Topic 9 - Consuming energy resources
1/33
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Non-renewable
A finite source energy that cannot be replace after it is used
Renewable
An infinite source of energy that will be regenerated by the environment
Recyclable
A source of energy that can be reused, if managed sustainably, so will last into the future
Negative impacts of fossil fuels
- Landscapes scarred by mining and drilling to extract energy resources
- release of CO2
- oil leaks from drilling rigs, pipelines and tankers
How access to energy resources is affected by access to technology and physical resources
Geology: Geology (rock type) affects whether, coal, oil and gas have formed. Some areas have the potential to access geothermal energy due to their location near plate margins or magma plumes e.g Iceland
Accessibility: Where energy sources are inaccessible: deep underground or under oceans: this increases the cost of accessing the source e.g the UK has large reserves of coal which are uneconomic to mine due to the depth below ground.
Economic development and tech: The development of a country affects the amount of technology available.
Energy production may rely on high levels of technology and highly skilled staff which may not be available in developing countries including: Nuclear power and geothermal energy.
Climate and landscape influences: Climate can affect whether renewable energy is efficient. Solar power relies on clear skies. Wind power needs enough wind but not gusts.
Extremes of temperature can make the extraction of oil, gas and coal difficult. Hydroelectric power relies on steady levels of precipitation
What is the global pattern of energy use?
- Countries with the highest energy consumption per person tend to be developed countries and include Canada, Norway and Saudi Arabia. USA has 4.25% of the world's population but uses 16% of the world's energy
- Countries with the lowest energy consumption per person are developing countries which are all in Africa and include Niger, Chad and Tanzania
Why are there variations in the global pattern of energy use?
Levels of economic development:
- Industry, transport and IT are all vital for growing economies, all of which are energy dependant.
- Developed countries have the highest energy demands.
Reliance on traditional fuel sources:
- Approximately 2.4 billion people still rely in some way on traditional fuel sources for cooking and heating.
- An estimated 920 million people have no access to electricity at all - about 13% of the world's population.
Demand from different economic sectors:
- Developing economies are focused on primary economic activities such as agriculture which do not have a high energy demand
- Emerging countries such as India and China are focused on secondary economic activities so the high levels of manufacturing use lots of energy
- Developed countries are seeing a levelling off in demand for energy as manufacturing is reduced because increasing numbers of goods are imported
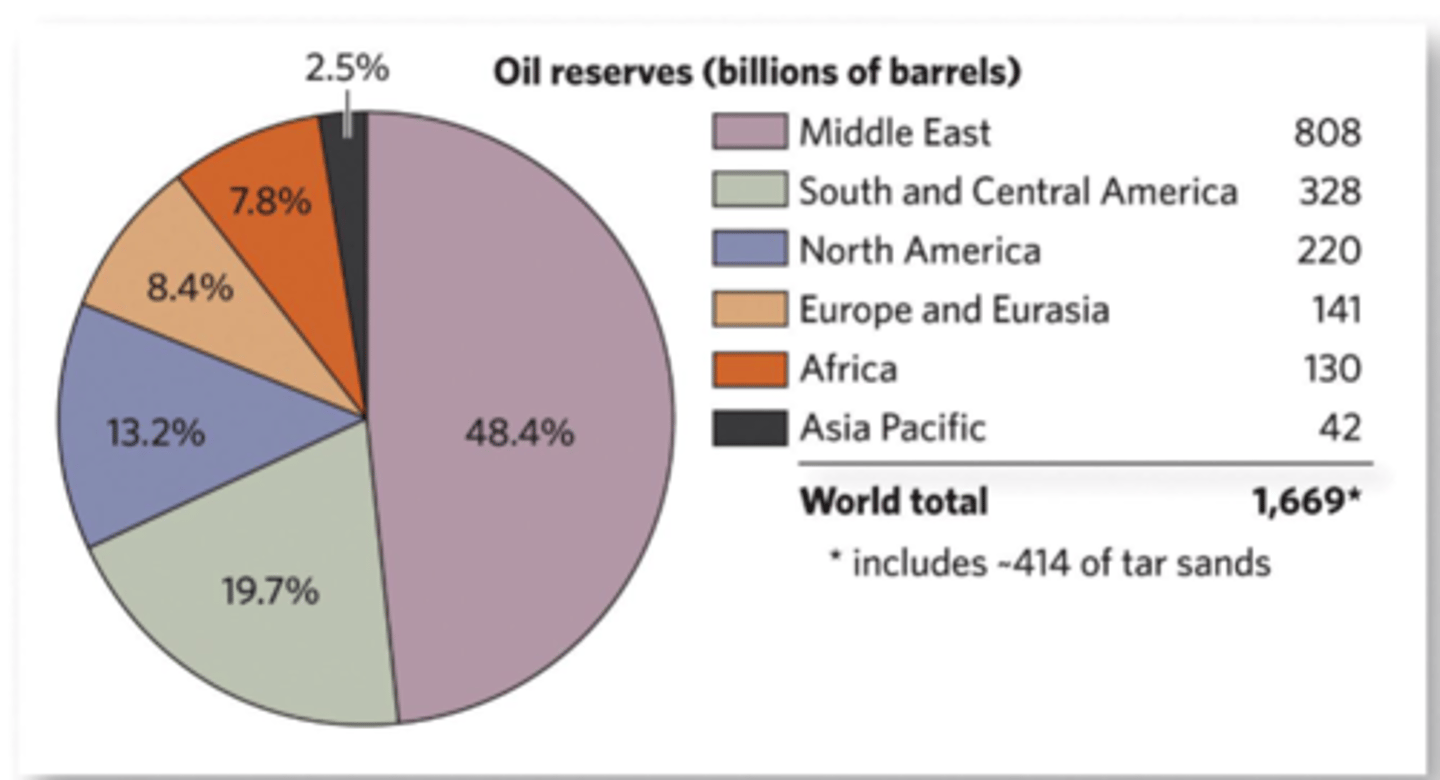
Global distribution of oil reserves
- Greatest in the Middle East - 808 billions of barrels which is well over double any other region
- Lowest in Europe - 12 billions of barrels
Global distribution of oil production
Greatest production in USA - 13.7 millions of barrels per day
Lowest production in Mexico - 2.7 millions of barrels
Why is oil consumption growing?
Rising per capita GDP: As countries become wealthier the demand for products increases and people have more things which use energy.
Rapid industrialisation in emerging economies: Increasing amounts of technology which use energy.
Rising supply leads to ... prices
Falling supply leads to ... prices
Rising supply leads to falling prices
Falling supply leads to rising prices
Rising demand leads to ... prices
Falling demand leads to ... prices
Rising demand leads to rising prices
Falling demand leads to falling prices
How are oil supply and prices affected by changing international relations?
Conflicts: The invasion of Ukraine by Russia led to oil prices increasing due to concerns about global supply.
Diplomatic relations: In 2010 Venezuelan President Chavez threatened to stop oil sales to the USA resulting in rising prices.
How are oil supply and oil prices affected by economic factors?
Periods of recession versus boom: 2003-2008 Emeging countries such as the BRICs undergo rapid economic growth and industrialisation - increasing demand so prices increase. In 2008 the financial crisis and recession led oil prices to fall steeply due to decreasing demand as businesses close and incomes fall.
Over or under supply: In 2013-14 a rivalry between Saudi Arabia and Iran led Saudi Arabia to increase the supply of oil which caused the price to fall.
A decrease in supply leads to an increase in price such as in the period following the Iranian Revolution in 1979
Conventional
Established technologies that have been used for many decades
Unconventional
New technologies where the impacts may not be fully understood
Economic benefits of developing new conventional oil and gas sources in ecologically-sensitive and isolated areas - the Arctic
- Exploration of new areas creates many jobs and boosts the economy.
- Oil sales enable countries such as Norway to invest in social benefits/childcare
- Education and care of the elderly are also funded in part through the sale of oil and gas
- Natural gas makes up 13% of Russia's exports
- Over 50% of Alaska's income comes from oil and gas
Economic costs of developing new conventional oil and gas sources in ecologically-sensitive and isolated areas - the Arctic
- Damage to Arctic fisheries and impact on the way of life of indigenous communities e.g the Nenets
- Increased potential for oil spills e.g 1989 Exxon Valdez oil spill in Alaska
- Oil spills will impact on many animals including whales, seals, polar bears, birds and whales, risk of extinction of species
Environmental costs of developing new UNconventional oil and gas sources in ecologically-sensitive and isolated areas - tar sands.
- Decline of caribou, lynx and wolverine populations
- Water pollution - waste water leaks into water sources
- Destruction of natural habitats
- Greenhouse gas emissions from bitumen are higher than conventional oil
- Higher rates of air pollution than conventional oil and gas sources and possible links to higher - cancer rates
- Deforestation
- Acid rain
Environmental costs of developing new UNconventional oil and gas sources in ecologically-sensitive and isolated areas - shale gas.
- Contamination of groundwater
- Subsidence (sinking of an area of land)
- Methane emissions
- Small earthquakes
How can people become more energy efficient and reduce energy consumption in the home?
- energy efficient lightbulbs
- switching off lights when not in use
- double glazed windows, loft insulation
How can people become more energy efficient and reduce energy consumption in transport?
- Encouraging use of electric cars
- Congestion charging - London has a £15 Congestion charge and an Ultra Low Emissions Zone (ULEZ) where an additional charge is made on cars who don't meet emission standards
- Building of cycle lanes to encourage safe cycling
Costs and benefits of biofuels
Costs:
- Air pollution
- Produces greenhouse gases
- Expensive
- May lead to deforestation
- Increases competition for land
Benefits:
- Uses waste or biofuels which regrow
- Available in most locations
Costs and benefits of wind
Costs:
- Not reliable only works when the wind is strong enough but not too strong
- Visual pollution
- Noise pollution
Benefits:
- No greenhouse gas emissions once installed
- No air pollution
- Cheap to run
- Can be on land or offshore
Costs and benefits of solar
Costs:
- Expensive
- Not reliable only works when it is sunny
- Large numbers needs to produce energy
- Uses large areas of land
Benefits:
- No greenhouse gas emissions once installed
- No air pollution
- Can be used in most locations
Costs and benefits of HEP
Costs:
- Large areas of land are flooded behind the dam
- Visual pollution
- People and settlements may have to be relocated
- Expensive to build and maintain
Benefits:
- No greenhouse gas emissions
- Controls flooding downstream
- Often in sparsely populated areas
- May provide water storage for irrigation and domestic use
Costs and benefits of hydrogen
Costs:
- It is expensive
- It requires energy to produce the hydrogen
- Difficult and dangerous to store and move
Benefits:
- Hydrogen can be used as a substitute for oil
- It produces no greenhouse gas emissions or air pollution
- It is very efficient releasing more energy than any other fuel (except for nuclear)
Different groups have contrasting views which vary between two points:
- Business as usual which means that oil and gas will continue to supply most of the world's energy
- Sustainable energy use where renewables will replace fossil fuels and reduce emissions
Views of consumers about energy futures
- Mainly consume electricity produced by fossil fuels
- The additional cost often dissuades people from making sustainable choices
- Main concern is reliable and cheap energy
- Increased awareness of carbon emissions
Views of TNCs about energy futures
- Companies such as Shell, Exxon and BP who produce oil and gas supplies
- Shell supports innovation to reduce carbon emissions
- Continue to explore oil and gas reserves
- Aim to maximise their profits
Views of the government about energy futures
UK government views on energy future:
- Investment in nuclear energy such as Sizewell C
- Banning of new petrol and diesel cars from 2030
- £265 million in subsidies for renewable energy sources
- Main aim is to maintain energy security
Views of climate scientists about energy futures
- Most climate scientists (over 95%) support the consensus that climate change is caused by human activity
- They encourage more sustainable actions such as greater use of renewable energy
Views of environmental groups about energy futures
Support and promote sustainable options as a way to: Reduce emissions of greenhouse gases, protect wildlife and the environment
Factors which cause changing attitudes to unsustainable energy consumption and reducing carbon footprints
Rising affluence:
Greater wealth means that more people can afford
- energy efficient appliances
- homes improvements such as insulation, double glazing
- sustainable energy sources such as solar panels and air source heat pumps
- electric and hybrid cars
- more investment in renewable energy
Environmental concerns:
- Concern for the environment has increased due to the work of pressure groups such as Friends of the Earth, WWF and Greenpeace, greater prominence of environmental political parties .g the Green Party, increased awareness of the impact of utilising fossil fuels
- As people's main needs for food, water and shelter are met due to the development of countries they are no longer the main concerns. Pollution and environmental concerns become increasingly important to people
Education:
- Climate change, global warming and carbon footprints are increasingly part of the school curriculum
- Increased information from governments and environmental organisations about the impact of using fossil fuels