NRES 251 Exam 2
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Plant Available Water
Difference between field capacity and permanent wilting point
Field Capacity
Maximum amount of water the soil can hold
Permanent Wilting Point
Point where plant can no longer extract water from soil
Active Acidity
the quantity of hydrogen ions that are present in the soil water solution
Exchangeable Acidity
the amount of acid cations, aluminum and hydrogen, occupied on the CEC
Soil Structure
the way individual particles of sand, silt, and clay are assembled
Reserve/Residual Acidity
the combined acid potential of H+, Al+3, AI (OH)+2, and AI (OH)2+1 ions adsorbed on clay colloids,
pH
the log10 hydrogen ions (H+) in the soil solution
Water Potential
the tendency of water to move from one area to another
Infiltration
process by which water on the ground surface enters the soil
Surface Seals (Crusts)
the orientation and packing of dispersed soil particles that result from the physical breakup of soil aggregates due to raindrop impact
Compaction
when soil particles are pressed together, reducing pore space between them
Plastic Limit
the moisture content at which a fine-grained soil can no longer be remolded without cracking
Liquid Limit
the water content where the soil starts to behave as a liquid
COLE
Quantifies the expansiveness of a soil
To measure: Moisten soil to plastic limit and measure LM. Dry and measure LD. COLE is the % reduction in length of soil bar.
Soil Color
Hue/Value/Chroma
What soil color tells you: Comp of parent material, fertility, temp, drainage, soil classification
Hue: Dominant wavelength
Value: Brilliance of color/ light
Chroma: Relative purity of dominant wavelength
Thermal Conductivity
a measure of the soil's ability to conduct heat
Heat Capacity
characterizing the amount of heat that can be stored in soil
Isomorphic substitution
replacement of one atom by another of similar size in a crystal structure without disrupting or changing the crystal structure of the mineral
pH dependent charge
At low pH, soil charge becomes more positive. At high pH, negative charge increases. Overall charge is usually negative.
CEC
the total capacity of a soil to hold exchangeable cations
Capillary Rise –
Pore size, Wetting angle
etting angle
the ability to draw water upward, against the force of gravity through tiny channels or capillaries within the soil
Infiltration –
Particle size, Structure, Crusting, Runoff and Flooding
humus, clay, silt, sand, gravel
Structure-the grouping of soil particles (sand, silt, clay, organic matter, and fertilizers) into porous compounds.
Crusting- when rain separates the soil into very small aggregates and individual particles that cement into hard layers at the soil surface when drying occurs rapidly
Runoff- the likelihood for surface runoff to occur during rainfall or snowmelt
Flooding- those in which water covers the soil,
Plant Available Water –
Capillarity and matric potential
Soil texture, Pore size, Evaporation/Transpiration
Wetting angle and water retention
Water repellency and fire
Capillarity- the ability to draw water upward, against the force of gravity through tiny channels or capillaries within the soil
Matric potential-the pressure potential that arises from the interaction between water and the matrix of solid particles in which the water is embedded
Soil Texture-the proportion of sand, silt and clay sized particles that make up the mineral fraction of the soil
Transpiration-Plants put down roots into the soil to draw water and nutrients up into the stems and leaves
Wetting angle-angle between a water droplet and a solid surface
Water retention-strongly related to particle size
Water repellency- reduces the affinity of soils to water such that they resist wetting for periods ranging from a few seconds to hours, days or weeks
Fire- can make soil water repellent
Soil Acidity and pH
Components
Connection to CEC
Acidity- caused by organism metabolic processes, leaching of bases, redox rxns, weathering of minerals, rain
pH- Effective CEC changes with pH
○ Higher pH higher effective CEC (selectivity) ○ Higher pH leads to more negative charge associated with base cations
○ It is the percent saturation of acids or bases not the total number present that relates to pH ○ Fertility
Buffering Capacity
Resistance to a change in pH
pH 5-7 buffering from equilibrium of active, salt- replaceable and residual acidity
Addition of H - movement closer to surfaces
Removal of H - movement from surface to solution
Permanent charge
Variable charge
The negative charges associated with isomorphous substitution
pH-dependent charge
Soil Acidification
Carbonic acid
Acids from biological metabolism
Accumulation of OM
pH and nutrient availablility
pH determines nutrient availability
Building/Losing Soil Organic Matter
Adding OM decreases pH
Binds tightly to Al
Soil Consistence (strength)
The behavior of soil particles to applied pressure
Forces that resist applies pressure include:
Cohesion (Like substances)
Adhesion (Unlike substances)
Interlocking forces
Related to:
Particle size, clay content, type of clay content, water content
Classified based on moisture content
Atterberg limits: Water contents of fine-grained soils at different states of consistency (plastic and liquid limit)
Plasticity Index: PI = LL-PL
PI > 25 Is poor for construction
Hydrology and Water (Chapter 5)
a. Hydrologic cycle basics
b. Physical properties of water i. Why does it behave that way?
c. Adhesion, cohesion, and capillarity
d. Pore size and water potential
e. Components of total water potential
f. Plant available water i. Texture and organic matter effects
a.
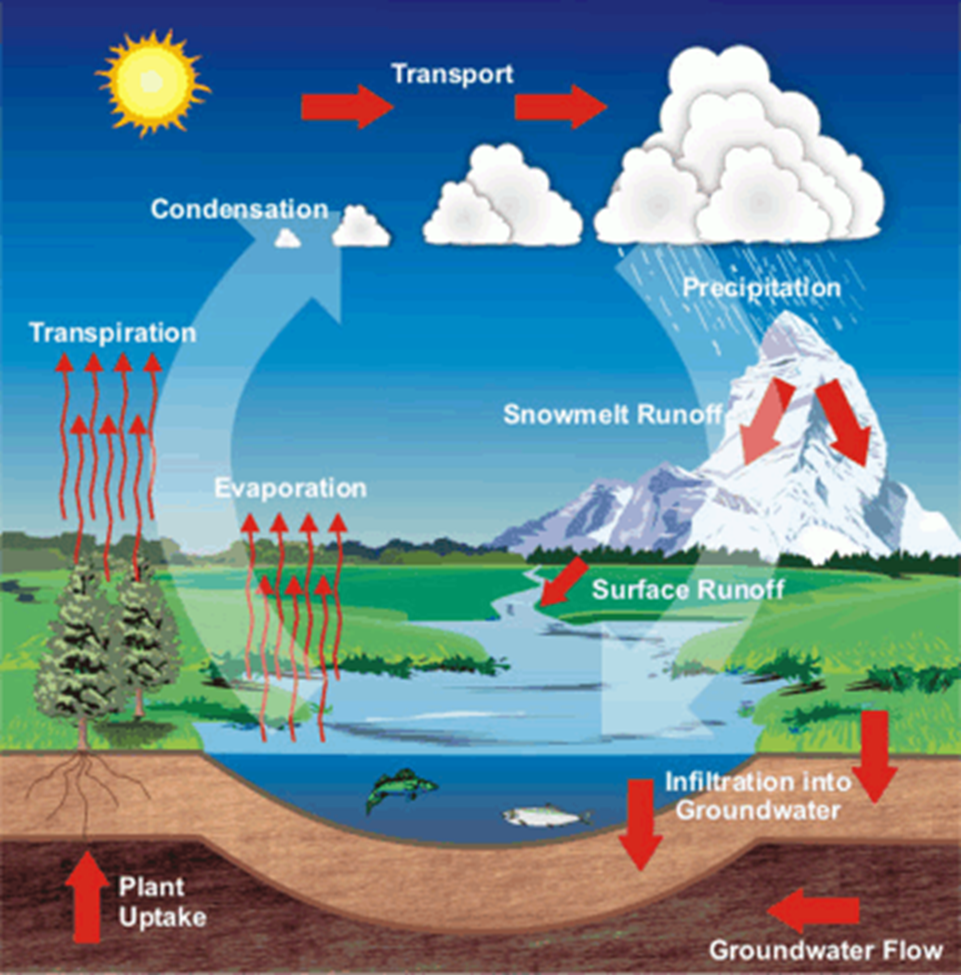
b. Cohesion, adhesion, surface tension
Density: water has a low density
c. Cohesion: attraction between like molecules
Adhesion: attraction between unlike substances
Capillarity: Water rises in a small tube against gravity
d.the amount of work needed to move water from a reference pool to another point.
e. gravitational, submergence, matric, osmotic potential energy
f. Type of plant, soil moisture tension, plant nutrients, soil layering
Soil Air and Temperature (Chapter 7)
a. Composition i. What is it and what affects it
b. What causes it to move i. Factors affecting air movement
c. Soil air and effects on oxidation and reduction
d. Soil Temperature i. Importance ii. Thermal properties iii. What influences temperature and thermal properties iv. Management to control soil temperature
a. Oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, humidity
b. Excess water rate of respiration, soil heterogeneity, subsoil vs surface soil
c. Redox and impact on soil color and classification
d. i. Biological activities, physical and chemical rxns.
ii. Heat capacity: Amt of energy needed to raise temp of a volume of substance by 1C
Specific Heat: # calories needed to raise temp of 1 gram of substance by 1C
iii. Location, face and angle of slope, large water bodies, vegetation, surface soil conditions
iv. Drainage, manage surface conditions
4. Colloids (Chapter 8)
a. Mineral structures i. 2:1 ii. 1:1 iii. Examples of each
b. Functions of colloids
c. Surface Area
d. Charge
e. CEC and AEC
a. i. Mica, illite, vermiculite, montmorillonite; chlorite (ex. smectite)
ii. kaolinite (ex. silicate clays)
b. Holds plant nutrients, retains pollutants, controls buffering, equilibrium between soil and solution
c. Very large surface area
d. Silicates- negative charge
non-silicates- positive charge due to covalent bonds
e. Cations able to exchange with other cations in the soil solution
Exchangeable anions held on positive charges – anion exchange capacity