W5 BIOSCEINCE
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
149 Terms
1
New cards
Describe the spinal cord (SC)
Long, thin, delicate structure protected by the vertebral column
2
New cards
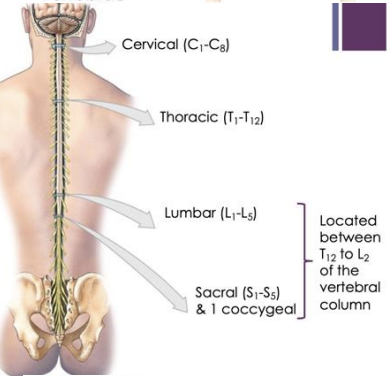
What are the 5 regions of the spinal cord?
3
New cards
What are mixed nerves?
Axons of sensory and motor neurone
4
New cards
Explain the difference between dorsal roots, dorsal root ganglion and ventral roots
**Dorsal roots:** axons of sensory neurons
**Dorsal root ganglion:** cell bodies of sensory nuerons
**Ventral root:** axons of motor neurone (somatic n autonomic)
\
\
**Dorsal root ganglion:** cell bodies of sensory nuerons
**Ventral root:** axons of motor neurone (somatic n autonomic)
\
\
5
New cards
What is the cauda equina?
The collection of nerves
6
New cards
What structures protect the spinal cord, and how?
**Spinal meninges:** pia mater, arachnoid mater, dura mater
* enable lumbar puncture
* doesn’t damage spinal cord > around L4-L5 (spinal cord ends around L1-L2)
* draw CSF for testing (check pathogens)
**Vertebral column:** helps in bending and turning
**CSF:** nourishes neural tissues > remove wastes
* enable lumbar puncture
* doesn’t damage spinal cord > around L4-L5 (spinal cord ends around L1-L2)
* draw CSF for testing (check pathogens)
**Vertebral column:** helps in bending and turning
**CSF:** nourishes neural tissues > remove wastes
7
New cards
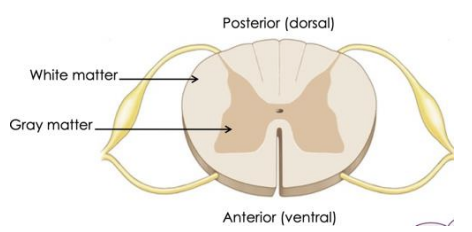
Describe the internal anatomy of the spinal cord?
* neural tissue (neurons, neuroglia)
* divided into left and right sides (2 grooves) > ventral median fissure & dorsal median sulcus
* areas of grey (outer) & white (inner) matter
* divided into left and right sides (2 grooves) > ventral median fissure & dorsal median sulcus
* areas of grey (outer) & white (inner) matter
8
New cards
What is the difference in the structure between grey and white matter?
**Grey matter:** neuron cell bodies, unmyelinated axons and neuroglia
* grey comminsure: axons cross from 1 side to other
\
**White matter:** superficial to grey matter > myelinated and unmyelinated axons
* anterior white comminsure
\
\
\
* grey comminsure: axons cross from 1 side to other
\
**White matter:** superficial to grey matter > myelinated and unmyelinated axons
* anterior white comminsure
\
\
\
9
New cards
What is the difference in the organisation of grey and white matter?
**Grey matter:** gray horns
* sensory nuclei: cell bodies of spinal cord interneurons
* somatic motor nuclei: cell bodies of lower motor neurons
* autonomic motor nuclei: cell bodies of preganglionic neurons (glands, cardiac, smooth muscles)
\
**White matter:** white columns (bundles of axons)
* ascending tracts: sensory input > brain
* descending tracts: motor output > away
* sensory nuclei: cell bodies of spinal cord interneurons
* somatic motor nuclei: cell bodies of lower motor neurons
* autonomic motor nuclei: cell bodies of preganglionic neurons (glands, cardiac, smooth muscles)
\
**White matter:** white columns (bundles of axons)
* ascending tracts: sensory input > brain
* descending tracts: motor output > away
10
New cards
List the functions of the spinal cord
1. A two way conduction pathway to and from the brain
2. Spinal reflexes (gray matter) ; somatic reflex (skeletal muscle), autonomic reflex (smooth muscle)
11
New cards
Which ascending tract conducts crude touch, deep pressure, pain and temperature? Name the neurons, tract and location of tracts (white matter)
Spinothalamic pathway
* First, second and third- order neurons
* Anterior spinothalamic tract (crude touch, deep pressure)
* Lateral spinothalamic tract (pain, temp)
* Lateral and anterior white columns
* First, second and third- order neurons
* Anterior spinothalamic tract (crude touch, deep pressure)
* Lateral spinothalamic tract (pain, temp)
* Lateral and anterior white columns
12
New cards
Which ascending tract conducts fine touch, light pressure, vibration and proprioception (conscious)? Name the neurons, tracts and location of tracts (white matter)
Posterior column pathway
* First, second, third-order neurons
* Fasciculus gracilis tract
* Fasiculus cuneatus tract
* Posterior white columns
* First, second, third-order neurons
* Fasciculus gracilis tract
* Fasiculus cuneatus tract
* Posterior white columns
13
New cards
Which ascending tract conducts proprioception (unconscious)? Name the neurons, tracts and location of tracts (white matter)
Spinocerebellar pathway
* First and second-order neurons
* Anterior spinocerebellar tract
* Posterior spinocerebellar tract
* Lateral white column
* First and second-order neurons
* Anterior spinocerebellar tract
* Posterior spinocerebellar tract
* Lateral white column
14
New cards
Which descending tract conducts somatic motor output (skeletal muscle - limbs)? Name the neurons, tracts and location of tracts (white matter)
Lateral corticospinal pathway
* Upper and lower motor neurons
* Lateral corticospinal tract
* Lateral white column
* Upper and lower motor neurons
* Lateral corticospinal tract
* Lateral white column
15
New cards
Which descending tract conducts somatic motor output (skeletal muscle - axial skeleton)? Name the neurons, tracts and location of tracts (white matter)
Anterior corticospinal pathway
* Upper and lower motor neurons
* Anterior corticospinal tract
* Anterior white column
* Upper and lower motor neurons
* Anterior corticospinal tract
* Anterior white column
16
New cards
what is the spinal cord
long, thin, delicate tubular structure
17
New cards
what protects the spinal cord
vertebral column
18
New cards
what does spinal cord pass through
vertebral foramen of each vertebra
19
New cards
where does the spinal cord end in adults
between L1 and L2
20
New cards
where does the spinal cord end in infants
L4
21
New cards
what does the spinal cord terminate in
cone shaped structure called conus medullaris
22
New cards
what anchors the spinal cord to the coccyx
filum terminale
23
New cards
5 regions of the spinal cord
cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
24
New cards
how many segments are there
31
25
New cards
how many segments in cervical region
8
26
New cards
how many segments in thoracic region
12
27
New cards
how many segments in lumbar region
5
28
New cards
how many segments in sacral region
5
29
New cards
how many segments in coccygeal region
1
30
New cards
what connects to each segment
a pair of spinal nerves
31
New cards
where do spinal nerves emerge from
vertebral column
32
New cards
what do spinal nerves branch to form
peripheral nerves that innervate all parts of the body (except the head)
33
New cards
what do spinal nerves contain
axons of sensory and motor (somatic and autonomic) neurons
34
New cards
how do spinal nerves connect to the spinal cord
by the dorsal and ventral nerve roots
35
New cards
what do dorsal roots contain
axons of sensory neurons
36
New cards
what does the dorsal root ganglion contain
cell bodies of sensory neurons
37
New cards
what do ventral roots contain
axons of motor neurons (somatic & autonomic)
38
New cards
the \_________, \___________ and \____________ nerve roots travel beyond the \_________ \______________ to reach the vertebral region from which the \________, \__________ and \_______________ spinal nerves emerge.
lumbar, sacral, coccygeal, conus medullaris, lumbar, sacral, coccygeal
39
New cards
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord (lumbar, sacral and coccygeal nerve roots)
40
New cards
how is the spinal cord protected
- vertebral column
41
New cards
- cerebrospinal fluid --\> also nourishes the neural tissue and removes waste products
42
New cards
- spinal meninges
43
New cards
spinal meninges are continuous with
the cranial meninges
44
New cards
spinal meninges extend beyond the spinal cord to
the second sacral vertebra (S2)
45
New cards
what is a lumbar puncture (spinal tap)
insertion of a needle into the subarachnoid space beyond L3
46
New cards
does lumbar puncture damage the spinal cord
no
47
New cards
what is lumbar puncture used for
- withdraw CSF fluid for diagnostic testing (e.g. meningitis) or reducing intracranial pressure.
48
New cards
- used to administer medications
49
New cards
what separates outer dura mater from vertebral column
epidural space - site of anaesthetic administration
50
New cards
What are denticulate ligaments?
extension of the pia mater
51
New cards
what do denticulate ligaments do
prevent lateral movements of the spinal cord
52
New cards
what grooves divide the neural tissue (neurons and neuroglia) of the spinal cord into left and right side?
- anterior (ventral) median fissure
53
New cards
- posterior (dorsal) median sulcus
54
New cards
what areas is neural tissue of spinal cord organised into
gray matter and white matter
55
New cards
what is gray matter composed of
neuron cell bodies (mainly), unmyelinated axons and neuroglia
56
New cards
what does gray matter vary in
size and shape down the length of the spinal cord
57
New cards
what does gray matter enclose
central canal --\> filled with cerebrospinal fluid
58
New cards
what is the gray commissure
site where axons cross from one side of the CNS to the other
59
New cards
what is gray matter subdivided into
gray horns (anterior, posterior, lateral)
60
New cards
what do gray horns contain
sensory or motor nuclei
61
New cards
function of posterior gray horns
sensory
62
New cards
function of anterior gray horns
somatic motor function
63
New cards
function of lateral gray horns
autonomic motor function
64
New cards
what do sensory nuclei of the posterior gray horns contain
cell bodies of spinal cord interneurons
65
New cards
what do cell bodies of interneurons do
receive and process incoming sensory input
66
New cards
what do somatic motor nuclei of the anterior gray horns contain
cell bodies of lower motor neurons
67
New cards
what do cell bodies of lower motor neurons do
receive outgoing somatic motor output
68
New cards
what do autonomic motor nuclei of the lateral gray horns contian
cell bodies of preganglionic neurons
69
New cards
what do cell bodies of preganglionic neurons do
receive outgoing autonomic motor output
70
New cards
site of integration for spinal reflexes
gray matter
71
New cards
what do reflex integration centres do
- receive and interpret incoming sensory input
72
New cards
- decide on and generate the motor output that causes the reflex response
73
New cards
what do the reflexes rapidly and involuntarily stimulate
- skeletal muscle contractions \= somatic reflex (e.g. patellar reflex)
74
New cards
- smooth muscle contractions of visceral organs (e.g. bladder) or gland secretions \= autonomic reflex
75
New cards
white matter location in relation to gray matter
superficial to gray matter
76
New cards
what is white matter composed of
myelinated (mainly) and unmyelinated axons
77
New cards
what is the anterior white commissure
site where axons cross from one side of the CNS to the other
78
New cards
what is white matter subdivided into
white columns
79
New cards
what do white columns contain
ascending and descending spinal cord tracts \= bundles of axons
80
New cards
what do spinal cord tracts of white matter do
conduct sensory or motor information between the spinal cord and brain
81
New cards
what do ascending tracts do
conduct sensory input to the brain
82
New cards
what do descending tracts do
conduct motor output away from the brain
83
New cards
ascending tracts (6)
fasciculus gracilis, fasciculus cuneatus, lateral spinothalamic, anterior spinocerebellar, posterior spinocerebellar, anterior spinothalamic
84
New cards
white column location of fasciculus gracilis
posterior white columns
85
New cards
white column location of fasciculus cuneatus
posterior white columns
86
New cards
sensory information conducted by fasciculus gracilis
fine touch, vibration
87
New cards
sensory information conducted by fasciculus cuneatus
light pressure, proprioception
88
New cards
white column location of lateral spinothalamic tract
lateral white columns
89
New cards
sensory information conducted by lateral spinothalamic tract
pain and temperature
90
New cards
white column location of anterior spinocerebellar tract
lateral white columns
91
New cards
white column location of posterior spinocerebellar tract
lateral white columns
92
New cards
sensory information conducted by spinocerebellar tracts
proprioception
93
New cards
white column location of anterior spinothalamic tract
anterior white columns
94
New cards
sensory information conducted by anterior spinothalamic tract
crude touch, deep pressure
95
New cards
ascending tracts (2)
lateral corticospinal, anterior corticospinal
96
New cards
white column location of lateral corticospinal tract
lateral white columns
97
New cards
motor output conducted by lateral corticospinal tract
somatic motor output that controls the skeletal muscles of the limbs.
98
New cards
L for Lateral \= L for limbs
99
New cards
white column location of anterior corticospinal tract
anterior white columns
100
New cards
motor output conducted by anterior corticospinal tract
somatic motor output that controls the skeletal muscles of the trunk (axial skeleton)