GV-4 Cystic Fibrosis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is CF caused by?
- Recessive mutation in one single gene (CFTR).
What can CF cause?
Impaired function of organs with secretory function, eg:
- Eccrine sweat glands.
- Epididymis and vas deferens (males infertile due to blocked duct).
- Nasal polyps.
- Pancreas + digestion issues.
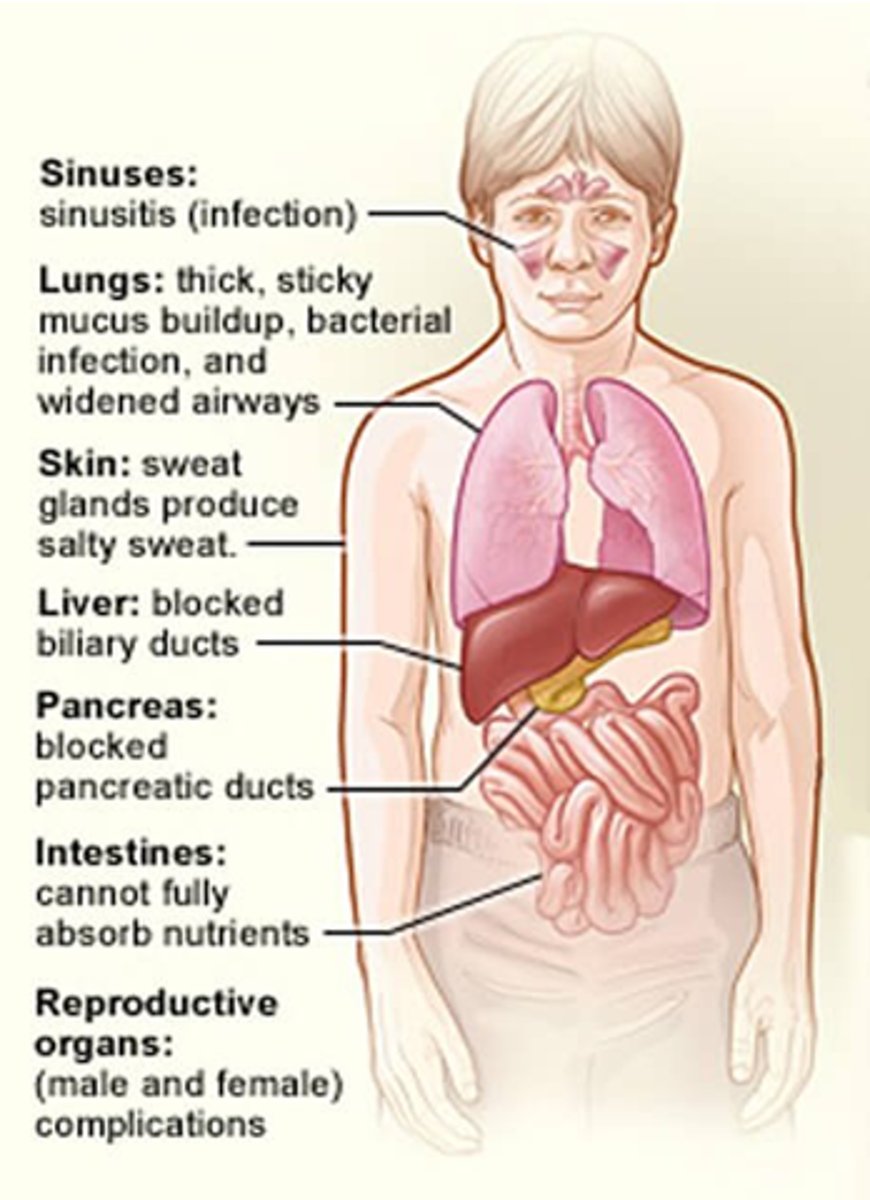
How can CF affect the lungs?
Thick, sticky mucus build up, bacterial infections and widened airways.
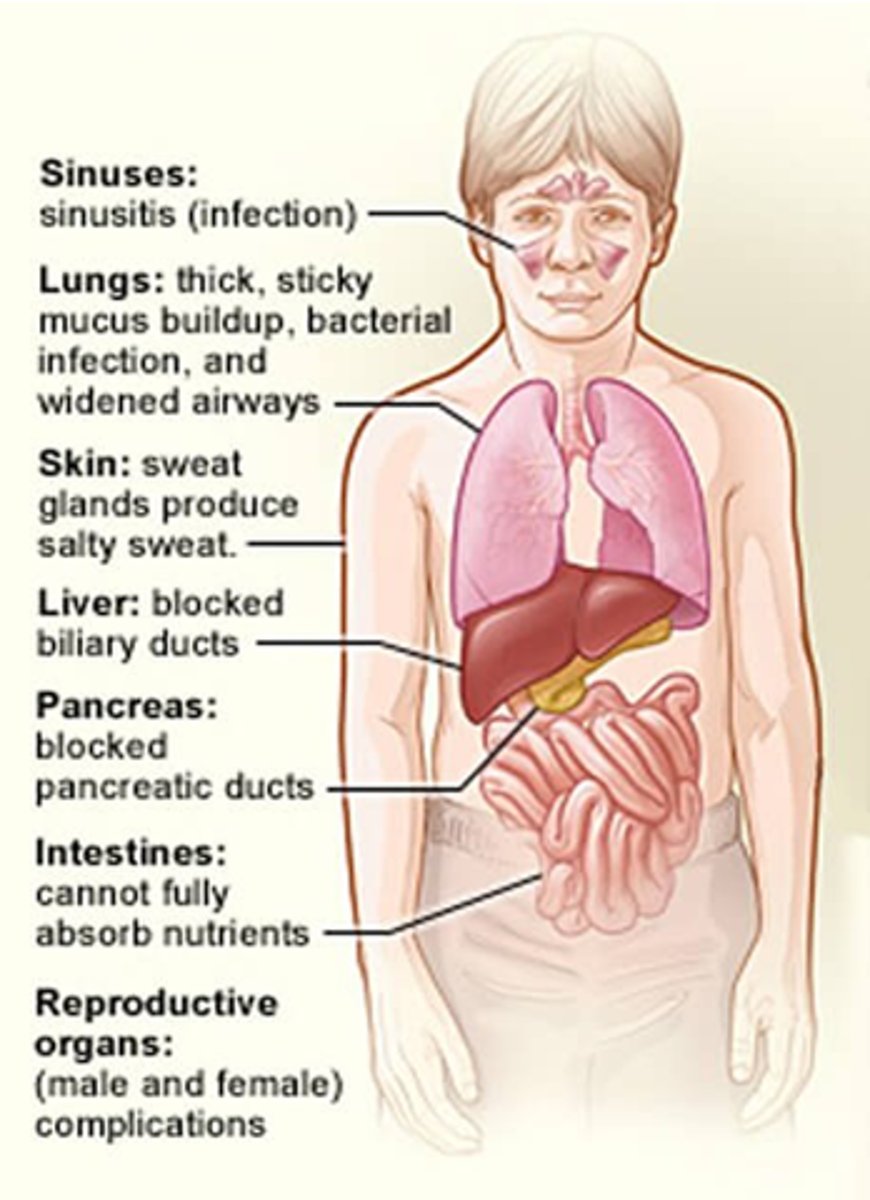
How can CF affect skin?
Sweat glands produce salty sweat (Cl- channels non-functional).
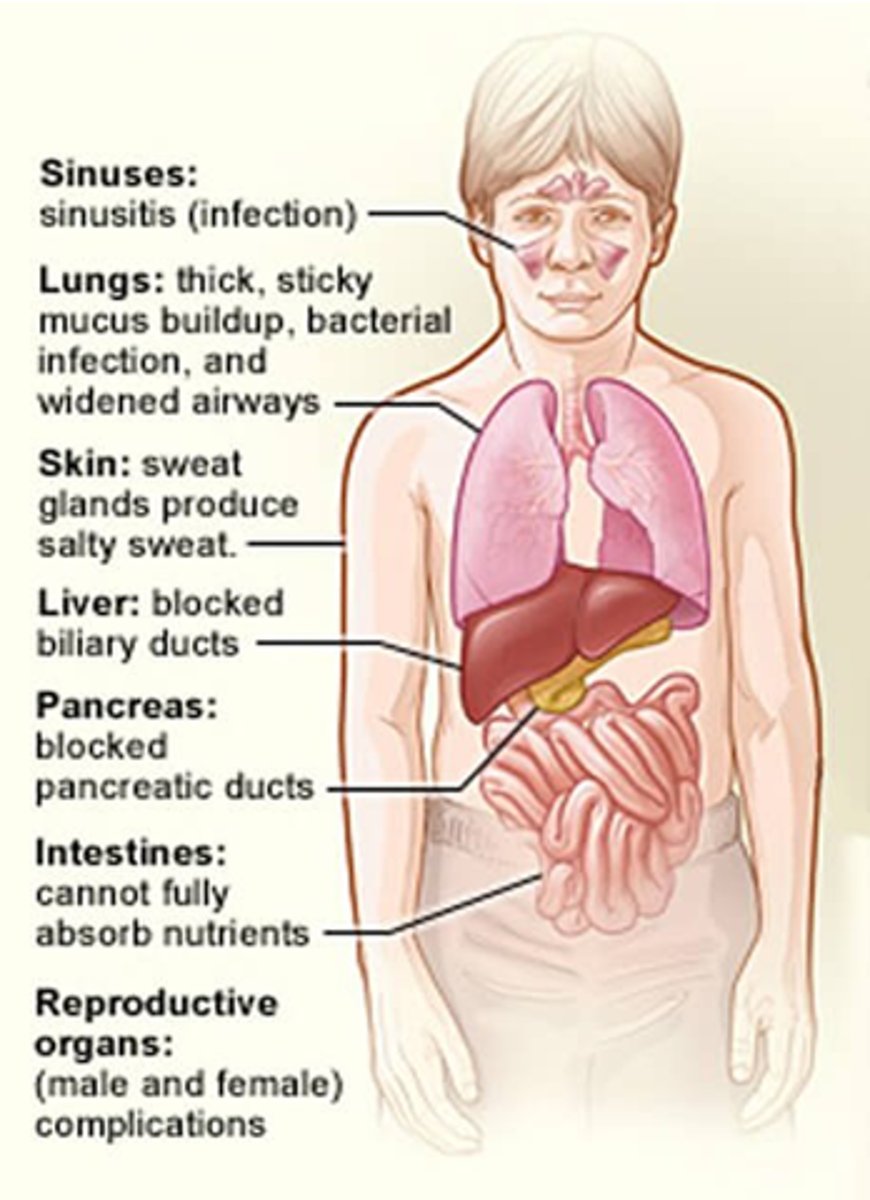
How does CF affect the liver?
It blocks biliary ducts
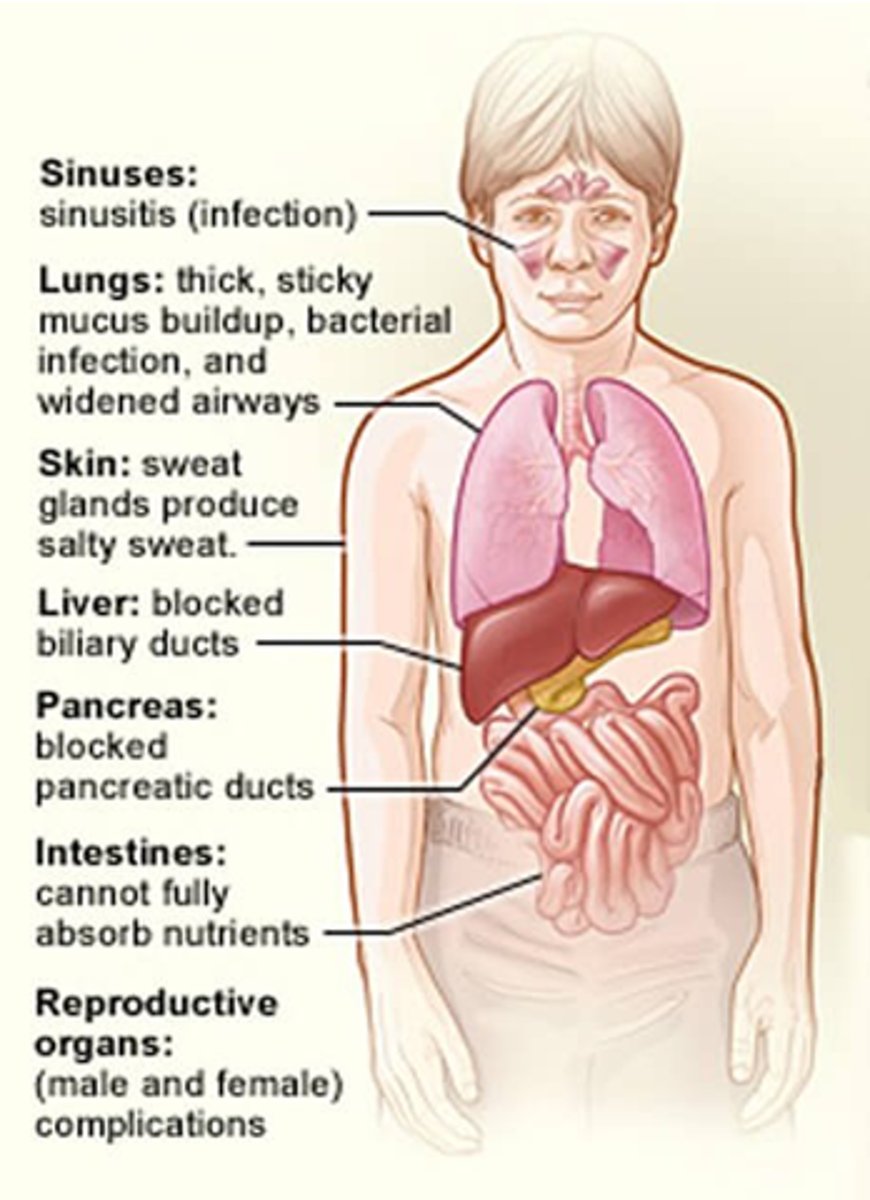
How does CF affect the pancreas?
- Block pancreatic ducts.
- Lack of pancreatic enzyme secretion.
- Reduced insulin.
How is CF screened for?
- ImmunoReactive Trypsinogen (IRT) Guthrie test - all newborns.
- Genetic screening.
- Sweat test.
What is the Guthrie Test (IRT)?
- Trypsinogen made by pancreas.
- Secretion into gut impaired in CF.
- So trypsinogen elevated in blood.

What are we testing for in the sweat test for CF?
Elevated skin Cl- levels.

Nearly all CF patients have pancreatic insufficiency due to lack of pancreatic protease, amylase and lipase.
So how do we avoid malnutrition?
Pancreatin!
- Lipase, protease, amylase enzymes.
- In enteric capsules to overcome GA inactivation.
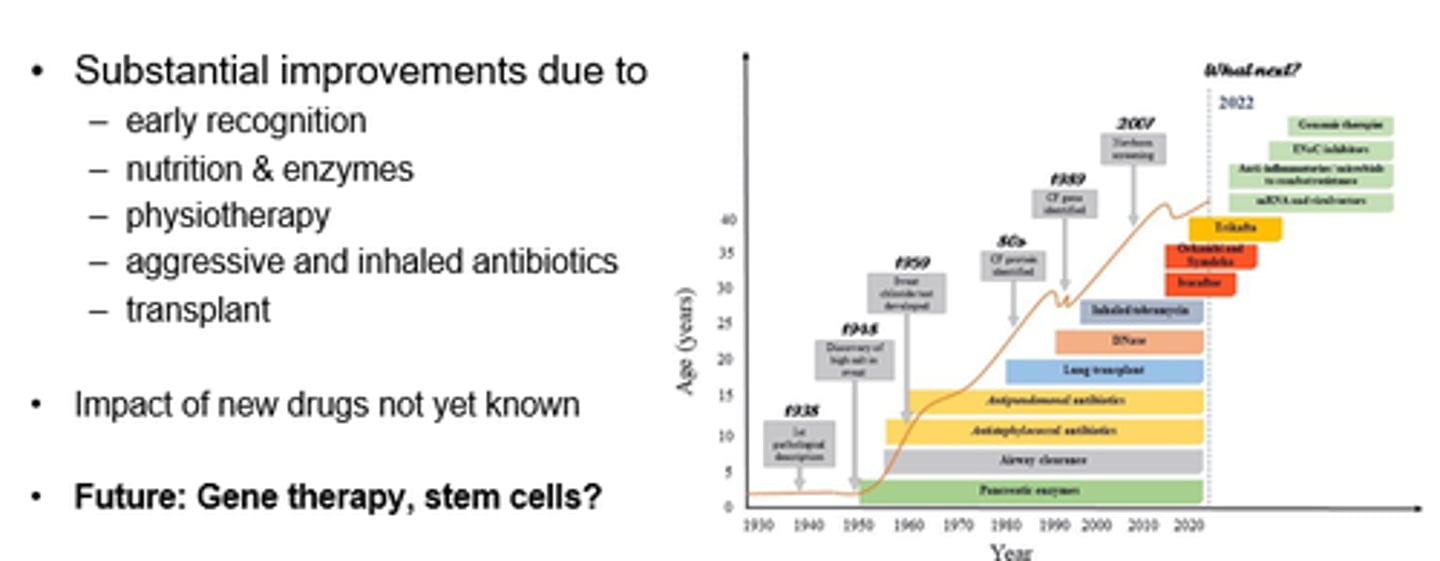
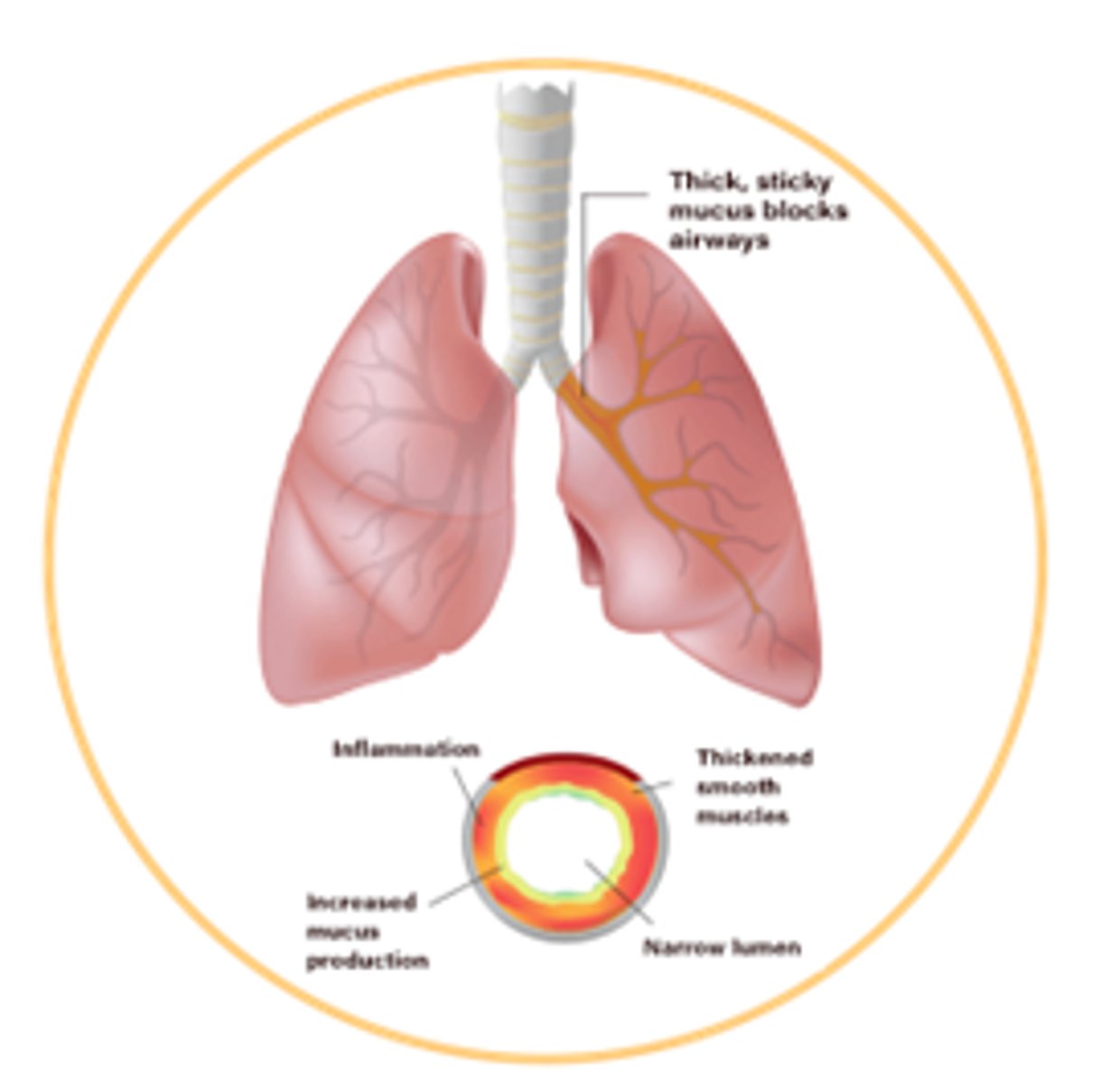
Why is lung disease now the main mortality cause in CF?
- Mucus plugging and structural changes.
- Massive neutrophil infiltration in airways.
- Inflammatory damage to airway tissue.
- Decline in lung function.
- Epithelial damage.
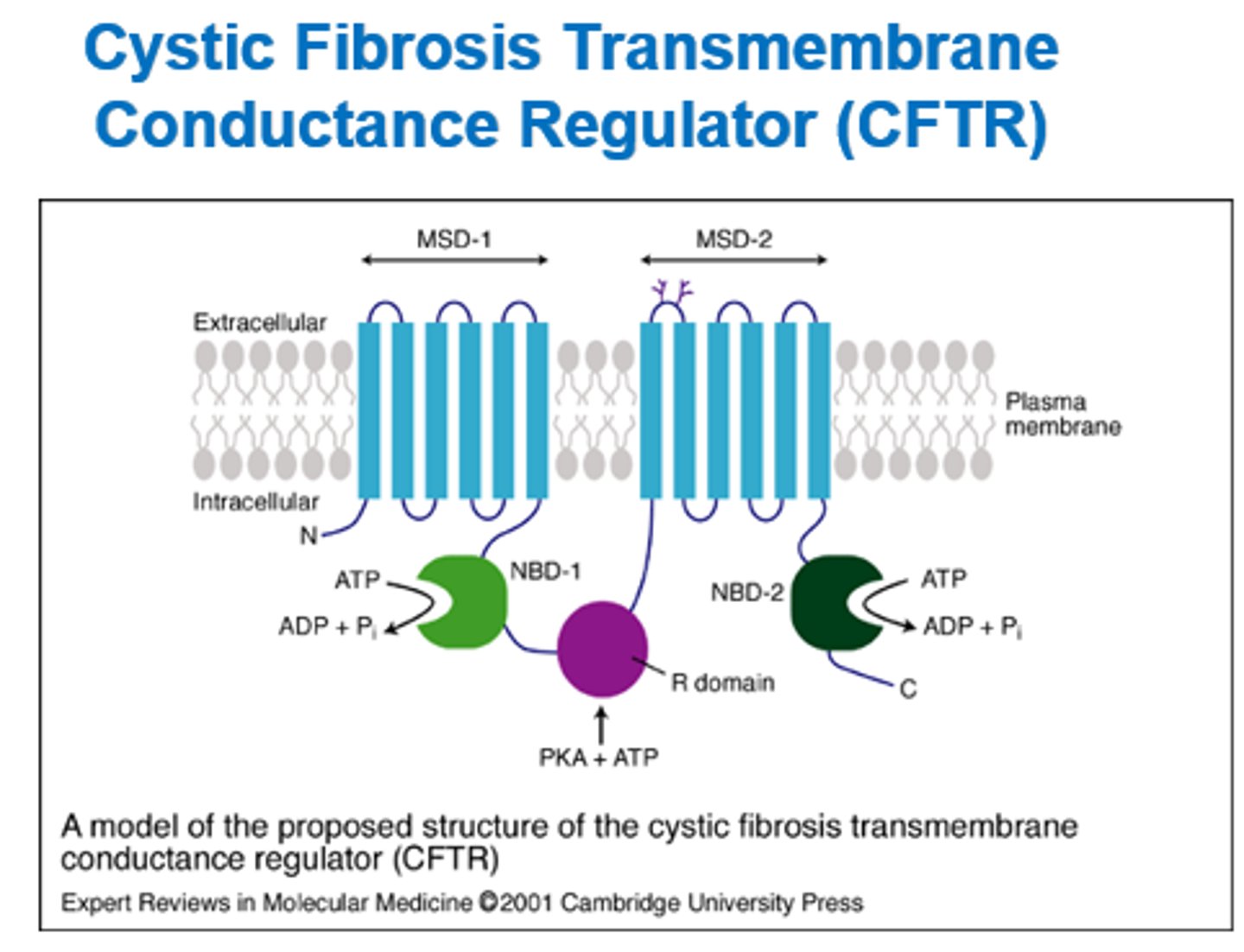
What is the CFTR and what does it do?
Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane conductance regulator.
- Ion membrane channel that controls Cl- movement from inside to out of cells.
- Nuclear binding domains regulate opening and closing.
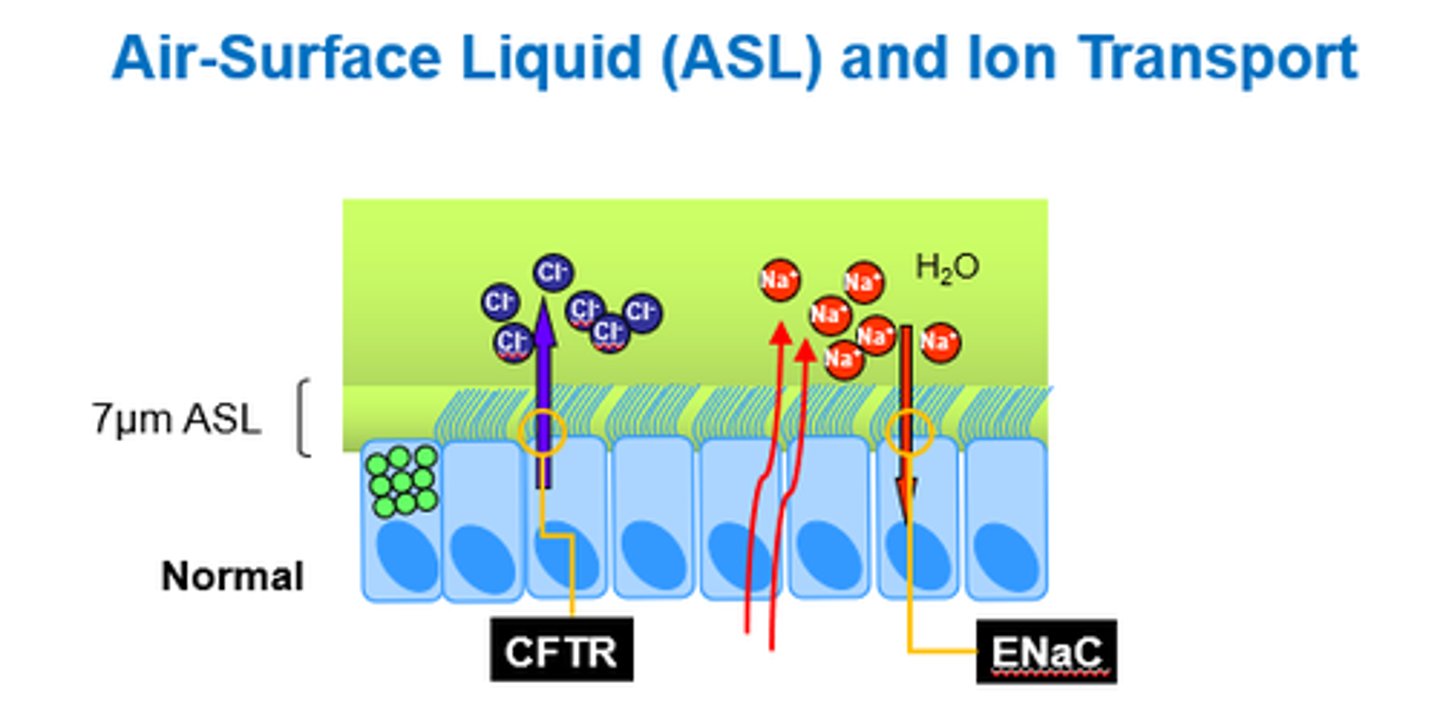
How does the CFTR ion channel normally function?
- CFTR channel opens and Cl- moves out.
- Na+ and water also move out.
- Causes airway hydration.
- ENaC (epithelial Na channel) opens, and Na+ goes back in (with water)
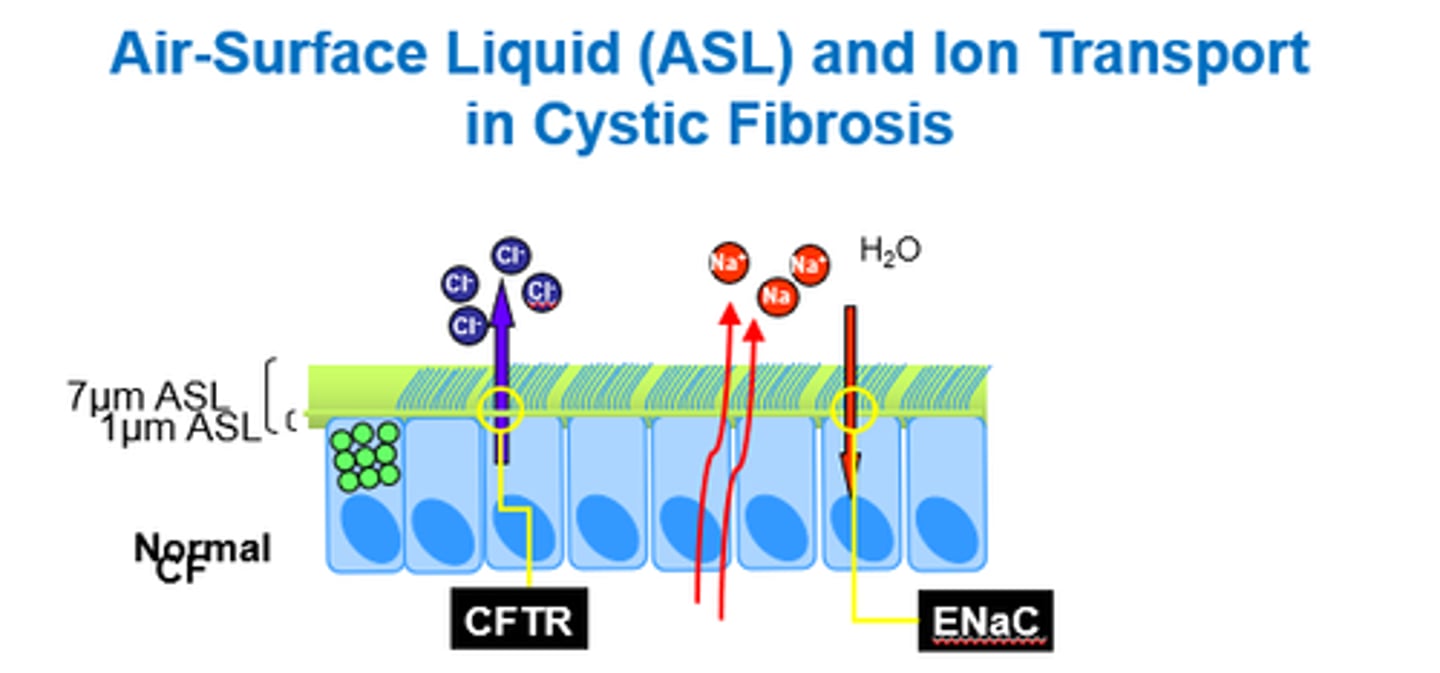
How does the CFTR channel functio in CF?
- Problems with channel openings.
- Less Cl- moves out.
- So less Na+ and water move out of cell.
- Doesn't affect mucus production, but water isn't there to dilate it down, so it gets extra thick and sticky.
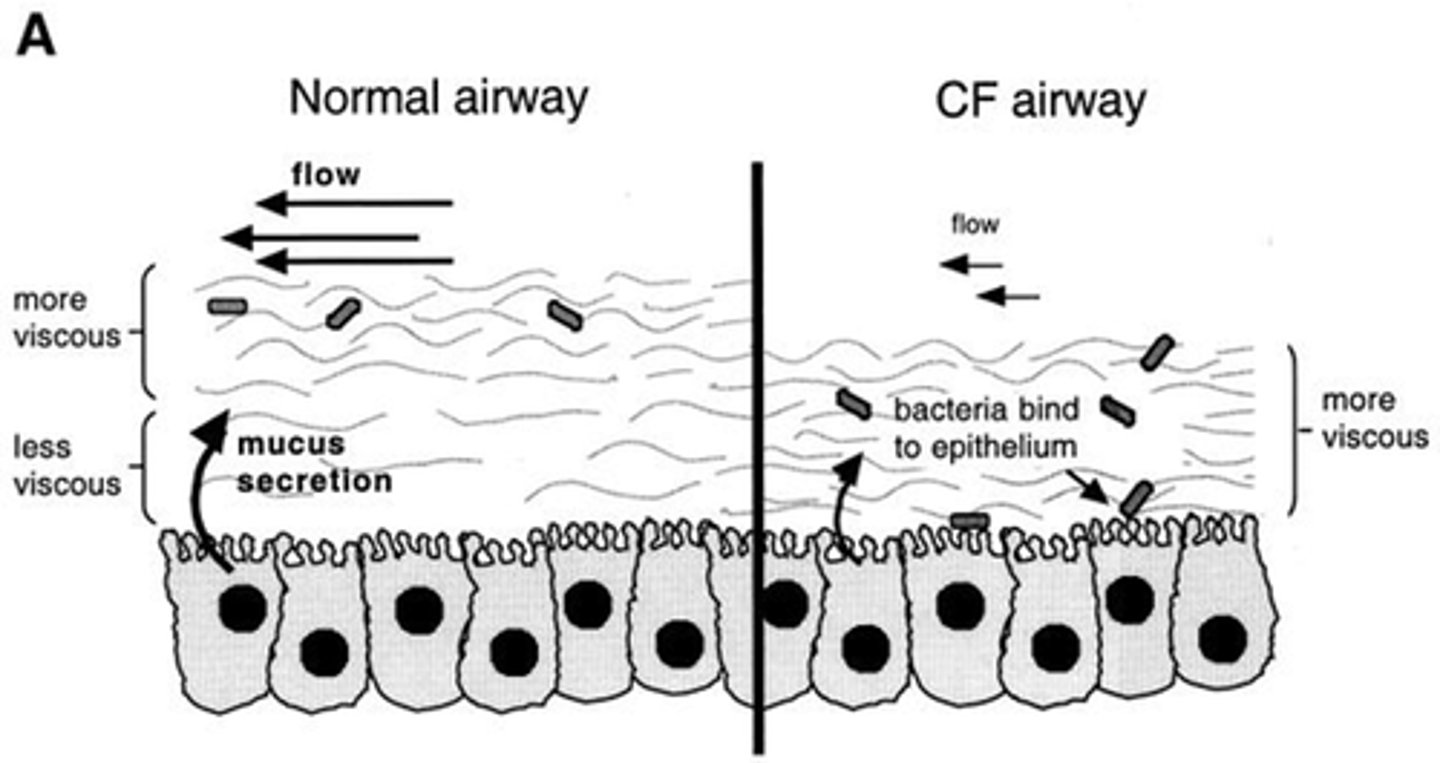
Why is mucus sticky in CF?
- Due to low water volume.
- Less water moves out of cells with Na+ and Cl- due to faulty channel.
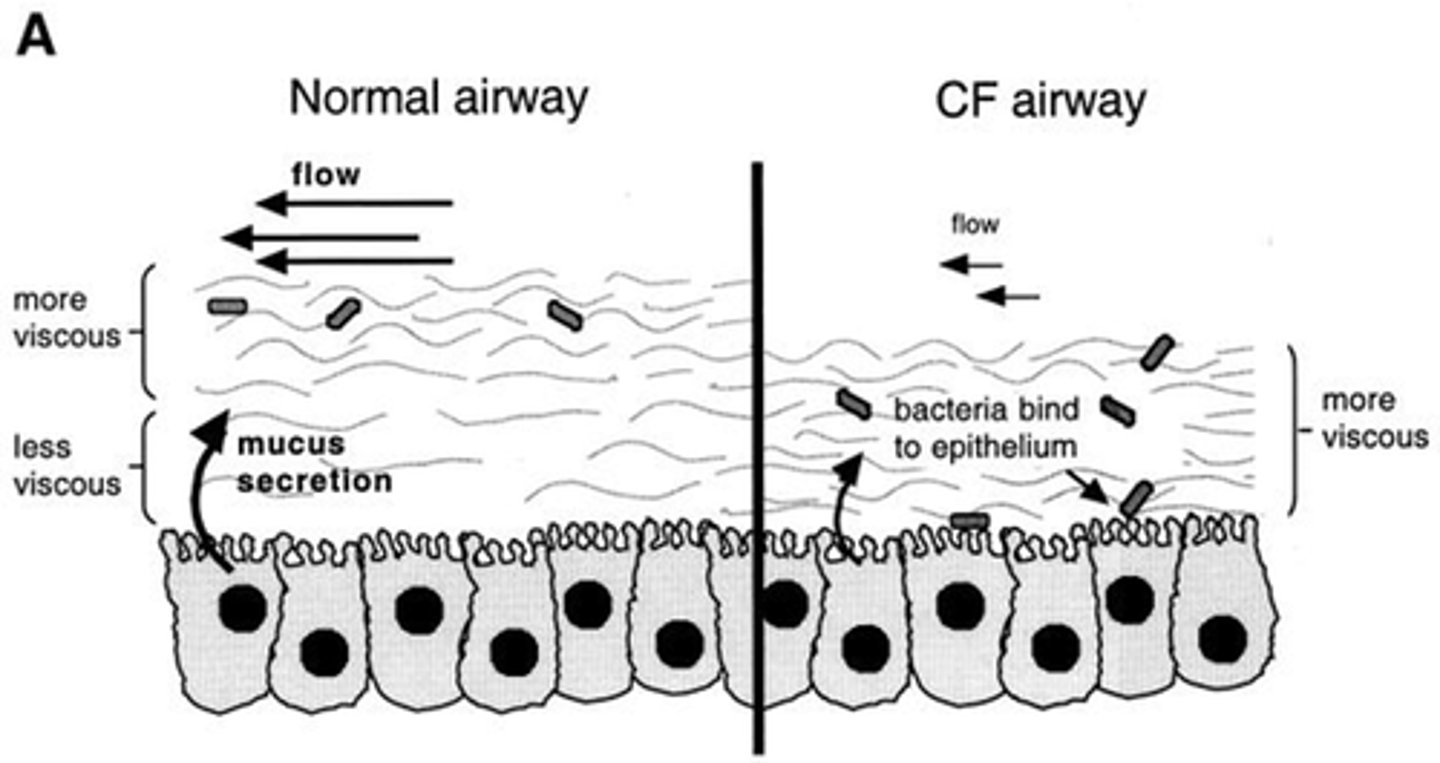
Why is viscous, sticky mucus a problem in CF?
- Makes it hard to clear - obstruction.
- Makes bacteria hard to clear - infection risk increases.
- Provides growth environment for bacteria.
How can we attempt to treat sticky mucus in CF? Why is this not that effective?
Give saline - ENaC are active so it gets cleared quickly.
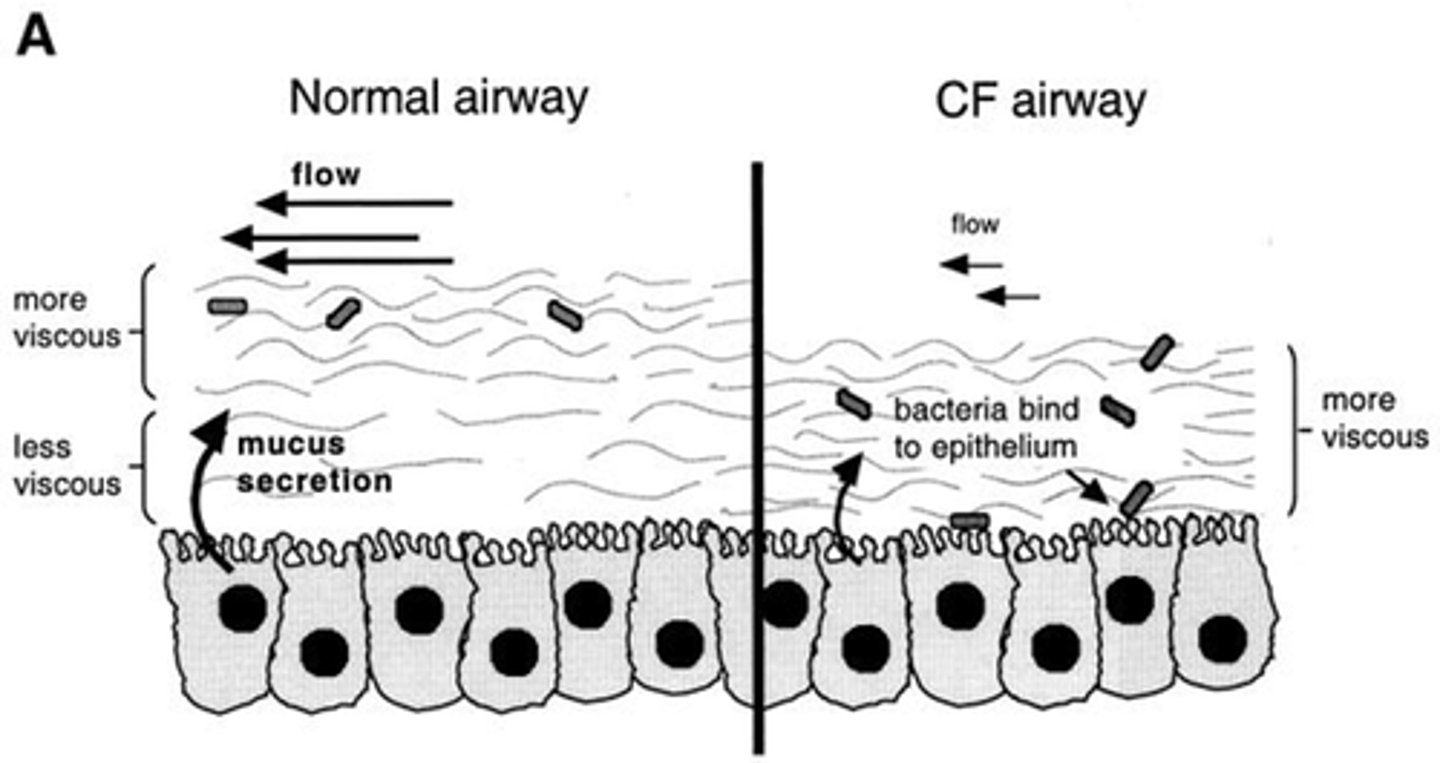
What are some common bacteria that cause lung infections in CF?
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenza.

What are some established therapies in CF?
- Pancreatic enzyme supplements eg Creon.
- Abx against pathogens eg inhaled Tobramycin.
- Beta-agonists (to activate residual CFTR activity?).
- Osmotic agents: Hypertonic saline, mannitol.
- Mucolytics.
Name some mucolytics that can be used in CF.
Recombinant DNAase:
- breaks down very viscous mucus.
- CF mucus contains large amounts of DNA from inflammatory cells and bacteria.
N-acetyl cysteine.
How are antibiotics used in CF?
- Prophylactic flucloxacilliin in infants ( for S. aureus).
- Regular swab or sputum cultures.
- Early oral or IV interventions.
- Inhaled abx useful - direct to site of action, minimise off-target fx.
What is the main approach to treating CF?
Targeting CFTR gene mutations.
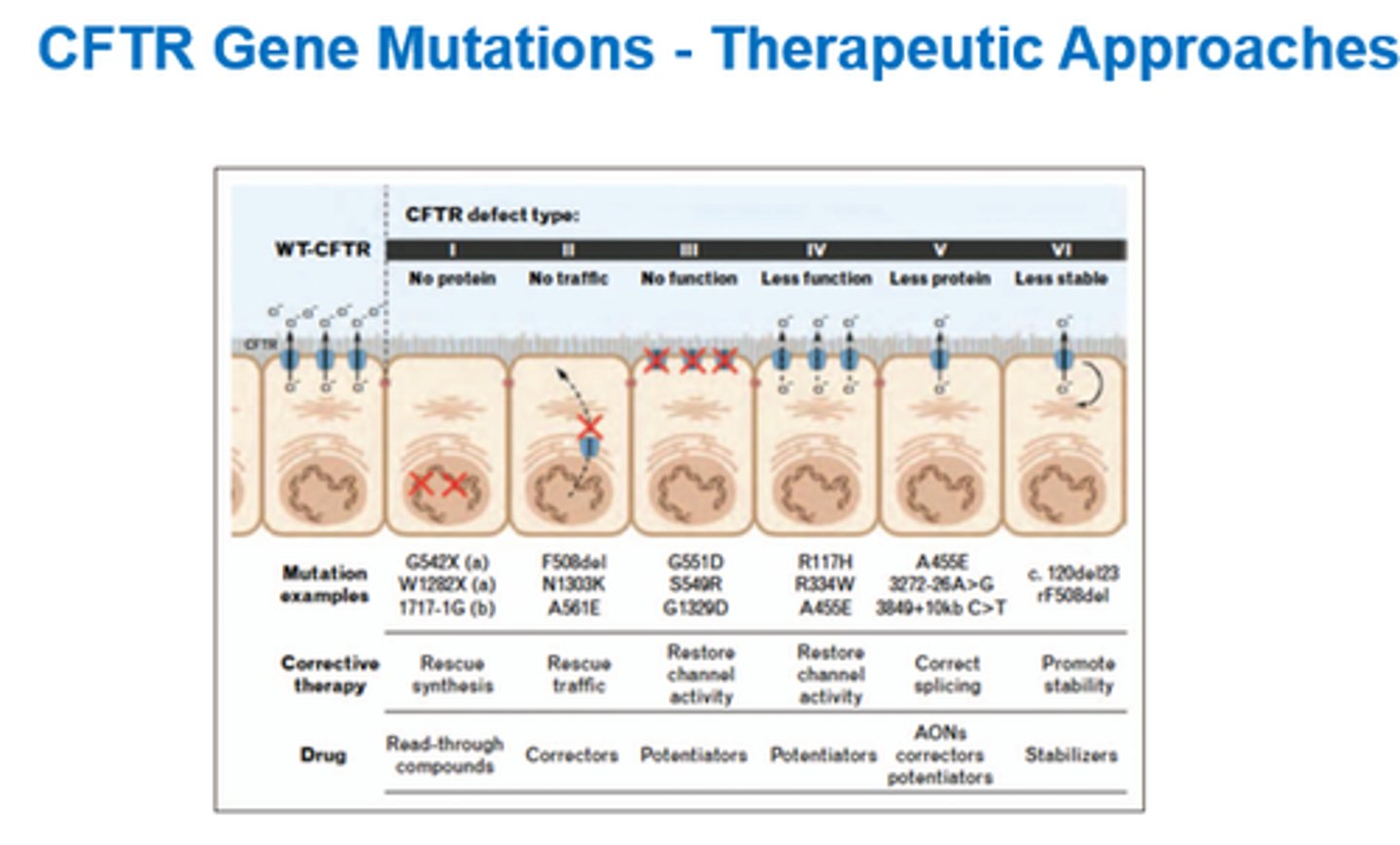
What are 4x types of CFTR modulators?
- Correctors.
- Potentiators.
- Amplifiers.
- Stabilisers.

What do Correctors do?
Overcome folding defects.

What do Potentiators do?
Modulate gating characteristics.

What do Amplifiers do?
Enhance the amount of functional protein.

What do Stabilisers do?
Maintain protein shape and function.

What type of CFTR modulator is Orkambi?
Corrector + Potentiator

What type of CFTR modulator is Symdeko?
Corrector + Potentiator

What type of CFTR modulator is Trikafta/Kaftrio?
2x Correctors + a Potentiator

What are CACC activators?
Calcium-Activated Chloride Channel activators.
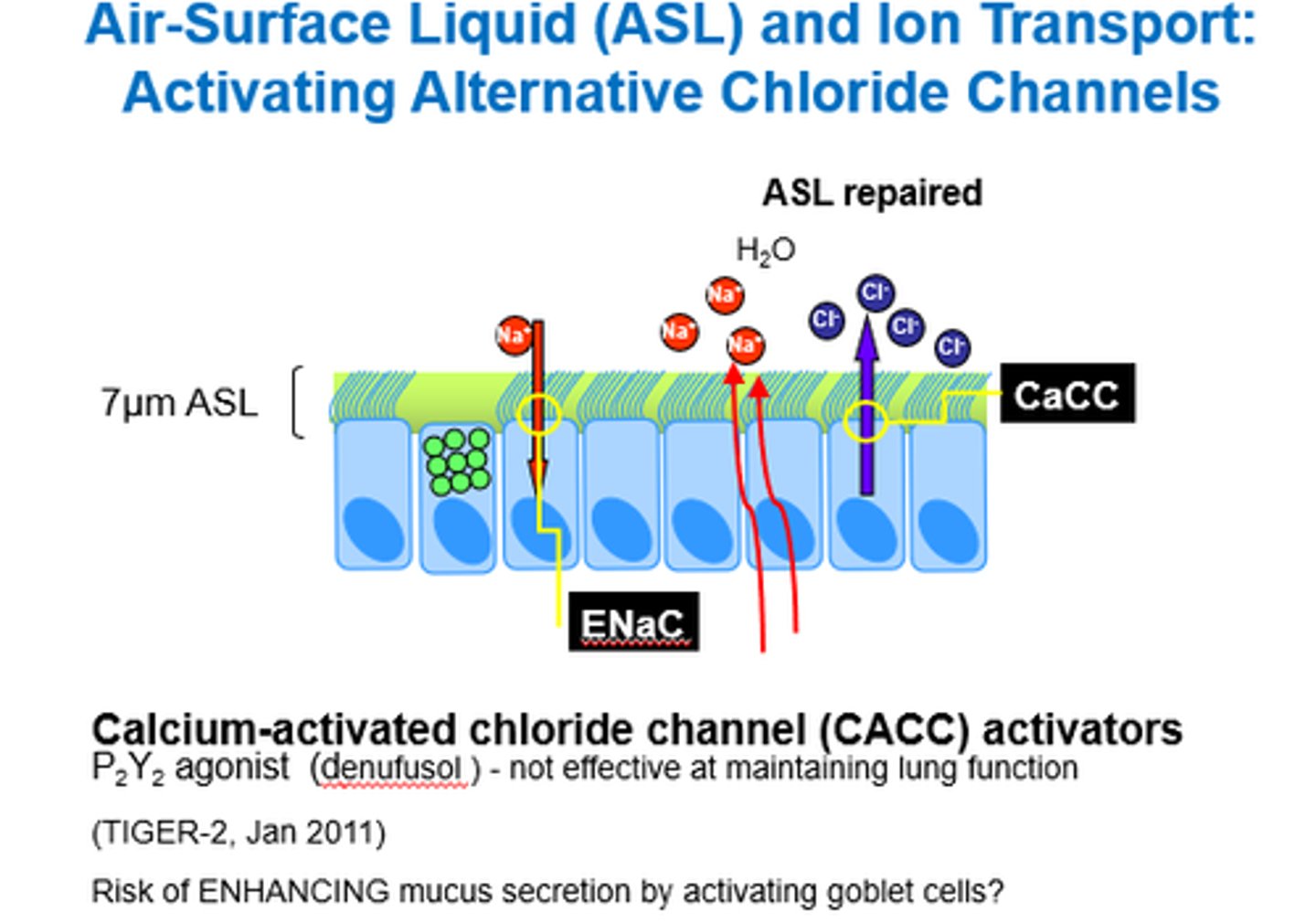
What do CACC Activators do?
How effective are they?
Activate alternative chloride channels.
- Not as effective bc channel also involved in secreting mucus from goblet cells.
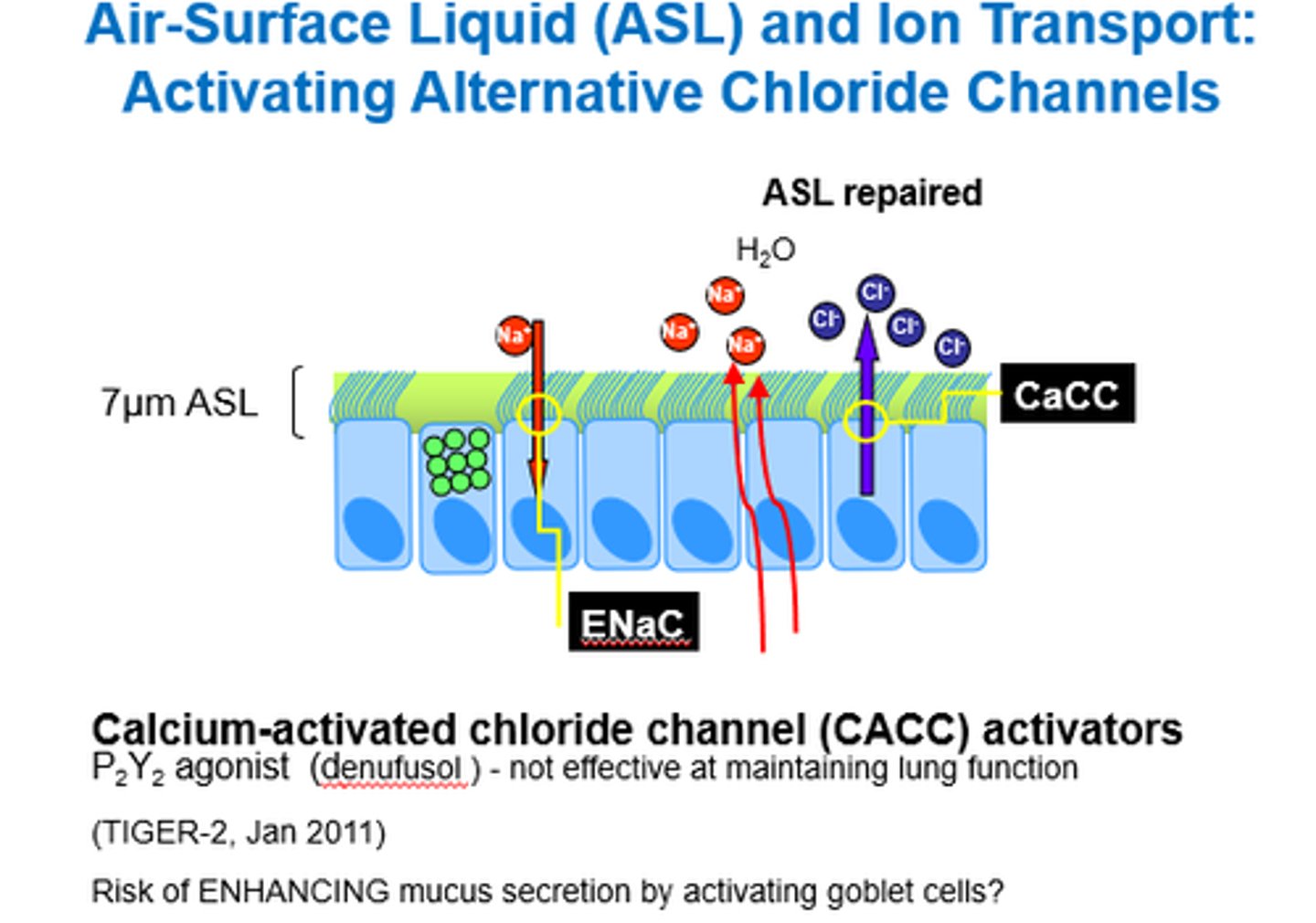
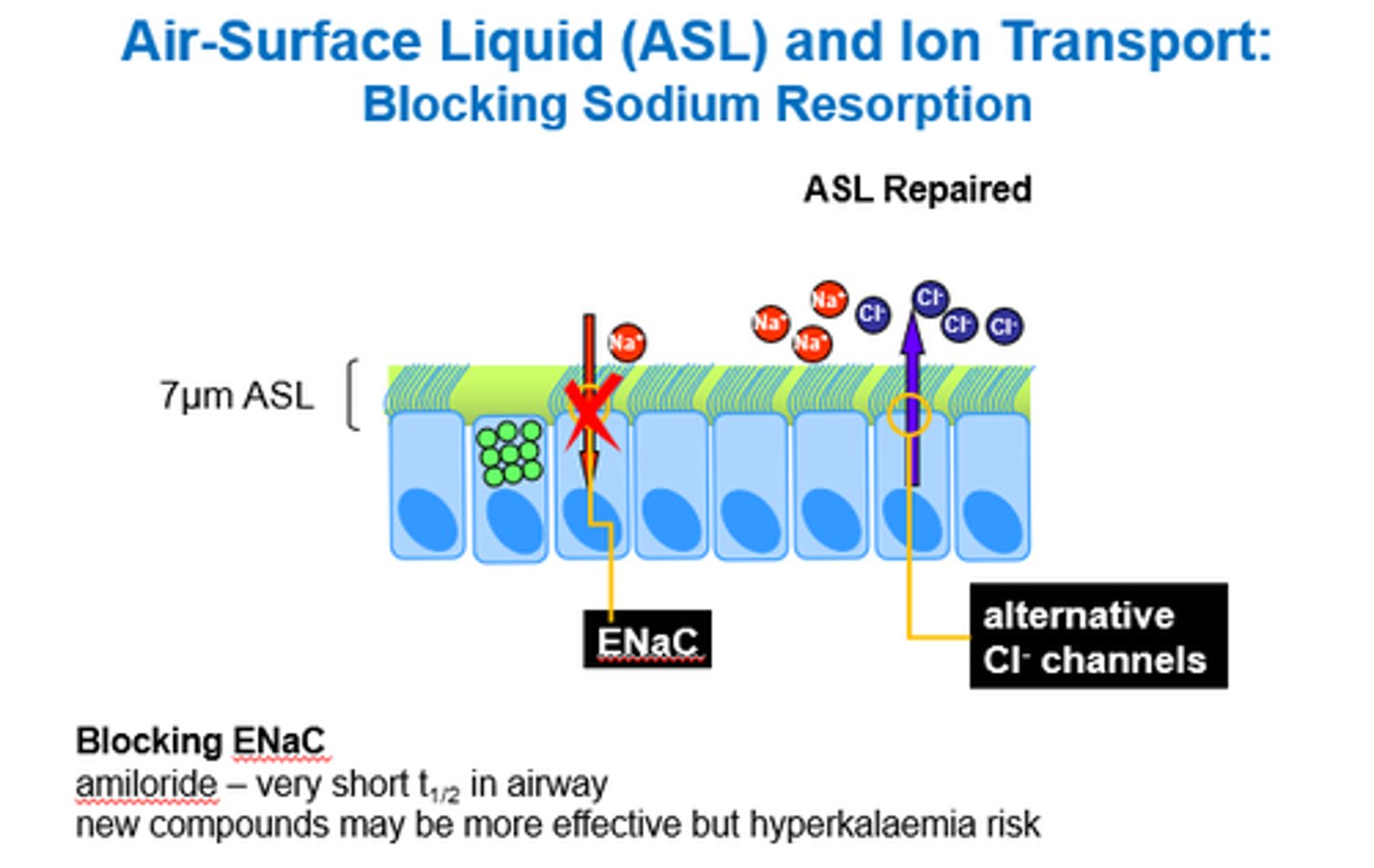
What can we use Amiloride for in CF?
Blocking ENaC (Epithelial Na Channels).
Na channel blocker!
Name some anti-inflammatory therapies that can be used in CF.
- Glucocorticoids.
- Macrolides - azithromycin?
- High dose Ibuprofen.
- Brensocatib which inhibits neutrophil elastase.

Summarise how we can manage CF.
- Nutrition management with enzyme supplements.
- PERT - oral Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy.
- Abx.
- Anti-inflammatory therapies (NSAIDs/GCs).
- Mucus hydration (hypertonic saline).
- Mucolytics.
- CFTR modulators.
- CACC activators.
- ENaC blockers.