Final Study Guide (Quizzes)
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
Properly donning and doffing orthotic devices, maintaining appropriate schedules of orthotic use, and maintaining orthotic devices is an ADL
True
Which of the following is NOT TRUE regarding gait training?
None. All of the above are true statements.
Gait training may address the biomechanical problems of walking such as limited stride after an injury
Gait training may address balance concerns or an altered center of gravity as the result of an injury.
Gait training may address the neuromotor deficits that impact walking, such as decreased initiation time in the affected leg after a stroke
Gait training may involve the use of orthotic devices or ambulation aides.
Which of the following lists ambulation aids in order from most supportive to least supportive?
FWW -> hemi-walker -> quad cane -> single point cane
The type of ambulation aide may change due to the nature of the activity or the type of surface.
True
Which of the following is a consideration for safe ambulation?
All of the above
Weight bearing precautions
Cognitive limitations
Motor skill deficits
Which orthotic provides stability, alignment, and protection while allowing anterior-posterior movement of the ankle?
Hinged AFO
The type of ambulation aide may change over time due to improvements or due to progression/exacerbation of health impairment.
True
Using the occupation-based approach regarding the use of ambulation aides, OT practitioners must consider?
all of the above
the client’s role in the activity
desire to complete the functional activity
client factors and limitations
safety in performing the activity
It is NOT important for the OTA to follow through on recommendations made by the PT regarding gait.
False
Most serious falls take place in which room of the home?
bathroom
When ambulating with a patient, you should position yourself
slightly behind and to one side of the patient
The use of a mobility device or ambulation aide simplifies the task for the client.
False
Each transfer is unique and requires assessment of the environment and medical precautions.
True
It is generally the PT’s responsibility to train family members in safely performing transfers in the home.
False
It is often important to cue the client to or assist the client in scooting forward on the initial surface prior to performing a transfer.
True
It is important to drape a dependent client’s arms around your neck while performing a transfer.
False
It is best practice to use a gait belt for every client/patient transfer.
True
Verbal and/or physical cues are often helpful in bringing a client into midline prior to performing a transfer, therefore improving self-awareness, balance, and safety during the transfer.
True
The practitioner may need to assist the patient into a slight posterior pelvic tilt prior to transferring.
False
Armrest is removed, patient’s weight is shifted forward, and ankles point toward target surface. Client requires limited weight bearing as they do not come to a full stand.
(Bent) Squat Pivot Transfer
Can be modified to perform with 2 person assist, 1 person assist or modified independence. Armrest is removed and additional equipment is required.
Sliding Board Transfer
Often used when surfaces cannot be moved closer (ex. toilet cannot be moved, chair cannot fit in bathroom). Armrests are not removed. Client needs to bear weight and be able to step with assistance.
Stand-Step-Pivot Transfer
Armrest is removed, patient’s ankles point toward target surface, patient’s legs are both supported by therapist. The patient has minimal to no functional ability.
One Person Dependent Transfer
Used when client can bear some weight, can push off of chair arms, client’s ankles point toward goal and client stands with assist.
Stand Pivot Transfer
Typically used for dependent or total assist patients where additional help is needed
Two Person Dependent Transfer
Patient performs 50-74% of the transfer or the helper must lift the legs in/out of bed
Moderate Assistance
Transfer takes more time or uses an assistive device
Modified Independent
Client is unable to assist in transferring process
Total Assistance/Dependent
Patient requires lifting and lowering assistance or they perform 25-49% of the transfer
Maximal Assistance
Helper must position chair and remove armrests, give verbal cues for safety or sequencing
Supervision/Set-up/SBA
Patient requires assistance for one leg OR assistance for balance; patient performs 75% or more of the transfer
Minimal Assistance
Transferring is the process of __________________________________________________________.
moving a patient from one surface to another surface.
List 3 different things that the OT practitioner must consider before or during the transfer process to ensure the transfer is performed safely.
make sure that pt's feet are planted firmly on the ground, make sure pt's hands are on the shoulders or waist of OT practitioner, make sure to "sandwich" the weaker leg
List at least 3 tips for using proper body mechanics during transfers as the therapist
make sure to lift with your legs, do not twist your torso, keep your spine straight
List 2 types durable medical equipment (DME) that may be used in a client's home.
hoyer lift and gait trainer
Describe 2 safety concerns for transferring a client in/out of a car.
making sure that the client doesn't grab the door when transferring and make sure to protect the patient's head from hitting the frame of the car when transferring
Make 2 recommendations that would increase the safety of a patient with balance concerns during showering.
installing grab bars or having a tub bench or shower chair
Identify 2 different benefits of weight bearing
when using a standing frame for weightbearing it allows for blood to circulate in the LE to prevent ulcers and allows for the client have a sense of normalcy in being able to weightbear
Grandma has bad knees and cannot get up from the toilet or couch without assistance. Provide 2 possible modifications for improved independence.
install foot lifts to the bottom of the couch for easier transfer from sit to stand. install toilet commode to allow for an easier tansfer from sit to stand from toilet.
A client recently had a hip replacement but had a tub at home. Identify which piece of DME you would recommend and why? (Hint: hip precautions)
I would recommend a tub bench because when transferring to the tub it requires that the client has strength in the BUE. The tub bench also doesn't require for the patient to need to stand up as it is similar to a board pivot transfer where the client can easily slide onto the bench.
Identify 3 considerations for utilizing a mechanical lift versus a functional transfer with a patient.
client's body weight, limitations of disability, and well-being of caregiver
A person who had a total hip replacement is returning home. What is the BEST type of chair for them to sit in?
Above knee height
An individual who uses a wheelchair is being discharged from a rehabilitation facility to home. In determining accessibility of the interior home environment, what area should be the MOST concerning to the OTA?
Doorway widths and threshold heights
A COTA is assisting an individual with mild hemiparesis in transferring from the wheelchair to a tub transfer bench using a stand-pivot transfer technique. After locking the brakes, what is the FIRST verbal cue the COTA gives to the individual?
Scoot forward to the edge of the seat
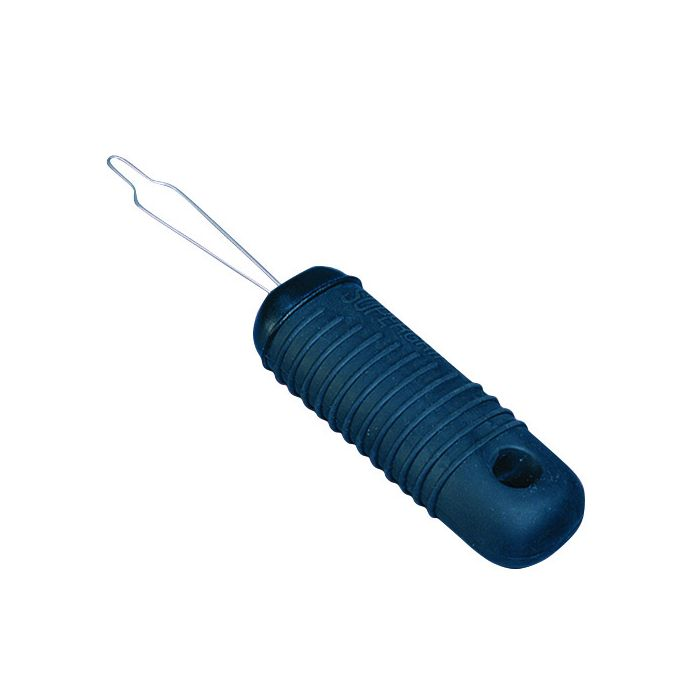

What is this item? What is it used for? Discuss who would likely benefit from the use of this item
button hook: used for slipping buttons through and out of button holes more easily when dressing with a shirt that has buttons. A client with decreased fine motor skills would benefit from the use of the item as pulling a button through a button hole requires the use of fine motor skills to complete.
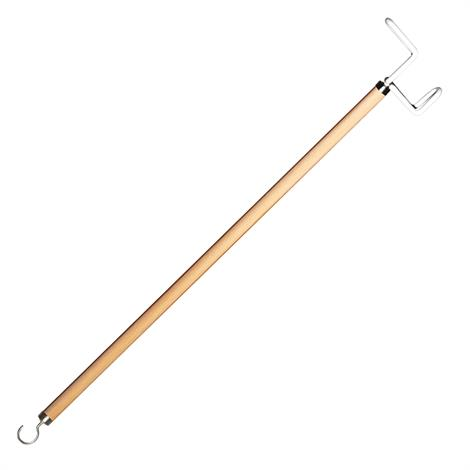

What is this item? What is it used for? Discuss who would likely benefit from the use of this item
dressing stick: used for donning and doffing clothes, socks, and can be used to help pull a zipper up and down. A client with precautions, like hip precautions, would use this item as the 'no bending past the 90 degrees' would require the client to use a dressing stick to reach lower extremities like the foot to pull socks off.
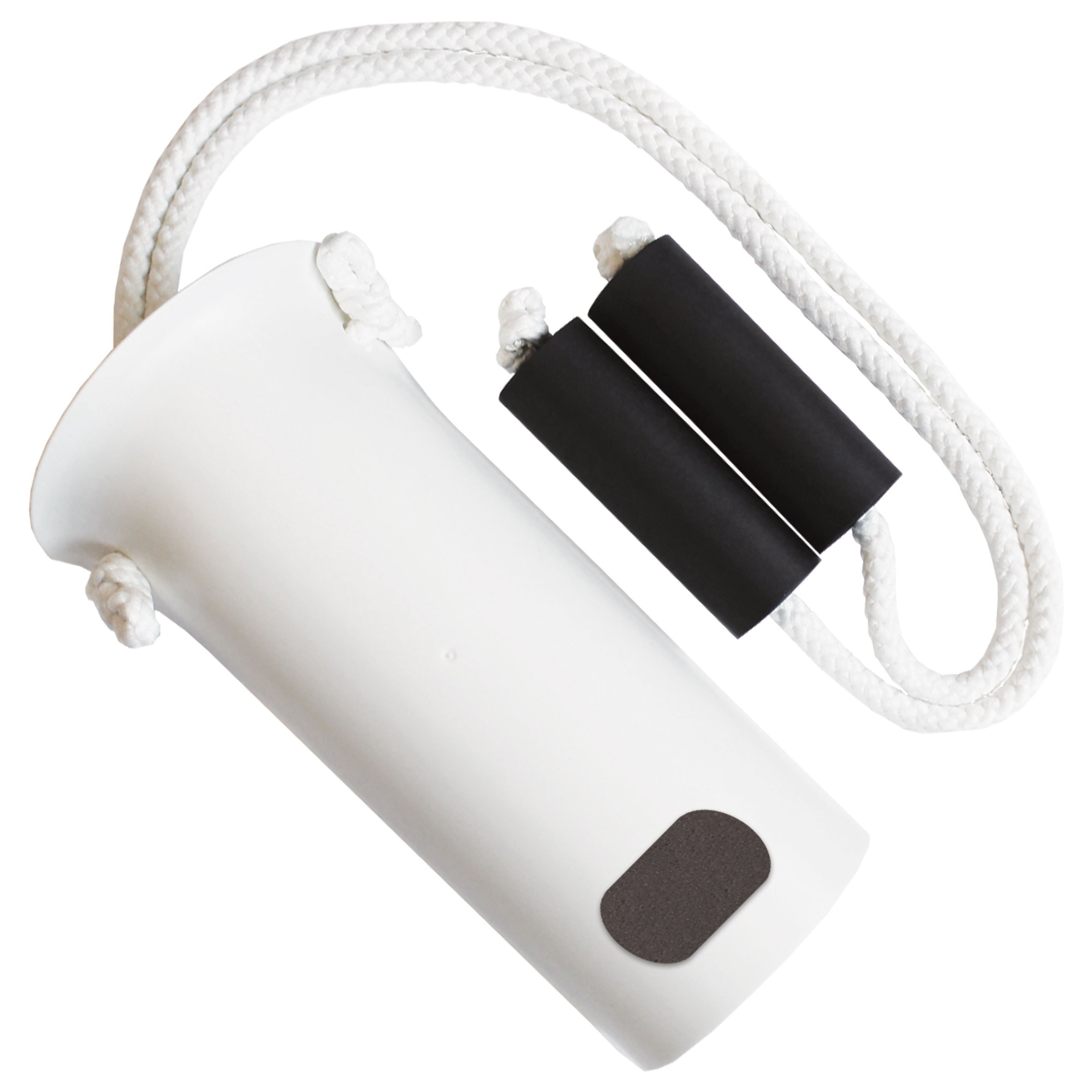

What is this item? What is it used for? Discuss who would likely benefit from the use of this item
sock aid: used for donning socks. Clients with precautions, like hip precautions that prevent bending past 90 degrees, would benefit from this item as the client can't bend down to pull a sock with their hands and this item would allow the client to stay within the precautions and still be independent.

What is this item? What is it used for? Discuss who would likely benefit from the use of this item.
long handled sponge: used for washing hard to reach areas like the the lower extremities. Clients with precautions that prevent them from bending past the 90 degrees, like hip precautions, could benefit from this item as it allows the client to still be able to reach areas that they cant reach with their hands with the help of this item and stay independent.
Describe two differences between Rehabilitative Technologies and Assistive Technologies?
Rehabilitative Technologies is restrorative and Assistive Technologies is compensatory
(this is only one)
An OTA is teaching an individual who has a traumatic brain injury to use an assistive technology device. The OTA should FIRST focus on the individual’s
ability to control the technology.
These technologies 'assist' a person with disabilities to perform a task
Assistive Technologies
These technologies help to restore an individual to a prior level of function.
Rehabilitative Technologies
Intended to meet the needs of people with a wide range of abilities
Universal Design
Category of devices that control electrical devices in the individual's immediate environment
Electronic Aids for Daily Living (EADLs)
Uses technology to allow communication without assistance
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AACs)
This form of assistive technology looks as various ways to adapt input and output as well as performance enhancements
Computer access
An OTA is working in an intensive care unit with an individual on a respirator. To assist the individual in communication, the OTA should:
Introduce a low-tech communication board.
Rehabilitative technology is meant to be used within the client’s home over a long period of time.
False
An OTA is providing training to an individual who is an office assistant on using an alternative keyboard layout. To help the individual achieve success, the OTA should INITIALLY suggest:
using e-mail
An OTA is teaching an individual to use an electronic aid to daily living (EADL). The OTA should INITIALLY assess the individual’s ability to:
Understand which control operates which device.
“Assistive Technology” includes only electronic devices, not items such as a pen and paper to write when you are unable to talk or the use of a picture communication board.
False
Identify two considerations an OTA would consider when teaching a client to use assistive technology?
if the client is able to use the AT to complete the activity and if the client will benefit from using AT.
Assistive Technologies are NOT expected to change the basic ability of the user.
True
Which of the following is NOT an accessibility requirement for ADA compliant ramp
Ramps for wheelchairs should have a ratio of 1:20 slope
An OTA is working with a patient who has difficulty using the stairs in their home but needs to access their bedroom which is on the second floor. What could the OTA recommend:
Lift
The OTA is working with a patient who requires the use of a wheelchair for functional mobility in the kitchen. The best environmental adaptation for this patient is:
all of the above
Use an angle mirror so they can see the stove top easily
Remove cabinets from under the sink for increased accessibility to the sink
Lower the counter top height for wheelchair access
Describe two adaptations for computer workstation ergonomics.
using an ergonomic chair when using a computer screen and also positioning the screen of the computer so that the head is able to look straight and don't have to bend their neck to see the screen.
Name two environmental modifications for a bathroom and state their purpose
covering for the pipes under a bathroom sink will prevent burns or scratches from occurring and having the bathroom mirror be no higher than 3" above a bathroom sink will allow clients who use a wheelchair to be able to see themselves without having to stretch to use the mirror.
Name two environmental modifications for a kitchen and state their purpose.
stove or faucet handles to more easily be able to turn the appliance on and off and lowered countertops that will allow a client that uses a wheelchair to better access items, like a pull out cutting board.
Describe one piece of equipment found in an ADA accessible playground.
ramps that will allow a child with a wheelchair to access a playground
According to ADA specifications, the minimum width for a ramp is:
36 inches
The OTA is conducting a home evaluation for an individual who has multiple sclerosis. The focus should include:
Fall prevention, adaptive devices, and simple modifications
An OTA is instructing an individual on a splint-wearing schedule. The OTA should recommend
building up tolerance by wearing the splint over a few days.
An OTA is instructing an individual on wearing a splint. The OTA should inform the individual to secure the strap
as tight as a watchband.
When fabricating a resting hand splint, the pattern should
resemble a mitten.
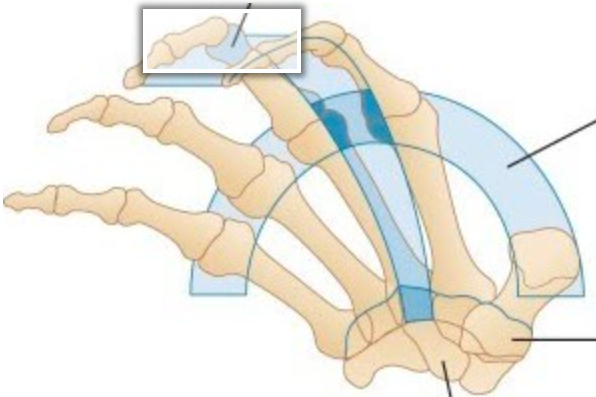
Label the arch identified in the image
Longitudinal Arch
Follows the lines of the Carpal and Metacarpal bones of the 3rd finger
Flexion and extension of the fingers occurs along this arch
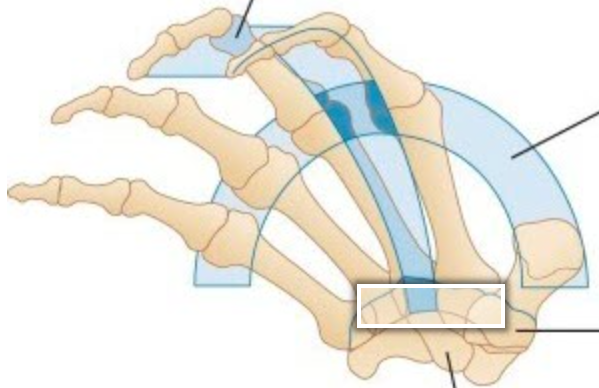
Label the arch identified in the image
Proximal Transverse Arch
Bony, fixed arch formed by the proximal row of the carpals and annular ligaments (carpal tunnel)
Within this arch- includes nerves, blood supply, and forms fulcrum for finger flexors
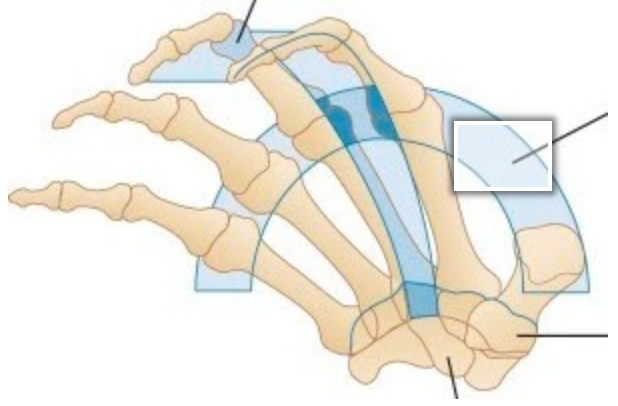
Label the arch identified in the image
Distal Transverse Arch (Metacarpal Arch)
Across metacarpal heads (knuckles)
Important for dexterity and functional hand use
Mobility of this arch is critical for hand functioning
A splint must be formed to preserve this arch to ensure maximal functional use of the hand while the splint is on or off.
Thumb Spica (Short Opponens)
De Quervain's Syndrome
Silver ring splint
Swan neck deformity
MCP dorsal blocking splint
Ulnar nerve injury
Resting hand splint
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Which type of prehension pattern would you use to pick up a nail?
3 jaw chuck when reaching to pick up the longer side of the nail.
Which type of prehension pattern would you use to pick up a Stanley tumbler?
cylindrical grasp when grasping the body of the tumbler.