Excretion as an example of homeostatic control
1/95
Earn XP
Description and Tags
5.1.2 in spec yellow mean check ppt
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
what is excretion
the removal of waste products of metabolism from the body
importance of removing metabolic wastes from the body
excess CO2 cause respiratory acidosis (lowers blood pH). amino acids are broken down into ammonia when in excess or due to transamination, ammonia is toxic ergo needs to be detoxified to prevent harm
what substances are excreted from the human body
carbon dioxide excreted from the lungs. bile pigments excreted in the bile. urea excreted by the kidneys in urine.
how do bile pigments form
the breakdown of haemoglobin from old red blood cells in the liver
Kupffer cell function
specialised macrophage breaks down old (senescent) erythrocytes, ingest foreign particles, protect liver from disease
sinusoids function
channel that blood flows through. close contact to hepatocytes. exchange materials bw blood and hepatocytes thru sinusoids
how are sinusoids different to capillaries
more porous walls, wider, close to hepatocytes
senescent meaning
cells or tissues that have permanently stopped dividing due to aging or damage, but do not die. remain metabolically active. accumulate in tissues, releasing molecules triggering inflammation
hepatic portal vein function
deoxygenated blood from digestive system containing glucose to liver
hepatic artery function
oxygenated blood to liver
bile duct function
liver bile > gall bladder
bile canaliculus function
collect bile secreted by hepatocytes and delivers to bile duct
bilirubin
waste product from breakdown of erythrocytes
hepatic vein function
blood leaves liver
what substances does bile duct contain
hydrogen carbonate ions, bile pigments, bile salts, cholesterol
order of bile entering digestive system from liver
bile canaliculus > bile duct > gall bladder > duodenum
role of the liver in the storage of glycogen
blood glucose rise, insulin rise, hepatocytes convert glucose > glycogen. blood glucose fall, glucagon rise, glycogen > glucose
glycogenolysis
glycogen > glucose (LYSIS = break down)
glycogenesis
glucose > glycogen (GENISIS = bible create)
the role of the liver in detoxification
liver detoxifies poisonous substances from metabolic reactions/alcohol/drugs.
hydrogen peroxide example of detoxification
toxic byproduct of metabolic reactions. hydrogen peroxide split by catalase in hepatocytes into oxygen and water
ethanol example of detoxification
active drug in alcohol. ethanol broken down by alcohol dehydrogenase in hepatocytes into ethanal. convert into ethanoate
what can ethanoate be used for
build fatty acids (phospholipids/triglycerides), respiration
the role of the liver in the formation of urea as part of the ornithine cycle
ammonia (NH3) + CO2 > H20 + citrulline. citrulline + NH3 > arginine + H20. arginine + H20 > urea.
roles of hepatocytes
metabolism, detoxification, storage of vitamins (A + D), minerals (iron), protein synthesis, cholesterol synthesis
features of hepatocytes
very metabolically active, large nuclei, prominent Golgi apparatus, many mitochondria
difference bw transamination and deamination
Transamination = transfer of an amino group from one molecule to another. deamination = removal of an amino group from a molecule, releasing it as ammonia
what happens during deamination
amine group is removed from a molecule, O2 + aa > keto acid + ammonia
liver role in protein metabolism
hepatocytes synthesise most plasma proteins ergo have lots ribosomes. hepatocytes do transamination helpful bc ensures aa not in diet are still available
liver role in deamination
main role of liver. removes amine group. 02 + aa > keto acid + ammonia. body cannot store excess protein or aa ergo hepatocytes prevent waste.
role of liver in deamination control
ammonia is highly toxic. ammonia > urea by ornithine cycle (enzyme controlled reactions). high concentrations of urea = toxic. blood concentration of urea is not high.
structure of liver
divided into lobes. divided into cylindrical lobules. branches of hepatic artery and portal vein enters lobules where blood mixes in sinusoids.
what is cirrhosis of the liver
normal liver tissue replaced by scar tissue. causes = genetic, hep C, alcoholic. hepatocytes cannot divide anymore. body more vulnerable to toxins.
explain how the structure of the liver is adapted for its functions in the body [6marks]
gross structure of kidney
cortex, medulla, pelvis, capsule, ureter, renal artery, renal vein
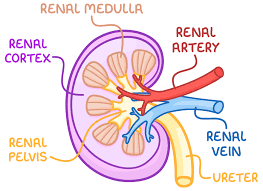
cortex
dark colour. outer layer. ultrafiltration occurs here. lots capillaries carrying blood from renal artery > nephrons.
medulla
lighter colour. tubules and collecting duct of nephron here.
renal pelvis
chamber where urine collects before passing to ureter.
nephron in kidney structure
afferent arteriole > glomerulus > bowman’s capsule > proximal convoluted tubule > descending limb > loop of Henle > ascending limb > distal convoluted tubule > collecting duct > ureter
what is the kidney responsible for
osmoregulation. excretion of nitrogenous waste. ammonia > urea > urine.
distal convoluted tubule structure
second tubule, after loop of Henle
glomerulus structure
tangle of capillaries. podocytes holding capillaries in place.
glomerulus function
knot of capillaries in Bowmans / renal capsule
bowman’s capsule structure
cup-shaped. contains glomerulus. layer 1 = capillary endothelial cells (has fenestrations = allow fluid out capillary). layer 2 = basement membrane (no holes). layer 3 = podocyte (hold capillary in place)(has holes)
bowman’s capsule function
ultrafiltration - more blood goes into glomerulus than leaves.
proximal convoluted tubule structure
first coiled tubule after bowman’s. cortex of kidney.
proximal convoluted tubule function
selective reabsorption - substances needed by the body are reabsorbed
loop of Henle structure
high solute concentration in tissue fluid in medulla = low water potential in medulla. region bw descending and ascending limb is interstitial region.
loop of Henle function
maintain negative water potential in medulla so is reabsorbed bc water moves high water potential > low water pot
descending limb
thin wall. water permeable. impermeable to Na+ Cl- ions. interstitial fluid is high concentrated so water moves out loop of Henle by osmosis. descending limb starts in cortex ends in medulla
ascending limb
thin area = NaCl diffuses to interstitial fluid. thick area = NaCl actively transported to interstitial fluid. impermeable to water. permeable to Na+ and Cl- ions bc has many ion channels/carriers. ascending limb starts in medulla ends in cortex. filtrate very dilute
distal convoluted tubule function
reabsorbs water and ions = balance water needs of body. permeability of walls varies by level of ADH (anti diuretic hormone). body lack salt = Na+ actively pumped out tubule > Cl- follows down electromagnetic gradient (Na+ makes it more positive then Cl- follows Na+ to balance the charge)
collecting duct structure
collecting duct function
where concentration and volume of urine is determined. water move out by osmosis (high concentration in medulla created by LoH). permeability of collecting duct controlled by ADH.
difference bw afferent and efferent arterioles
afferent has wider lumen. more blood can enter than exit. high pressure in bowman’s. fluid diffuse into bowman’s form ultrafiltrate.
what does ultrafiltrate contain
proteins with RMM less than 69,000. water, urea, salts, ions, amino acids, hormones, glucose, vitamins, drugs, ethanol
ADH
Anti Diuretic Hormone
process of ultrafiltration
small molecules filtered out under pressure to Bowman’s capsule forming ultrafiltrate
process of selective reabsorption
1) Na+ actively transported > blood. lowers Na+ concentration in cells. diffusion gradient bw nephron and cells. 2) Na+ and aa move in cell by facilitated diffusion with co-transporter. 3) water moves in cell by osmosis bc lower water potential in cell bc high solute concentration.
process of the production of urine
filtrate enters collecting duct. whether strong / dilute urine produced dependant on ADH
glomerulus endothelium of blood capillary structure and function
structure - very thin, fenestrations
function - barrier to cells, platelets, plasma proteins, allow small molecules in bowman’s via fenestrations under high pressure
basement membrane of glomerulus structure and function
structure - meshwork of collagen and glycoprotein fibres.
function - water & small molecules pass, prevent large proteins (RMM>6900) pass
epithelium of Bowman’s capsule
made up of cells modified for filtration = podocytes
podocytes structure
each cell has many foot like extensions = pedicels. pedicels wrap around capillaries in glomerulus linking with neighbouring extensions. fit together closely leaving 25nm wide filtration slits where filtered fluid passes through.
what needs to be reabsorbed from proximal convoluted tubule into the blood
most molecules aside from urea (although some does end up getting reabsorbed)
why do cells lining the proximal convulated tubule have microvilli
increase SA for better reabsorption
Why do cells lining the proximal convoluted tubule have many mitochondria
reabsorption requires active transport, which requires ATP, produced by mitochondria
what process is responsible for the reabsorption of ions / glucose and aa / water
ions = active transport. glucose and aa = co-transport. water = osmosis
basal vs apical surface
in proximal convoluted tubule: basal surface = PCT side closest to blood of vasa recta. apical surface = PCT side closest to nephron
role of the loop of Henle
maintain negative water potential (high solute conc) in medulla by building NaCl concentration in medulla. water removed from tubules by osmosis >interstitial medulla fluid > blood
how does the loop of Henle work
1) ascending limb cells actively pump Cl- first then Na+ out filtrate > medulla.
2) water remains bc ascending limb is impermeable to water.
3) interstitial fluid around loop of Henle become very saturated in medulla.
4) water moves out descending limb, LoH permeable to water but not solutes = filtrate becomes very concentrated
5) water removed > vasa recta due to osmotic gradient made by blood proteins
6) filtrate becomes more concentrated as move down descending limb
7) up ascending limb, NaCl pumped out = filtrate become less concentrated
the role of osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus
monitors water potential. affect ADH release by pituitary
how does osmoregulation occur
water potential monitored by osmoreceptor in hypothalamus. ADH released by pituitary makes collecting duct more permeable to water. water reabsorbed = blood water potential back to normal. volume and concentration of urine affected
define osmoreceptors
specialised receptor cells that shrink when water potential is low = stimulating neurosecretory cells
define neurosecretory cells
cells that release hormone(s) (like ADH) into the blood when an action potential passes
define hypothalamus
area of brain containing cells that monitor blood water potential, temperature, produce ADH
define posterior pituitary
back area of pituitary gland that secretes ADH into blood
negative feedback when water potential increases above the normal (body has too much water)
osmoreceptors swell > neurosecretory cells stop secreting > ADH decreases in the blood > collecting duct is less permeable to water > high volume of dilute urine
negative feedback when water potential decreases below the normal (body has too little water)
osmoreceptors shrink > neurosecretory cells secrete ADH > ADH increases in blood > collecting duct is more permeable to water > low volume of concentrated urine
how does ADH affect the nephron
ADH in blood detected by cell surface receptors in collecting duct wall > enzyme controlled reactions > vesicles containing aquaporins fuse to the membrane > more water can be reabsorbed via osmosis (medulla has higher salt concentration than filtrate > water moves into medulla then vasa recta)
aquaporin
water permeable channels allowing water to be reabsorbed from the filtrate into the blood
what happens to the urine when ADH is released
lots of ADH = lots of aquaporins present in the filtrate side of the collecting duct membrane = lots of water reabsorbed = smaller volume concentrated urine is produced. water not reabsorbed passes to bladder as urine to be expelled
what can be found from testing urine samples
diabetes = glucose present. nephritis = proteins and blood cells. bacterial infection = leukocytes. muscle damage = creatinine. pregnancy = hCG hormone. drug taking - steroids, cannabis, performance-enhancing ect
how are monoclonal antibodies produced
mouse is vaccinated with hCG vaccine > mouse spleen cells form antibodies, which are fused with myeloma cells (tumour cells) > forms hybridoma cells > grown in lab and those that produce anti-hCG antibodies are separated > Anti-hCG antibodies are collected
how do pregnancy tests work
1) monoclonal antibodies for hCG are tagged with a coloured bead. urine moves up strip carrying mobile monoclonal antibodies. hCG binds to monoclonal antibodies, if present, creating hCG antibody complex. 2) band of immobilised antibodies at first line specific to hCG. hCG antibody complexes held here = first blue line. 3) band of immobilised antibodies at second line bind to monoclonal antibodies released from start of strip released from start of strip regardless if hCG attached = second blue line
why does a pregnancy test taken before 6 days after fertilisation give inaccurate results
concentration of hCG is too low to measure so test result is negative
why are urine tests often done instead of blood test
less invasive, cheaper, faster
how is urine moved along test strip
capillary action
causes of kidney failure
kidney infections = damage of podocytes/tubules. raised blood pressure = damage structure of epithelial cells/basement membrane in Bowmans. genetic conditions = polycystic kidney disease causes healthy tissue to be replaced by cysts.
symptoms of kidney damage
protein / blood in urine, loss of electrolyte balance (excess ions), urea build up in blood (toxic = damage cells), high blood pressure (high salt = low water potential = water enter blood by osmosis = high press), weakened bones (calcium lost), pain in joints, anaemia (kidneys cannot produce erythropoietin = RBC production reduced)
Erythropoietin
Erythropoietin is a hormone, primarily produced by the kidneys, that stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells.
treatments for kidney failure
renal dialysis (haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis) or kidney transplant
effect of kidney failure on glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
kidney failure = significant decrease in GFR bc the kidneys' filters are damaged, = reduced ability to filter waste from the blood. More creatinine means kidneys not working properly bc its has not been excreted.
define glomerular filtration rate
GFR = measure of how much blood passes through the glomeruli each minute = tests how well the kidneys are functioning = blood test measures the levels of creatinine in blood
kidney failure effect on electrolyte balance
Kidney failure causes electrolyte imbalances by disrupting the kidneys’ ability to filter and regulate minerals. This can lead to dangerously high potassium levels (hyperkalemia), high phosphate levels, low calcium levels (hypocalcemia), and low sodium levels (hyponatremia). imbalances can result in confusion, irregular heartbeat, muscle cramps, and fatigue.
3 layers forming barrier between capillary blood and bowman’s capsule
capillary endothelial cells, basement membrane, podocyte