Chap 6 blood / hematopoiesis (part 2)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
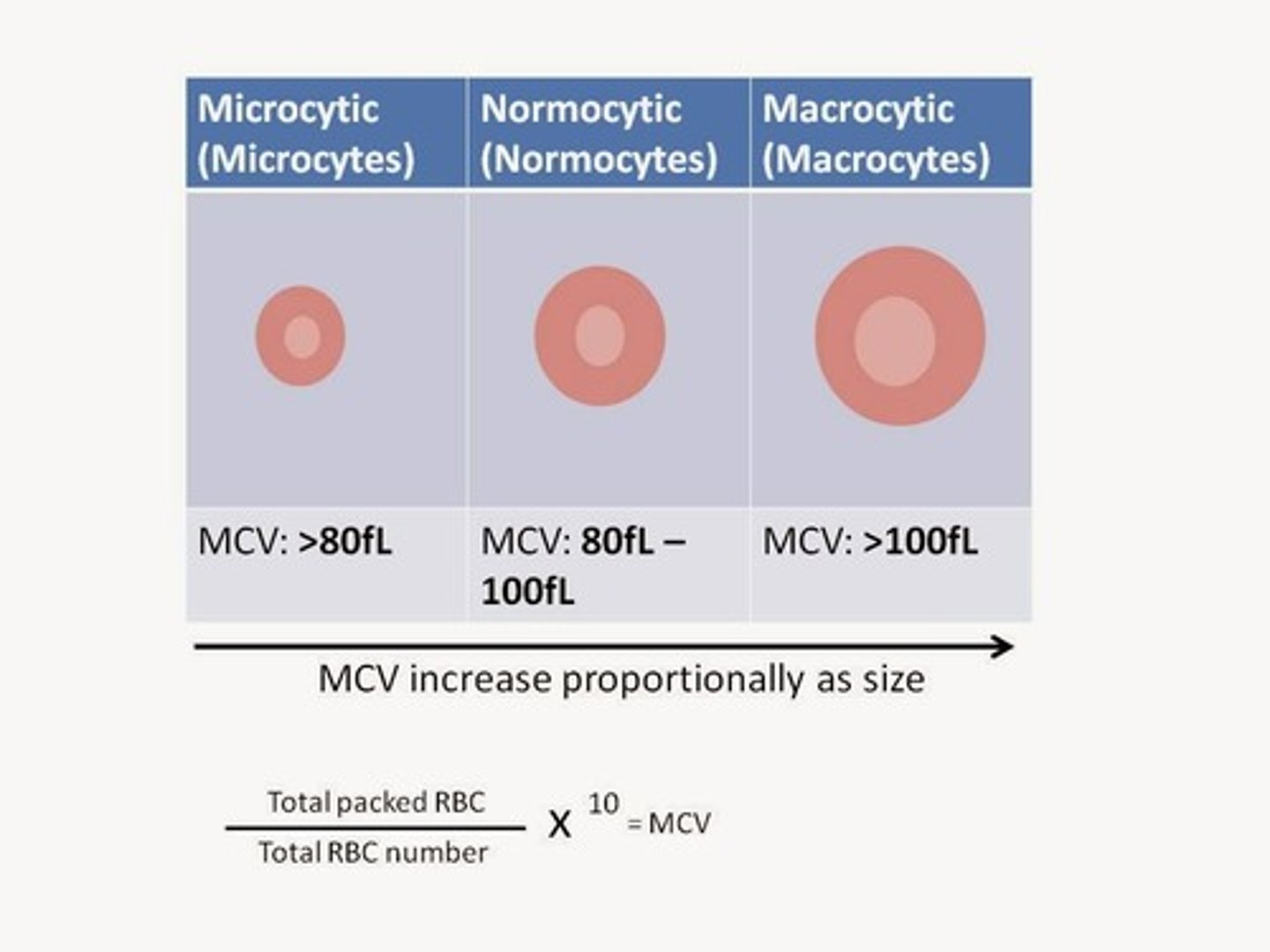
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
Indicates the oxygen-carrying capacity of blood
80-100
Pagocytosis
Engulfing of foreign solids by (phagocytic) cells.
antigen presenting cells
immune cell that boosts immune responses by showing antigens on its surface to other cells of the immune system
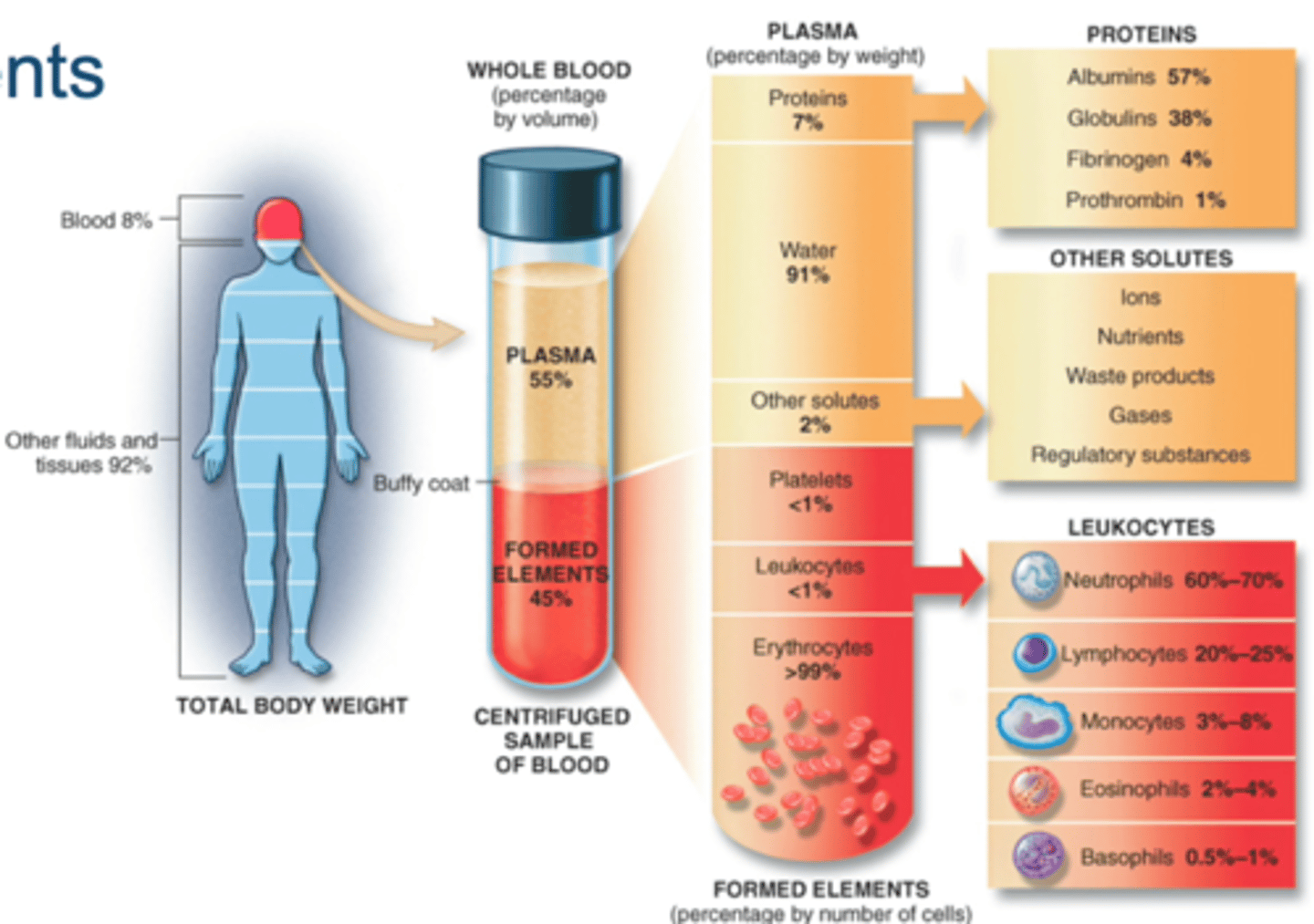
formed elements
red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets
RBC (erythrocytes) diameter and thickness
- size = 7-8 µm diamerter
- thickness = 12-25 µm thick
RBC (erythrocytes) structure
- has a biconcave structure
- has no nucleus
- has no mitochondria (its anaerobic)
- does not go through mitosis
- gets darker as you move away from the center
- is eosinophilic (no basophilic nuclei)
- cytoplasm is filled with hemoglobin
----------------------------------
Wright and Giemsa stains both use methylene blue and eosin to view RBC
----------------------------------
- transports, oxygen and carbon dioxide
RBC (erythrocytes) biconcave structure
it's biconcave because it allows for more surface area
----------------------------------
the more surface area the more volume
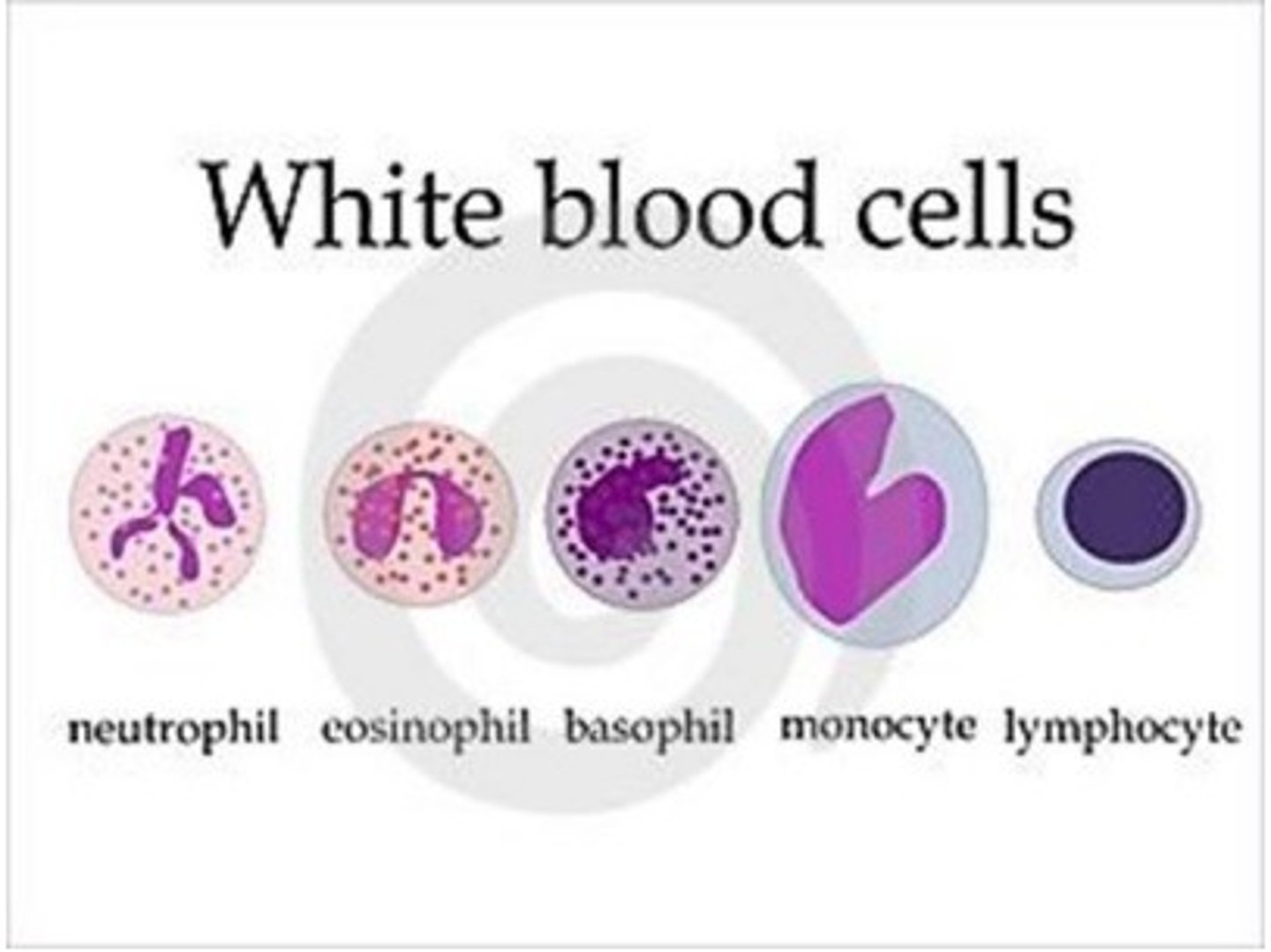
WBC (leukocytes)
The fucntion is to recognize antigens, produce antibodies to fight infections
----------------------------------
can be categorized into two types
- Agranulocytes
- granulocytes (polymorphonucleocytes)
Agranulocytes (WBC/leukocytes)
NO membrane-bound granules in the cytoplasm
----------------------------------
2 forms of agranulocytes:
- lymphocytes
- monocytes
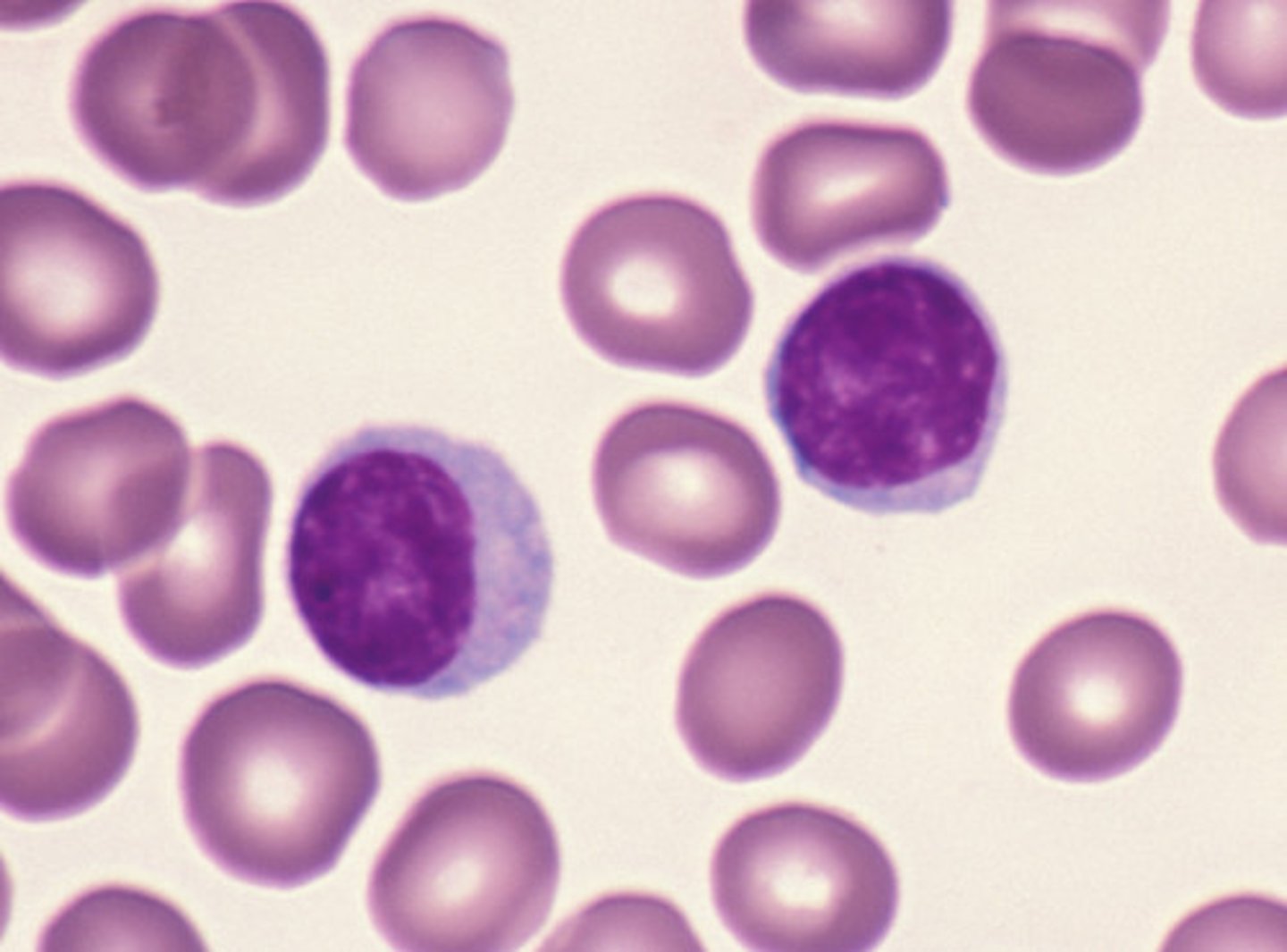
Lymphocytes (Agranulocytes)
smallest in WBC (slightly bigger than RBC)
- has a round nucleus
- minimal cytoplasm (halo) around the nucleus
- functions may vary depending on its type
----------------------------------
makes up 20-25 % of all WBC
types of lymphocytes
T cells, B cells, Null/NK cells
----------------------------------
all are involved in either cellular immunity and humoral immunity
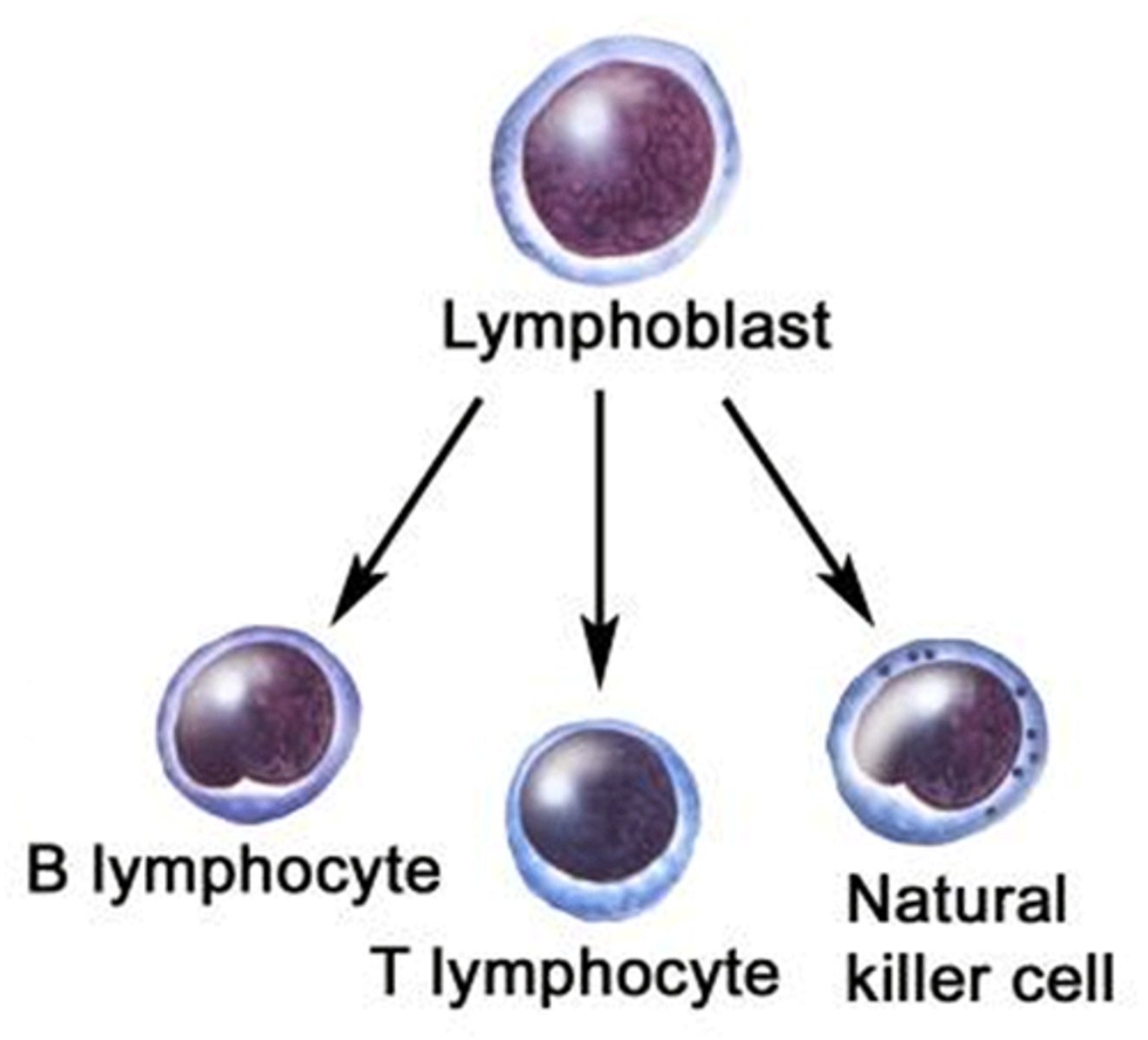
T cells (lymphocytes)
produce substances that attack infected cells in the body
----------------------------------
involved in cellular immunity
----------------------------------
(may look like B cells but the location of where its developed matters)
- developed in the thymus
B cells (lymphocytes)
produce antibodies
----------------------------------
involved in humoral immunity
----------------------------------
(may look like T cells but the location of where its developed matters)
- developed in the lymph node
Null (NK) cells (lymphocytes)
Produce plasma cells that attack pathogens in infected areas and secrete antibodies to defend against viruses
- (target and kill infected cells.)
----------------------------------
- developed in the lymph node, thymus, liver, uterus
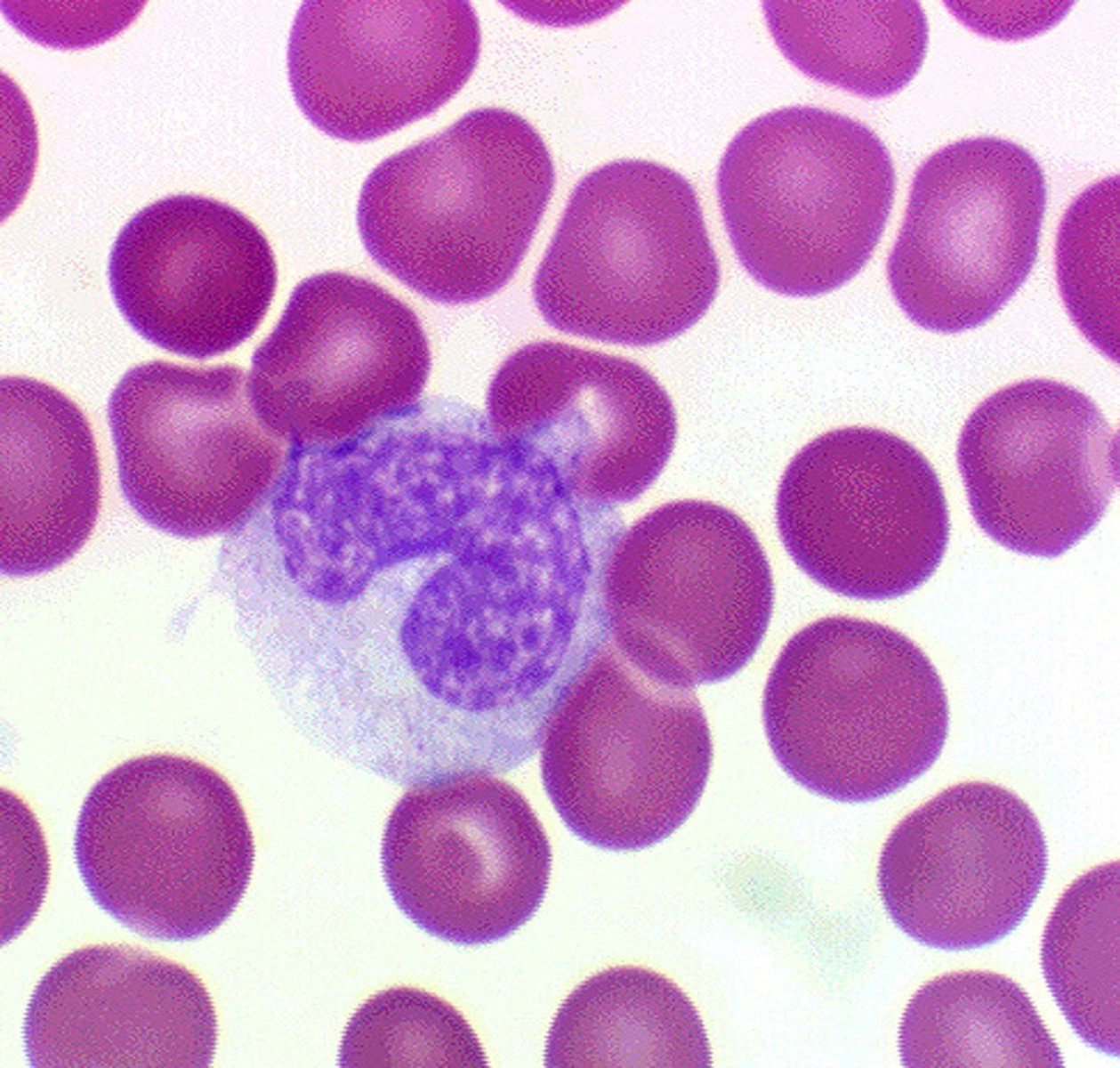
Monocytes (Agranulocytes)
Largest of all leukocytes (it may look like a lymphocyte but its bigger)
- has a kidney bean shape
- cytoplasm tends to be pale blue or gray (filled with ribosomes)
- as they leave the circulation, they differentiate into macrophages
----------------------------------
function:
- perform phagocytosis and antigen presentation
- activate lymphocytes to mount an immune response
- can transform into antigen-presenting cells (ACPs)
- Can leave blood and enter tissues, transforming into macrophages
----------------------------------
makes up 3-8% of all WBCs
Granulocytes (WBC/leukocytes)
the technical name is polymorphonucleocytes
----------------------------------
HAS membrane-bound granules in the cytoplasm
- has multi-lobed nuclei
- has cytoplasmic secretory
----------------------------------
3 forms of granulocytes
- neutrophils
- eosinophils
- basophils
Neutrophils (granulocyte)
- large blood cell
- has a multi-lobe nucleus (still one nucleus but has multiple lobes)
- contains neutrophilic granules in the cytoplasm (does not pick up color when looking through a microcope)
- ONLY cell to have a "drum stick"
----------------------------------
engulfs foreign and damaged cells (phagocytosis); most numerous of the leukocytes
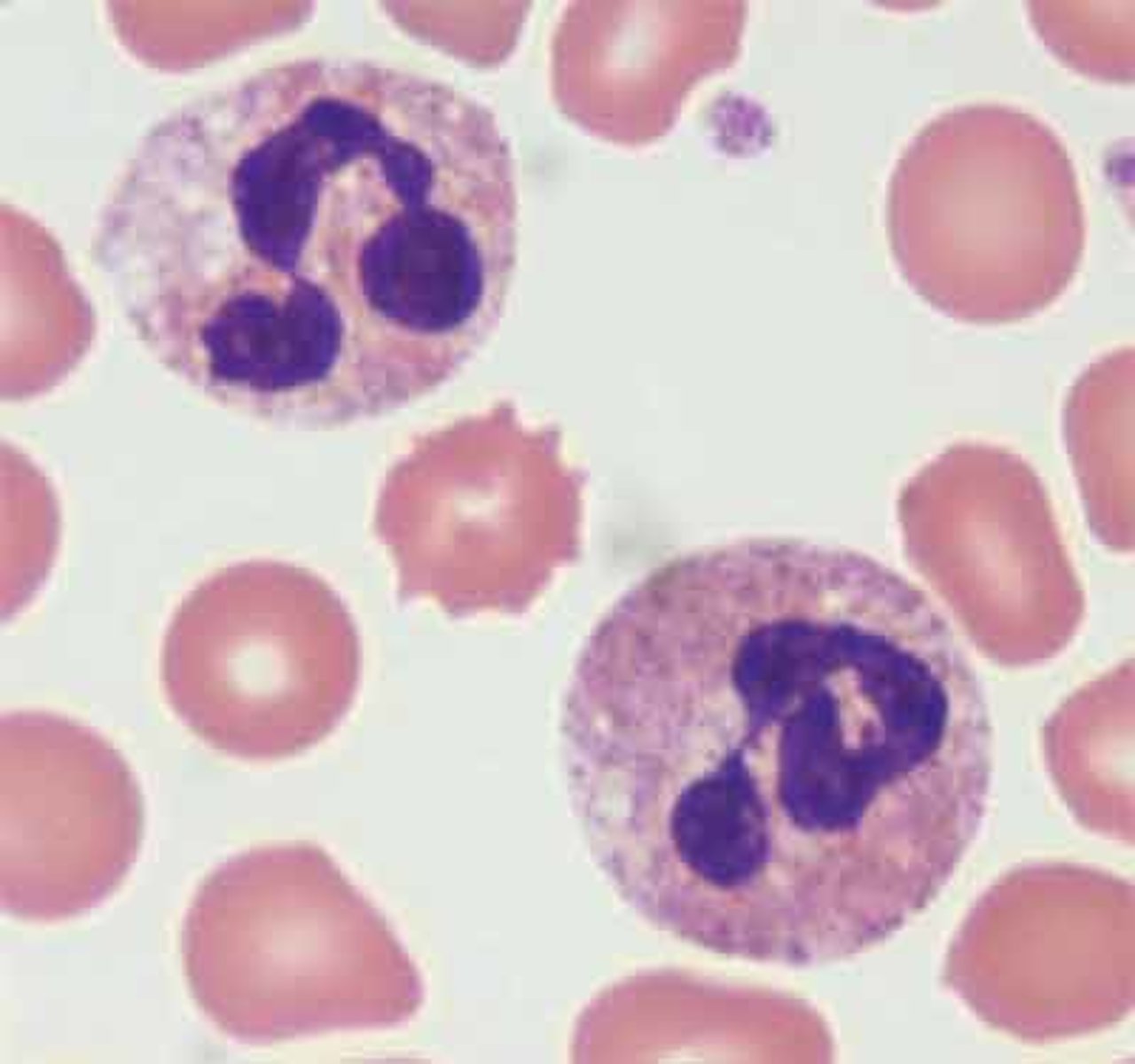
Drum stick (neutrophils)
little branch on the multi-lobe granules
----------------------------------
an expression of an x chromosome cell in which more than one is present
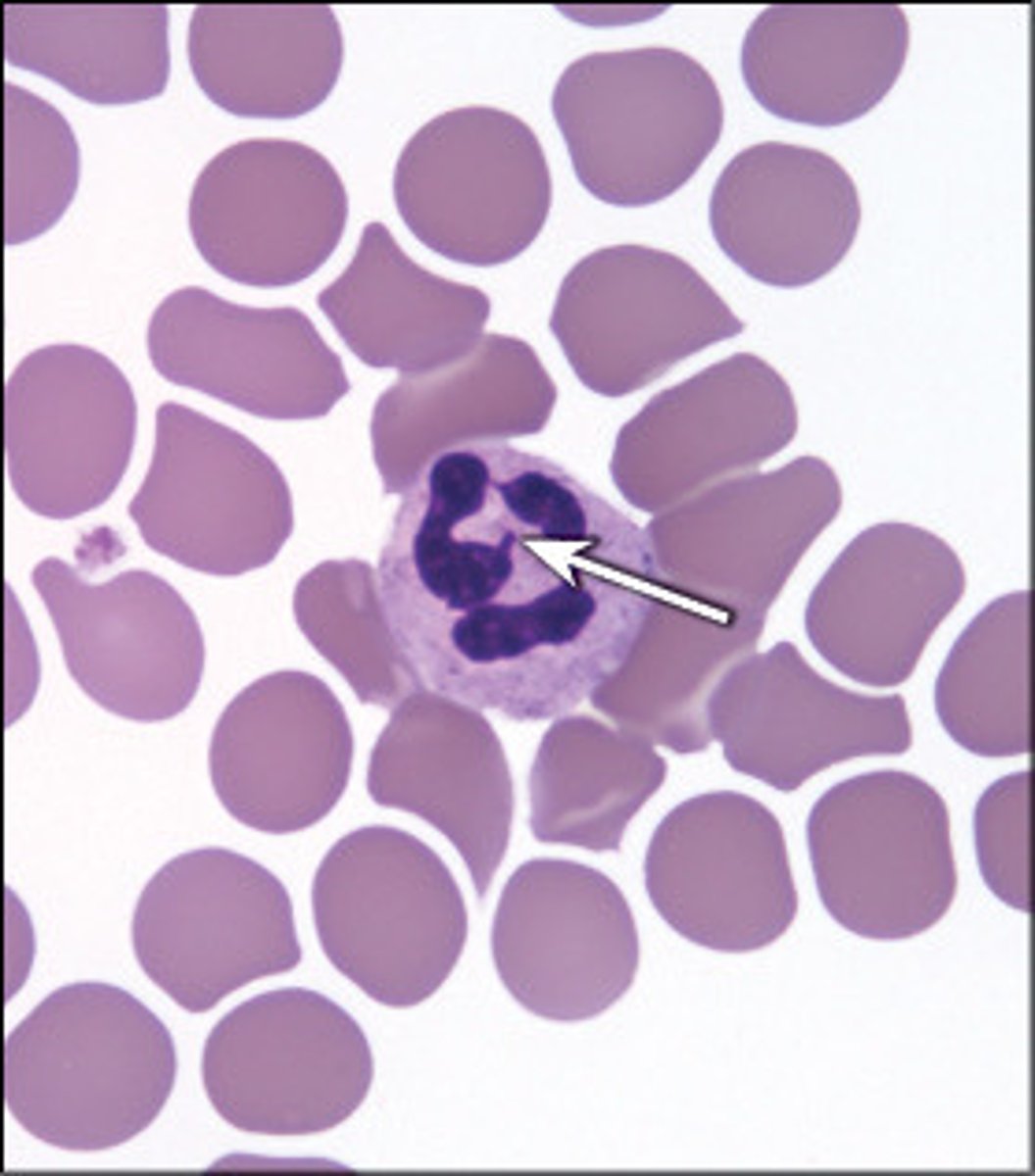
Eosinophils (granulocyte)
the largest granulocyte
- has a bilobed nucleus
----------------------------------
Eosinophils granules account for 2-5% of WBCs
-have red-staining, bilobed nuclei
-Have red to crimson (acidophilic) large, coarse, lysosome-like granules
-phagocytize cells infected with combat parasites
-Lessen the severity of allergies by phagocytizing immune complexes and by releasing antihistamines
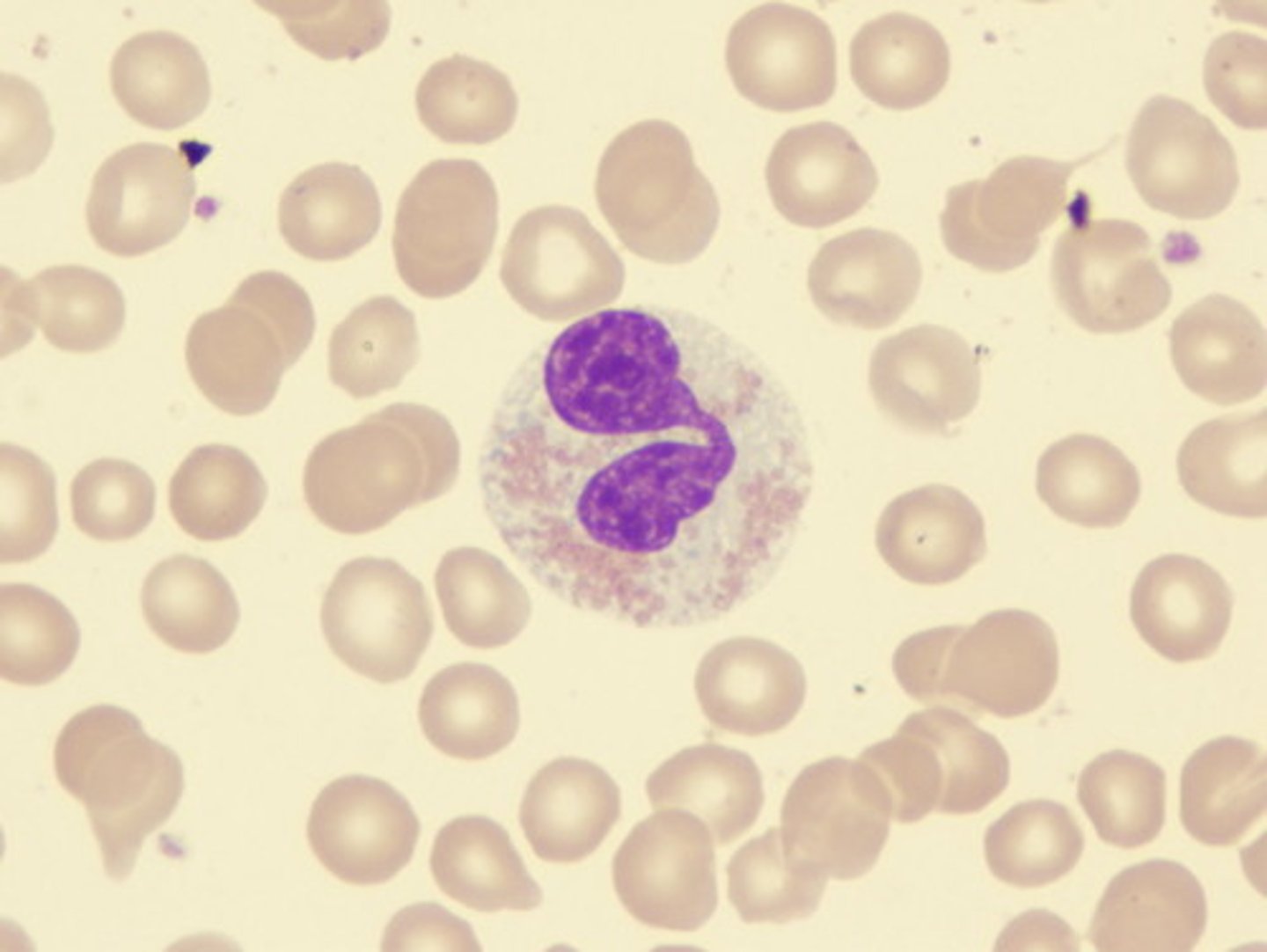
Basophils (granulocyte)
the smallest in the granulocytes
- has a C or S-shaped nucleus
- even in thickness
- contains a concealed granule
-----------------------------------
function:
- modulate inflammation responses
- secrete histamine
- produce antigen presentation cells
-----------------------------------
makes up <1% of all WBC
(Least abundant type of WBC)
mnemonic for the 5 types of leukocytes
"Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas"
-----------------------------------
Never = neutrophils 60-70 % of all WBC
Let = Lymphocytes 20-25 % of all WBC
Monkeys = Monocytes 3-8 % of all WBC
Eat= Eosinophils <5 % of all WBC
Bananas= Basophils <1 % of all WBC
-----------------------------------
Neutrophils= most abundant
basophils= Least abundant/rarest
Platelets (thrombocytes)
cellular fragments in the blood that stick together, forming a clot
- anucleate (does not contain nucleus)
-fragments of megakaryocytes
-----------------------------------
function:
- to prevent and stop bleeding when a blood vessel is damaged
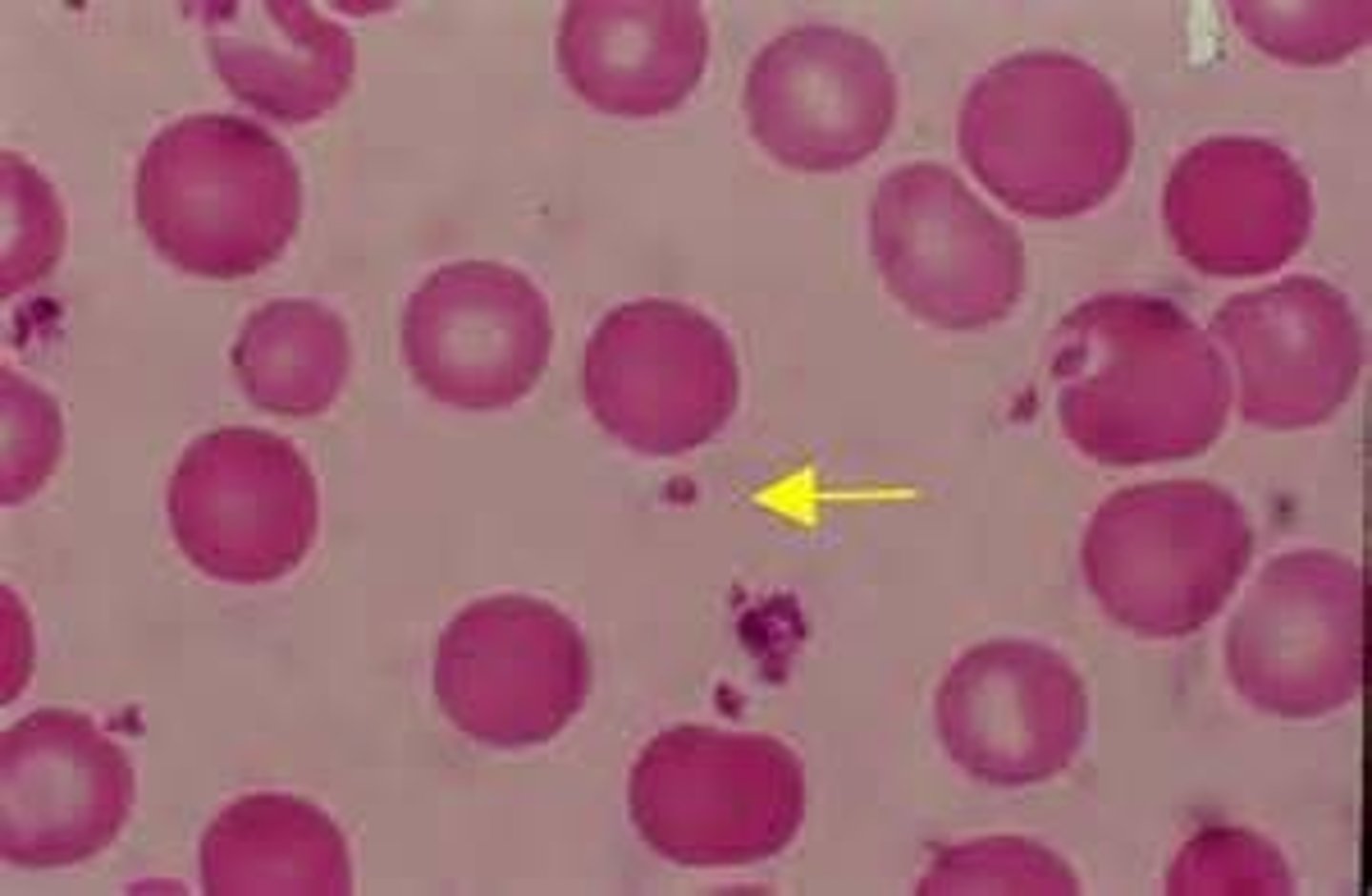
megakaryocytes
just another term for bigger platelets
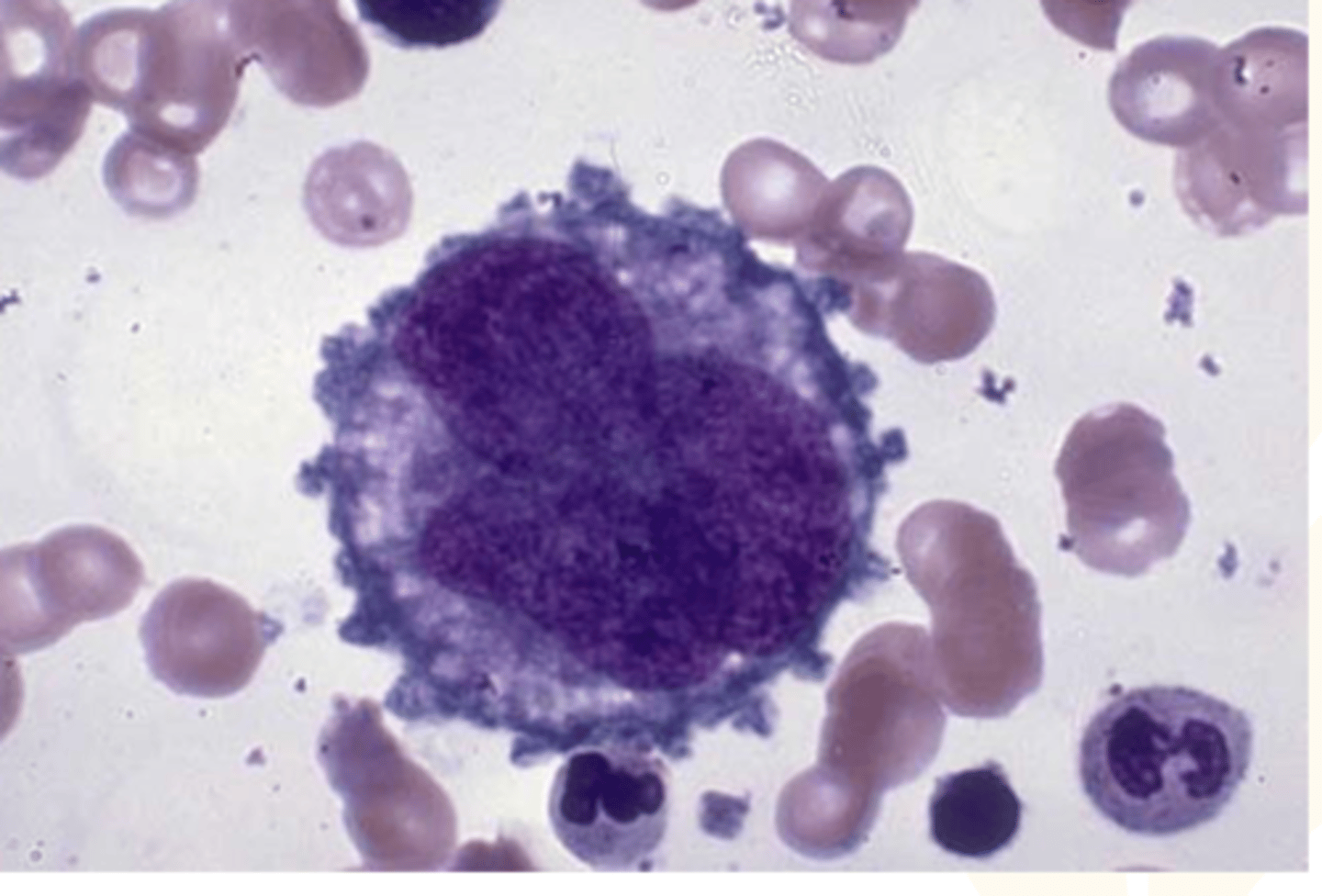
hematopoiesis/hemopoiesis (red bone marrow)
production of blood cells typically found in the red marrow of a bone
----------------------------------
Postnatal blood cell development
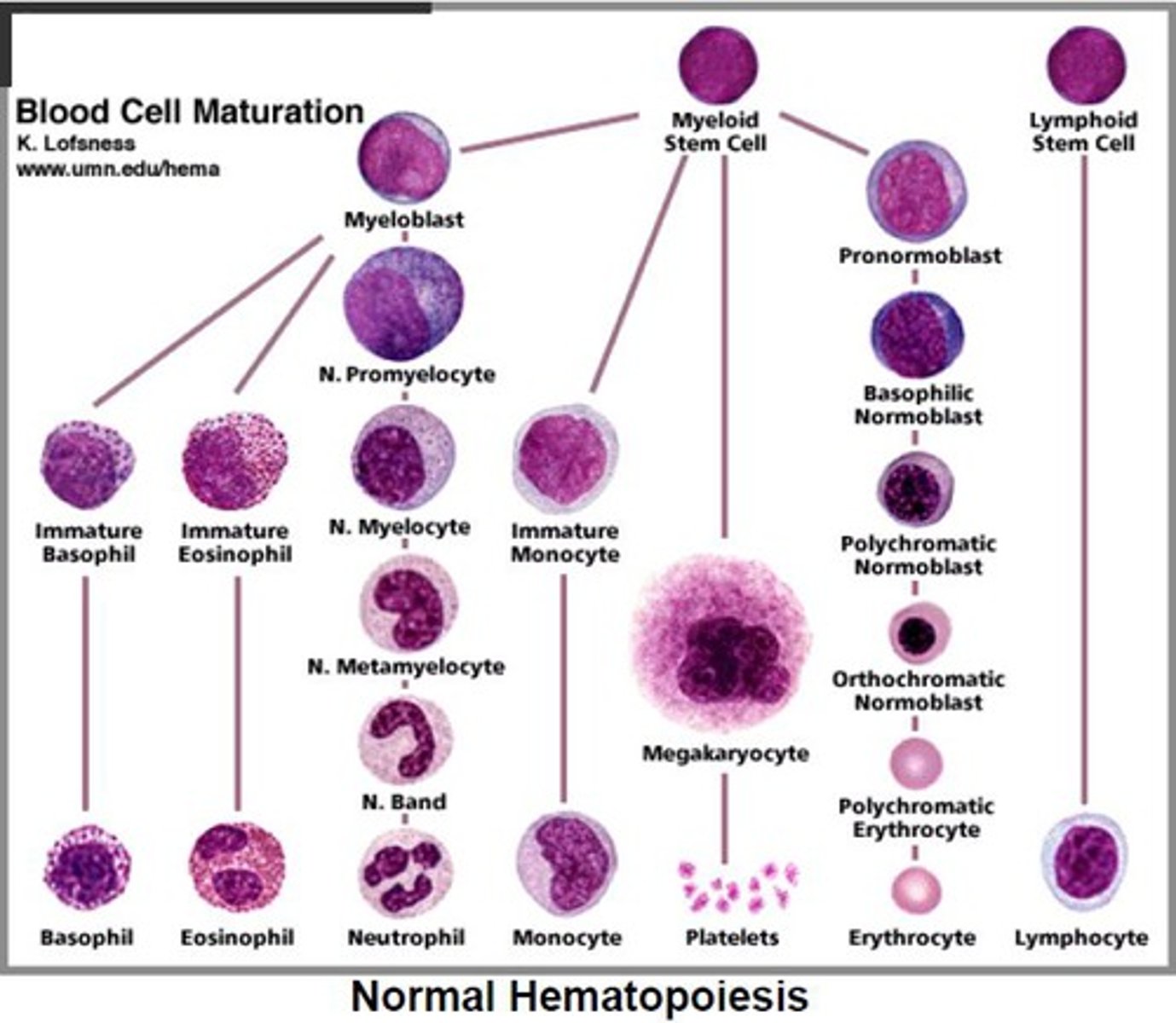
fat (yellow marrow)
yellow bone marrow is mostly made of mostly fat and contains stem cells that can become cartilage, fat, or bone cells .
- most red marrow is converted to yellow marrow (as you age)
Birth to adulthood
- birth: all bones contain red marrow
- adulthood: most bones that contained red marrow is now yellow marrow
--------------------------------------
Most Red Marrow (at adulthood) is present in the:
- flat cranial bones
- ribs
- sternum
- vertebrae
- ends of large long bones
(Some yellow marrow may revert to red marrow)