable plasma membrane
- Ions and large polar substances can diffuse through the plasma membrane without assistance
- The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that serves as barrier for a cell
- The plasma membrane's phospholipid bilayer contains hydrophilic phosphates and hydrophobic fatty acids
Ions and large polar substances can diffuse through the plasma membrane without assistance
_____ bacteria lack an outer membrane, have a thick layer of peptidoglycan, contain teichoic acid in their cell wall and stain purple on the Gram stain.
- Gram-negative
- Gram-positive
- Gram-variable
- Acid-fast
Gram-positive
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about acid-fast bacteria.
- Genera Nocardia and Mycobacterium are acid-fast and stain blue during the acid-fast staining procedure
- Acid-fast bacteria have a waxy lipid called mycolic acid in their cell membranes
- Acid-fast staining is important in the diagnosis of leprosy and tuberculosis
- Genera Nocardia and Mycobacterium are acid-fast and stain red/pink during the acid-fast staining procedure
- Acid-fast staining is important in the diagnosis of leprosy and tuberculosis
- Genera Nocardia and Mycobacterium are acid-fast and stain red/pink during the acid-fast staining procedure
Choose the FALSE statement about cellular transport mechanisms.
- Osmosis is the passive movement of water from a low-solute concentration to a high-solute concentration
- Facilitated diffusion does not require energy and uses membrane proteins to move substances down their concentration gradient
- Active transport requires energy and uses carrier proteins to move substances against their concentration gradient
- Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration
Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration
Considering the process of osmosis, what will occur if a bacterial cell is put into a hypotonic solution?
- The cell will lose water and undergo plasmolysis
- The cell will absorb salt from its environment
- The cell will swell up with water and this may result in lysis if its cell wall is damaged
- There will be no net movement of water into or out of the cell
The cell will swell up with water and this may result in lysis if its cell wall is damaged
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about prokaryotic external appendages.
- Fimbriae aid in gene transfer through conjugation
- Flagella allow for motility
- Pili allow for adhesion, movement, and aid in gene transfer through conjugation
- The glycocalyx promotes adhesion and interferes with phagocytosis
- Flagella allow for motility
- Pili allow for adhesion, movement, and aid in gene transfer through conjugation
- The glycocalyx promotes adhesion and interferes with phagocytosis
Which of the following allows the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi to move in a corkscrew motion?
- Lophotrichous flagella
- Monotrichous flagellum
- Amphitrichous flagella
- Periplasmic flagellum
Periplasmic flagellum
Prokaryotic cells house a single circular chromosome in their __________.
- nucleus
- nucleoid region
- Ribosomes
- periplasmic space
-nucleoid region
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about the prokaryotic cytoskeleton.
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton contains standard actin and tubulin proteins
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton directs construction of a rigid cell wall
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton acts as a scaffolding to organize mitosis
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton provides general organization of the cytoplasm
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton directs construction of a rigid cell wall
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton provides general organization of the cytoplasm
What organelle present in Prokaryotes resembles one found also in Eukaryotes and provides support for the Endosymbiont Theory?
- Prokaryotes have a ribosome with an 80S sedimentation rate
- Prokaryotic ribosomes build proteins by linking amino acids together. Because of their smaller size and mass, they are often targets of antibiotics that will only harm them and not the larger ribosomes present in the patient's own body
- Prokaryotic ribosomes have a lower overall mass and diameter that matches those measurements found in the ribosomes of Eukaryote chloroplasts and mitochondria
- Eukaryotic organelles called chloroplasts and mitochondria carry out their own protein synthesis independent of the rest of the cell using 70S ribosomes.
Prokaryotic ribosomes have a lower overall mass and diameter that matches those measurements found in the ribosomes of Eukaryote chloroplasts and mitochondria
All of the following are examples of inclusion bodies in prokaryotic cells except __________.
- carboxysomes
- magnetosomes
- glycogen granules
- endospores
endospores
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about spore-forming bacteria.
- Spore-forming bacteria, such as Clostridium, contain heat- and chemical-resistant layers around the spore coat, making them difficult to destroy
- Spores contain a low amount of dipicolinic acid, which contributes to the heat resistance of spores
- Only gram-positive organisms are spore forming
- Disinfectants such as bleach are sporicidal and are effective in destroying spores
- Spore-forming bacteria, such as Clostridium, contain heat- and chemical-resistant layers around the spore coat, making them difficult to destroy
- Disinfectants such as bleach are sporicidal and are effective in destroying spores
Tumbles occur when
- the flagella undulate
- the flagella rotate clockwise
- the flagella stop rotating
- the flagella rotate counterclockwise
the flagella rotate clockwise
Which of the following types of bacterial cells would have only a single flagellum?
- Peritrichous
- Monotrichous
- Amphitrichous
- Lophotrichous and monotrichous
- Lophotrichous
monotrichous
Peritrichous bacteria make a run when
- the flagella turn clockwise and become bundled
- the flagella turn counterclockwise and become bundled
- the flagella turn counterclockwise and separate
- the flagella turn clockwise and separate
the flagella turn counterclockwise and become bundled
Which of the following types of bacterial cells would have flagella located at only one end of the cell?
- Lophotrichous and monotrichous
- Amphitrichous
- Monotrichous and amphitrichous
- Lophotrichous
- Monotrichous
- Peritrichous
Lophotrichous and monotrichous
What makes phospholipid membranes good at keeping some molecules out, and allowing others to freely pass?
- They are completely hydrophilic
- They are positively charged
- They have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
- They are completely hydrophobic
They have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
Integral proteins are mostly involved in
- transport function
- enzymatic function
- receptors
- recognition sites
transport function
How does water enter and exit a cell?
- By simple diffusion across the membrane
- By use of a peripheral transport protein
- By simple diffusion or by use of an integral transport protein
- By use of an integral transport protein
By simple diffusion or by use of an integral transport protein
A glycoprotein
- can be used as a receptor
- can be used in enzymatic functions
- is a type of peripheral protein above that can be used as a receptor or in enzymatic functions
- is a type of peripheral protein
is a type of peripheral protein above that can be used as a receptor or in enzymatic functions
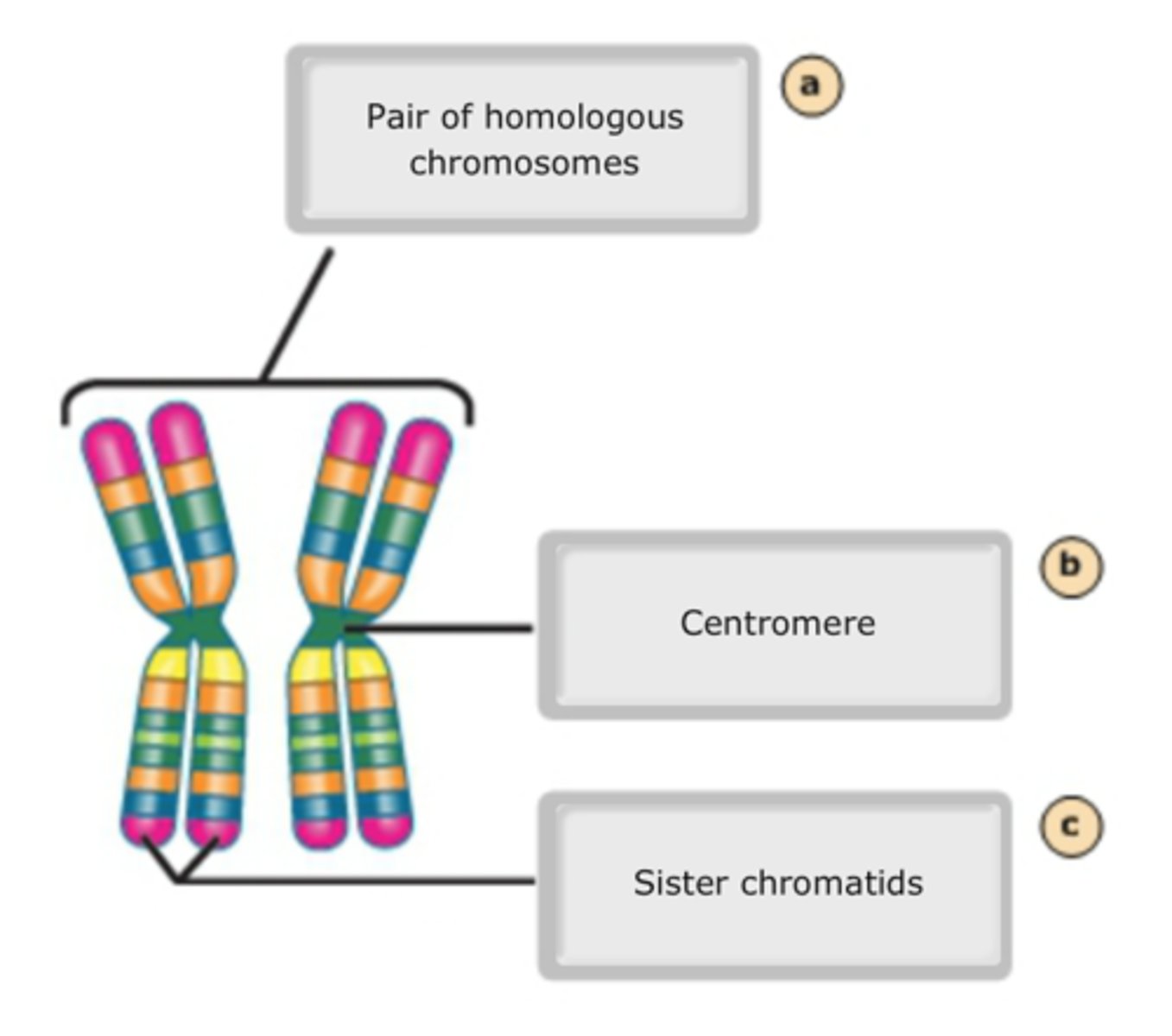
Identify the chromosome structures
A biochemical analysis of an unknown bacterium reveals that the microbe has teichoic acids in its cell wall. What other feature would you expect to find in the cell wall of this bacterium?
- Porins
- Lipopolysaccharide
- Outer membrane
- Thick layer of peptidoglycan
Thick layer of peptidoglycan
Globomycin is an antibacterial drug that targets an outer membrane lipoprotein called prolipoprotein. Based solely on its mode of action, would you expect globomycin to be effective against Gram-positive and/or Gram-negative bacterial pathogens?
- Globomycin should target both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial pathogens
- Globomycin should only target Gram-positive bacterial pathogens
- Globomycin should only target Gram-negative bacterial pathogens
- Globomycin will not be an effective treatment for either Gram-positive or Gram-negative bacterial pathogens
Globomycin should only target Gram-negative bacterial pathogens
Streptococcus pyogenes, the causative agent of strep throat, has a cell wall composed of a thick layer of peptidoglycan and is notably missing an outer membrane. Based on this information, what color would you expect S. pyogenes to appear after a successful Gram stain?
- Brown
- Pink
- Purple
- Colorless
Purple
Decolorization is a critical differentiation step in the Gram stain procedure. What effect does the acetone-alcohol decolorizer have on Gram-positive cells during the Gram stain procedure?
- It dehydrates the thick peptidoglycan layer, helping to trap the primary dye within the cell wall
- It fixes the bacterial cells to the slide so they are not rinsed away during staining
- It forms large complexes with crystal violet which get stuck in the thick peptidoglycan layer
- It dissolves the outer membrane, allowing the primary dye to be more easily rinsed away
It dehydrates the thick peptidoglycan layer, helping to trap the primary dye within the cell wall
Which of the following statements correctly contrasts characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Prokaryotes include bacteria and protists; eukaryotes include plants and animals
- Prokaryotes reproduce only asexually; eukaryotes reproduce only sexually
- Prokaryotes are all unicellular; eukaryotes can be either unicellular or multicellular
- Prokaryotes have RNA genomes; eukaryotes have DNA genomes
Prokaryotes are all unicellular; eukaryotes can be either unicellular or multicellular
Which of the following statements correctly differentiates extracellular structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Prokaryotic cells only may have one flagellum that rotates like a propeller; eukaryotic cells have multiple flagella that wave back and forth
- Prokaryotic cell walls are made of peptidoglycan; eukaryotic cell walls are made of pseudopeptidoglycan
- Prokaryotic flagella are built from flagellin protein; eukaryotic flagella are built from tubulin protein
- Prokaryotic cells may use cilia for motion while eukaryotic cells use fimbriae, but both are short hair-like surface structures
Prokaryotic flagella are built from flagellin protein; eukaryotic flagella are built from tubulin protein
Which of the following intracellular structures are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
- Ribosomes
- Chloroplasts
- Cytoskeleton
- Golgi apparatus
- Mitochondria
- Lysosomes
- Nucleus
- Ribosomes
- Cytoskeleton
Choose the TRUE statement about the Domain Bacteria.
- Bacteria inhabit extreme environments and are not linked to human diseases
- The Domain Eukarya is more closely related to the Domain Bacteria than to the Domain Archaea
- The Domains Bacteria and Archaea are genetically identical
- The Domain Bacteria is made up of prokaryotes and likely originated 3.8 billion years ago
The Domain Bacteria is made up of prokaryotes and likely originated 3.8 billion years ago
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about prokaryotic cells.
- Most of a prokaryote's nutrients are obtained through diffusion
- Prokaryotes do not change shape or arrangement to enhance their survival
- All prokaryotes lack a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
- All prokaryotes are unicellular organisms
- Most of a prokaryote's nutrients are obtained through diffusion
- All prokaryotes lack a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles
- All prokaryotes are unicellular organisms
Choose the statement which best defines a pleomorphic organism.
- Pleomorphic organisms lack the ability to take on different forms such as shape or arrangement
- Pleomorphic organisms can take on different forms, which enhances their survival and transmission to a human host
- Pleomorphic organisms do not impact an organism's ability to form a biofilm
- Pleomorphic organisms can alter their size but not their shape
Pleomorphic organisms can take on different forms, which enhances their survival and transmission to a human host
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about binary fission in prokaryotic cells.
- Binary fission frequency differs between species and is affected by environmental conditions
- Binary fission is a type of sexual reproduction which introduces genetic variation from parent to offspring
- Binary fission results in offspring, which are genetically identical to the parent cell
- Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction that is simpler than mitosis
- Binary fission frequency differs between species and is affected by environmental conditions
- Binary fission results in offspring, which are genetically identical to the parent cell
- Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction that is simpler than mitosis
Choose the FALSE statement regarding prokaryotic plasma membranes.
- The plasma membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that serves as barrier for a cell
- Gases, water, and small non-charged substances can diffuse through the selectively permeable plasma membrane
- Ions and large polar substances can diffuse through the plasma membrane without assistance
- The plasma membrane's phospholipid bilayer contains hydrophilic phosphates and hydrophobic fatty acids
Ions and large polar substances can diffuse through the plasma membrane without assistance
_____________ bacteria lack an outer membrane, have a thick layer of peptidoglycan, contain teichoic acid in their cell wall and stain purple on the Gram stain.
- Gram-negative
- Gram-variable
- Gram-positive
- Acid-fast
Gram-positive
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about acid-fast bacteria.
- Genera Nocardia and Mycobacterium are acid-fast and stain red/pink during the acid-fast staining procedure
- Genera Nocardia and Mycobacterium are acid-fast and stain blue during the acid-fast staining procedure
- Acid-fast bacteria have a waxy lipid called mycolic acid in their cell membranes
- Acid-fast staining is important in the diagnosis of leprosy and tuberculosis
- Genera Nocardia and Mycobacterium are acid-fast and stain red/pink during the acid-fast staining procedure
- Acid-fast staining is important in the diagnosis of leprosy and tuberculosis
Choose the FALSE statement about cellular transport mechanisms.
- Facilitated diffusion does not require energy and uses membrane proteins to move substances down their concentration gradient
- Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration
- Osmosis is the passive movement of water from a low-solute concentration to a high-solute concentration
- Active transport requires energy and uses carrier proteins to move substances against their concentration gradient
Diffusion is the passive movement of substances from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration
Considering the process of osmosis, what will occur if a bacterial cell is put into a hypotonic solution?
- The cell will absorb salt from its environment.
- The cell will swell up with water and this may result in lysis if its cell wall is damaged
- The cell will lose water and undergo plasmolysis
- There will be no net movement of water into or out of the cell
- The cell will swell up with water and this may result in lysis if its cell wall is damaged
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about prokaryotic external appendages.
- Flagella allow for motility
- Fimbriae aid in gene transfer through conjugation
- Pili allow for adhesion, movement, and aid in gene transfer through conjugation
- The glycocalyx promotes adhesion and interferes with phagocytosis
- Flagella allow for motility
- Pili allow for adhesion, movement, and aid in gene transfer through conjugation
- The glycocalyx promotes adhesion and interferes with phagocytosis
Which of the following allows the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi to move in a corkscrew motion?
- Monotrichous flagellum
- Amphitrichous flagella
- Periplasmic flagellum
- Lophotrichous flagella
Periplasmic flagellum
Prokaryotic cells house a single circular chromosome in their __________.
- nucleus
- nucleoid region
- periplasmic space
- Ribosomes
nucleoid region
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about the prokaryotic cytoskeleton.
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton acts as a scaffolding to organize mitosis
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton provides general organization of the cytoplasm
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton contains standard actin and tubulin proteins
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton directs construction of a rigid cell wall
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton provides general organization of the cytoplasm
- The prokaryotic cytoskeleton directs construction of a rigid cell wall
What organelle present in Prokaryotes resembles one found also in Eukaryotes and provides support for the Endosymbiont Theory?
- Prokaryotic ribosomes have a lower overall mass and diameter that matches those measurements found in the ribosomes of Eukaryote chloroplasts and mitochondria
- Eukaryotic organelles called chloroplasts and mitochondria carry out their own protein synthesis independent of the rest of the cell using 70S ribosomes
- Prokaryotes have a ribosome with an 80S sedimentation rate
- Prokaryotic ribosomes build proteins by linking amino acids together. Because of their smaller size and mass, they are often targets of antibiotics that will only harm them and not the larger ribosomes present in the patient's own body
Prokaryotic ribosomes have a lower overall mass and diameter that matches those measurements found in the ribosomes of Eukaryote chloroplasts and mitochondria
All of the following are examples of inclusion bodies in prokaryotic cells except __________.
- carboxysomes
- glycogen granules
- magnetosomes
- endospores
endospores
Choose the TRUE statement(s) about spore-forming bacteria.
- Spore-forming bacteria, such as Clostridium, contain heat- and chemical-resistant layers around the spore coat, making them difficult to destroy
- Spores contain a low amount of dipicolinic acid, which contributes to the heat resistance of spores
- Disinfectants such as bleach are sporicidal and are effective in destroying spores
- Only gram-positive organisms are spore forming
- Spore-forming bacteria, such as Clostridium, contain heat- and chemical-resistant layers around the spore coat, making them difficult to destroy
- Disinfectants such as bleach are sporicidal and are effective in destroying spores
Which of the following statements is
FALSE?
- Archaea and Bacteria are prokaryotic domains
- Both Archaea and Bacteria are unicellular
- Prokaryotes are unicellular and lack a membrane-bound nucleus
- Eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells
- Eukaryotes have a much simpler genetic makeup than prokaryotic cells
Eukaryotes have a much simpler genetic makeup than prokaryotic cells
Why are most prokaryotic cells small?
- Intracellular inclusions demand that cell size be small
- A high surface area-to-volume ratio helps smaller cells divide easier
- A low surface area-to-volume ratio helps smaller cells divide easier
- Nutrient diffusion is most efficient for smaller cells
- Storage bodies within a cell enable cells to be small so they need fewer nutrients
Nutrient diffusion is most efficient for smaller cells
Which of the following cell shapes look like a comma?
- coccobacilli
- bacilli
- stella
- vibrio
- spirochetes
vibrio
Cell shape is determined by which of the following?
- whether or not the species uses a flagellum
- whether or not the species is pathogenic
- cell wall and cytoskeleton components
- the way cells move through their media
- the way cells divide
cell wall and cytoskeleton components
Which of the following arrangements is sometimes referred to as having a beads-on-a-string appearance?
- streptobacilli
- palisade
- streptococci
- diplococci
- staphylococci
streptococci
Bacterial cells that have the ability to take on different cell shapes are known as
- biphasic
- pleomorphic
- chemotactic
- pallidic
- pyloric
pleomorphic
True or False:
Spirochetes move in a corkscrew-rotary motion due to a specialized periplasmic flagellum.
True
A clinical microbiologist is studying a suspected E. coli UTI in a patient. After obtaining a sample from the patient and immediately performing a Gram stain, the bacterial cells were determined to be Gram-negative with a filamentous shape. However, after culturing the sample for 24 hours, the cells were observed to be Gram-negative bacillus-shaped cells. What is the most likely explanation for these results?
- The patient has a viral rather than a bacterial infection
- The sample was contaminated during culturing
- The organism is pleomorphic and displays different characteristics when grown in a lab than during an infection
- The bacterial species mutated from a filamentous to a bacillus-shaped bacterial species
- the Gram staining procedure was defective
The organism is pleomorphic and displays different characteristics when grown in a lab than during an infection
Membrane proteins perform all of the following functions EXCEPT
- enzymes
- receptors
- blocking cell division
- anchors
- transporters
blocking cell divisions
Why are Gram-negative bacteria more resistant than Gram-positive bacteria to damage by certain chemical agents like lysozyme?
- Gram-negative bacteria contain peptidoglycan in their cell wall
- Gram-negative bacteria have a thicker layer of peptidoglycan in their cell wall
- Gram-negative bacteria have an outer membrane as part of their cell wall
- Gram-negative bacteria lack a cell wall
- Gram-negative bacteria have porins
Gram-negative bacteria have an outer membrane as part of their cell wall
In which of the following environments do Gram-positive NOT have a survival advantage over Gram-negative bacteria?
- needing to adhere to a host
- mechanical crushing
- abrasive environment
- dry environment
- exposure to penicillin-based drugs
exposure to penicillin-based drugs
Why is it so difficult to kill acid-fast bacteria?
- The bacteria are very motile and can travel to areas with a lower concentration of hazardous chemicals
- They form endospores that are highly resistant to antibiotics
- The acid in the bacteria denatures most antibiotics before they can work
- The bacteria are able to quickly break down several types of antibiotics before the concentration can reach dangerous levels
- Mycolic acid in the cell wall makes it very difficult for antimicrobial drugs to enter cells
Mycolic acid in the cell wall makes it very difficult for antimicrobial drugs to enter cells
What term most correctly describes when energy released by the flow of an ion from high to low concentration fuels the transport of an unrelated substance from low to high concentration but in the same direction?
- tertiary active transport
- primary active transport
- symport
- antiport
- phosphotransferase system
symport
Short, bristle-like structures that extrude from the surface of a prokaryotic cell are called
- flagella
- fimbriae
- mating bridges
- pili
- cilia
fimbriae
Which of the following structures allow bacteria to transfer genetic information through conjugation?
- capsule
- slime layer
- fimbriae
- glycocalyx
- pili
pili
Bacteria that have flagella distributed all over the cell surface are described as (having)
- lophotrichous
- monotrichous
- amphitrichous
- peritrichous
- periplasmic flagella
peritrichous
True or False:
Prokaryotic cells that move in response to oxygen levels are said to display chemotaxis.
False
True or False:
A capsule is one type of glycocalyx that is fairly unorganized and loosely associated with the cell wall.
False
True or False:
A bacteria's DNA can be found in the nucleus of the cell.
False
True or False:
A capsule is a well-organized glycocalyx that causes increased phagocytosis by host immune cells during an infection.
False