aggregate supply✅
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Aggregate supply
The quantity of goods and services that producers in an economy are willing and able to supply at a given level of price
SRAS
Short run aggregate supply is the total quantity of goods and services an economy can produce at a given pice level, with some factors of production fixed
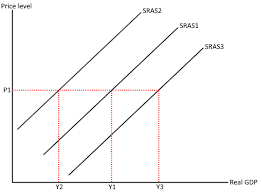
What causes a shift in aggregate supply
Cost of production
External factors and aggregate supply
Commodity prices
Volatile exchange rates
Level of net migration
Import tariffs
LRAS
Long run aggregate supply is the total amount of goods and services and economy can produce in the long run assuming all factors of production are flexible
2 types of LRAS
Keynesian LRAS (Keynes)
Classical LRAS (Hayek)
Classical LRAS
A vertical curve at full employment levels, classical economists believe in the long run the economy will always self correct to full capacity
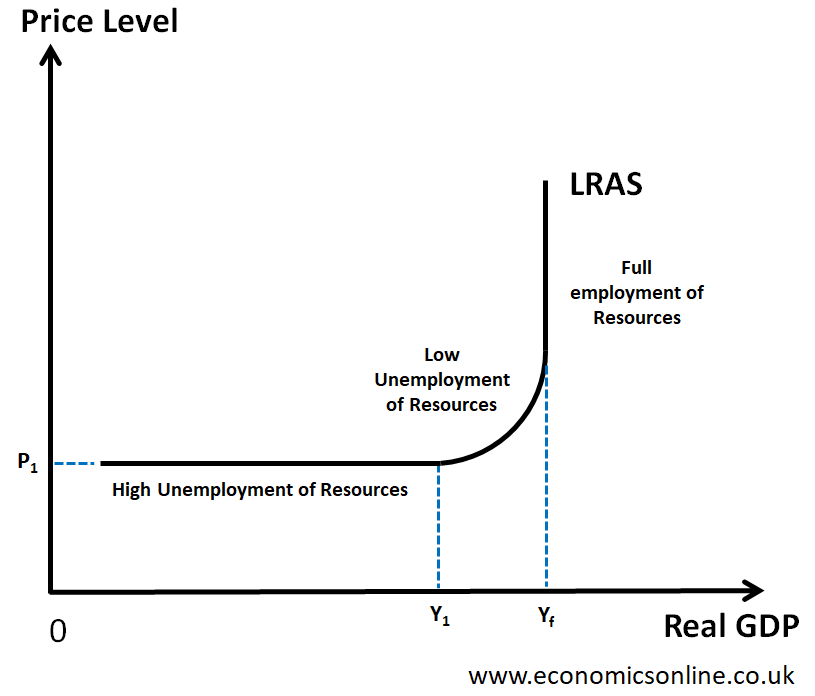
Keynesian LRAS
The LRAS curve has 3 sections
An economy can remain below full employment due to price and wage rigidities
Government intervention is needed to stimulate demand and move towards full capacity
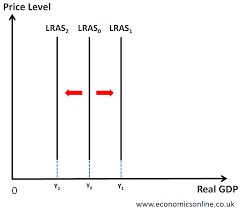
Shifts in LRAS
Shifts in LRAS occur because the quantity and/or quality of factors of production have changed
Capital
Land
Labour
Enterprise
Shifts in LRAS - Capital
Improvement in technology = better machines
Division of labour (specialisation) = higher productivity
Shifts in LRAS - Enterprise
More competition = more efficiency
Lower taxes and less regulations = more innovation
Shifts in LRAS - Land
Improving mining techniques = more raw materials extracted
Shifts in LRAS - Labour
More migrants/higher birth rates/higher participation rates/high retirement ages = more workers
Improved health = less absenteeism
Better education and training = improved skills
Bottlenecks
Bottle necks occur when output is on the inelastic part of the LRAS curve with no easy way to remedy the problem
This can lead to higher price levels
A bottleneck is any factor that delays or restricts production, leading to shortages, higher prices, and slower economic activity
Reasons for bottlenecks
Lack of raw materials
Lack of land
Lack of skilled labour
Insufficient capital