Chemistry Final Exam <3
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/159
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
1
New cards
Organic compounds
Covalent bonds
2
New cards
Organic compounds
Poor conductors of electricity
3
New cards
Organic compounds
Non polar
4
New cards
Organic compounds
Low Boiling and Melting point
5
New cards
Organic compounds
High Flammability
6
New cards
Organic compounds
Non soluble in water
7
New cards
Organic compounds
C and H, sometimes O, S, N , O, Cl, F, Br, I
8
New cards
Inorganic compounds
Metals and nonmetals
9
New cards
Inorganic compounds
Ionic bonds
10
New cards
Inorganic compounds
High Boiling and Melting points
11
New cards
Inorganic compounds
Low Flammability
12
New cards
Inorganic compounds
Soluble in water
13
New cards
Bonds of Carbon
4
14
New cards
Catenation
Property of organic compounds that allows them to form an almost infinite number of C + H chains
15
New cards
Skeletal Formula
The lines represent bonds between carbon atoms
16
New cards
Molecular Formula
The total of atoms in the compound
17
New cards
Expanded Formula
All bonds and atoms are shown
18
New cards
Condensed Formula
Shows the atoms but leaves out the unpaired electrons
19
New cards
Boiling point
Physical property of petroleum components that allows its refining in the fractional distillation column.
20
New cards
Saturated carbons
All single bonds
21
New cards
Unsaturated carbons
double or triple bonds
22
New cards
Sigma bonds
Any bond between atoms (only one per bond)
23
New cards
Pi bond
Any additional bond to a single bond
24
New cards
Top of the distillation tower
Less Carbons
Less Melting/Boiling points
Less density
Gas State
Less Melting/Boiling points
Less density
Gas State
25
New cards
Bottom of the distillation tower
More Carbons
More Melting/Boiling points
More density
Almost Solid State
More Melting/Boiling points
More density
Almost Solid State
26
New cards
Hybridization of single bonds
sp3
27
New cards
Angle of single bonds
109\.5°
28
New cards
Geometry of single bonds
Tetrahedral
29
New cards
Hybridization of double bonds
sp2
30
New cards
Angle of double bonds
120°
31
New cards
Geometry of double bonds
Trigonal planar
32
New cards
Hybridization of triple bonds (or 2 double bonds)
sp
33
New cards
Angle of triple bonds (or 2 double bonds)
180°
34
New cards
Geometry of triple bonds (or 2 double bonds)
Linear
35
New cards
Primary carbons
carbon attached to another carbon
36
New cards
Secondary carbons
carbon attached to two other carbons
37
New cards
Tertiary carbons
carbon attached to three other carbons
38
New cards
Quaternary carbons
carbon attached to four other carbons
39
New cards
Smaller molecules
More Soluble / Lower Boiling Points
40
New cards
Larger molecules
Less Soluble / Higher Boiling Points
41
New cards
Alkanes
Only single bonds
42
New cards
Alkenes
at least one double bond
43
New cards
Alkynes
at least one triple bond
44
New cards
Polarity of Organic Compounds
**Least Polar** --- Alkane < Aromatic< Ether< Halocarbons< Ester< Aldehyde< Ketone
45
New cards
Use of Alkanes
Fuels
46
New cards
Use of Alkenes
Fruit Ripening
47
New cards
Use of Alcohol
Wine / Beer
48
New cards
Use of Ketones
Remove Paintings (Acetone)
49
New cards
Use of Carboxylic acids
Bee and Ant Stings / Vinegar
50
New cards
Use of Amines
Medicines
51
New cards
Use of Amides
Peptide bonds in proteins
52
New cards
Use of Esters
Perfumes in Fruits and Flowers
53
New cards
Use of Halocarbons
Propellant / Refrigeration (Chloro fluoro carbons)
54
New cards
Carbohydrates
Major source of energy from our diet
C, H, O
Produced by photosynthesis in plants
C, H, O
Produced by photosynthesis in plants
55
New cards
Monosaccharides
the simplest form of carbohydrates, also known as simple sugars. They are composed of a single sugar unit and cannot be broken down into smaller sugars.
56
New cards
Disaccharides
Contain 2 monosaccharide units
57
New cards
Polysaccharides
Contain many monosaccharide units
58
New cards
Monosaccharides classification by number of carbons
Triose / Tetrose / Pentose / Hexose
59
New cards
Monosaccharides classification by functional group
Aldose (aldehyde group and hydroxyl groups)
Ketose (ketone group and hydroxyl groups)
Ketose (ketone group and hydroxyl groups)
60
New cards
Important Disaccharides
Maltose, Lactose, Sucrose
61
New cards
Maltose
Glucose + Glucose
62
New cards
Lactose
Glucose + Galactose
63
New cards
Sucrose
Glucose + Fructose
64
New cards
Glucose
Structure
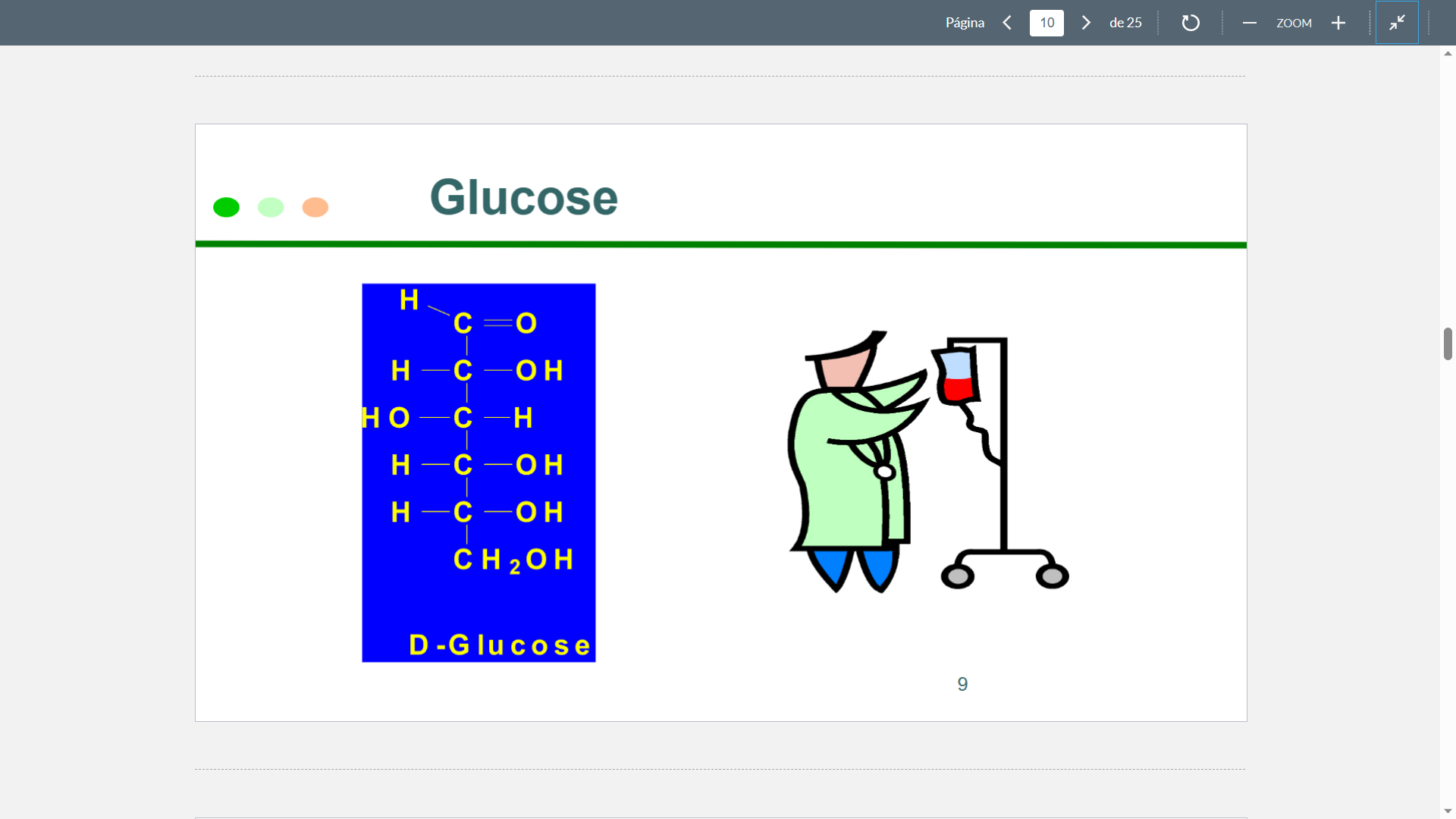
65
New cards
Fructose
Structure
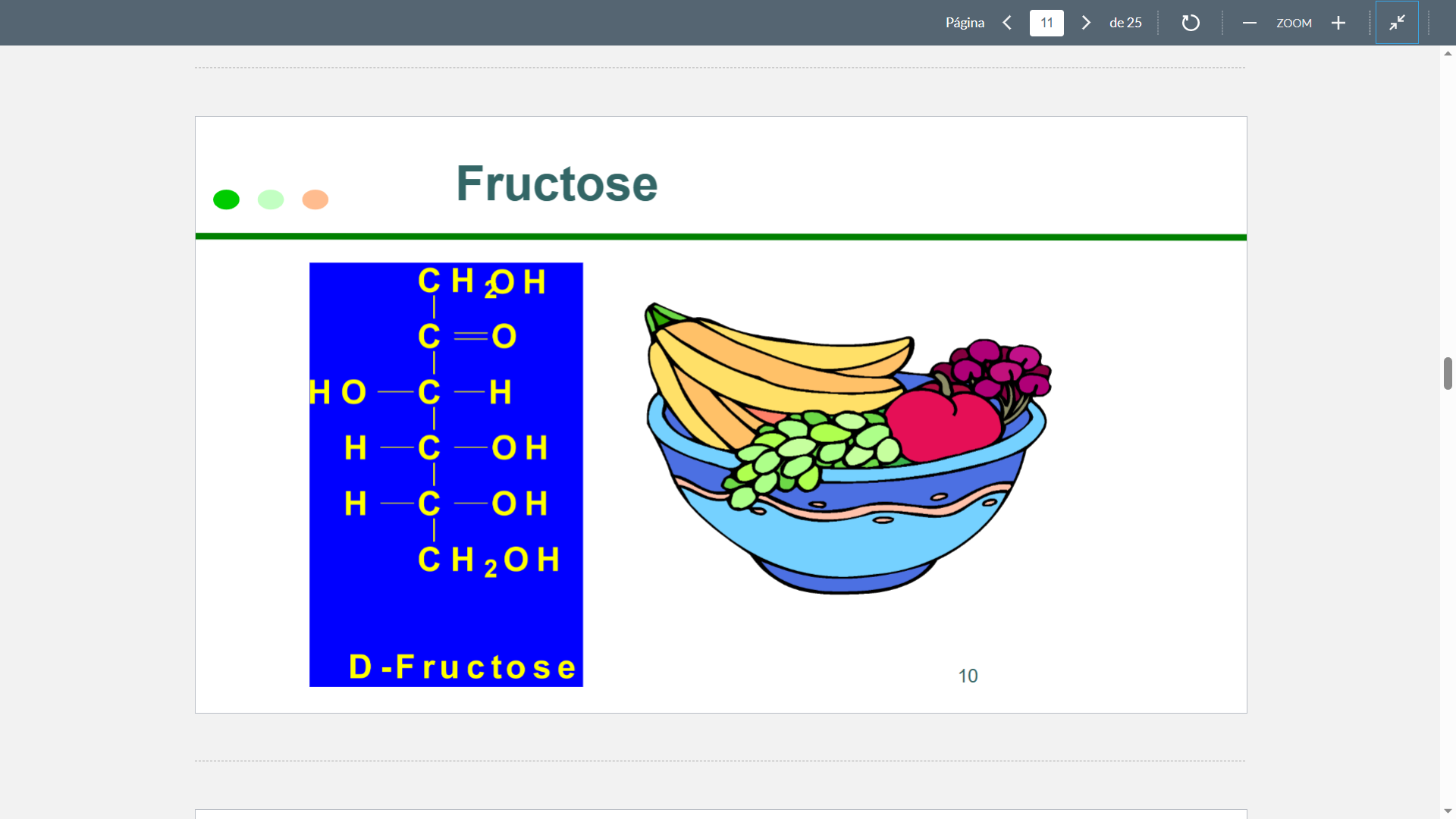
66
New cards
Galactose
Structure
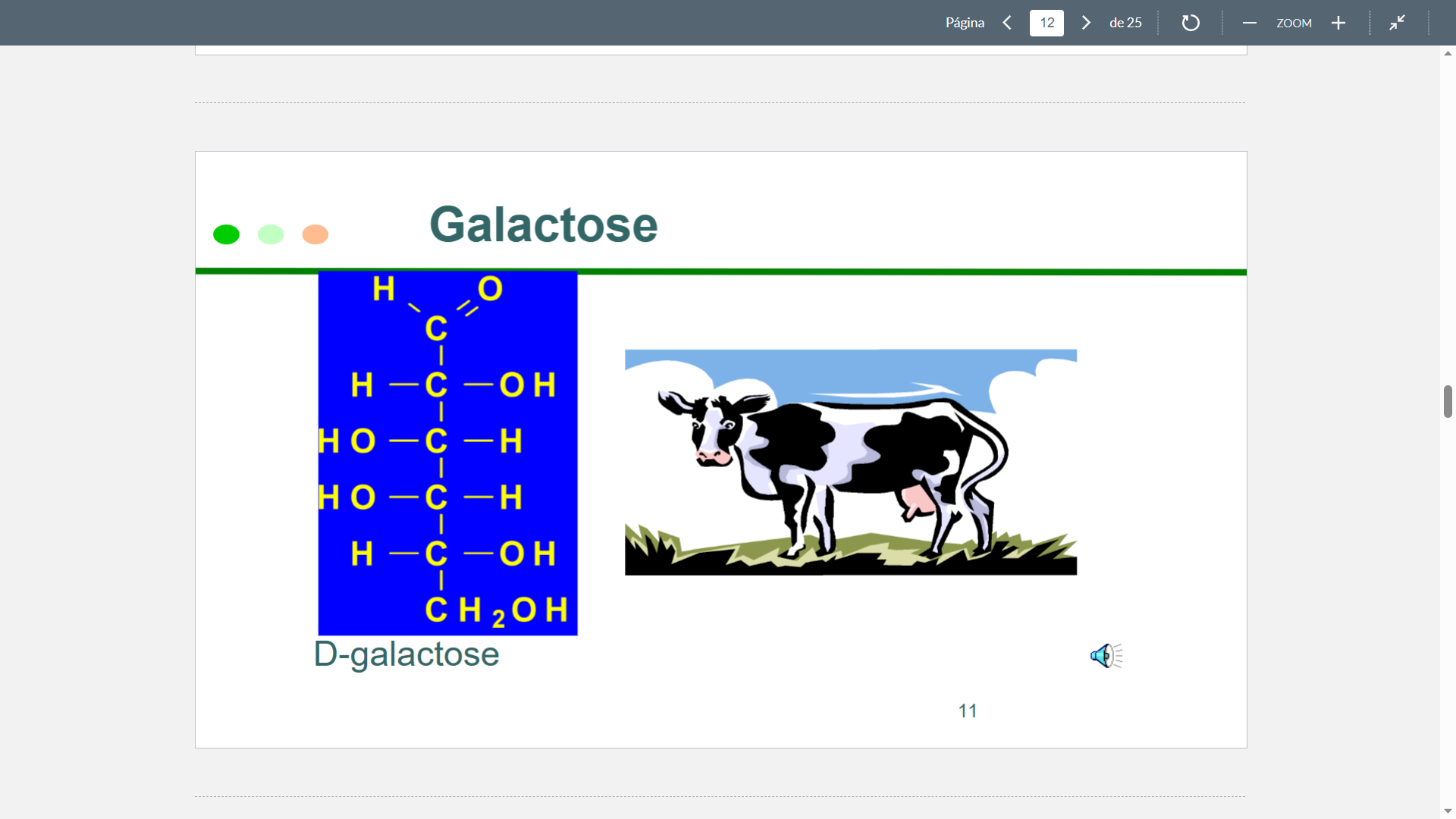
67
New cards
Glycosidic bond
A covalent bond that connects a carbohydrate molecule to another molecule, which can be another carbohydrate or a non-carbohydrate molecule.
68
New cards
Alpha glycosidic bonds
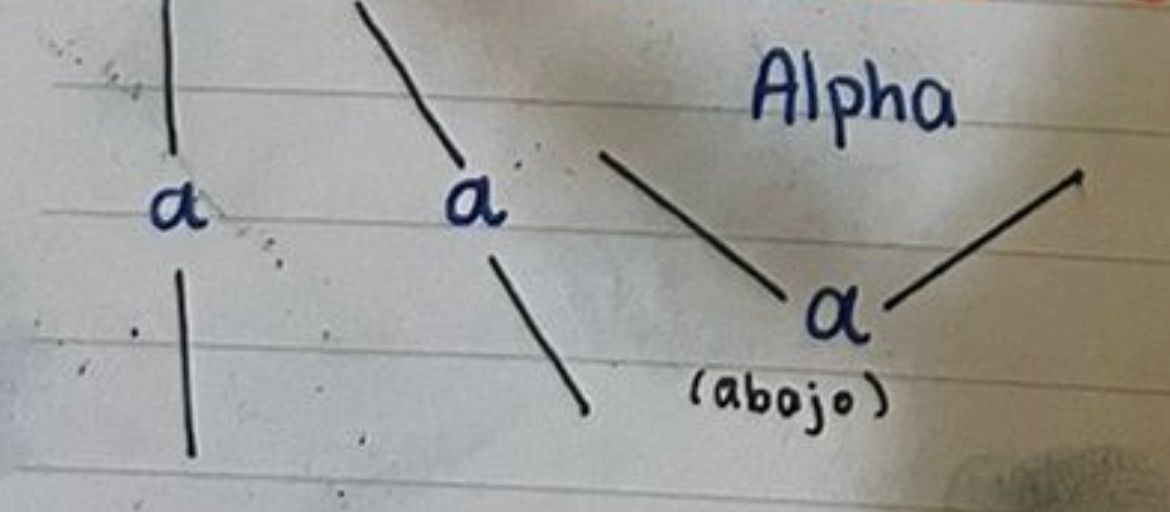
69
New cards
Beta glycosidic bonds
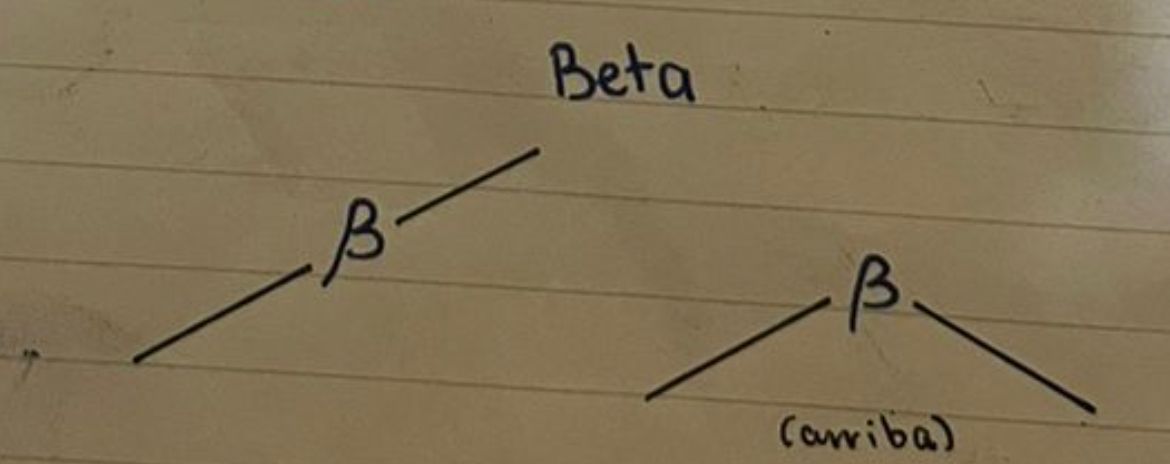
70
New cards
Important Polysaccharides
Starch / Glycogen / Cellulose
71
New cards
Starch
Amylose and Amylopectin
72
New cards
Glycogen
Energy storage in animals, fungi and bacteria
73
New cards
Cellulose
A complex carbohydrate that provides structural support to plant cell walls. Its main function is to maintain the shape and rigidity of plant cells, allowing them to maintain their structure and resist external pressures.
74
New cards
Amylose Structure
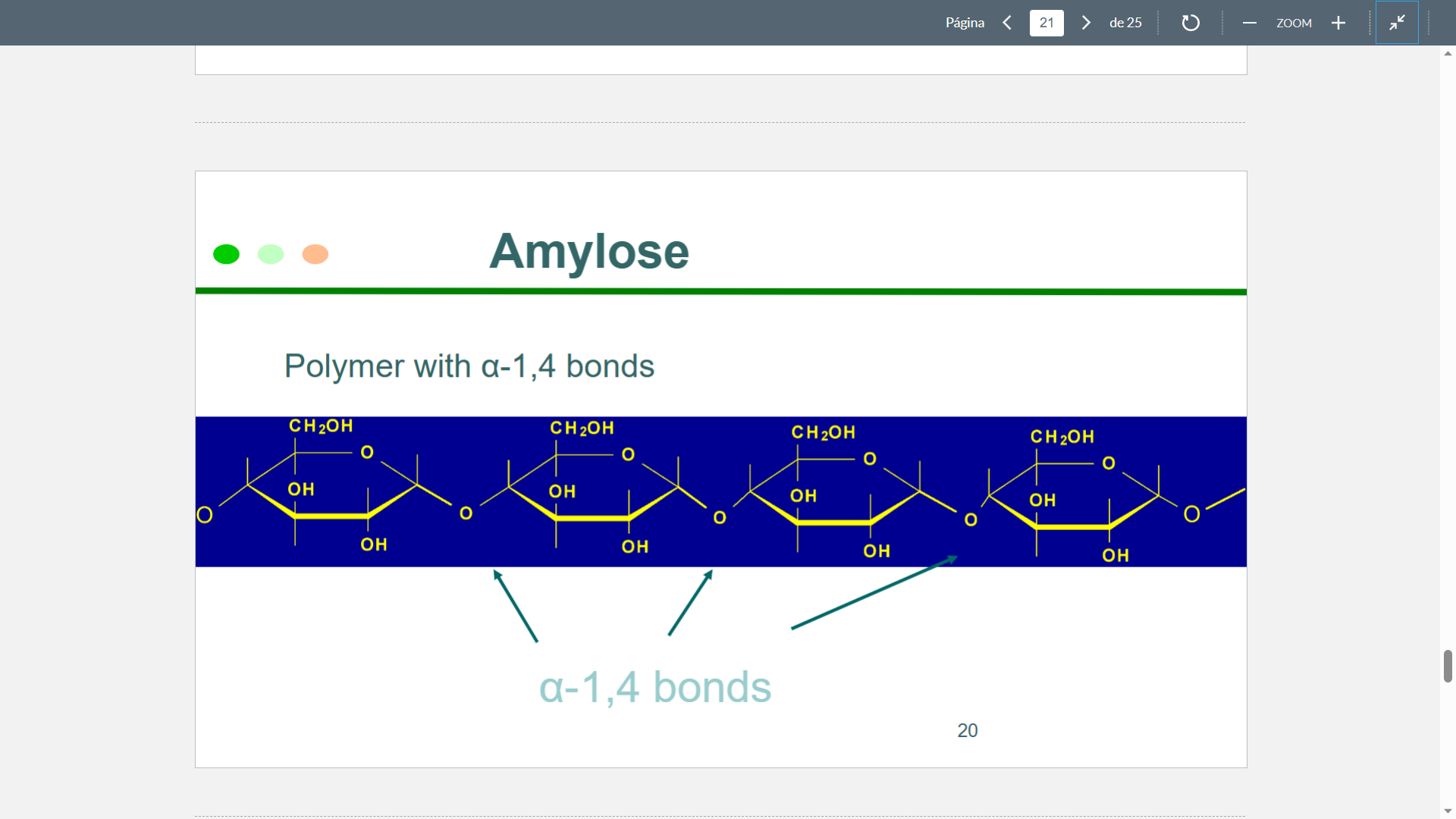
75
New cards
Amylopectin
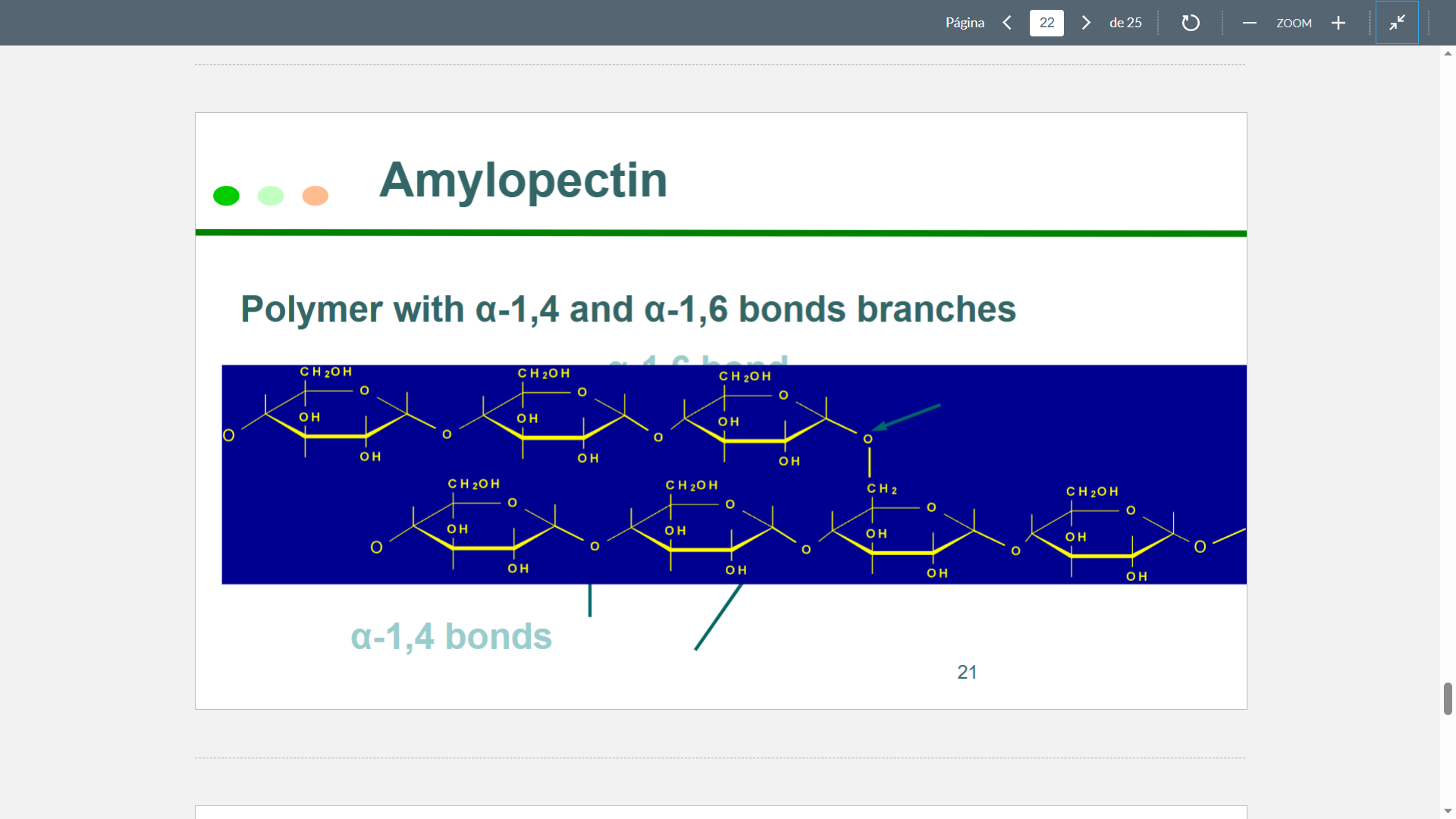
76
New cards
Lipids
Not very soluble in water (hydrophobic). \n Are soluble in organic solvents (alcohol, acetone)
77
New cards
Lipids classification
Oils / Fats / Waxes / Phospholipids / Steroids
78
New cards
Oils
Made mostly of unsaturated fatty acids
Liquid at room temperature
Come from plants
Liquid at room temperature
Come from plants
79
New cards
Fats
Made mostly of saturated fatty acids
Solids at room temperature
Come from animals
Solids at room temperature
Come from animals
80
New cards
Saturated Fatty Acids
Only single bonds
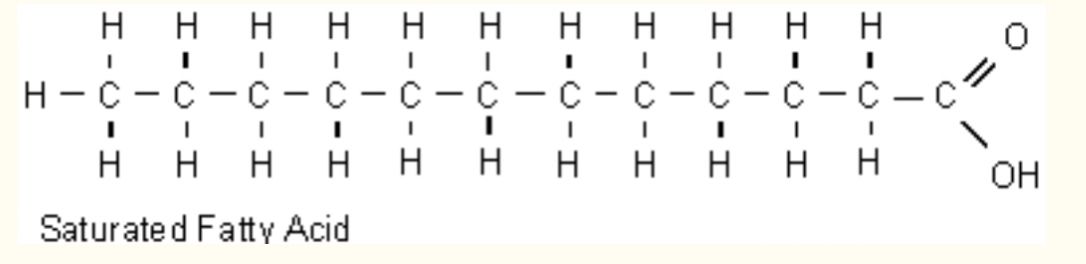
81
New cards
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Double bonds
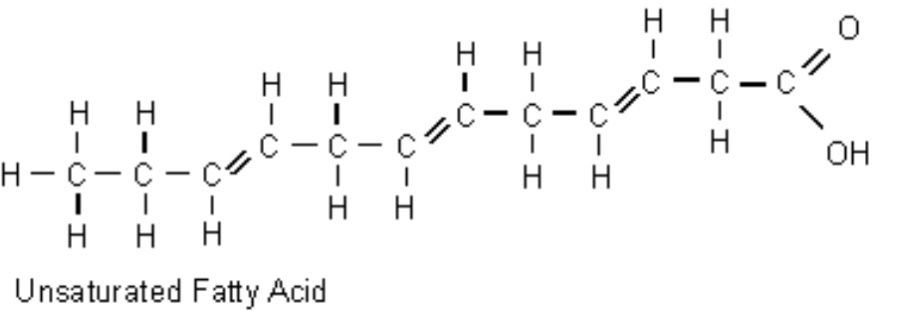
82
New cards
Triglycerides
Are composed of three fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule (ESTERIFICATION REACTION) and are used by the body as a source of energy.
83
New cards
Fatty Acids: Melting Points
Saturated: Higher Melting Point
Unsaturated: Lower Melting Point
Unsaturated: Lower Melting Point
84
New cards
Fatty Acids
Long chain carboxylic acids
12-18 carbon atoms
Insoluble in water
Classified as Saturated or Unsaturated
12-18 carbon atoms
Insoluble in water
Classified as Saturated or Unsaturated
85
New cards
Waxes
Esters made of one long alcohol and one long saturated fatty acid
86
New cards
Phospholipids
* Major components of \n all cell membranes as \n they can form lipid \n bilayers.
* Lipid bilayers are \n impermeable to most \n water-soluble \n molecules.
* They prevent the \n entrance of \n undesirable \n molecules into the \n cell.
* Lipid bilayers are \n impermeable to most \n water-soluble \n molecules.
* They prevent the \n entrance of \n undesirable \n molecules into the \n cell.
87
New cards
Phospholipids structure
A diglyceride, a phosphate group and a simple organic molecule

88
New cards
Diglyceride
Hydrophobic (not soluble in water) and apolar part of a phospholipid
89
New cards
Phosphate group
Hydrophilic (soluble in water) and polar part of a phospholipid
90
New cards
Steroids
Contain 3 cyclohexane rings and 1 cyclopentane ring
91
New cards
Steroid nucleus
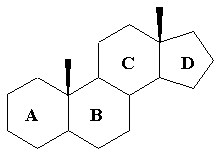
92
New cards
Cholesterol
The most abundant steroid in the body
Has methyl CH3- groups, alkyl chain, and -OH \n attached to the steroid nucleus.
Has methyl CH3- groups, alkyl chain, and -OH \n attached to the steroid nucleus.
93
New cards
Cholesterol in the body
* Obtained from meats, milk, and eggs
* synthesized in the liver
* Cell membranes, brain and nerve tissue, steroid hormones and Vitamin D
* Clogs arteries
* synthesized in the liver
* Cell membranes, brain and nerve tissue, steroid hormones and Vitamin D
* Clogs arteries
94
New cards
Steroid hormones
* Chemical messengers in cells
* Sex hormones:
Androgens in males (testosterone)
Estrogens in females (estradiol)
* Sex hormones:
Androgens in males (testosterone)
Estrogens in females (estradiol)
95
New cards
Proteins
Macromolecules, polymers, constructed from one or more unbranched chains of amino acids
96
New cards
Monomers
Proteins - Amino acids
Lipids - Fatty acids
Carbohydrates - (mono)saccharides
Lipids - Fatty acids
Carbohydrates - (mono)saccharides
97
New cards
Amino acids
Building blocks of proteins.
98
New cards
Amino acids structure
Carboxylic acid group
Amino group
R **(gives unique characteristics)**
Amino group
R **(gives unique characteristics)**
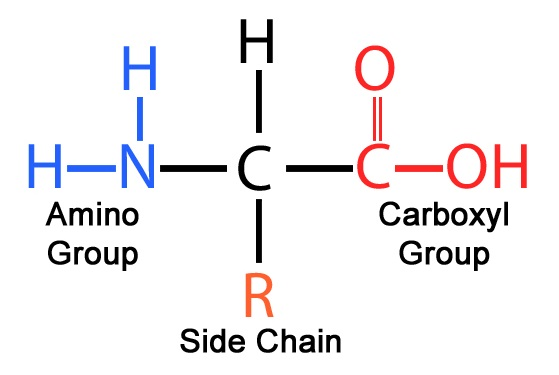
99
New cards
Amino acids in food
Food contain approximately 20 common amino acids
100
New cards
Foods of animal origin
meat, fish, eggs and dairy products (good sources of good-quality, complete protein)