Reproduction Module 4
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Gestational age
From 1st day of a woman’s last menstrual period (LMP) to the age of pregnancy.
Fetal age
From the date of conception
Fetal age must be __ weeks less than gestational age.
*Onset menstruation is 14 days after ovulation
2
Why is gestation divided into 3 trimesters?
Clinical tracking with each 12-14 weeks characterized by a specific maternal physiological changes and fetal development stages.
1st Trimester
Week of conception to 13th week of gestation
All organ systems are being developed (before visibility)
Mom: increased blood supply for nutrient and oxygen transport, and elevated HR
Hormonal changes: fatigue, morning sickness, headaches, and constipation
2nd Trimester
Week 13-26 of gestation
Fetal organs continue to develop and uterus expands
~20: hair, nails, and reproductive organs are developed (sex), fetus starts to kick
Bones and teeth continue to harden, and NS becomes functional
Symptoms: body aches, dizziness (low BP), and swelling of hands and feet
3rd Trimester
Week 27-birth (37-42)
Fetus gains weight a slow grows lenghtwise
Respiratory system matures just before birth
woman visits healthcare / 2 weeks until last month were it is every week
What is checked during the maternal visits?
BP, urine samples for signs of urinary tract infections and other issues, and check cervix and the baby’s position (cephalic or breech).
Cephalic
Head-down
Breech
Bottom-down
Why are gestational weeks 3-10 so important? *1st trimester
Teratogens
What are examples of teratogens?
Radiation, alcohol, or certain prescription medications
Preterm
Birth before 37 weeks
maternal complications
worsening health outcomes for baby the earlier
Full Term
37-40 weeks “optimal time”
at 41 weeks = late term
Post Term
More than 42 weeks
risk for complications increase for both mom and fetus
Obstetricians induce labour at 41-42 weeks
Postnatal Period or Pnerperium
6-week period after pregnancy
Mom undergoes physical and psychological changes as the body returns to its pre-pregnancy condition
Naegele’s Rule
Calculating the delivery date assuming the gestational age of 280 days.
(Last day of LMP) - (3 months) + (1 year and 7 days) = Estimated Date of Delivery
What are the 2 stages of fetal development?
Embryonic and fetal
Embryonic stage
first 8 weeks
during 1st trimester
major morphological changes with all organ structures being established “carnegie stages”
Carnegie Stages
Morphological changes of the embryonic period into 23 stages.
Fetal stage
after 8th week (~10 weeks gestation, after Carnegie stage 23)
final weeks of 1st trimester to birth
growth and development of structure
Embryonic Period: Week 1-2
First 2 weeks (preimplantation) zygote goes towards the uterine cavity for cleavage.
Becomes a blastocyst
After hatching from the zona pellucida the blastocyst implants into the uterine wall and develops the germ layers giving rise to organ systems
Embryonic Period: Week 3-4
Mesoderm layer differentiates into muscle, kidneys, bones, and the heart
Ectoderm layer differentiates into nervous tissues and skin
Endoderm layer into digestive tract, lungs, and liver
Primordial germ cells migrate towards the gonadal ridges
Wolffian and Mullerian ducts form
Early BV, RBV, and primitive heart appear in week 3.
Week 4 -- primitive heart beats ~113 bpm first functioning organ of the embryo (only 2 chambers joined by contractile tubes)
In weeks 3-4 of the embryonic period the mesoderm layer differentiates into…
Muscle, kidneys, bones, and the heart
In weeks 3-4 of the embryonic period the ectoderm layer differentiates into…
Nervous tissues and skin
In weeks 3-4 of the embryonic period the endoderm layer differentiates into…
Digestive tract, lungs, and liver
Embryonic Period: Week 5
4 chambers heart are visible
Upper and lower limbs bud from embryo and grow
Cerebral hemispheres become visible
Embryonic Period: Week 6
Primordial germ cells arrive and invade the gonadal ridges
Heart and lungs descend to the thorax
Heart starts to beat at a regular rhythm
Embryonic Period: Week 7-8
Embryo transitions into fetal stage
Fingers are visible
Cartilage is replaced by bone
Gonads differentiate
M -- primitive testes begin their descent
Genitals are undifferentiated until week 9
Fetal Period (Week 9-birth)
Begins after Carnegie stage 23 (~week 9 of gestation) and continues until birth
Continued growth and development of the organs
Fetus grows rapidly in length and weight
Fetal Period: week 8
Embryo tail disappears and is now called a fetus.
Fetal Period: week 11
lemon, all major organs have formed
Fetal Period: week 14
avocado
Fetal Period: week 21
grapefruit
Fetal Period: week 29
coconut
Fetal Period: week 38
watermelon
During which weeks is ultrasound monitoring?
18-22
Why do pregnant woman need ultrasound monitoring?
Visualize and evaluate specific fetal structures after all major organs have been developed (during 2nd trimester).
What are the different reasons and evaluations done during an ultrasound?
Confirm pregnancy and location (detect ectopic)
Confirm # babies in uterus
Determine gestational age for due date and milestones
Eval fetal growth with movement, breathing, and HR
Eval placenta and fluid levels (amniotic to protect fetus)
Identify birth defects
Determine fetal position before delivery
Other prenatal tests
Placenta
Temporary organs developed from both maternal and fetal tissues during pregnancy to help fetus development.
What does the placenta do?
Nutrient
Termo-regulation
Waste
Gas exchange (blood)
What are the 3 main types of placental structures and their species.
Epitheliochorial (cows, pigs, and horses)
Endotheliochorial (dogs and cats)
Hemochorial (humans, mice, and rabbits)
Epitheliochorial
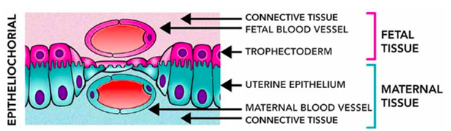
least invasive, when maternal blood is seperate from fetal by 3 tissues: endothelium, CT, and epithelium
Endothliochorial
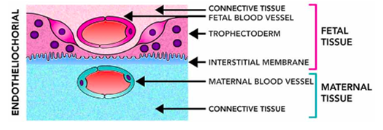
Maternal blood is separated from fetal membranes by layer of maternal endothelium and interstitial tissue.
Hemochorial
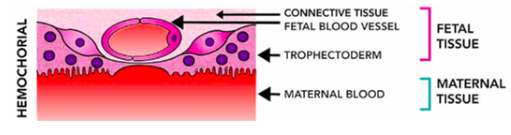
Human placenta allows fetal membranes to be bathed directly with maternal blood.
What are the primary functions of the placenta?
nutrition + O2 exchange
protection from xenobiotics
hormone protections for maternal metabolism fetal growth and others
excretion of waste
attachment to uterine wall
When does the placental start to form?
Immediately at the invasion of the embryo. Embryo survives pre-implantation period and forms initial attachment to uterine wall -- placenta bury itself into the decidua.
Placental formation begins with implantation when the _________ or _______ layer (outer layer) initiates the attachment to the maternal decidua.
Day 9 post-fertilization, trophoblast cells grow and divide the decidua, anchoring and invading the uterine surface to try to reach and access the maternal BV.
trophectoderm, trophoblast
After initial invasion (~day 7 post fertilization), trophoblast differentiate into…
cytotrophoblast and syncyntiotrophoblast
Cytotrophoblast
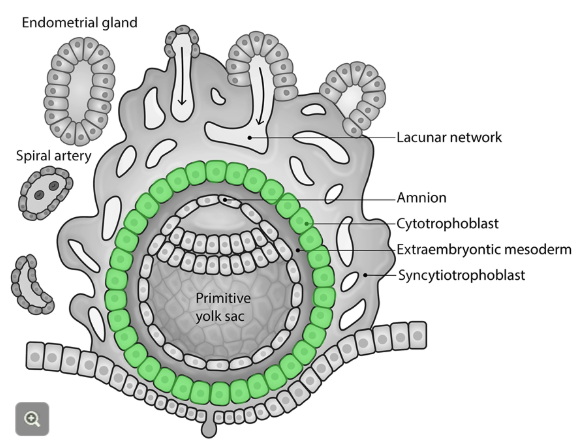
Inner layer of trophoblast cells
Produces proteolytic enzymes to facilitate invasion of the decidua
These cells replenish the cells of the outer syncytium layer "germinal cells of the syncytium"
Has clear cell border and 1 nucleus
Syncyntiotrophoblast
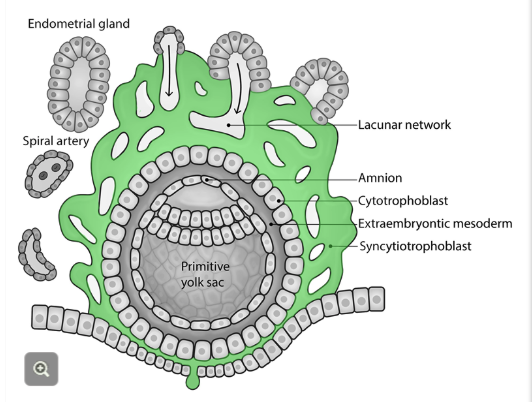
Composed of cytotrophoblast cells that fuse together into a multinucleate, continuous cell layer (w/o cell borders) --> syncytium
Comprises the outermost layer of the trophoblast cells
Actively migrates + invades the decidua
Will become the blood-placental barrier
As the layer expands, hollow spaces lacunae form and continue to grow where they will fuse to become intervillous space.
Explain the differentiation of the inner cell mass during invasion.
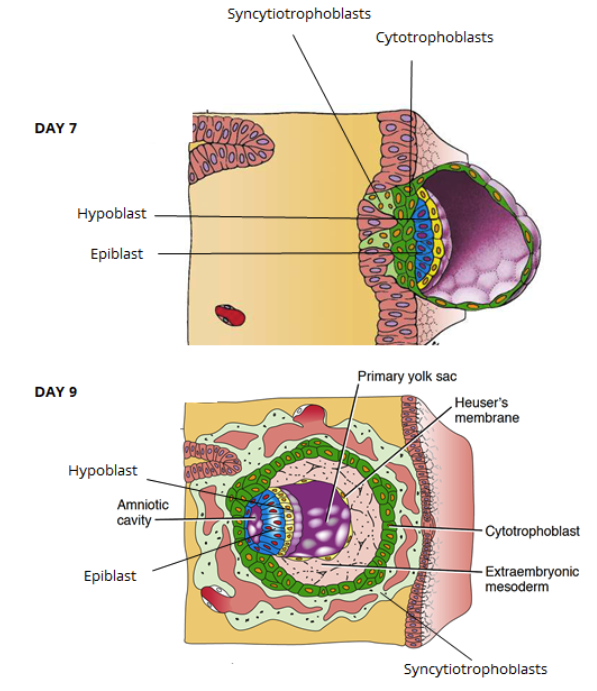
Outer trophoblast layer differentiates and invades the decidua, inner structures of the blastocyst also develop
Inner cell mass = bilyered embryonic disc (epiblast and hypoblast)
~day 9 hypoblast gives rise to extraembryonic mesoderm (layer b/w outer cytotrophoblast and inner cell mass)
Supports the development of amnion, yolk sac, and chorionic villi of the placenta
What is chorionic villi?
Cytotrophoblast layer continues to grow and cells form finger-like projections through syncytium.
What are the stages of development for the chorionic villi?
primary, secondary, tertiary
These structures are the ones in direct contact with the maternal blood.
Primary, secondary, and tertiary villus
Primary villus
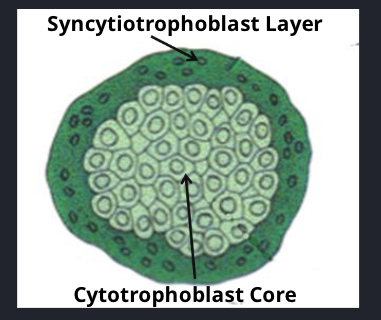
Form as the cytotrophoblast cells invade and protrude into the syncytiotrophoblast layer.
Small and avascular.
Cytotrophoblast core
Surrounded by syncytium
Secondary villus
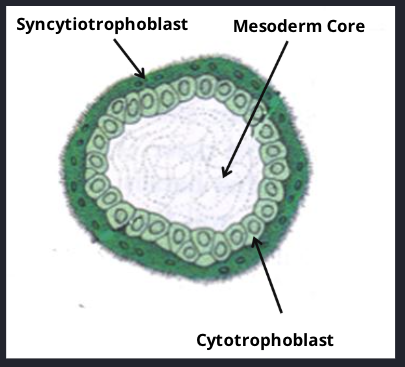
Extraembryonic mesodermal core
Covered by cytotrophoblast cells + outer synciotrophoblast layer
Tertiary villus
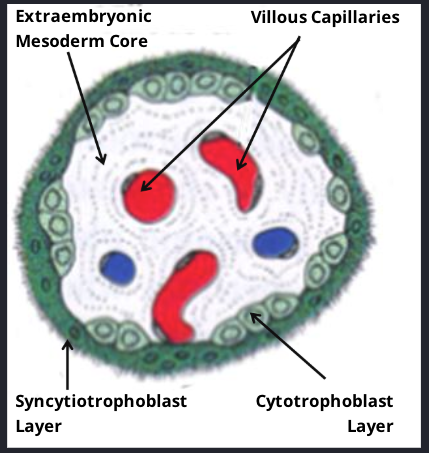
Embryonic BV develop in mesodermal core develop forming this structure
Extraembryonic mesodermal core with villous capillaries
Covered by cytotrophoblastic and syntiotrophoblastic layers
How does the cytotrophoblastic shell form?
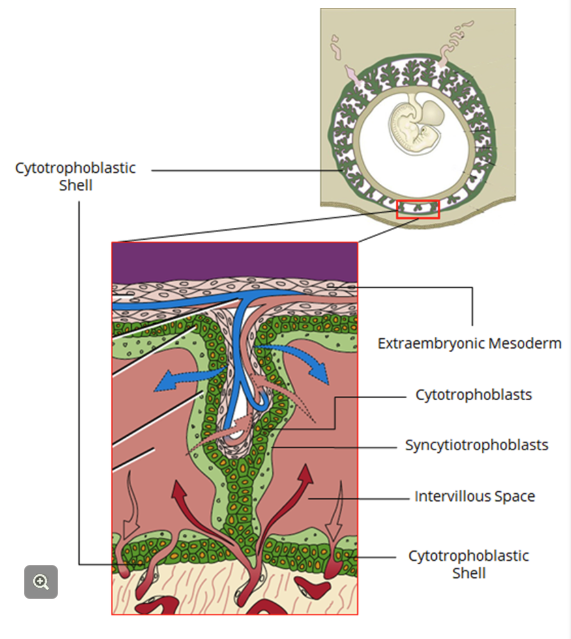
Cytotrophoblast proliferate laterally = cytotrophoblastic shell surrounding syncytiotrophoblast and entire embryo
Anchoring villi = 3 villi connects shell to chorionic plate
These will grow villous branches "floating villi"
Space b/w villi = intervillous space (b/w shell and plate)
Where circulation will pool and bathe the chorionic villi.
Plate + shell = surround embryo and form the chorion
How are asymmetrical villi formed?
1 and 2 villi project uniformly from the entire surface of the chorionic plate, however, 3 villi develop asymmetrically
Grow to anchor sides of the embryo where is faces the maternal decidua
Chorion frondosum
highly villous area at the fetal side of the placenta
Chorion laeve
villi on the opposite side of the fetus that atrophy.
Decidua Basalis
Side where chorion frondosum attaches
Decidua capsularis
*doesn’t intereact with chorionic villi and later becomes smooth
Opposite side surrounding embryo
What is the function of the additional fetal membranes?
Extraembryonic membranes layers projecting from the placenta surrounding and protecting the development of the fetus
Additional fetal membranes: Amnion
Innermost membrane surrounds embryo
Transparent with amniotic fluid
Protects embryo from mechanical stress + impact
Additional fetal membranes: Yolk sac
Small sac on ventral surface of embryo
Most important function in early prego
Source of primordial germ cells and blood cells
Regresses in later stages of prego
Additional fetal membranes: Allantois
Hollow sac on tail end of yolk sac
Contributes to nutrition and excretion
Helps form umbilical cord
Additional fetal membranes: Chorion
Outermost fetal membrane
Surround all other membranes of the embryo
Forms the fetal side of the placenta
Includes chorion frondosum and chorion laeve
Additional fetal membranes: Extraembryonic coelom
Space b/w amnion and chorion.
Extravillous trophoblasts
highly invasive type of cytotrophoblast arising from the tip of anchoring villi.
Spiral artery remodelling
extravillous trophoblast migrating toward the decidua in endothelium towards maternal arteries causing modifications in myometrium.
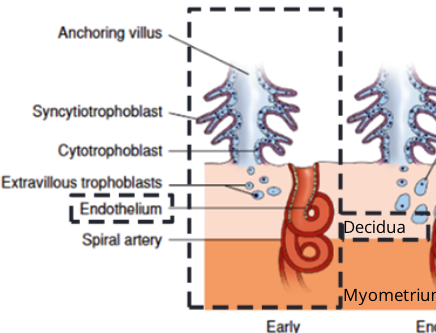
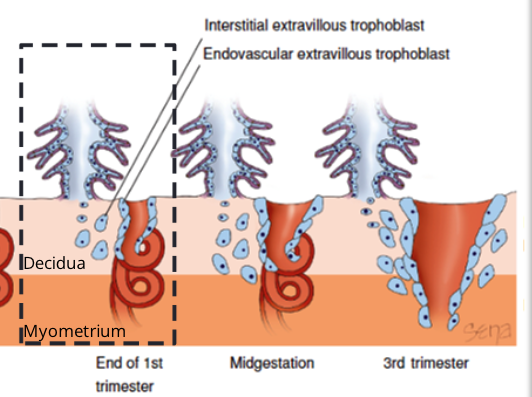
Spiral artery remodelling steps
Early Pregnancy --> extravillous trophoblast proliferate from anchoring villi invading maternal decidua
End of 1st Trimester --> Extravillous differentiates into 2 types:
Interstitial --> cell invade deeper into decidua and surround spiral arteries
Endovascular --> cells penetrate the lumen of uterine spiral arteries
Midgestation --> both types of extravillous trophoblasts are involved in degradation of maternal vascular endothelium, and the replacement of SM + CT of arteries with fibrous material.
Result = maternal spiral arteries become wider = decrease vascular resistance = higher V of blood flow
3rd Trimester --> blood supply to the uterus + placenta increases x10 factor compared t non-pregnant uterus (due to spiral artery remodelling)
What is the function of the placental circulation?
Acts as the interface b/w 2 circulatory systems: uteroplacental (maternal-placental) and fetoplacental blood circulation
Uteroplacental circulation
Begins at the end of 1st trimester --- although maternal BV continue to be remodeled until 3rd trimester
Blood flow from uterine spiral arteries --> intervillous space allows for exchange of O2 and nutrients b/w maternal blood and fetal BV (w/in chorionic villi)
In-flowing arterial blood = push deoxy blood --> endometrial veins --> back into maternal circulation
Fetoplacental circulation
Attached via umbilical cord
Transports O2 + nutrients to and from the mothers blood w/o mixing.
Umbilical cord has 3 vessels:
1 umbilical vein --> carries oxygenated, nutrient from placenta -> fetus
2 umbilical arteries --> carries deoxy, nutrient-depleted blood from fetus -> placenta
Maturation of the placenta
Continues to grow in thick and circumference until end of 4th month of gestation
Increased thick is due to length and branching of villi in chorion frondosum with expansion of the intervillous space
After 4th month… no increase in thickness anymore, but as the fetus grows, the placenta circumference compensates.
The feto-placental barrier is made by what?
extraembryonic membranes and placenta
The feto-placental barrier is created by?
syncytiotrophoblast that enclose the intervillous space
What are the 2 functions of the feto-placental barrier?
prevent maternal immune rejection (immune tolerance)
protects the fetus from pathogens (via vaginal canal) ARE ABLE TO CROSS
hCG is produced by what?
Produced by trophoblast cells (especially syncyn.) shortly after develop and invade decidua.
What is the function of hCG?
Sub LH and survives corpus luteum to continue to produce E + P
Changes in sex hormones during pregnancy: 1st trimester
Embryo implantation = 5-6 after ovulation
Corpus luteum starts to degrade ~10 days after ovulation
hCG appears 10th day ovulation (4 days after implantation to stop corpus from degrading
Changes in sex hormones during pregnancy: 2nd trimester
12th week development -- placenta produces enough P + E to sustain
hCG decreases + corpus degrades b/w 13-17th week of gestation
Changes in sex hormones during pregnancy: 3rd trimester
Increased P + E until end of pregnancy
Other hormonal changes during pregnancy by the endocrine glands: anterior pituitary gland
2-3 fold englargement
Other hormonal changes during pregnancy by the endocrine glands: ACTH
determines the lengths of gestation and timing of parturition *some is produced by the placenta
Other hormonal changes during pregnancy by the endocrine glands: P + E
suppress FSH and LH production
Other hormonal changes during pregnancy by the endocrine glands: TSH
increase TH by 40-100% increasing maternal metabolic rate, meeting nutrient demands.
Thyroxine can cross the placenta for the first 12 weeks to maintain thyroid function.
Other hormonal changes during pregnancy by the endocrine glands: ovary
since FSH + LH are suppressed there is no ovulation
After birth it takes 2 months-1 year for hormonal cycle to be restaured
Other hormonal changes during pregnancy by the endocrine glands: Prolactin (PRL)
mammary glands to produce milk
proliferation of glandular epithelial cells + presecretory alveolar cells of breast growth
After birth this is burst in response to suckling.
Progesterone
prepares and maintains endometrium by increasing blood flow in uterine lining and thick cervix
Estrogen
increases steady throughout, responsible for physiological changes that maintains the normal pregnancy and prepares the uterus for parturition.
Physiological changes: mammary glands
E + P + PRL, the breasts increase in size throughout pregnancy
Ducts, alveoli and mammary epithelium undergo hyperplasia in prep for lactation.
1st milk = "colostrum" appears in alveoli of the acinar glands as early as 2nd trimester
Physiological changes: Uterus
Uteroplacental blood flow x2 by mid-gestation due to spiral artery remodeling
Uterus is stretched to accommodate the fetus, placenta, and amniotic fluid causing hypertrophy of muscle cells of myometrium
Physiological changes: Cervix
Cervix softens due to CT remodeling
Cervical glands x2 in # and create a mucus plug acting as a barrier to protect the uterine contents from infection
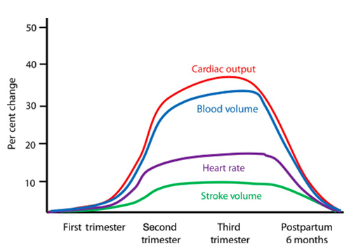
Circulatory system
Cardiac output increases as early as 5 weeks of gestation
CO increases 50% by mid-prego, as a result of increased HR + stroke V
Increase in blood B + RBC mass
Increase blood flow to placenta causes drop in total vascular resistance
These changes begin to reverse as early as 2 weeks postpartum
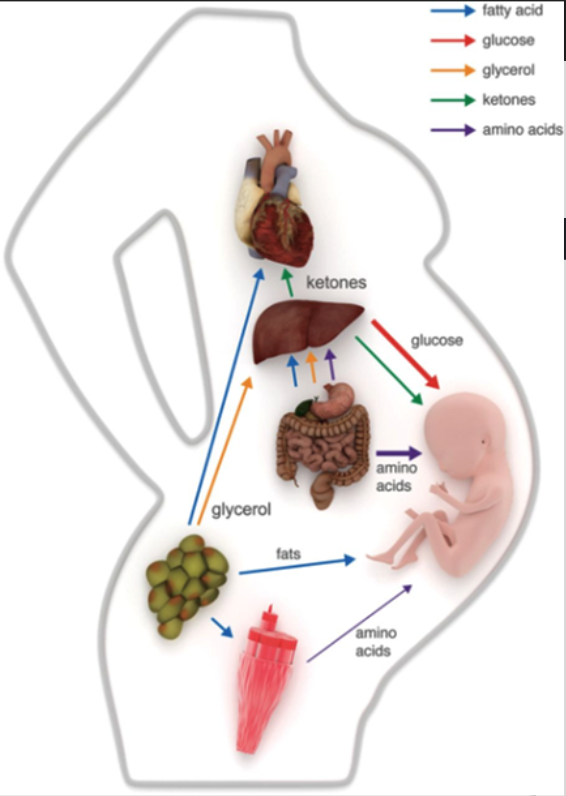
Metabolic system
Peak 3rd trimester -- phase of greatest fetus growth
starts anabolic → catabolic directing nutrients to fetus
Insulin resistance develops in early prego
Late prego -- maternal adipose tissue releases FA for use in liver + muscle
Liver = metabolise FA -> ketones used in brain, muscle, and fetus
Also uses glycerol + AA -> synthesize glucose for the fetus
MSK system
Lumbar lordosis
Increased joint mobility due to ligamentous laxity, specifically in the sacroiliac joints (facilitate delivery)
Stretch abdominal ligaments = diastasis recti
Immune system
Trophoblast cells produce factors suppressing maternal immune response
Immune tolerance prevents rejection of paternal antigens by the fetus
Makes women more susceptible to infectious diseases and less susceptible to inflammatory diseases.
uNKC secrete factors promoting early vascular remodelling and help fetal tolerance -- "critical for prego establishment"
# decline at midprego, reaching normal levels at term