Autonomic Motor System
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
ANS= Visceral Motor System
innervate smooth and cardiac muscle, and glands
make adjustments to ensure optimal support for body activites
subconcious
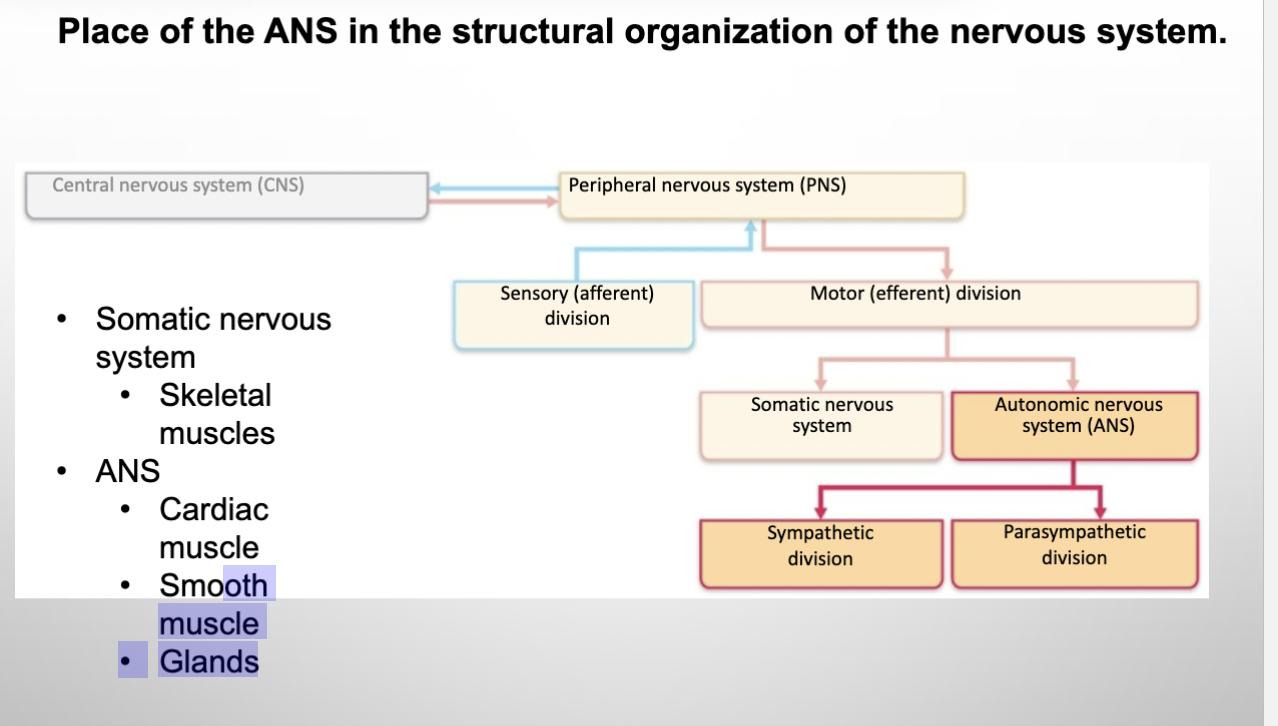
Part of the motor system of the Nervous System - Slide 3
Parasympathetic and Sympathetic divisions
Cardiac, smooth, glands
Differs from somatic nervous system (skeletal muscles)
Two-neuron Chain for ANS Pathway
Preganglionic neuron`
Postganglionic (ganglionic neuron)
Preganglionic neuron
Thin
Lightly-myelinated preganglionic axon
Short distances
Release Ach
Postganglionic (ganglionic) neuron
In autonomic ganglion outside of CNS
Nonmyelinated postganglionic axons
Extends to effector organ
Short distances
Release Norepinephrine (NE) or Ach
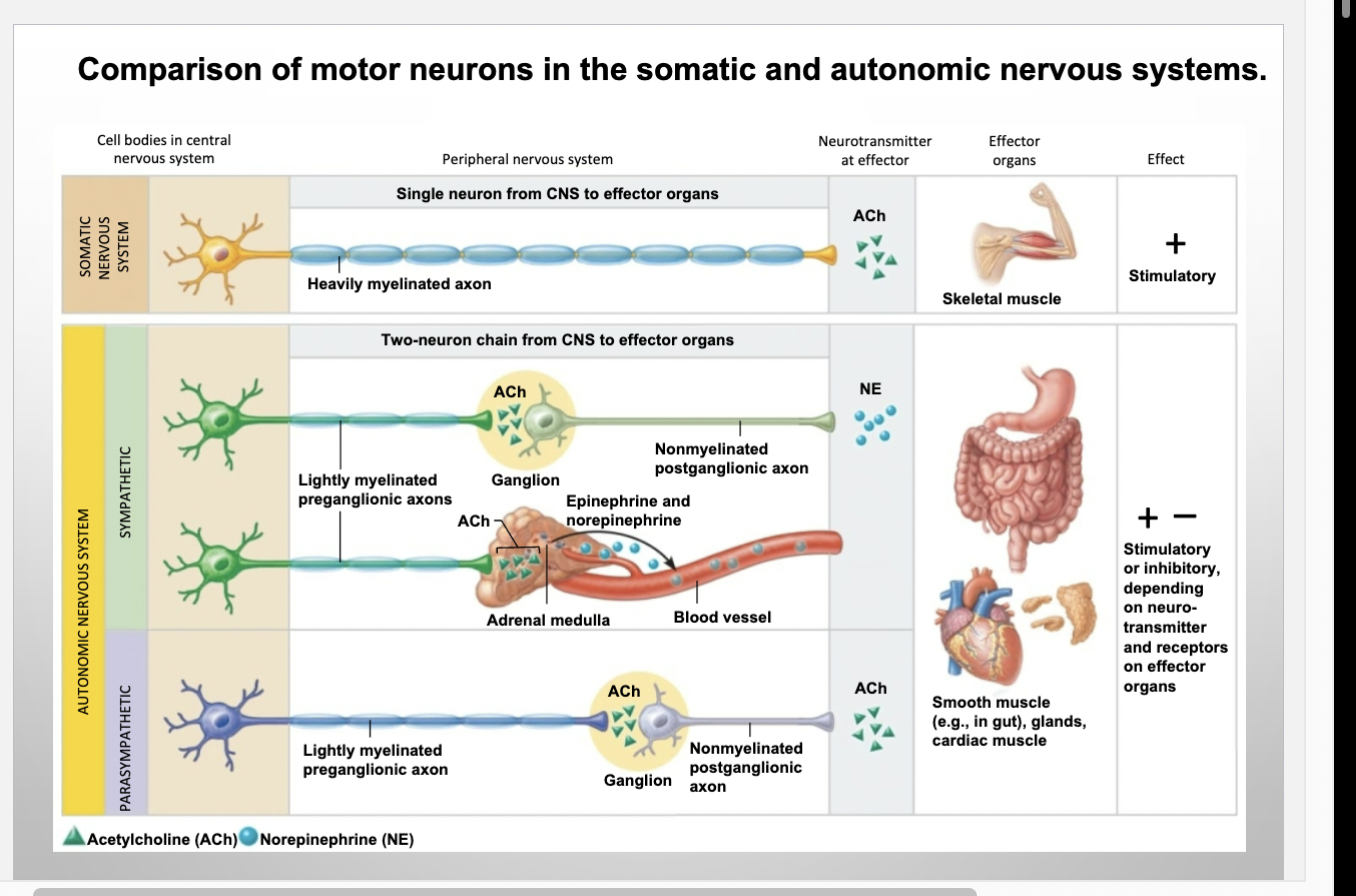
Somatic nervous system vs ANS
Somatic
all somatic motor neurons release acetylcholine (ach)
effects always stimulatory
ANS
Preganglionic- release ach
Postganglionic- release either norepi(NE) or ach
Simulatory or inhibitory depending on receptor type
2 divisions of ANS
Sympathetic
Parasymphathetic
All visceral organs served by both divisions but cause opposite effects (DUAL INNERVATION to maintain homeostasis)
Parasympathetic system
Promotes maintenance activities
Conserves Body energy (digest and rest, defecation)
Affect bp, heart rate, repiratory rates, gastrointestinal tract activity high, pupils constricted (close vision)
Sympathetic Division
Mobilize body during activity (fight or flight)
Exercise, excitement, embarrassment ( inc heat rate, bp, sweaty skin, dilated pupils)
During Vigorous physical activity (blood to skeletal muscles and heart, dialte bronchioles, liver releases glucose)
2 types of neurotransmitter fibers
Cholinergic Fibers
Adrenergic fibers
Colinergic fibers
release ach neurotransmitter
all ans preganglionic axons
all parasympathetic postganglionic axons at effector synapse
Adrenergic Fibers
release NE neurotransmitter
most sympathetic postganglionic axons
exception: sympathetic postganglionic fibers secrete ach at sweat glands
2 Types of Cholinergic receptors bind ACH
Nicotinic
Muscarinic
Nicotinic Cholinergic receptor
sarcolemma of skeletal muscle cells
• all postganglionic neurons (sympathetic and parasympathetic)
• hormone-producing cells of adrenal medulla
• effect of ach at nicotinic receptors is always stimulatory
• opens ion channels, depolarizing postsynaptic cell
Muscarinic Cholinergic receptor
all effector cells stimulated by postganglionic cholinergic fibers
• effect of ach at muscarinic receptors
• can be either inhibitory or excitatory
• depends on receptor type of target organ
2 classes of Adrenergic receptors
Alpha (subtypes a1, a1)
Beta (subtypes b1, b2)
effects of ne depend on which subclass of receptor predominates on target organ
5 drugs that affect receptors
Atropine
Neostigmine
Over the counter for colds, allergies, nasal congestion
Albuterol
Propanolol- beta block
Atropine
anticholinergic
blocks muscarinic ach receptors
used to prevent salivation during surgery, and to dilate pupils for examination
NEOSTIGMINE
• inhibits acetylcholinesterase that breaks down ach
• used to treat myasthenia gravis
OVER-THE-COUNTER DRUGS FOR COLDS, ALLERGIES, AND NASAL
CONGESTION
stimulate a-adrenergic receptors
leads to decreased mucus production
Albuterol
drugs that attach to b2 receptors to dilate lung bronchioles in
asthmatics
enhance sympathetic activity – stimulate receptors
PROPANOLOL – BETA BLOCKER
treat high blood pressure, severe chest pain and other cardiovascular abnormalities – slows down heart rate
decrease sympathetic activity
Control of ANS Function
hypothalamus—main integrative center of ans activity
subconscious cerebral input via limbic system structures on hypothalamic centers
other controls come from cerebral cortex, reticular formation, and spinal cord
HYPOTHALAMUS
main integrative center of ans activity
Hypothalamic Controls
control may be direct or indirect (through reticular system)
centers of hypothalamus control
heart activity and blood pressure
body temperature, water balance, and endocrine activity
emotional stages (rage, pleasure) and biological drives (hunger, thirst, sex)
reactions to fear and "fight-or-flight" system
Cortical Controls
connections of hypothalamus to limbic lobe allow cortical influence on ans
voluntary cortical control of visceral activities
is possible
biofeedback
awareness of physiological conditions with goal of
consciously influencing them
biofeedback training allows some to control
migraines and manage stress