L5 Patterning the Embryo (Imported from Quizlet)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
The many anteroposterio genes in drosophila can be broadly grouped into a ...?
Hierarchy
What do initial material gradients result in?
Expression of Gap genes that define different regions in the embryo
What do Gap genes lead to?
Periodic expression of the pair-rule genes -> these specify the so called para-segments and foreshadow segmentation of the larva
What do the segmentation genes elaborate and when does this happen?
Patterning within each para-segment, patterning of these segments happens when the embryo has cellularised -> cell-to-cell signalling is essential to coordinate this patterning process
A final group of genes are the ______ _____ genes and they determine the _______
Homeotic selector, identity
A gradient of nuclear localisation of the dorsal protein is _____ on ventral side and ____ on dorsal side
High, low
The promotors of important D/V genes require what to be activated
Different levels of dorsal protein
The promoters of _____ and _____ genes have ____ affinity dorsal binding sites
Twist, snail, low
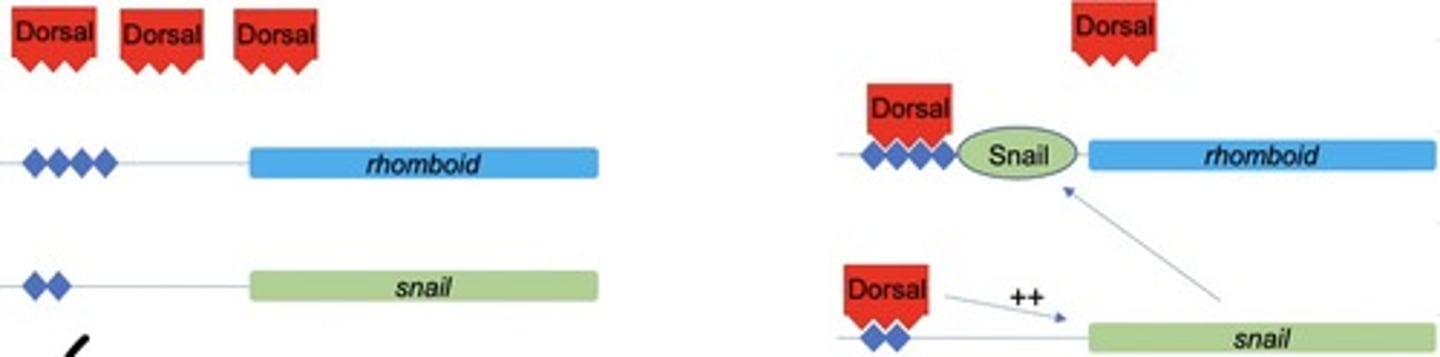
Promoters of twist and snail are only expressed when a ____ level of nuclear dorsal is present and make _________
High, mesoderm
Rhomboid has _____ affinity dorsal binding sites in its promoter, it is ________ by twist and snail
High, repressed
Rhomboid is expressed _______ on both sides of ______ and make _________
Laterally, mesoderm, neuroectoderm
The nuclear gradient of dorsal leads to expression of what?
Different genes along the D/V axis
Dorsal is a _______ _____ and can work in this way because different genes have different ______ _______
Transcription factor, activation thresholds
Low level of nuclear dorsal = ?
Rhomboid expression
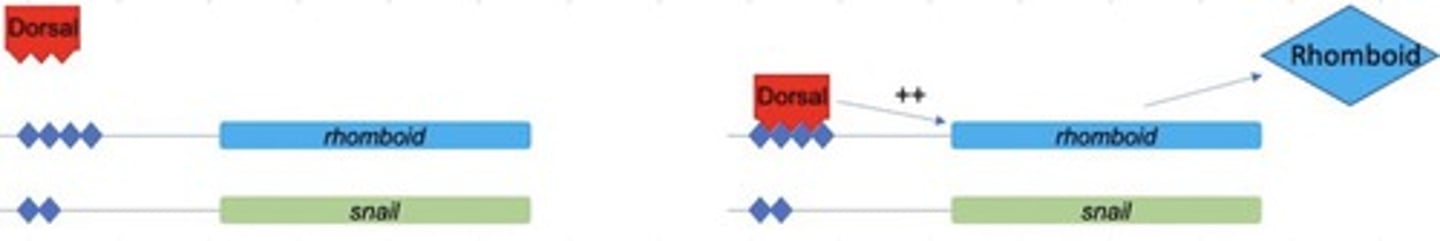
High level of nuclear dorsal = ?
Snail expressed, interferes with rhomboid expression
What act together in a complex manner in the dorsal ectoderm to set up a second signalling centre on the dorsal side of the embryo?
Decapentaplegic (DPP), short gastrulation, tolloid, twisted gastrulation, screw
The second signalling centre on the dorsal side of the embryo's signal is conserved in vertebrates, what is this signal known as?
BMP signal
The antero/posterior gradients of bicoid and nanos lead to what?
Activation of a number of genes encoding transcription factors which are known as Gap genes
A primary target is the ________ gene, together with bicoid set up the expression of other ______ genes
Hunchback, Gap
What kind of code do Gap genes create and what does it define?
They create a combinatory code that defines different regions in the embryo
What are Gap genes required for?
Striped pair-rule expression
The gap genes lead in the next step to expression of the _____-_____ genes in a ________ manner
Pair-rule, segmented
The striped expression of that prefigures segments of the embryo is not driven by a ______ ____-____ _____ rather each stripe is driven by a specific ___ ____ _________
Periodic wave-like process, gap gene combination
Each individual stripe is generated by what?
A specific gap gene combination
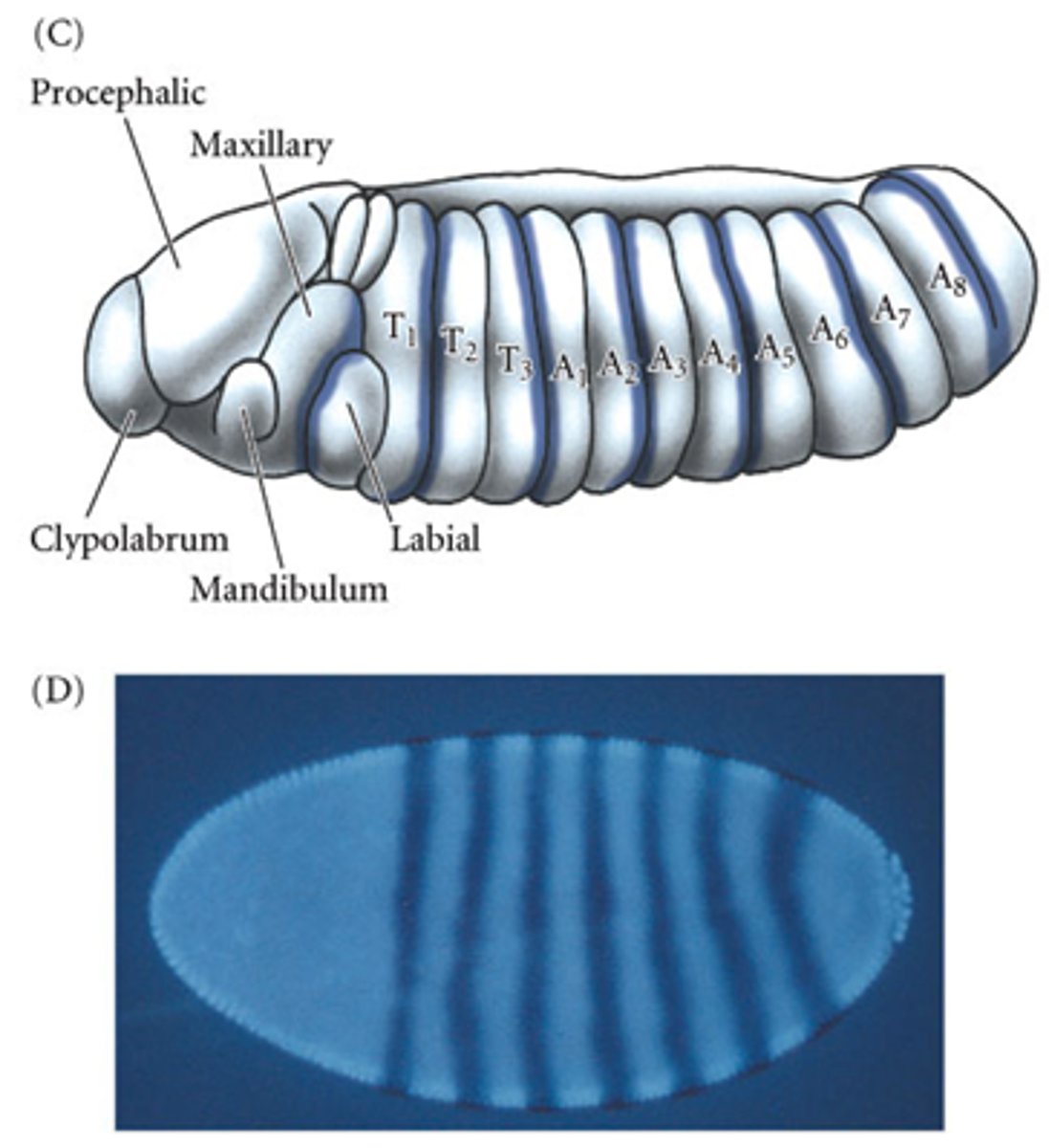
Pair-rule expression stripes are slightly _____ relative to the visible segments
Shifted
The anterior part of the even skipped expression stripe forms the _______ of the A larval segment
Posterior
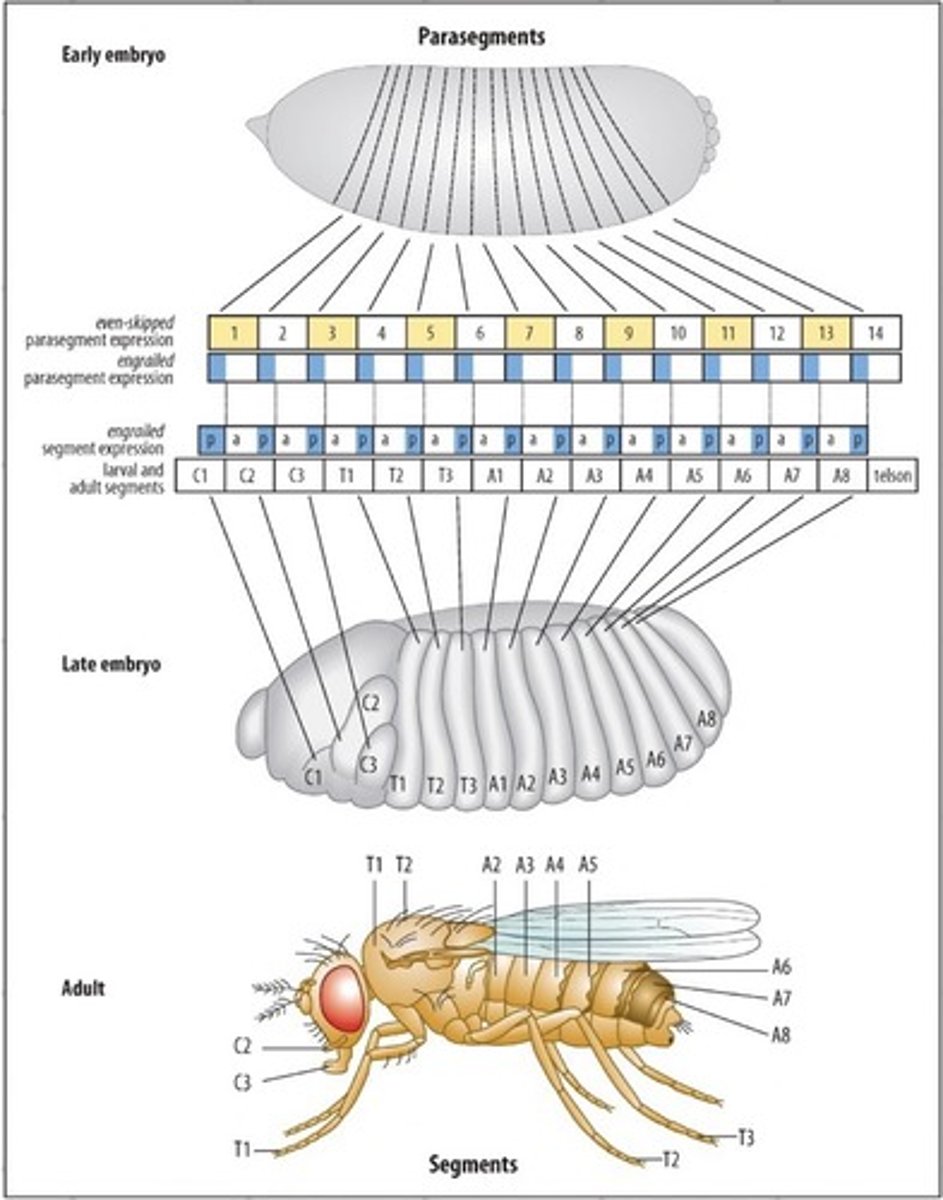
The pair-rule gene expression stripes are known as ...?
Para-segments
The stripes of gene expression do not exactly correspond to what?
The visible segments that are formed during segmentation
The segmentation gene elaborate what?
The pair-rule pattern into a segmentation pattern
High levels of Ftz or Eve switch on ________ -> 14 stripes
Engrailed
High levels of Eve and Ftz drive expression of a ______ _____ which leads to formation of __ _______, one in each segment
Transcription factor, 14 stripes
What is directly driving the pattern of the cuticle?
The 14-striped expression of engrailed and some other genes
The future visible segments are formed with the _______ ______ cells forming the ________ ______ of the segment, by this time the embryo has been cellurlarised
Engrailed positive, posterior boundary
In addition to the transcriptional regulator engrailed (En) two highly important signalling proteins are expressed in adjacent cells, what are they?
Wingless (Wg) and Hedgehog (Hh)
Wingless and hedgehog are first expressed under the influence of the ____-____ gene then as a result of a ______ ____
Pair-rule, feedback loop
Expression of Wingless is maintained by ...?
Hedgehog
Expression of engrailed and hedgehog is maintained by ...?
Wingless
By the time intra segment patterning happens, what has happened to the embryo?
It has cellularised
In order to coordinate patterning, what do these coordinating signals need to do?
Act across all cell membranes
The future segments are formed with _______ ______ cells as the ______ _______
Engrailed positive, posterior boundary
Wingless and hedgehog are protein signals that ...?
Act across cell boundaries
The precise pathways used by Wg and Hh to influence transcription in drosophila are also important in other multicellular organisms (True or False)
True
What does reduced or aberrant activity of Wg or Hh lead to?
Variety of congenital defects
What does inappropriate activation of Wg and Hh cause?
Cancer
The segments are unique elements that often have unique structure depending on what?
Their position along the A/P axis
What do homeotic selector genes (Hox genes) do?
Specify their identity
How were hox genes discovered?
Through sometimes bizarre mutations in drosophila
What is meant by homeotic mutations?
One structure is replaced with another
In most organisms the hox genes are a single complex, known as what?
The hox complex
In drosophila the hox complex is broken into how many pieces?
2
What does the order of hox genes on the genome reflect?
Their spatial and timing of expression
3' first and most _______ and 5' last and most _______
Anterior, posterior
The hox gene complex is highly conserved in most organisms, humans have _ complexes -> that is thought to be the case because during the evolution of the vertebrate 2 whole genome duplications have occurred
4
In the lineage leading up to the fishes a 3rd duplication has occurred and they have even more hox complexes than humans (True or False)
True
What is the bithorax complex responsible for?
Diversification of the posterior segments
Example: bithorax complex with regulates more posterior development
If all 3 genes with name Ubx, AbdA, AbdB are lost you can see that most segments (excluding the extreme ones) take on a T2 fate, a "default state"
Then if you start adding different genes back -> segments are formed, a complex sort of combinatorial code
Although in vertebrates the situation is much more complex as there are 4 hox complex they are also important for what?
Assigning regional identity in the A/P axis