Lecture 10 - Simple Harmonic Motion
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is simple harmonic motion
oscillatory motion for which resisting force is directly proportional to the negative displacement
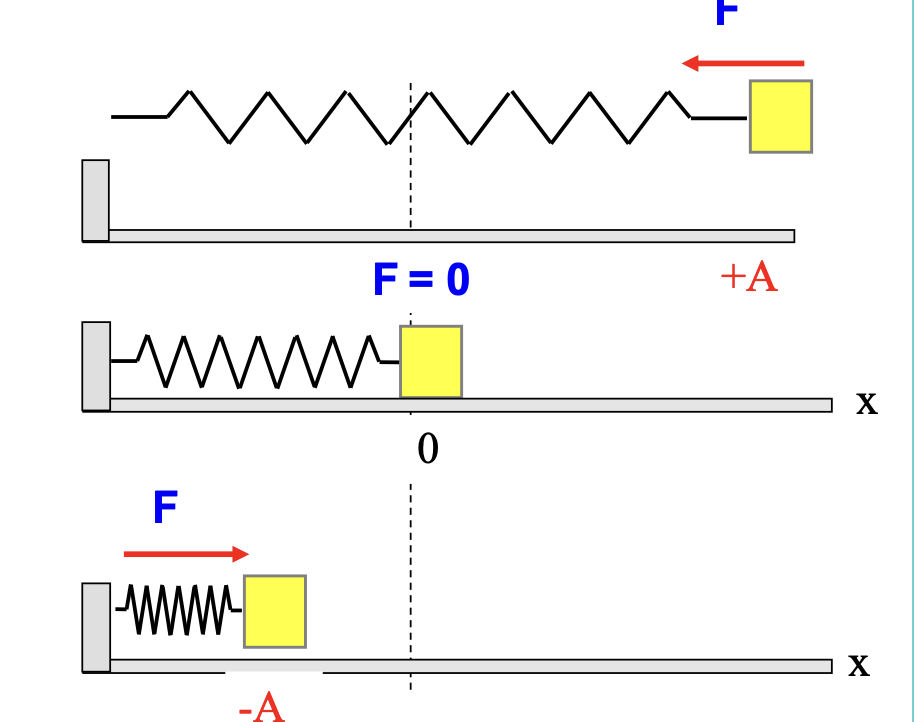
what is k
spring stiffness constant
what is x in SHM
displacement
what is the maximum displacement in SHM
the greatest distance from the equilibrium point is called amplitude A
What is a cycle in SHM
the complete to and fro motion from the same initial position back to that same point
what is a period in SHM
represented by symbol T = the time required to complete one cycle
What is frequency (f) in SHM
the number of cycles per second in Hertz (Hz)
1 Hz = 1 cycle per second
frequency and period are … related
inversely
any oscillating system for which the net restoring force is directly proportional to the negative displacement is said to exhibit …
SHM
A) Is the acceleration constant at all locations?
B) At what location is acceleration = 0.
C) is the speed of mass constant at all locations
D) at what location is v = 0
A) No, acceleration is directly proportional to displacement and therefore it changes with position
B) acceleration is 0 when x - 0 which is the equilibrium position, the spring is neither stretched nor compressed so there is no restoring force and therefore no acceleration
C) no, mass slows down near the turning points and speeds up near equilibrium
D) at the maximum displacement or amplitude (at the end points)
Total energy =
KE of mass + Elastic PE of spring
NOTE: if no friction, total energy remains constant
the period and sinusoidal nature of simple harmonic motion
an object of man m revolving anticlockwise in a circle of radius A, with constant speed Vmax on top of a table, if we look at this movement side on, it looks exactly like simple harmonic motion
vmax = T/2pi
how will the period change if…
m is doubled
k is doubled
T = 2pi root(m/k)
if m doubled, T increases by factor root 2
if k doubled, T decreases by factor root 2
A mass is suspended from the ceiling of an elevator by a spring, when the elevator is at rest, the period is T. What is happening to period when the elevator is accelerating upward?
the period does not change as T does not depend upon gravity
radians and degrees
2 pi = 360 degrees
A pendulum is suspended from the ceiling of an elevator. When the elevator is at rest, the period is T. What happens to the period when the elevator is accelerating upward
T = 2 pi root(L/g)
period will decrease, thus frequency will increase so pendulum will swing faster
what is the period on earth is the mass of bob is doubled for pendulum
T will remain the same