Skeletal System Physiology
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/155
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
156 Terms
1
New cards
what is a joint/articulation?
a place where adjacent bones or bone & cartilage comes together to form a connection
2
New cards
what joint has adjacent bones united by fibrous connective tissue?
fibrous
3
New cards
what joint has bones joined by hyaline cartilage/fibrocartiage?
cartilaginous
4
New cards
what joint has bones make contact w/in a joint cavity filled w/ lubricating fluid?
synovial joints
5
New cards
what are the functional movements of joints?
synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis, diarthrosis
6
New cards
what is the role of blood vessels in the cavities?
provides nutrients & circulates blood
7
New cards
what is the role of nerves in the bones?
sense pain, regulate blood supplies, bone growth
8
New cards
what are the 2 types of ossification?
intramembranous & endochondral
9
New cards
what is intramembranous ossification?
compact & spongy bone develops from sheets of mesenchymal connective tissue to form flat, cranial, & clavicle bones
10
New cards
what is endochondral ossification?
replacing hyaline cartilage at the base of the skull & long ones
11
New cards
what is appositional growth?
bone growth in diameter by osteoclasts reabsorbing old bone that lines the medullary cavity while osteoblasts produce new tissue beneath the periosteum
12
New cards
what is a transverse fracture?
occurs straight across the long axis of the bone
13
New cards
what is an oblique fracture?
occurs at an angle that isn’t 90 degrees
14
New cards
what is a spiral fracture?
bone segments are pulled apart as a result of a twisting motion
15
New cards
what is a comminuted fracture?
several breaks result in many small pieces between 2 large segments
16
New cards
what is a impacted fracture?
one fragment is driven into the other, usually from compression
17
New cards
what is a greenstick fracture?
a partial fracture in which only 1 side of the bone is broken
18
New cards
what is a open compound fracture?
at least 1 end of the broken bone tears though the skin & carries a high risk of infection
19
New cards
what is a closed fracture?
the skin remains intact despite break
20
New cards
what happens if there is no mechanical stress on the bones?
no stimulation of mineral salt & collagen fiber deposits to increase bone size & weight
21
New cards
what are some of the nutrients that affect bone health?
calcium, vitamin D, vitamin K, magnesium, fluoride, & fatty acids
22
New cards
what hormones influence osteoblasts & maintain the matrix?
growth hormone, thyroxine, calcitriol, estrogen & testosterone
23
New cards
what does the growth hormone do?
maintaining osseous tissue, calcium retention, chondrocyte proliferation to stimulate bone growth
24
New cards
what is osseous tissue?
hard, dense connective tissue that form most of the skeleton & support structure
25
New cards
what are sesamoid bones?
small, round bones that form in tendons & protects it by helping them overcome compressive forces
26
New cards
what is the only sesamoid bone?
patellae
27
New cards
what is the medullary cavity?
a hollow region in the diaphysis filled w/ yellow marrow
28
New cards
where do tendons & ligaments attach to the bone?
periosteum
29
New cards
what is articular cartilage?
a thin layer of cartilage that reduces friction & absorbs shock
30
New cards
what are the 3 classes of bone markings?
articulations, projections, & holes
31
New cards
what is an articulation?
where 2 bone surfaces come together w/ one surface rounded & the other cupped to conform to one another
32
New cards
what is a projection?
area of a bone that projects above the surface of the bone which serves as attachment points for tendons & ligaments
33
New cards
what does the size & shape of a bone do?
indicates the forces exerted though the attachment to the bone
34
New cards
what is a hole?
opening/groove that allows blood vessels & nerves to enter the bone
35
New cards
what is the head of a bone?
prominent rounded surface
36
New cards
what is the facet of a bone?
flat surface
37
New cards
what is the condyle of a bone?
rounded surface
38
New cards
what is the protuberance of a bone?
protruding
39
New cards
what is the process of a bone?
prominence feature
40
New cards
what is the spine of a bone?
sharp process
41
New cards
what is the tubercle of a bone?
small, rounded process
42
New cards
what is the tuberosity of a bone?
rough surface
43
New cards
what is the line of a bone?
slight, enlongated ridge
44
New cards
what is the crest of a bone?
ridge
45
New cards
what is the fossa of a bone?
elongated basin
46
New cards
what is the fovea of a bone?
small pit
47
New cards
what is the sulcus of a bone?
groove
48
New cards
what is the canal of a bone?
passage in bone
49
New cards
what is the fissure of a bone?
slit though bone
50
New cards
what is the foramen of a bone?
hole though bone
51
New cards
what is the meatus of a bone?
opening into canal
52
New cards
what is the sinus of a bone?
air-filled space in bone
53
New cards
How many bones are in adults?
206 bones
54
New cards
How many bones are there in babies?
300 bones
55
New cards
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
support, protection, movements, calcium & phosphorus storage, hemopoiesis, detoxification, provision of muscle attachment
56
New cards
What are the 5 types of bones?
long, flat, short, irregular, sesamoid
57
New cards
What are examples of long bones?
femur, humerus
58
New cards
What are examples of flat bones?
skull, rib, sternum
59
New cards
What are examples of short bones?
carpals, tarsals
60
New cards
What are examples of irregular bones?
vertebrae, hip bones
61
New cards

What class of bones is this?
long bones
62
New cards
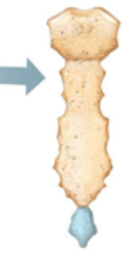
What class of bones is this?
flat bones
63
New cards
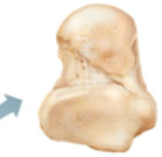
What class of bones is this?
short bones
64
New cards
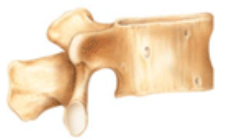
What class of bones is this?
irregular bones
65
New cards
What is the term for blood cell production?
hematopoiesis
66
New cards
Where does hematopoiesis occur as a child?
red marrow in long bones
67
New cards
Where does hematopoiesis occur in an adult?
red marrow in flat bones
68
New cards
Where do blood cells exit from the bone?
blood vessels
69
New cards
What are bones made of?
calcium phosphate/carbonate \[hydroxyapatite\], collagen, bone tissue marrow
70
New cards
What are the 3 regions of the bone?
proximal & distal epiphysis, diaphysis, epiphyseal line/plate
71
New cards
What are the epiphysis?
top & bottom part of the bone
72
New cards
What is the diaphysis?
shaft/body of a bone
73
New cards
How does the epiphyseal plate become a line?
the plate is the area where the bone grows from & the line is the scar that stops the growth
74
New cards
Is the inner & outer part of the bone spongy or compact?
spongy inner & compact outer
75
New cards
What is a spongy bone also called?
cancellous, trabecular
76
New cards
what does the trabeculae part of the bone do?
provides balanse to the dense/heavy compact bone to make it lighter & easily movable
77
New cards
what does the cancellous part of the bone do?
contains the nutrients that get transported to the osteocytes & wastes removed from them
78
New cards
What does the cancellous part of the bone contain?
volkmann’s canal, endosteum, osteocyte, central haversion canal, rings of osteocytes
79
New cards
What is the role of volkman’s canal?
a channel that transmits blood vessels & connects osteons together
80
New cards
What is the endosteum?
a layer of connective tissue in bone on the inner surface of the bone
81
New cards
What are the parts of the osteon?
growth hole, ring of osteocytes, central canal, lacuna, & canaliculus
82
New cards
What is the lacuna?
tiny cracks & hole locations where osteocytes are created & live
83
New cards
What is the canaliculus?
communication & channels among lacunas for osteocites to move within
84
New cards
What is the central haversian canal?
tubes in cortical holding the blood vessels, nerve fibers, & capillaries
85
New cards
What are the rings of osteocytes called?
lamellae
86
New cards
What is the periosteum?
layer of connective tissue surrounding the bone that supplies the bone with blood to helps repair damage
87
New cards
What are the 2 types of marrow?
yellow & red
88
New cards
Which bone marrow is of adipose & fat as adults?
yellow bone marrow
89
New cards
Which bone marrow forms blood cells as children?
red bone marrow
90
New cards
What is the 1st stage of ossification?
formation of bone collar around hyaline cartilage model
91
New cards
What is the 2nd stage of ossification?
cavitation of the hyaline cartilage within the cartilage model
92
New cards
What is the 3rd stage of ossification?
invasion of internal cavities by the periosteal bud & spongy bone formation
93
New cards
What is the 4th stage of ossification?
formation of medullary cavity as ossification continues with appearance of secondary ossificaiton in epiphyses
94
New cards
What is the 5th stage of ossification?
full ossification where hyaline cartilage remains only in the epiphyseal plates & articular cartilages
95
New cards
What is the formation of long bones called?
endochondral
96
New cards
What is the formation of flat bones called?
intramembranoys
97
New cards
What is calcification?
the deposit of calcium, collagen, protein, & ground substances to grow bone
98
New cards
From which direction does the bone grow?
middle outwards to accomodate more bone marrow
99
New cards
What helps break & make the bone while it grows?
osteoblasts & osteoclasts
100
New cards
What is the role of osteoblasts?
forms bone tissue in the outer rings & later becomes osteocytes