Cell membrane and movement across it
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Describe the cell membrane and what it is made up off
describe of phospholipid
Has a hydrophilic phosphate head and has 2 a hydrophobic fatty acid tails. These form a bilayer when water is around so the hydrophilic phosphate heads are interacting with the water. This acts as a barrier. Different membranes contain different fatty acids. These alter the strength and flexibility of the membrane
what are the different types of protein found in the cell membrane
integral and peripheral
what is an integral protein
These go all the way through the cell membrane and contain a channel
define and explain the role of a peripheral protein on the inner membrane
These sits on the inner membrane and tend to been enzyme. These catalyse reactions and produce products
define and explain the role of a peripheral protein on the outer membrane
These sit on the outer membrane and tend to be receptors. They have a specific binding site which certain hormones or other chemicals bind to. This then triggers a specific biological event or process. This is often used in negative feedback.
what is an peripheral protein
sits on one side doesn’t go all the way through
Receptor proteins
They must be on the outside of the cell membrane and have a specific binding site where hormones and chemicals can bind to form hormone receptors complexes
enzyme proteins
catalyse reactions in the cytoplasm or outside the cell
Recognition Proteins
Proteins involved in recognition have carbohydrates attaches which form an antigen. These are glycoproteins.
Structural Protein
what is the role of structural proteins on the inside and out side
Found mainly on the inside surface membranes and are attaches to cytoskeleton. They help maintain structure and shape and motility. If on the outside then used for cell adhesion
define what simple diffusion (lipid diffusion) over a membrane is
Is the passive net movement of particles down a concentration gradients from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration resulting in equilibrium on either side of the membrane
what is equilibrium in diffusion
This is where there is the same conc of particles on either side of a membrane. particles are still moving randomly there jus isn’t a net or overall movement.
what molecules can use simple diffusion to get across this membrane
hydrophobic molecules and very small hydrophilic molecules eg CO2 O2 H2O
Facilitated Diffusion
This the passive net movement of particles down a concentration gradients from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration resulting in equilibrium on either side of the membrane using/ though a transport protein
name the 2 types of protein which are used in facilitated diffusion
channel and carrier proteins
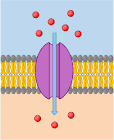
what is a channel protein and how can they control the entry of sunstances
These have a channel down the middle filled with water. This allows charged substances to diffuse across membranes. Most channels can be gated (opened or closed), allowing the cell to control the entry and exit of substances eg ions. In this way cells can change their permeability to certain ions. Ions like Na+, K+, Ca2+ and Cl- diffuse across membranes through specific ion channels
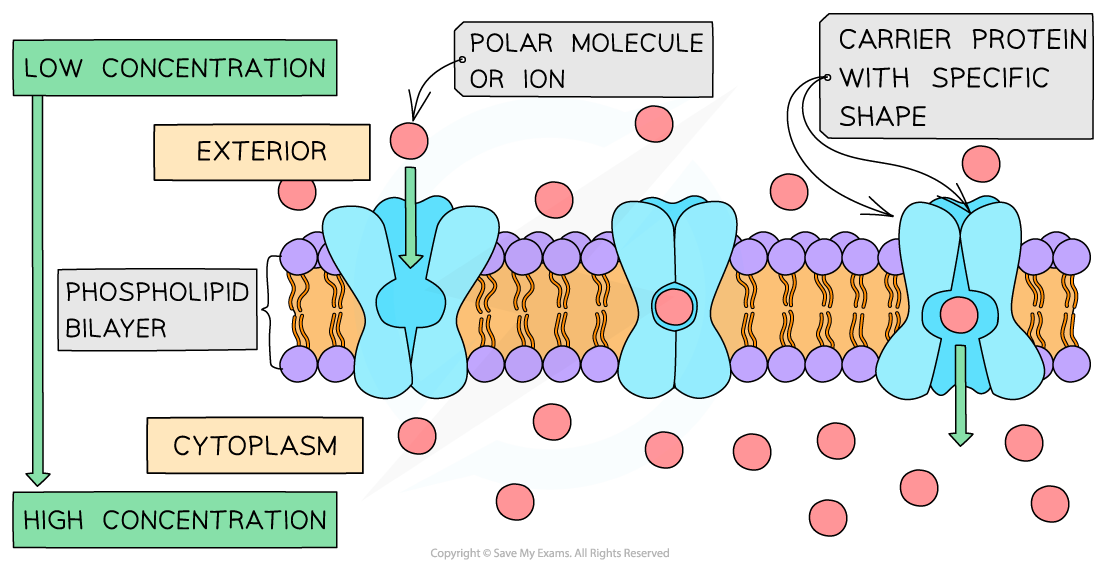
Carrier proteins
These have specific binding sites meaning that they only allow certain specific solute to bind . The substance will bind on the side where it at a high concentration and be released where it is at a low concentration.
what is a cotransport
Sometimes carrier proteins have two binding sites and so carry two molecules at once. For example is the sodium/glucose cotransporter
Osmosis
what is the concentration of water in cells
concentration of water is very high (about 55mol L-1) and it never changes.
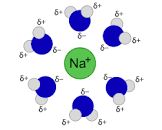
what is a hydration shell
A hydration shell is a layer of water molecules that surrounds a dissolved solute (like a salt or protein) in an aqueous solution. These water molecules interact with the solute, forming hydrogen bonds and creating a structured shell around it.
what is active transport
The active movement of substances from a low conc to a high conc up the concentration gradient using energy
how do carrier proteins use ATP
The protein binds a molecule of the substance to be transported on one side of the membrane, changes shape using energy from ATP splitting, and releases the molecule on the other side.
what is bulk transport and what does it move
This is how cells transport macromolecules such as proteins polysaccharides and even smaller cells. which are to big for other methods of transport.
Is it passive
no its a type of active transport so it requires ATP making it not passive.
what are the 2 types of bulk transport 1. out of a cell 2. into a cell
out = exocytosis
into = endocytosis
Explain the process of exocytosis
proteins in the Golgi undergo modification
The proteins bud off in a vesicle from the Golgi and move towards the cell membrane
The vesicle then fuse with the cell membrane and the protein is secreted
Explain the process of endocytosis
The particle causes the cell membrane folds inwards into a cavity.
This process is called invagination.
The membrane completely encircles the particles to form vesicles
The vesicle moves into the cell
If the material in the vesicle is a bacteria it will digested by lysosomes. However if its another material which is useful it can be delivered to different parts of the cell where there need.
what are the 2 different types of endocytosis
Phagocytosis = This is when solid material is taken into cells
Pinocytosis = when fluid eg liquid surrounding a cell is taken in
The effects of concentration difference on simple diffusion
increase in a linearly
The effects of concentration difference on facilitated diffusion
Has a curved relationship as the number of proteins available to facilitate becomes the limiting factor
The effects of concentration difference on active transport
As it doesn’t rely on the gradient there is no difference due to concentration gradient
protein lined poor
specific channel protein which transports polar solutes which through the gap
aquaporins
Can be added or removed to change how much water enter or leaves the cell. Its not a fix set number increases when there dehydrated and when your hydrated there less.
why does leakage from cell membrane increase
higher temp
higher EK
more movement of phospholipid
more gaps when they move
more diffusion
temp continues to increase proteins end up denatured
this means there are large gaps where things can rush and diffuse out
define what a hypotonic solution is
A hypotonic solution is a solution that has a lower concentration of solutes and a higher concentration of water compared to another solution or tissue
define what an isotonic solution is
An isotonic solution has the same solute concentration as the cell (no net movement of water).
define what a hypertonic solution is
A hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration (water leaves the cell).
what effects do these solutions have on cells with no cell wall eg animal cells
hypotonic= as there is more water in the solutions than the cell it moves into the cells by osmosis. This can cause the cell to burst by osmotic lysis.
isotonic= there is no movement conc of water is the same
hypertonic= there is higher conc of water inside the cell than outside in the solution . This causes the water to move out of the cell causing it to shrivel up and make the cytoplasm more concentrated.
what effects do these solutions have on cells with no cell wall eg animal cells
hypotonic= water enters the cell. The cell wall provides a compression force stopping the entry of water. This state is called turgor or turgid and is the most common in plants
isotonic = no movement no change this state is called flaccid
hypertonic= water leaves the cells. The cytoplasm shrinks making the contents more concentrated