Turbine Engines Jeppesen 3-A (Turbine Engines)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
4 types of gas turbine engines
-Turbojet
-Turboprop
-Turboprop
-Turbofan
(understand the general operating principles of each and their uses)
Bypass Ratio
The ratio of incoming air that bypasses the core to the amount of air that passes through the engine core.
(In reference to turbofan engines)
Ducted vs. Unducted Fans
For turbo fan engines, ducted fans are used today and have a shroud ducting the air around the engine, as opposed to ducted fans which have no cowling or duct to direct air around the engine. Unducted fan engines operate similar to a propeller.
7 Engine components of a turbine engine
1) Air inlet duct
2) Compressor section
3) Combustion section
4) Turbine Section
5) Exhaust section
6) Accessory section
7) Auxiliary systems (starting, lubrication, fuel supply, etc...all systems completely SEPERATE from the engine)
4 PRIMART components of a turbine engine
1) Compressor section
2) Combustion section
3) Turbine Section
4) Exhaust section
Is the air inlet duct a powerplant component?
NO. Only the inlet physically attached to the engine housing is considered apart of the powerplant, the cowling that brings in the air is an airframe item.
Properties of a subsonic inlet
Divergent shape that spreds air out;
-DECREASES velocity
-INCREASES pressure
Properties of a supersonic inlet
Convergent-Divergent shape that is used to slow the incoming airflow to subsonic speed before it reaches the compressor.
Properties of a Bellmouth Inlet
high efficiency when stationary or in slow flight; good for test cells and helicopters.
What systems in a turbine engine help eliminate FOD?
-inlet screen
-sand an ice separators.(series of sharp bends which prevents debris from reaching the engine because of the inertia of the particulate)
-Movable vane that diverts into the inlet airstream when on the ground or in the presence of FOD
-Bleed air sprayer that blows air at the ground in front of the inlet. not used anymore, can stir up FOD.
2 types of turbine engine compressors
-Centrifugal Flow Compressors
-Axial Flow Compressors
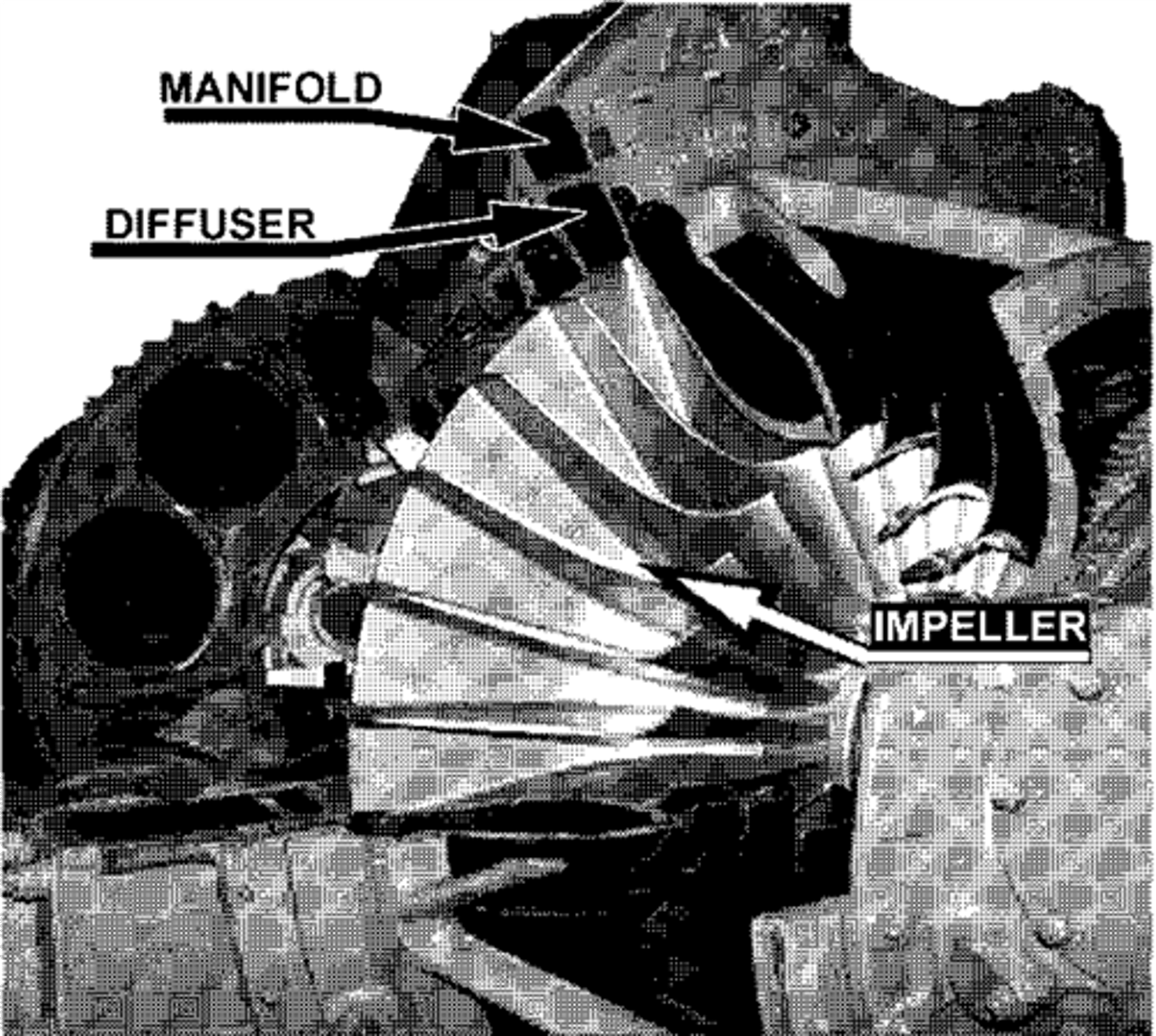
What is a diffuser?
section of a compressor section where air becomes dispersed; its velocity is decreased, and its pressure is increased.
What is the purpose of a compressor manifold?
To distribute the air in a smooth flow to the combustion section.
3 elements of a Centrifugal Flow Compressor
1) Impeller
2) Diffuser
3) Compressor Manifold
3 Centrifugal Flow Compressor setups in a turbine engine
1) Single-Stage Compressors
2) Double-Stage Compressors
3) Double-Sided impeller (technically double stage, but has two impellers back-to-back)
Pros/Cons of Centrifugal Flow Compressors
PROS:
- High compression ratio (15:1)
- Low cost
- Smaller physically in the engine compared to axial systems
- Simple to make
CONS:
- Inefficient after 2 stages (not scalable to large engies)
- Increase in drag due to large frontal area for air intake
2 elements of an Axial Flow Compressor
1) Rotor
2) Stator
Pros/Cons of Axial Flow Compressors
PROS:
- Extremely scalable, can have many stages.
- Straight-through airflow design improves efficiency
- small frontal area, lower drag than centrifugal
CONS:
- low compression ratio (1.25:1)
- high weight and starting power requirements
- expensive and difficult to manufacture
- Requires a divergent shape to keep air velocity constant while pressure gradually increased. (not really a pro or con)
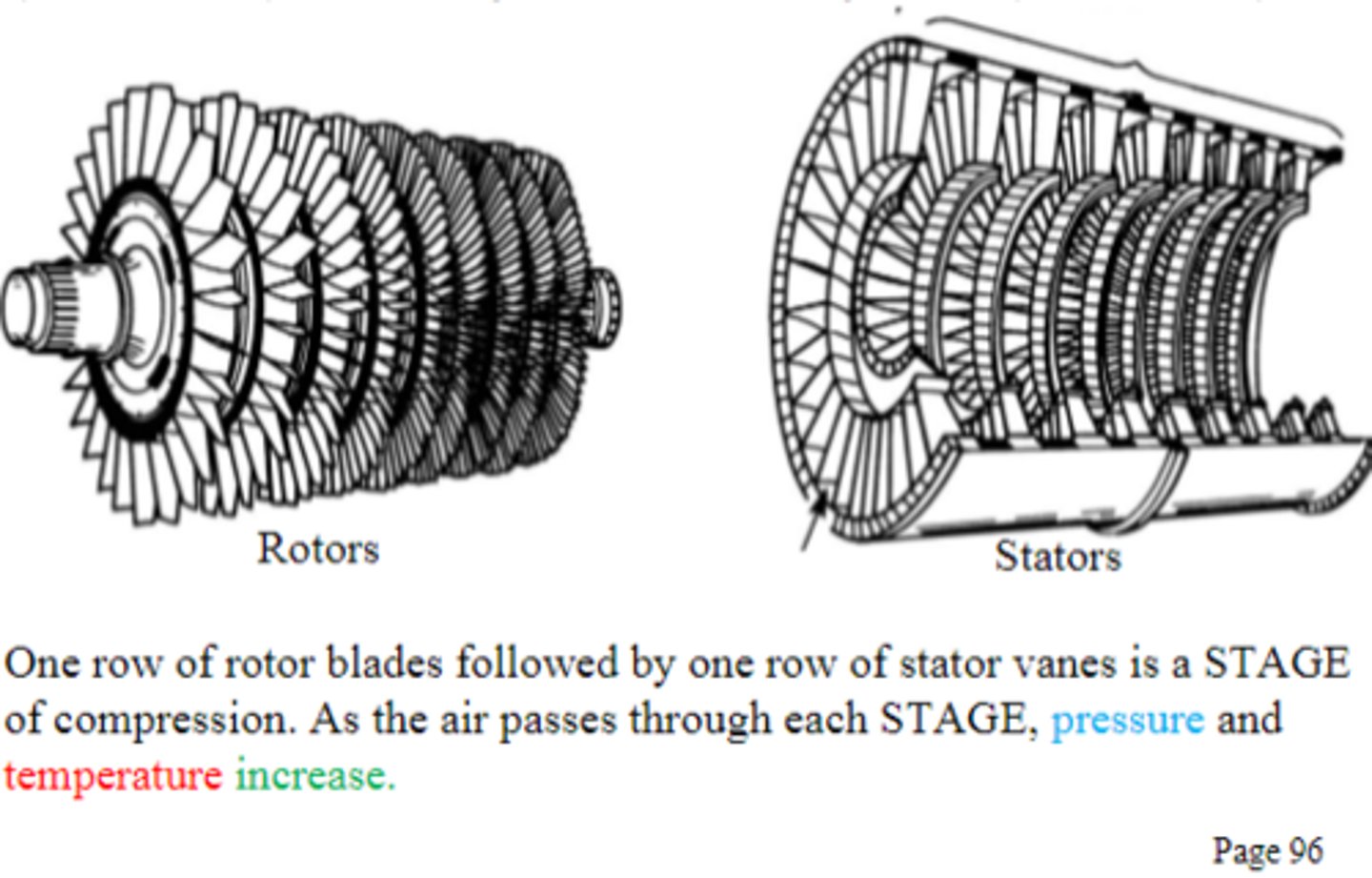
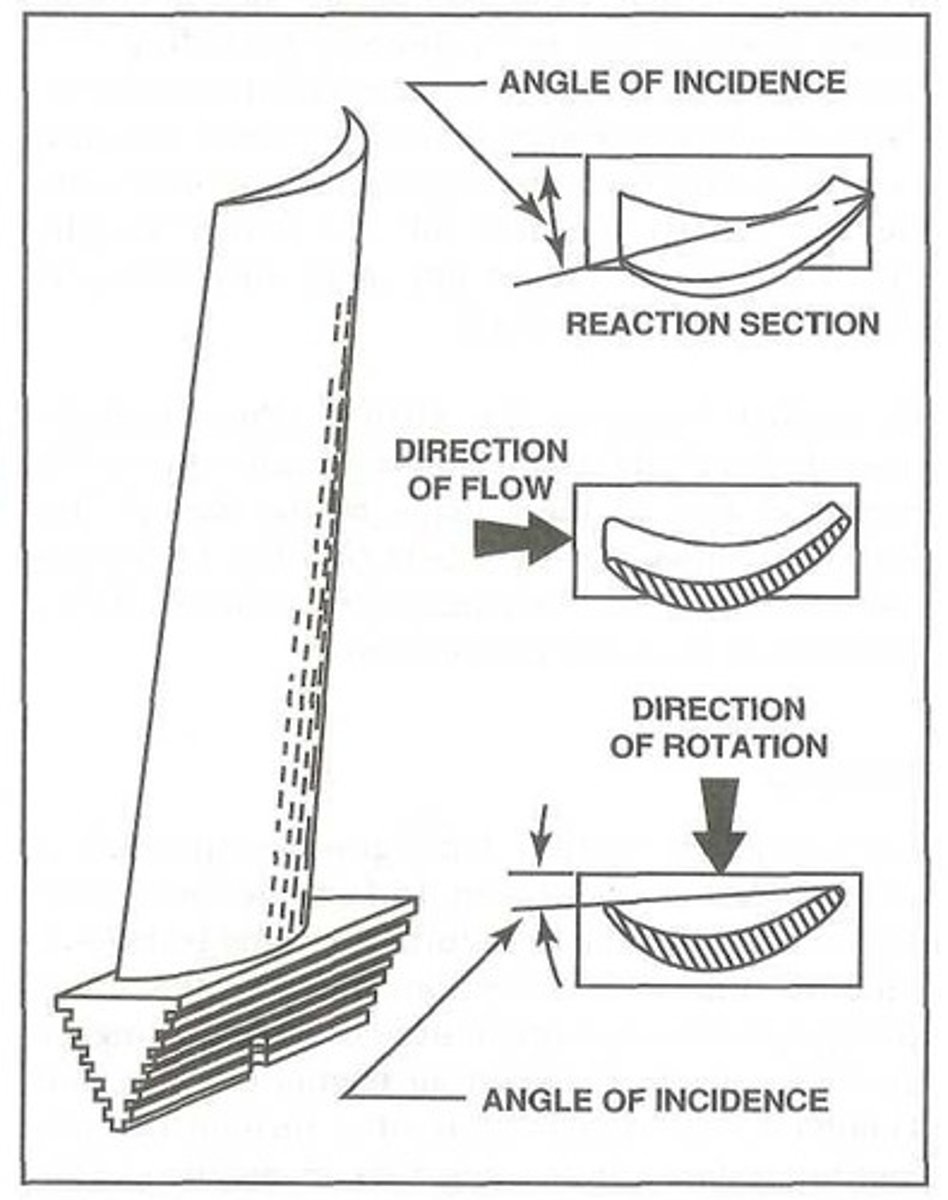
What is the purpose of a varied angle of incidence on axial flow rotor blades?
To compensate for variations in blade velocity caused by relative distance from the rotational axis.
what are the 3 main shapes of rotor blade roots?
1) Bulb
2) Fir Tree
3) Dove Tail
These are typically a loose fit, and have a pin or loc tab to hold them in place. the centrifugal force holds the blades in their correct position.
why do most compressors (and turbines) have small tip clearances?
To prevent air from traveling around the compressor and not being compressed. These clearances are typically in the thousandths of an inch.
What is the purpose of compressor stator Vanes?
- Diffuse air coming off the rotor, which DECREASES its velocity and INCREASES its pressure.
- Prevent swirling
What are Inlet Guide Vanes?
-Vanes in front of the first stage rotor blades.
-They direct airflow at the best angle while creating a swirling motion in the direction of engine rotation.
- Can be FIXED or VARIABLE. Variable inlet guide vanes automatically reposition themselves for best airflow.
Single vs Multiple-Spool Compressors
SINGLE:
- Single-spool compressors have a single shaft between the compressor(s) and turbine(s).
- drawbacks: rear compressor stages not operating efficiently. all stages must spin at the same RPM
Multiple:
-dual OR triple-spool compressors that allow multiple sections of the compressor and turbine sections to spin at their most efficient rates.
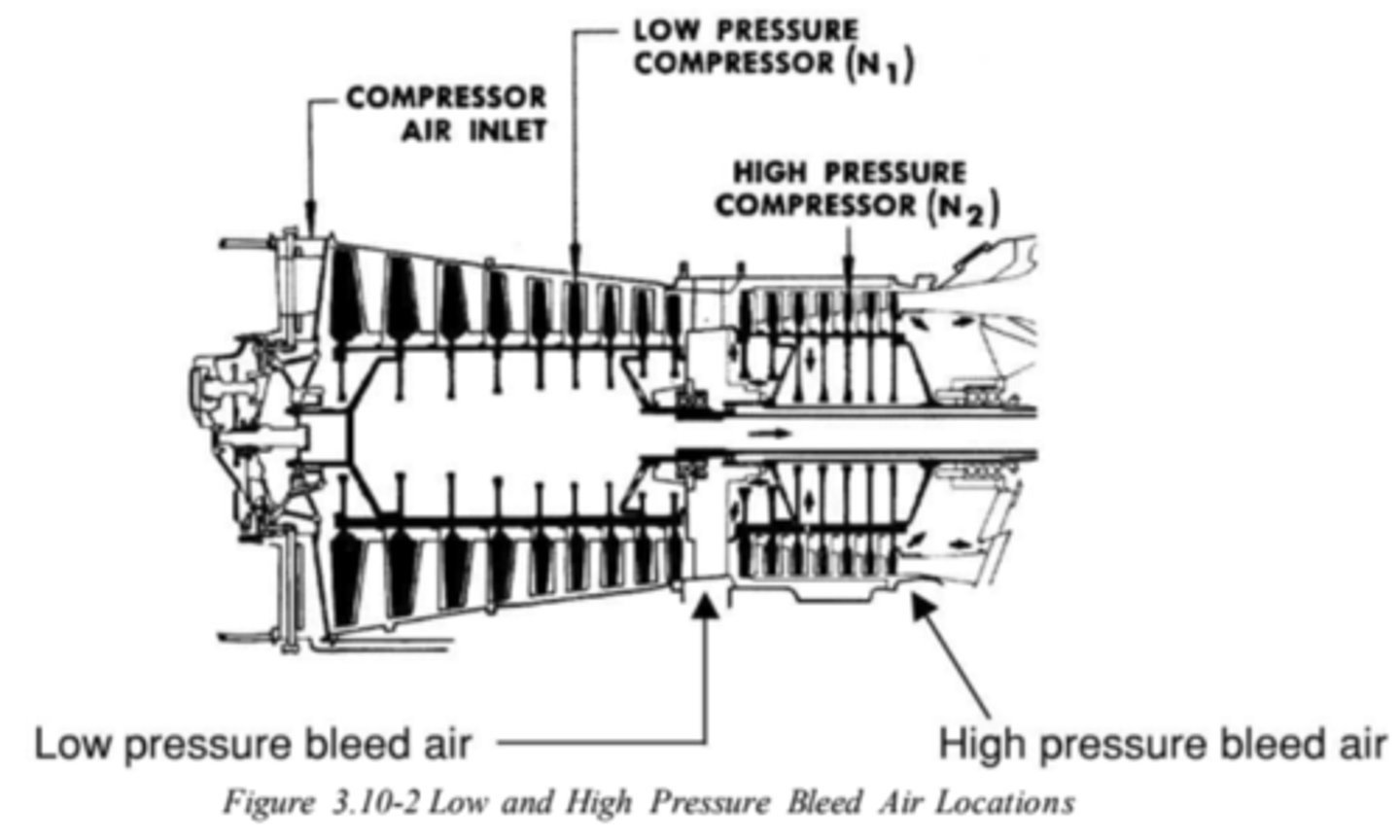
Stages of dual and triple-spool compressors
DUAL:
1) Low Pressure, or Low Speed (N1) (compressors towards the front)
2)High Pressure, or High Speed (N2) (compressors towards the rear)
TRIPLE:
1) Fan, or Low speed (N1)
2) Intermediate (N2) (Driven by singe turbine)
3) High-pressure (N3) (Driven by single turbine
What is a compressor stall?
an imbalance between inlet velocity and compressor rotational speed. Occurs when the compressor blade angle of attack exceeds the critical angle of attack.
Can be mild(transient stall) OR severe (developed stall)
2 ways to overcome a compressor stall
1) Reduce angle of attack on the rotor blades through the use of variable inlet guides or stator stator vanes
2) Bleed off air pressure from within the compressor to change the angle of attack of the compressor blades.
Uses of compressor bleed air
- Deicing
- Anti-icing
- Pneumatic engine starting
Where is a bleed air port located?
anywhere along the compressor stage; the choice depends on the pressure and temperature required for a particular function. air more rearward will be higher in pressure and temperature.
What is the purpose of a diffuser in an axial flow compressor?
Reduce speed of the air entering the combustion system by increasing air pressure to its highest value in the engine.
- The diffuser is typically a separate section bolted between the compressor and combustion section
Components of the Combustion Section
- One or more combustion chambers (combustors)
- Fuel Nozzle
- Ignitor plugs
- Fuel Drain
What is a combustor
A combustor is the combustion chamber of gas turbine engines, typically consisting of an outer casting with a perforated inner liner for air to enter.
Why is a fuel drainage system important in the combustion section of a turbine engine?
- Reduces the possibility of high EGT or TIT
- Prevents deposits caused by fuel residue
4 requirements of a combustor (for efficient burning)
1) Mix fuel/air in an optimal ratio
2) Burn the mixture as efficiently as possible
3) Cool the hot combustion gases to a temp that is suitable for the turbine blades
4) Distribute hot gases evenly to the turbine section
Primary vs Secondary flow air in the combustion section
PRIMARY FLOW: Directed inside the liner for combustion
SECONDARY FLOW: Directed around the combustion flames to prevent contact of flames with the combustion liner: (COOLING & INSULATION)
Flameout definition
condition where an excessively high-velocity airflow literally blows the flame out in the combustion chamber. flameout is mitigated by SWIRL VANES, which slow and spin air before entering the combustor.
Three basic types of combustion chambers
1) Can Type
2) Annular Type
3) Can-Annular Type
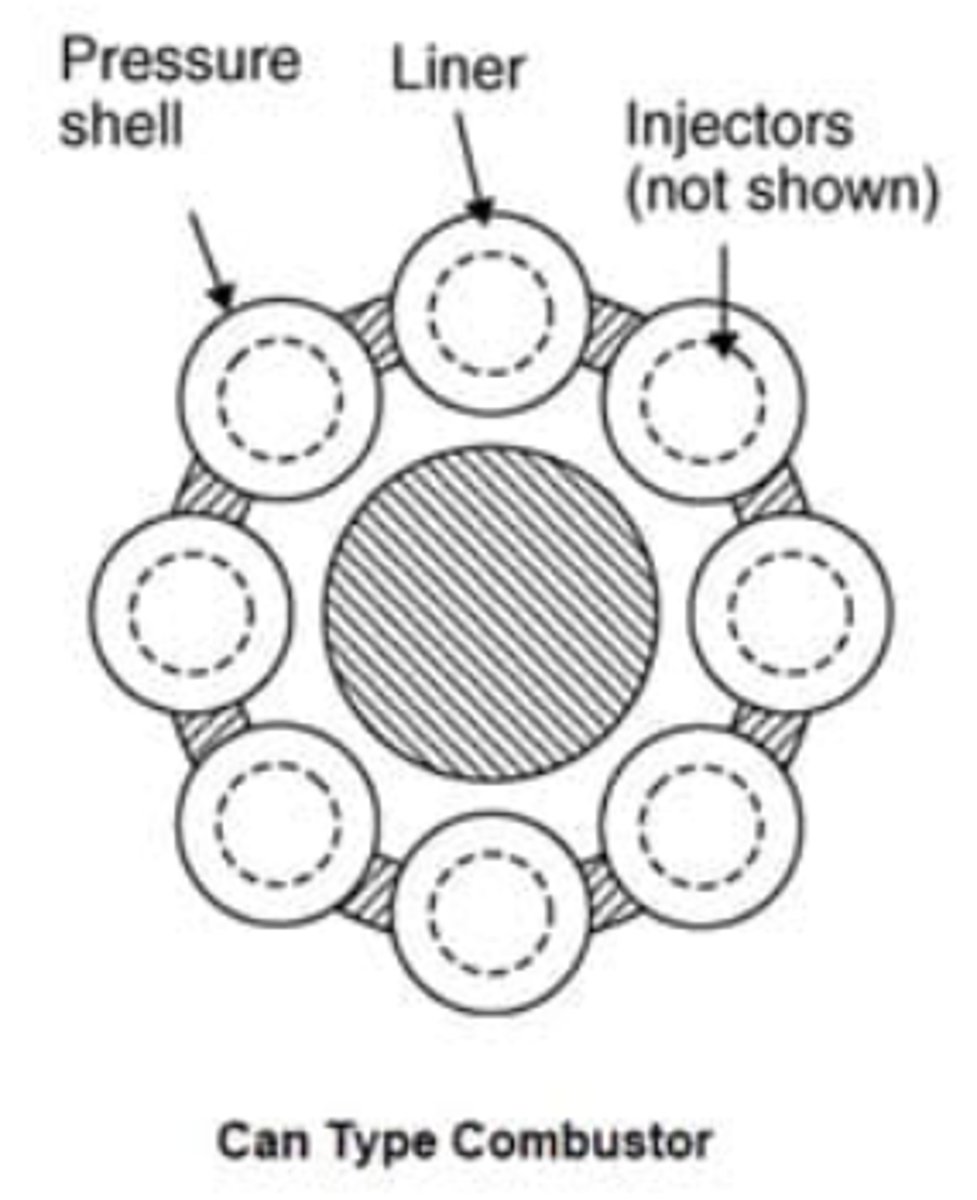
Can Combustor (definition, relevant information)
airflow is ducted to individual combustion cans that are arranged around the circumference of the burner section.
- Multiple-can systems have FLAME PROPIGATION TUBES that allows the flame to travel through the tubes to ignite all cans
- Good for centrifugal compressors
- Heavy, if multiple cans are needed
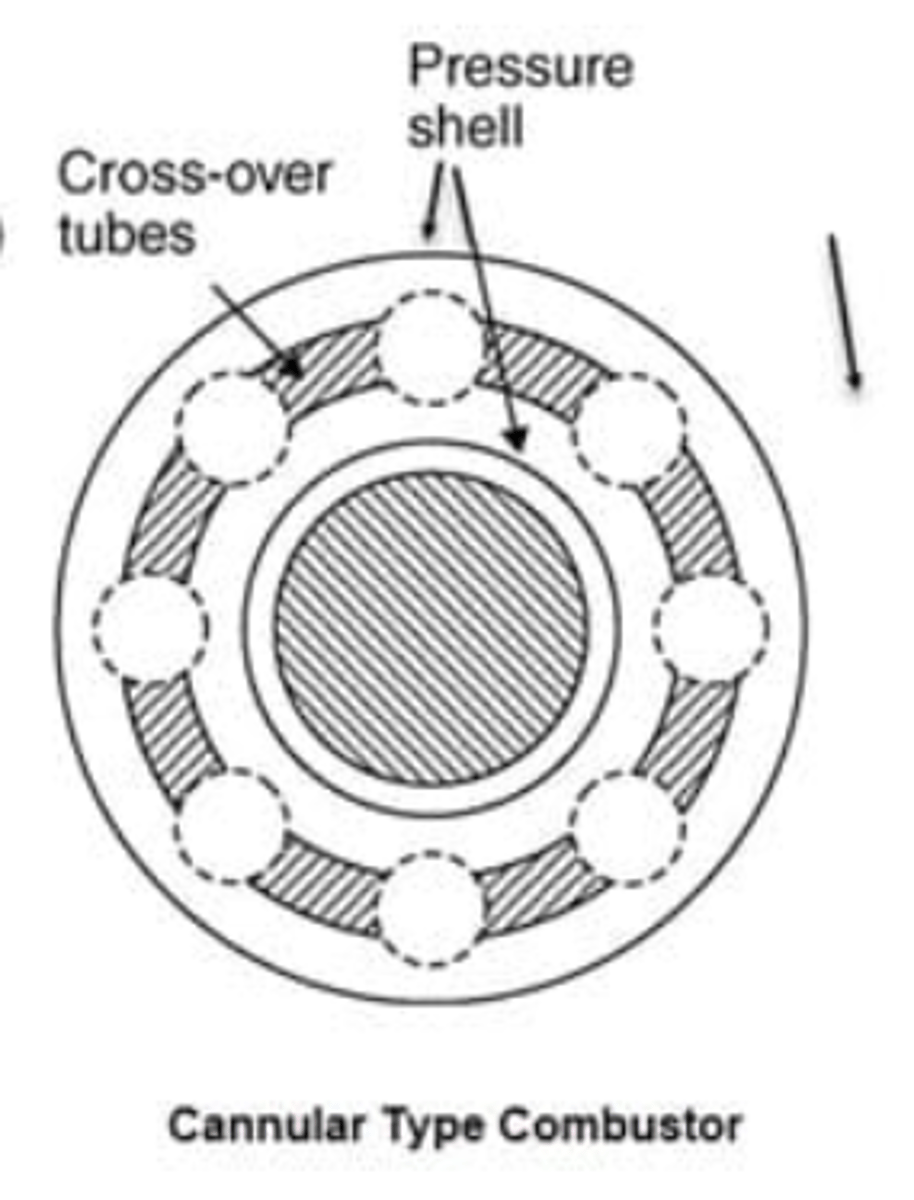
Annular Combustor (definition, relevant information)
One large unit, consisting of a housing and a liner that encircles the outside of the turbine shaft housing.
- REVERSE-FLOW (annular type) COMBUSTORS work the same, except the air flows around the chamber and enters from the rear.
- Annular type offers the most efficient combustion in terms of efficiency, weight, and physical size.
- Harder to remove, as complete separation of the engine is required.
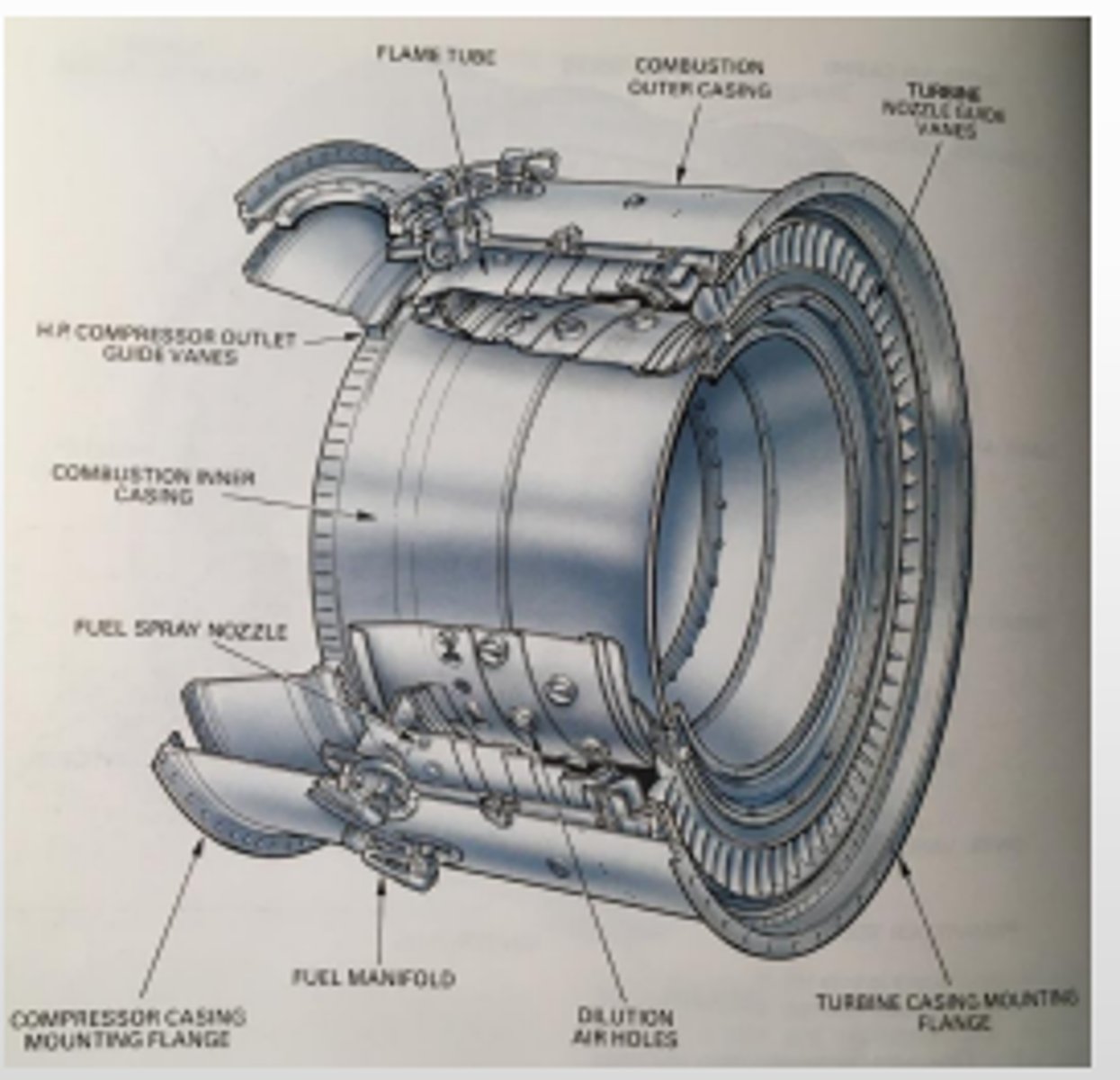
Can-Annular Combustor (definition, relevant information)
combination of the multiple-can combustor and the annular type combustor. consists of a removable steel shroud that encircles the entire combustion section.
- Has FLAME PROPIGATION TUBES that allows the flame to travel through the tubes to ignite all individual liners
- Combines the ease of overhaul and testing of the can arrangement with the compact design of the annular combustor
Two types of flameout
Lean Die-Out:
- Occurs at high altitude where low engine speeds and low fuel pressure form a weak fame that is extinguished in a normal airflow
Rich Blowout:
- Occurs during rapid engine acceleration with an overly rich mixture, where fuel temp drops below the temp necessary for combustion or there is insufficient airflow to support combustion
How much energy does a turbine in a turbojet engine absorb?
60% - 80%
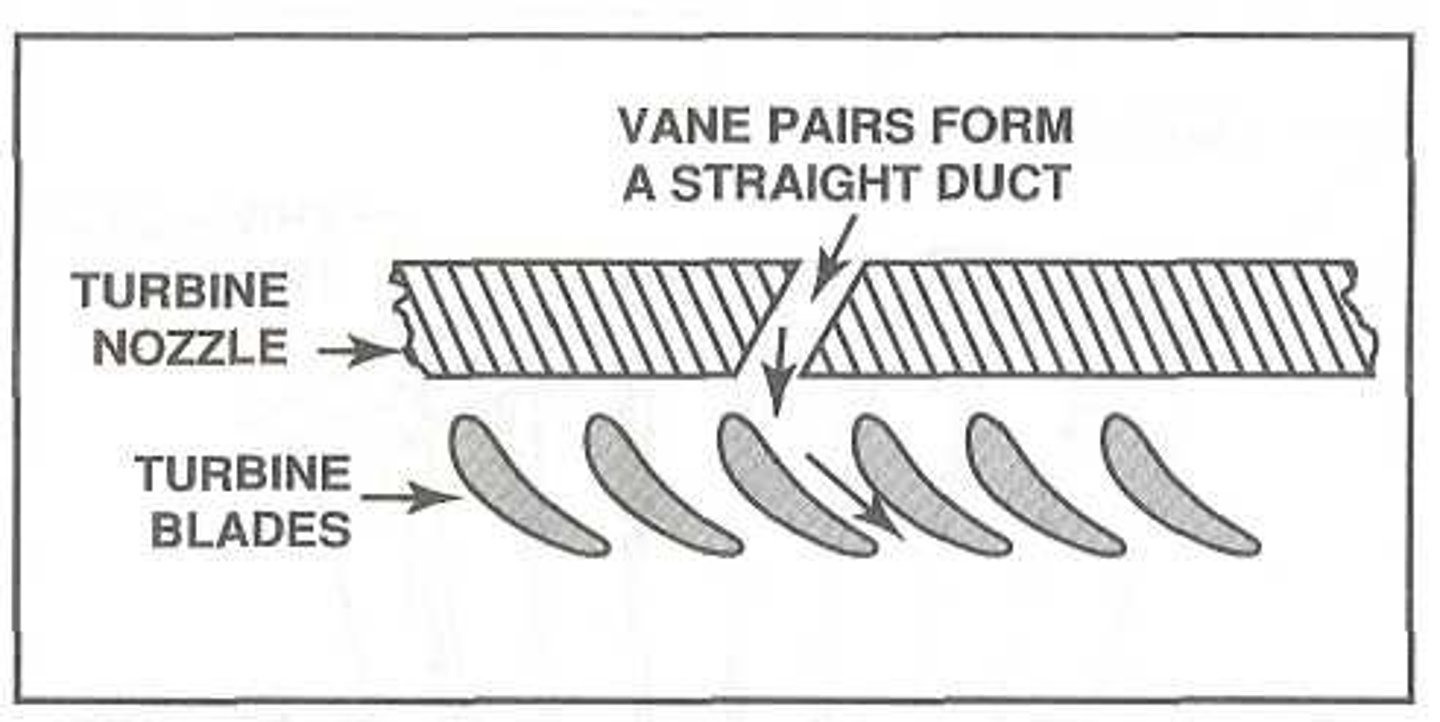
What is the purpose of a turbine nozzle?
to collect the high energy airflow form the combustors and direct the flow to strike the turbine rotor at the appropriate angle.
How does the turbine nozzle deal with the high temperatures of the combustor and permit thermal expansion?
1) Turbine nozzles are assembled loosely within the inner an outer shrouds to permit expansion
2) The vanes can be attached to the inner and outer shrouds, but the shrouds and vanes are all cut into segments together
What are the 4 basic elements of a turbine assembly?
1) Case
2) Stator
3) Shroud
4) Rotor
What is the difference between a turbine wheel and a turbine disk?
The turbine wheel consists of the turbine blades AND the turbine disk
The turbine disk anchors the turbine blades to the main shaft
What is creep?
The process of turbine blades expanding in length due to high heat and centrifugal loads
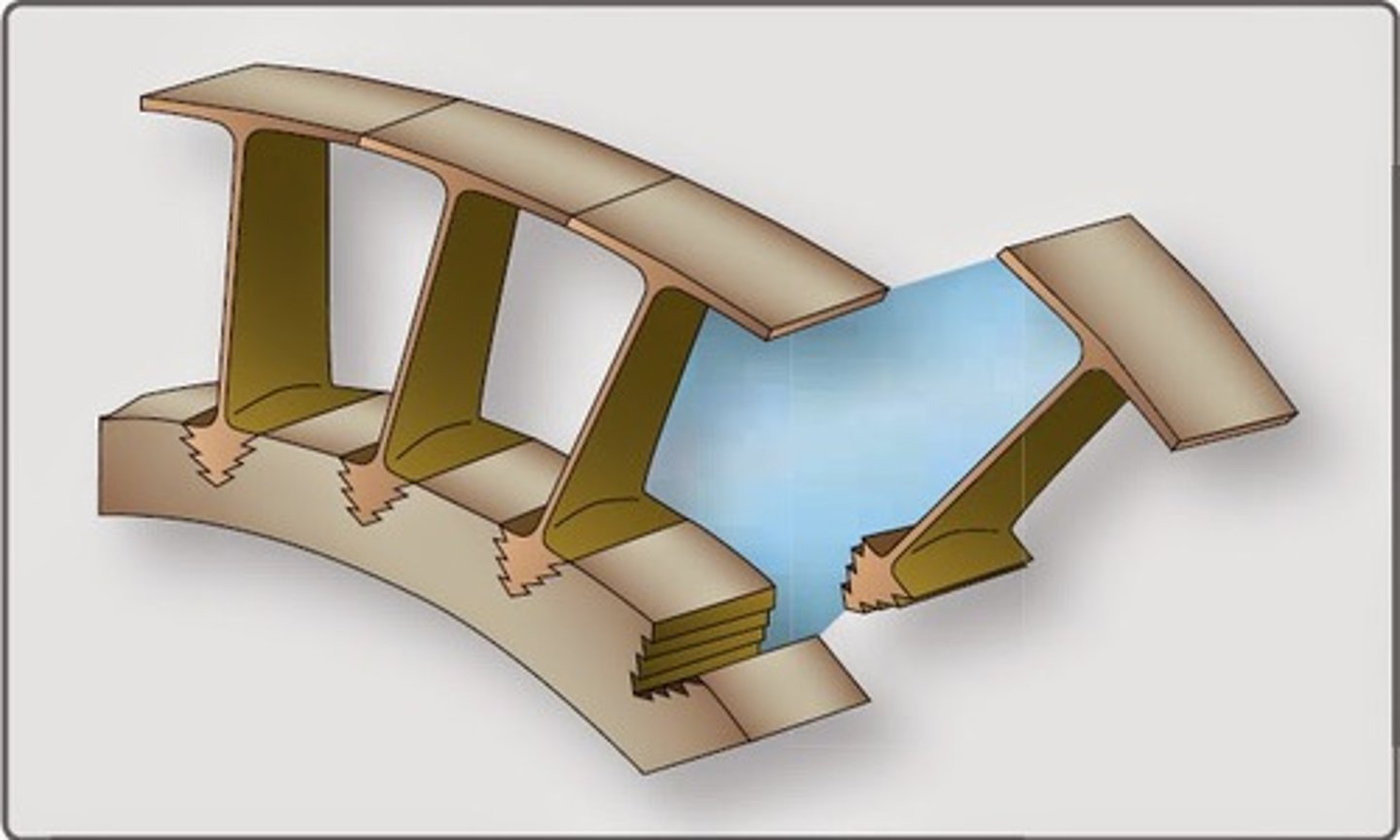
How are turbine blades attached to a turbine disk?
Via a loose fit when cold; also by fir tree slots cut into the turbine disk rim
What are the 3 types of turbine blades?
1) Impulse blades
2) Reaction blades
3) Impulse-Reaction blades
What are the characteristics of an Impulse turbine blade?
Blades change direction of airflow and cause no change in gas pressure or velocity
What are the characteristics of a Reaction turbine blade?
Blades produce a turning force by reducing pressure and creating a lifting force.
What are the characteristics of an Impulse-Reaction turbine blade?
Combination of an impulse and reaction turbine blade, where the base is impulse-shaped and the tip is reaction-shaped
Open VS Shrouded turbine blades
OPEN:
-high speed turbines
SHROUDED:
-slower rotational speeds
-shrouds contact each other, provide support
-reduced vibration
-increase efficiency (less air escaping around the KNIFE EDGE SEAL
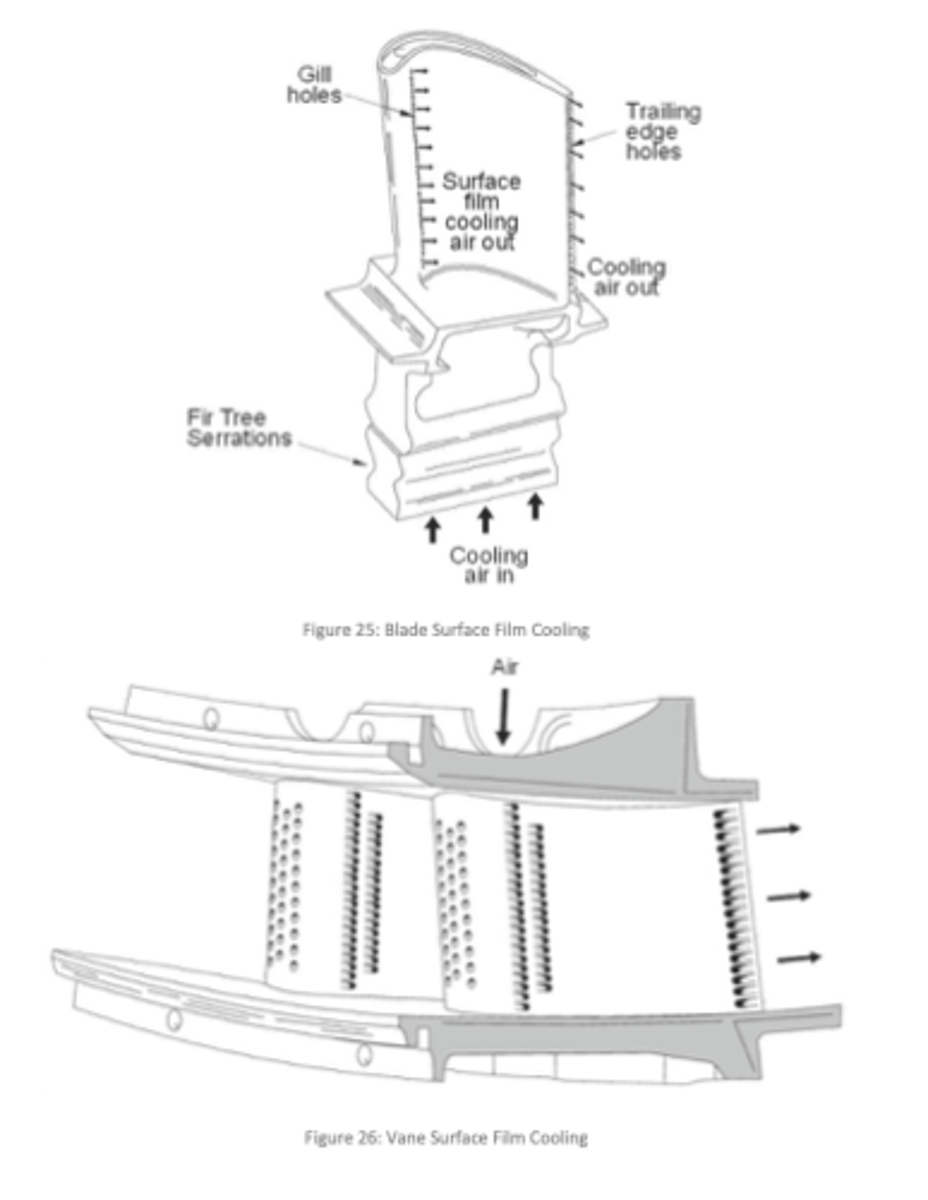
What is the limiting factor of a turbine engine?
Temperature of the turbine section.
How are turbine blades typically cooled?
internal cooling channels that route bleed air through the blade and out at the blade tips, trailing edge, and/or gill holes.
What is convection or film cooling (in reference to turbine wheels)?
The process of using bleed air to internally cool turbine blades through hollow blade channels
What is the purpose of an exhaust cone?
to channel and collect turbine discharge gases into a single jet
What are the 3 components of an exhaust cone assembly? (Picture)
1) Outer duct
2) Strut
3) Inner cone
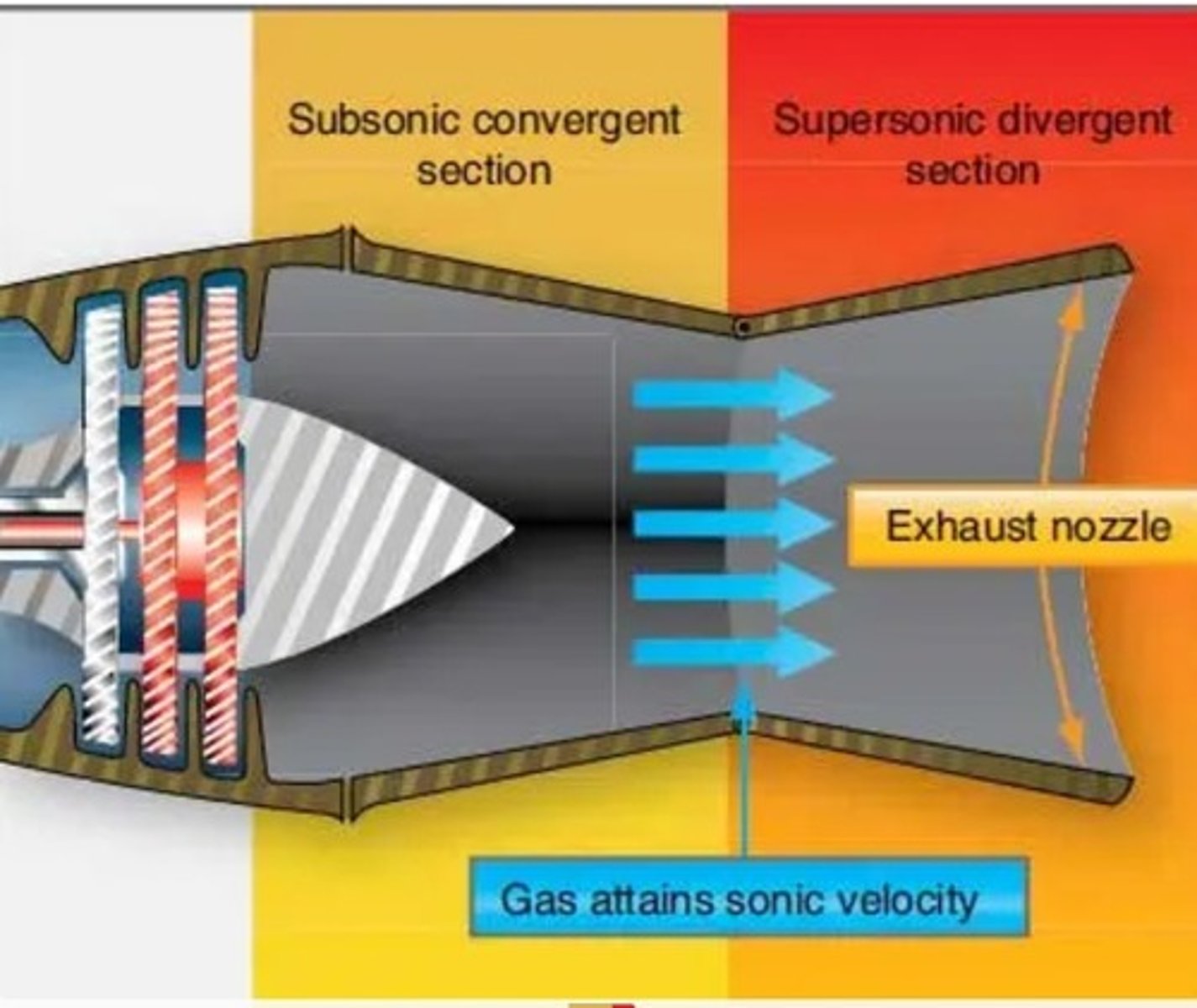
What are the two types of exhaust nozzle design on a turbine engine?
1) CONVERGING:
-Produces a venturi that accelerates the exhaust gases and increased thrust
2) CONVERGING-DIVERGING:
-Increase gasses to speed of sound, then accelerate further due to the inverting of Bernoulli's principle
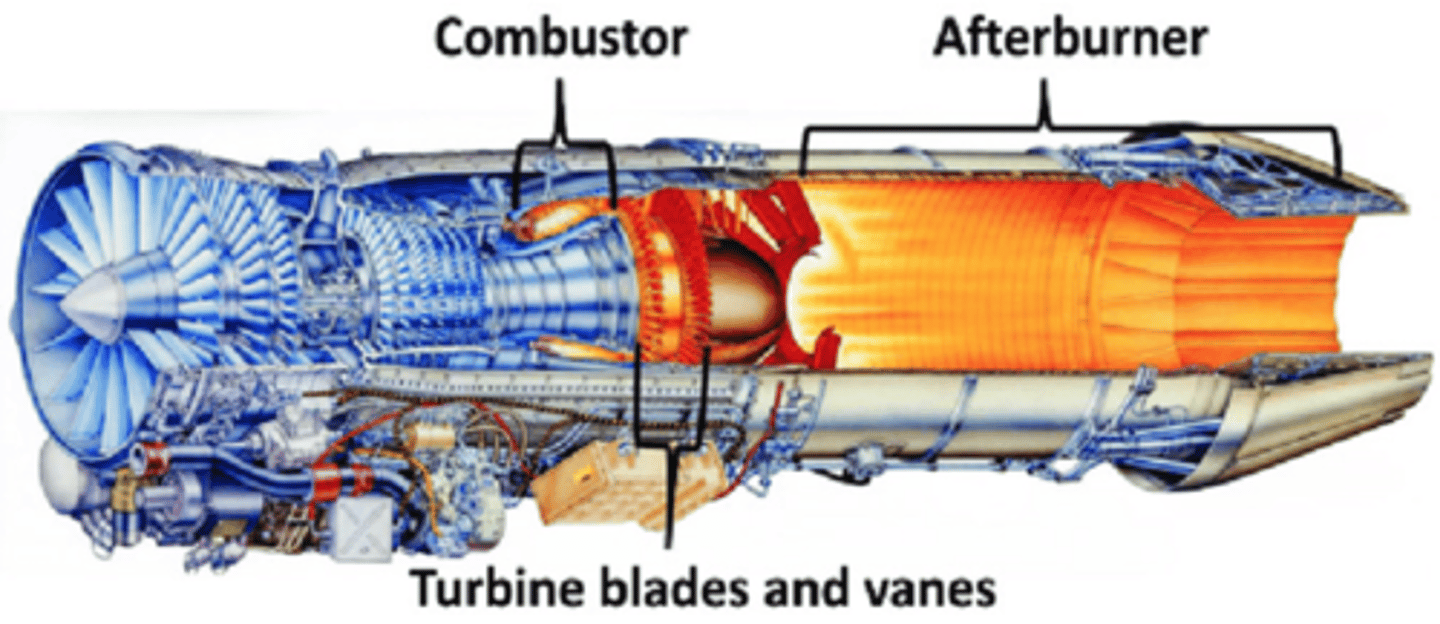
What are the 3 components in an afterburner?
1) Fuel manifold
2) Ignition source
3) Flame holder
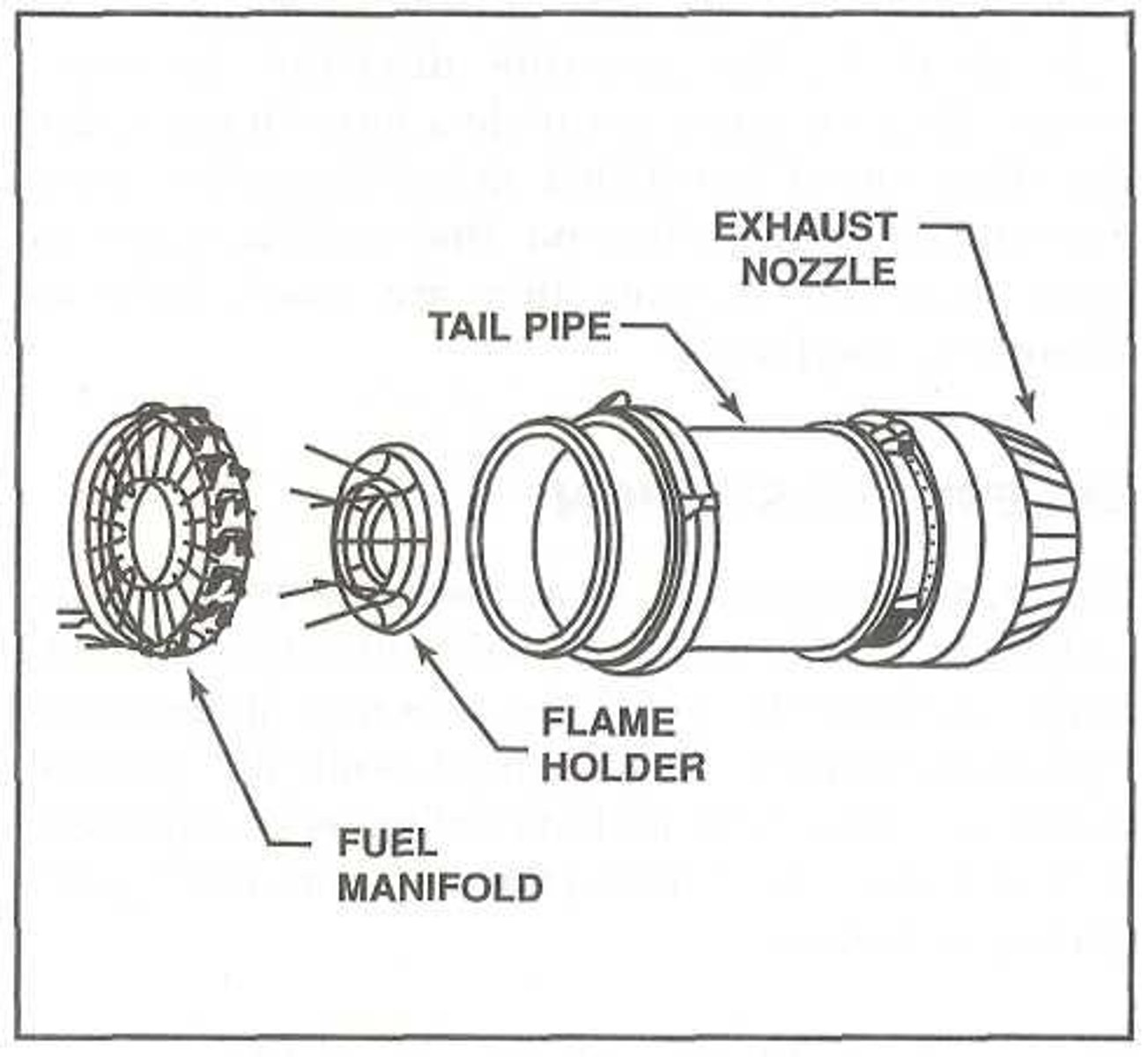
When is an afterburner typically used?
-During takeoff
-For short periods, due to intense heat generation
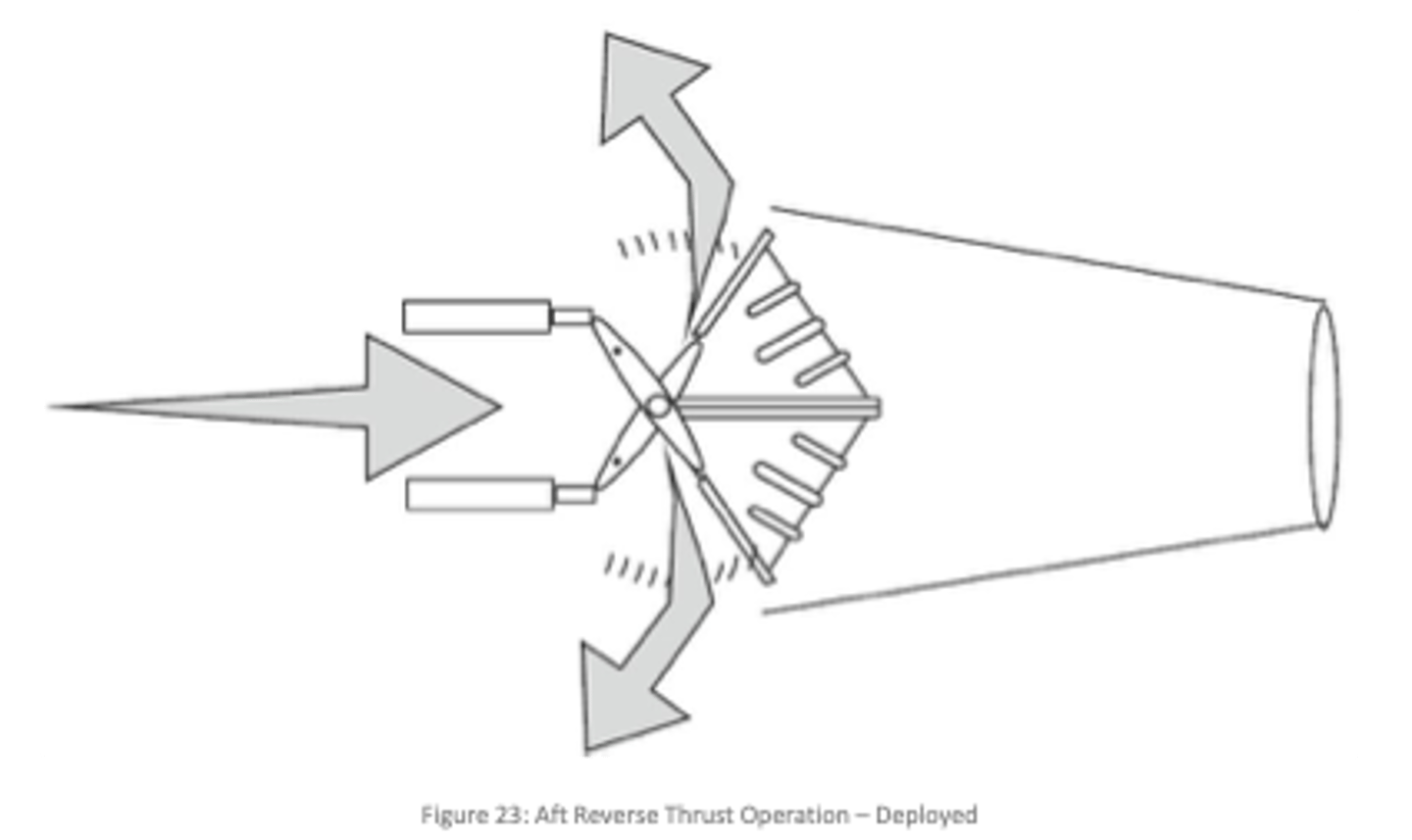
What is the purpose of a thrust reverser?
To redirect the flow of exhaust gases to provide thrust in the opposite direction AND/OR slow forward motion
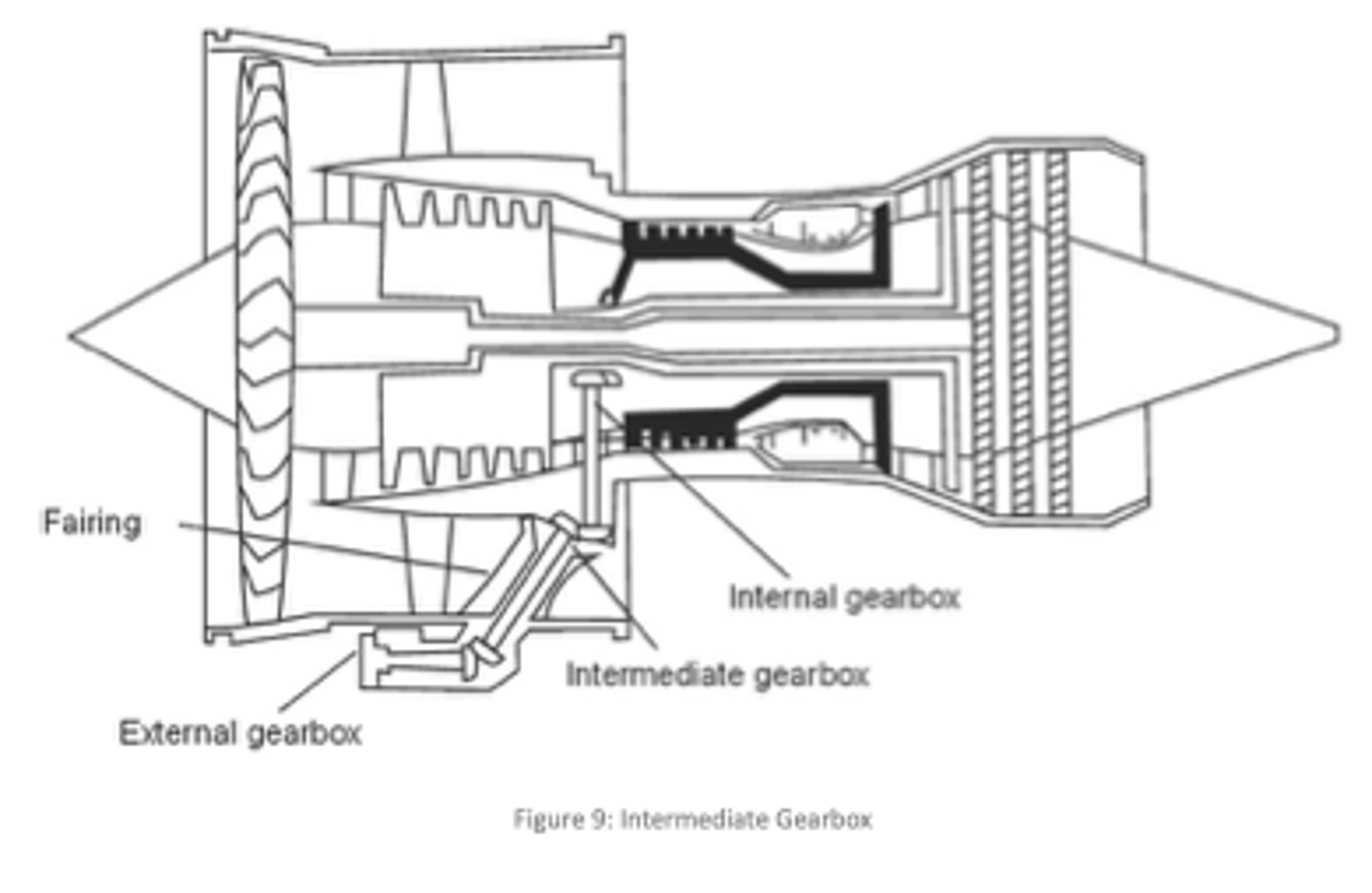
What are the Primary and Secondary functions of an accessory drive gearbox?
PRIMARY:
-Drive engine and aircraft accessories, including generators, hydraulic pumps, fuel pumps, and oil pumps
SECONDARY:
-Acting as an oil reservoir and housing the accessory drive and reduction gears
What is the purpose of an Intermediate or Transfer gearbox?
Reduce rotational speed of accessory drive shaft before the shaft reaches the main accessory gearbox
What differences are there between the mounts of turbofan engines vs turboprop engines?
Turboprop engines have heavier and stronger engine mounts due to higher torque loads.
What type of bearings are used in turbine engines?
Roller and ball bearings (too fast and hot for plain bearings)
What are the 3 types of oil seals in turbine engines?
1) Labyrinth Seal
2) Helical Seal
3) Carbon Seal
How does a Labyrinth Seal work?
Tiny whirlpools are formed in each groove slowing the escape of air and lowering the pressure
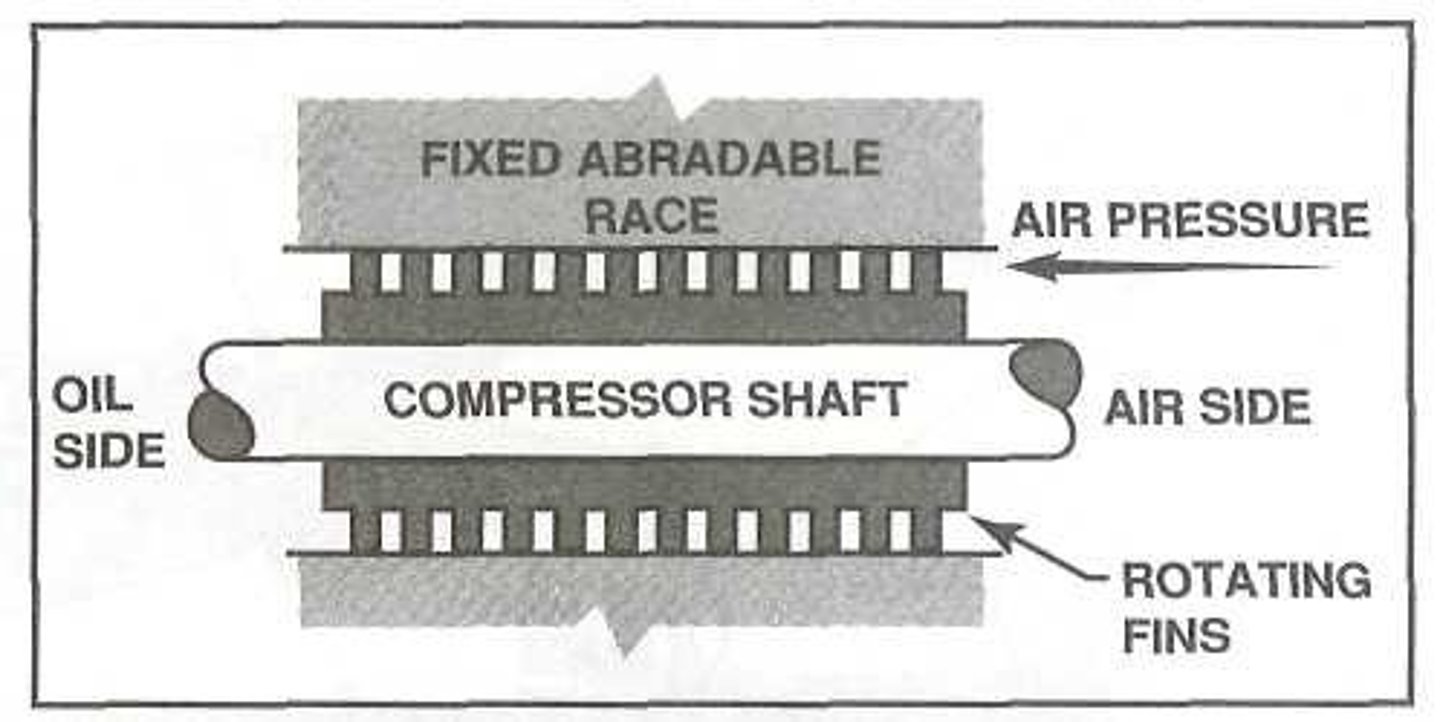
How does a Helical Seal work?
Similar to a labyrinth seal, except helical designs rely on reverse threading to prevent oil leakage.
How does a Carbon Seal work?
the seal is spring loaded so that it holds against a rotating shaft, preventing oil for moving between surfaces.
Free turbine vs Fixed shaft turboprop engine
FREE TURBINE:
an independent turbine drives the propeller, which is not attached to the main turbine.(PT6 type design)
FIXED SHAFT ENGINE:
The main power shaft goes directly into a gearbox to output low speed, high torque energy for the propeller. Everything is connected.
What can an APU supply for an aircraft?
-Bleed air for...
-heating
-cooling
-Anti-ice
-engine starting
-Hydraulic pump pressure
-Electrical power (generator)
-Fuel pump pressure