Advanced serology and immunology
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Prozone = _______ excess
▪ What type of effect can happen in this zone?
• What can correct this issue?
antibody
Very little lattice is produced, ppt is inefficient
Here you can correct by diluting the
sample (“high dose hook effect”)
What is the zone of Equivalence
[Antibody] = [Antigen]
Most efficient ppt and lattice formation
Postzone = excess
antigen
What are the 2 big differences between precipitation and agglutination?
precipitation- Soluble Ag + Ab to create an visible pcpt, it takes a long time, takes hours to days
agglutination- insoluble/ particulate Ag w/ soluble antibody clumps, takes minutes to hours
· Radial Immunodiffusion/Single Diffusion
Where is the Ab? Where is the Ag?
Ab is in the agar gel, ag is in the well and diffuses out
§ Fahey Method:
Logarithmic relationship between diameter of precipitin ring and antigen conc.
Mancini Method:
linear relationship between diameter squared of precipitin ring and antigen conc.
· Ouchterlony/Double Diffusion
o Where is the Ab? Where is the Ag? What is this technique used for?
both Ag and Ab diffuse in the gel, this is used for fungal antigen ID and ID antibodies associated with autoimmune disorders
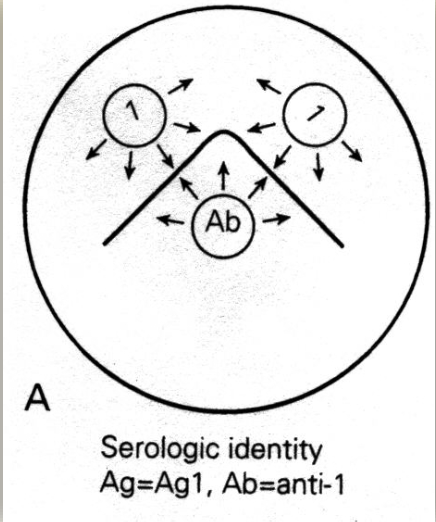
Identity
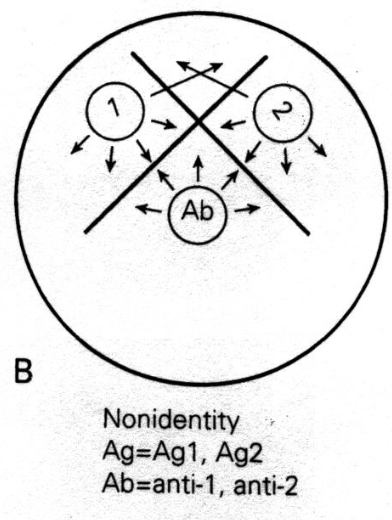
Non-Identity
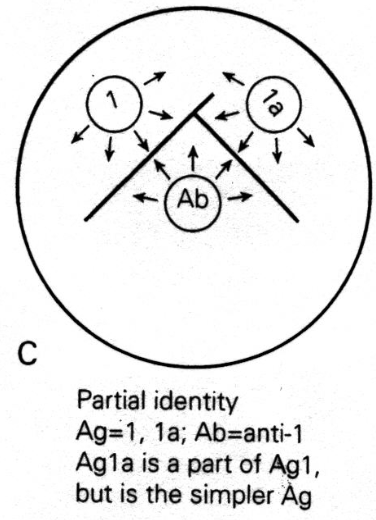
Partial Identity
· Turbidometry:
o How is this measured?
o What is the scatter proportional to?
Measured by light passing through
solutionIs a measure of light lost due to scatter
by lattice
Amount of scatter is proportional to
concentration of molecules in lattice
· Nephelometry:
o How is this measured?
o What is the scatter proportional to?
o Is more or less sensitive than turbidometry?
o Use in what type of testing
Measures light at a 10°-90 ° (usually 70°) angle
Scattered (reflected) light abs is
proportional to concentrationMore sensitive than turbidometry
Using a laser light makes it more
sensitive
Used in Complement component
concentration and Ab concentrations-
IgG, IgA, IgM
· Anti-Streptolysin O Titer (ASO)
o What is this testing used for?
o What is it not used for?
o What diseases can this help identify?
o What is added to create the Hemolysis control tube?
o What is added to create the RBC control tube?
o Interpretation: For example, an ASO titer with no hemolysis at 1:64 and hemolysis at 1:128 would be called TODD UNITS as a result.
recent infection of strep A
not diagnosing current infection
Scarlet fever, Rheumatic fever, glomerularnephritis
hemolysis control- RBC and SO
RBC control has RBC
64 Todd units
· Electroimmunodiffusion (EID) Laurell Rockets
o Is electrophoresed in a gel containing .
o What is directly proportional to the concentration of Ag?
ag; ab
area of the rocket (1/2xbasexheight)
· Counter Immunoelectrophoresis (CIE)
o Ag and Ab in and electrophoresed in gel
o Ag moves towards the Ab moves towards the .
o Precipitin line forms where there is
two seperate wells
anode; cathode
there is equivalence and identity
· Immunoelectrophoresis (IEP)
o After the Ag is placed in wells and electrophoresed, what is done?
o The equivalence zone =
troughs are cut in the gel
pcpt arc
· IFE – Immunofixation electrophoresis
o What are the 2 big steps:
§ 1
§ 2
o Where do the bands form?
o What is this now used to help classify?
1. Ab is overlaid after
2. electrophoresis
at the identity and equivalence
monoclonal gammopathies
· Western Blot
o What is this mainly used for in the medical laboratory?
confirmatory test to detect ab to HIV-1
· What is the difference between Sensitivity and Specificity?
o False Negatives yield lower .
o False Positives yield lower
sensitivity- detect small amounts
specificity- detect target without interference
sensitivity
specificity
· What is the big difference between heterogenous and homogeneous assays?
hetero- wash
homo- no wash
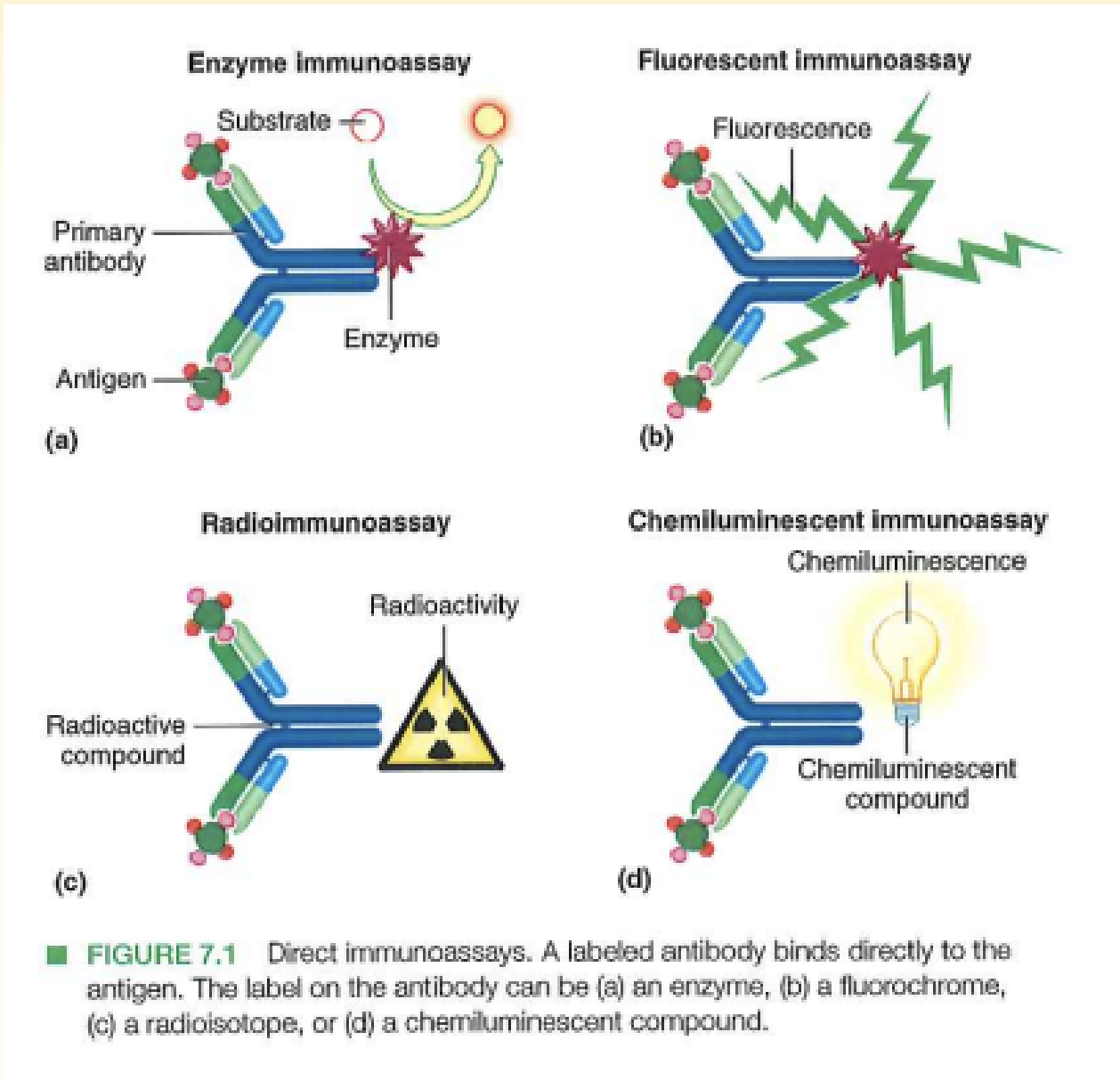
· How does a direct immunoassay detect?
uses labeled Ab binding to an Ag or labelled Ag binding to Ab
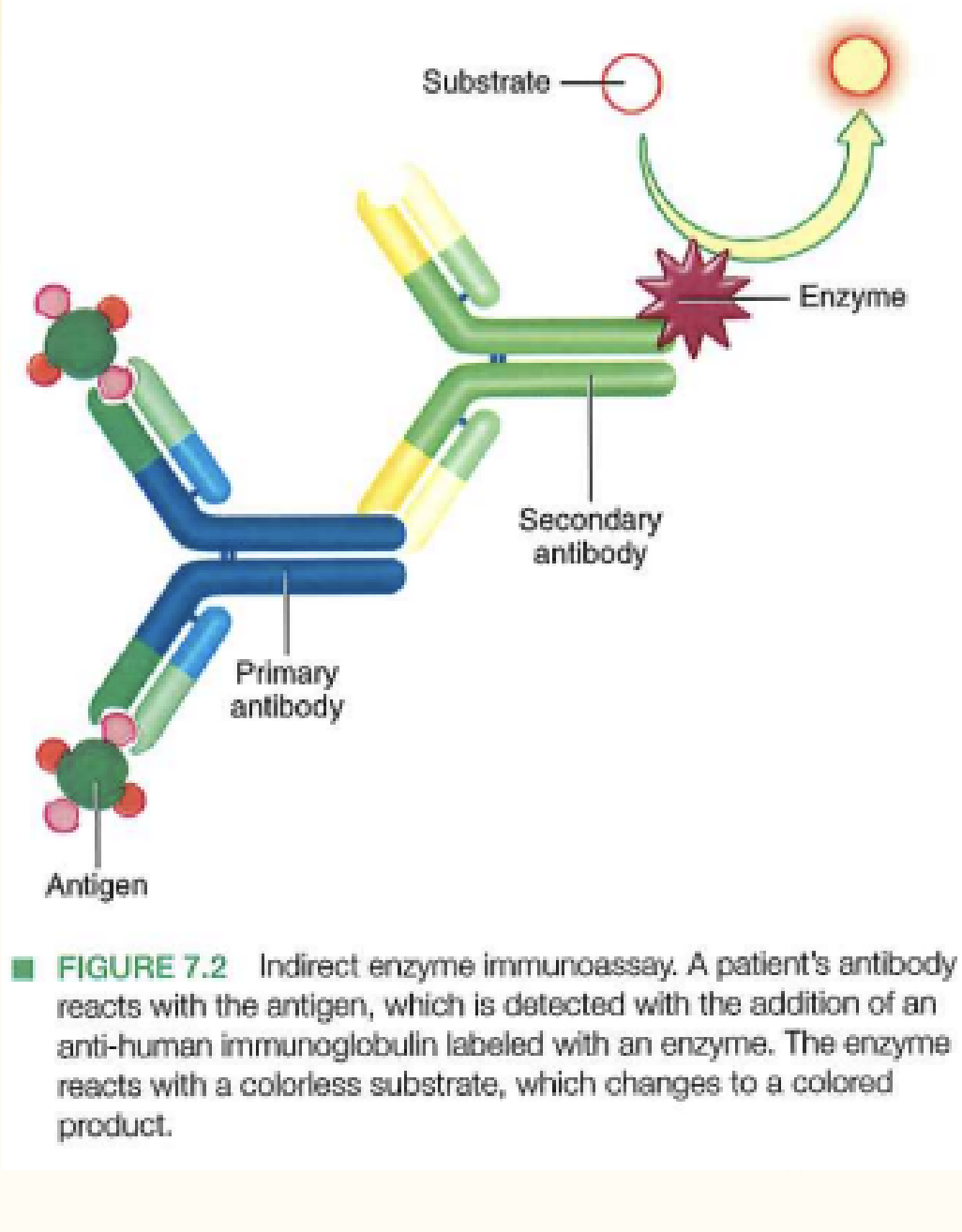
· How does an indirect immunoassay detect?
uses unlabelled Ag, unlabeled Ab and labeled antiglobulin to detect the initial Ab/Ag complex
o What is a big difference in steps for indirect vs direct immunoassay?
indirect uses 2nd wash step after more incubation
direct uses an immunoglobulin with a label and one wash
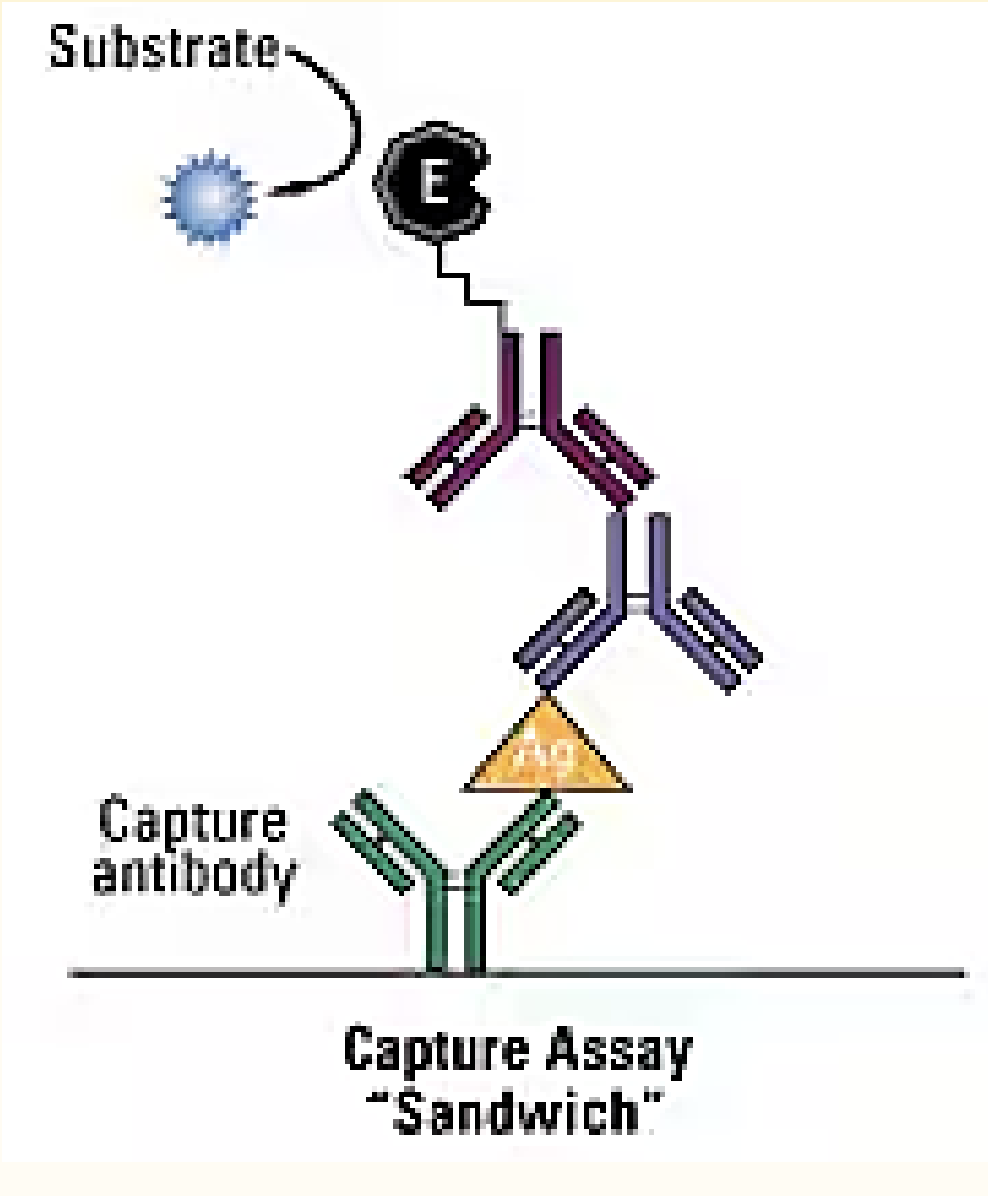
· How does a sandwich immunoassay detect?
o What does improper washing lead to?
captures Ag between 2 Molecules of Ab
false positives
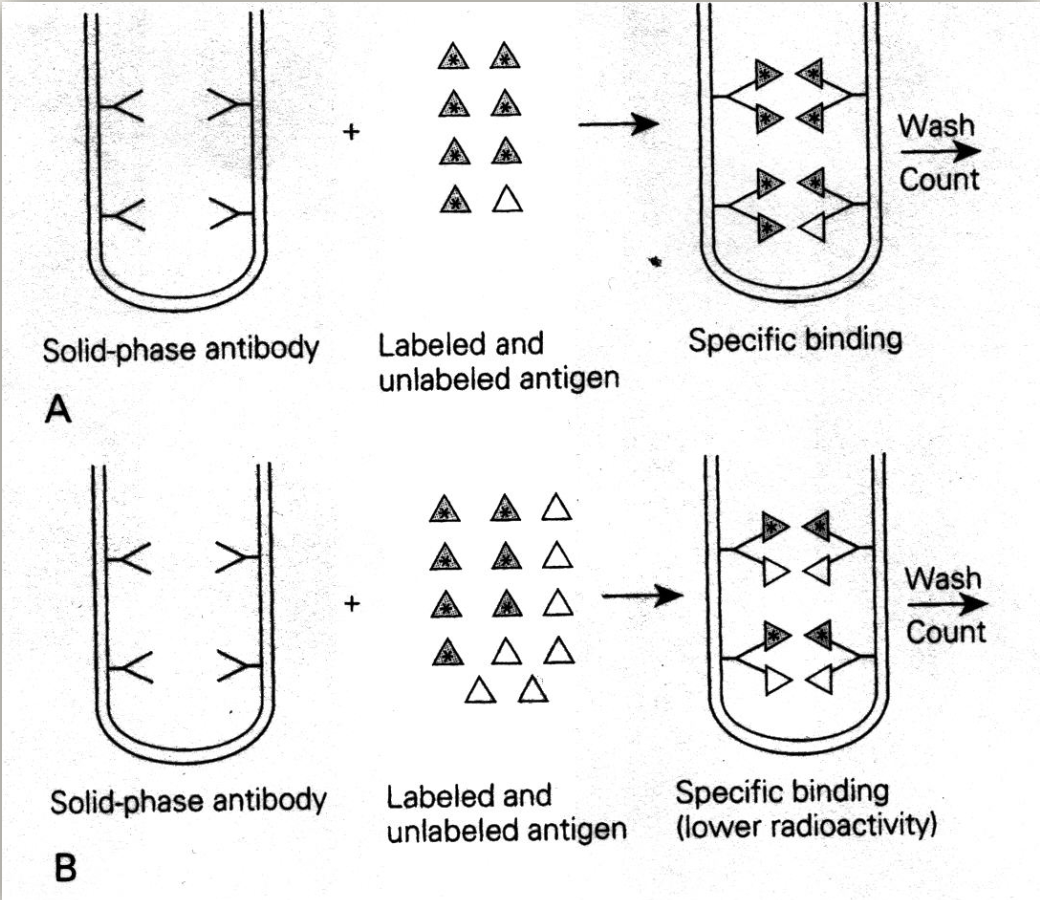
· How does a competitive immunoassay (like RIA) detect?
What is the relationship between the radioactive count and concentration of the Ag?
patient analyte competes with radiolabeled for binding sites on known amount of ab
the lower the radioactive count, the higher the concentration of the Ag
o Direct ELISA
Indirect Elisa
Sandwich ELISA
Competitive ELISA
o What are the 2 most frequently used enzymes in ELISA
horseradish peroxidase
alkaline phosphatase
o How does a direct fluorescent immunoassay detect
add fluorescein-labeled Ab to pt tissue on a slide; wash and examine under fluorescent scope
o How does an indirect fluorescent immunoassay detect?
add pts serum to rgt; wash, add fluorescein labeled AHG, wash and examine using fluorescent microscope
· Chemiluminescence is a commonly used label, how does it emit light?
excitation wavelength meets specific antibody and determines the color
o FPIA – a Competitive Assay – Fluorescence Polarization Immunoassay
§ What does a positive test show?
§ What does a negative test show?
reducing amount of polarized light
increased polarized light
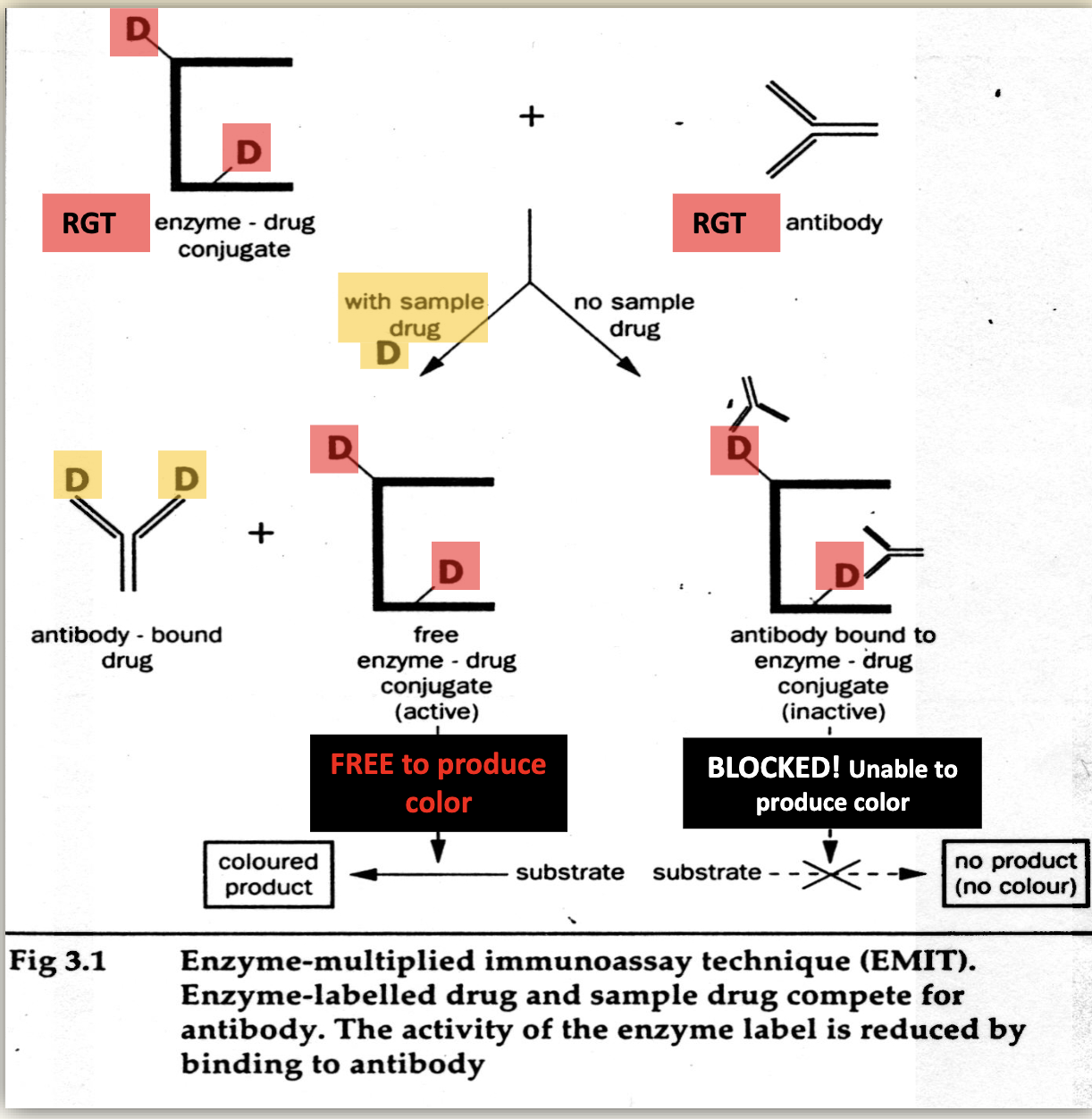
o EMIT – Enzyme Multiplied Immunoassay Technique
§ What is this commonly used to measure?
§ Draw out how a positive and negative test work. Note which one produces color.
small molecules such as drugs and hormones