The Skeletal System
5.0(3)Studied by 55 people
Card Sorting
1/154
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:49 PM on 10/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
1
New cards
What are the functions of the skeletal system?
-Support and protection
-Body movement
-Blood cell formation (hematopoiesis) occurs in bone marrow
-Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium)
-Body movement
-Blood cell formation (hematopoiesis) occurs in bone marrow
-Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium)
2
New cards
How many ones are you born with and how many do you have now?
You are born with about 270 but they fuse together to make 206
3
New cards
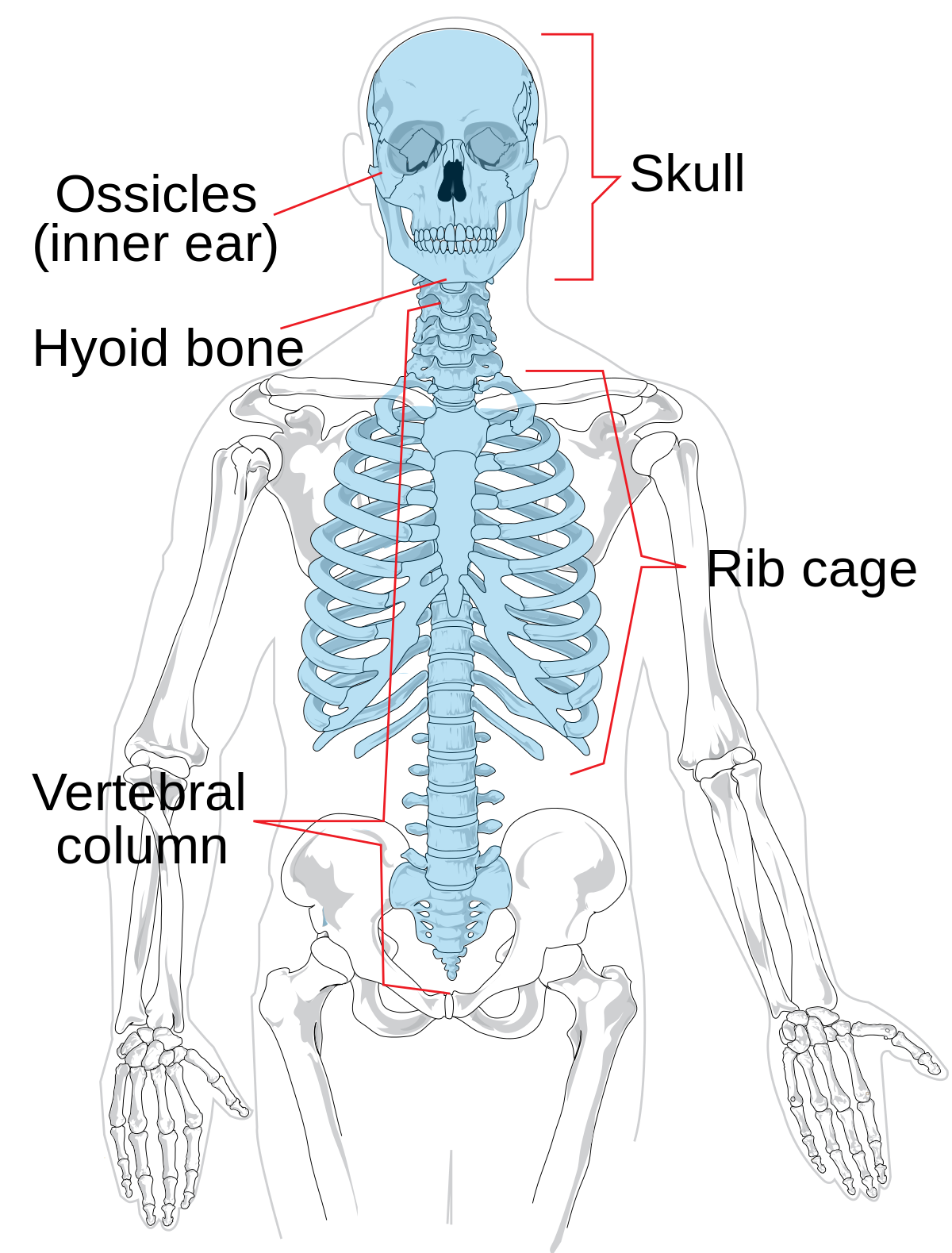
What does the axial skeleton consist of?
-Head, neck, trunk
-Skull
-Hyoid bone
-Vertebral column
-Thoracic cage (ribs, 12 pairs)
-Sternum
-Skull
-Hyoid bone
-Vertebral column
-Thoracic cage (ribs, 12 pairs)
-Sternum
4
New cards
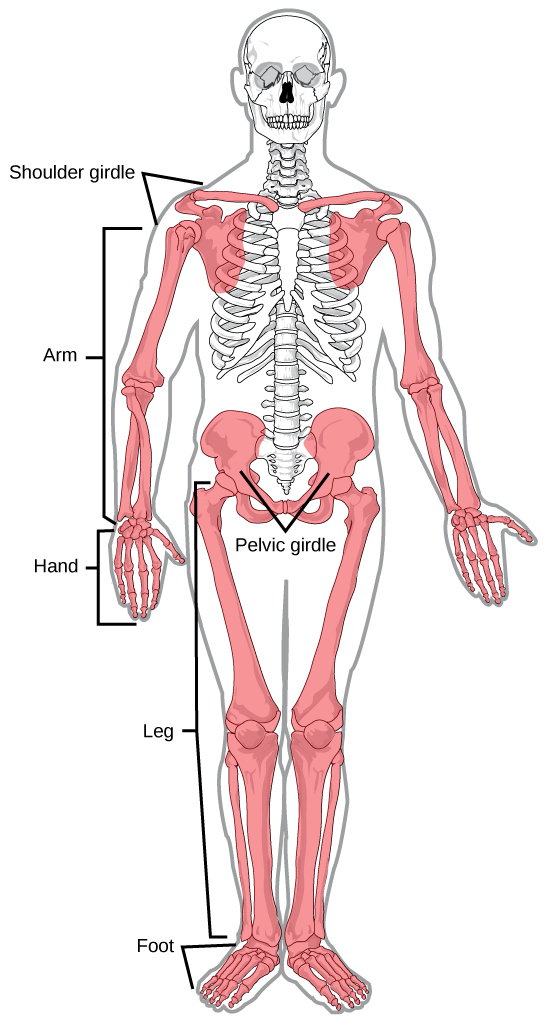
What does the appendicular skeleton consist of?
-Pectoral Gridle (scapula, clavicle, arms)
-Pelvic Gridle (coxal bones, legs)
-Pelvic Gridle (coxal bones, legs)
5
New cards
What does fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP) cause?
Causes soft tissue (muscles, tendons, ligaments) to turn to bone
6
New cards
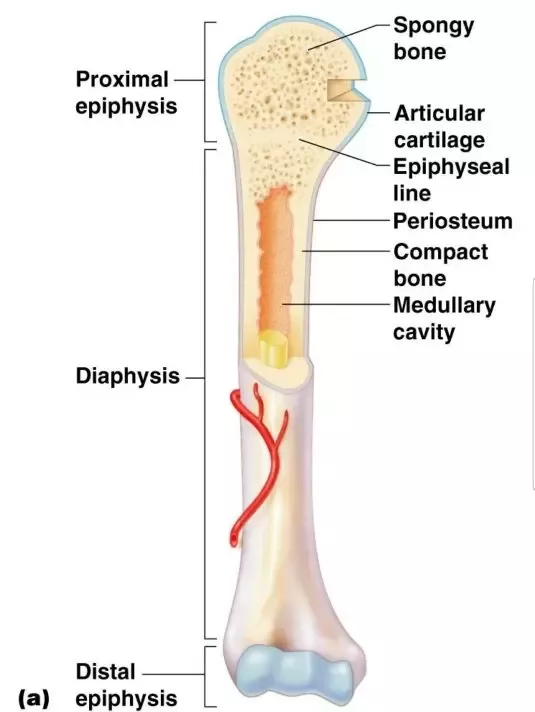
What does the long bone consist of?
-Epiphysis (end)
-Diaphysis (shaft)
-Articular Cartilage (hylaine cartilage, padding)
-Periosteum (membrane that covers entire bone)
-Medulla (contains marrow)
-Diaphysis (shaft)
-Articular Cartilage (hylaine cartilage, padding)
-Periosteum (membrane that covers entire bone)
-Medulla (contains marrow)
7
New cards
How are the epiphyses named?
By location
8
New cards
Closest epiphyses to the body's central ->
Proximal
9
New cards
Furthest epiphyses from the body's central ->
Distal
10
New cards
What is the function of flat bones? Give example
Protection -- sternum, ribs, skull, bones
11
New cards
What is the function of long bones? Give example
Support weight, movement -- femur, tibia, fibula, humerus, radius, ulna
12
New cards
What is the function of short bones? Give example
Stability, movement -- carpals, tarsals
13
New cards
What is the function of irregular bones? Give example
Protects organs -- vertebrae, pelvis
14
New cards
What is the function of sesamoid bones? Give example
Reinforce tendons -- patella (knee cap)
15
New cards
What is inside the long bone?
-Medullary Cavity: hollow, filled with yellow bone marrow
-Endosteum: lines of the medullary cavity
-Red Marrow: produces blood
-Yellow Marrow: fat storage
-Endosteum: lines of the medullary cavity
-Red Marrow: produces blood
-Yellow Marrow: fat storage
16
New cards
What are the types of bone tissue?
-Compact (wall of the diaphysis)
-Spongy/Cancellous (epiphysis) -> red marrow
-Spongy/Cancellous (epiphysis) -> red marrow
17
New cards
What is the epiphyseal line?
The growth plate
18
New cards
What is bone tissue called?
Osseous tissue
19
New cards
What is the matrix composed of?
Collagen and inorganic salts
20
New cards
What is osteocytes?
Mature bone cells, enclosed in tiny chambers called lacunae
21
New cards
The rings that form around the osteocytes are called?
Lamellae
22
New cards
What does the haversian canal house?
Blood vessels
23
New cards
What is a canaliculi?
Tiny canals that link osteocytes
24
New cards
What provides passageways for blood vessels?
Haversian and Volkmann canals
25
New cards
What is the process ossification?
Bone first forms as hyaline cartilage, then gradually changes into bone tissue
26
New cards
Primary ossification center increases...
Diameter
27
New cards
Secondary ossification center increases...
Length
28
New cards
Osteoblasts:
Creates osteocytes (blasts = produce)
29
New cards
Osteoclasts:
Bone resorption (clasts = destroy)
30
New cards
Define epiphyseal disk (growth plate)
A bond of cartilage between the epiphysis and diaphysis
31
New cards
Name the types of joints
-Synarthrotic: immovable joint, called sutures -> skull
-Amphiarthrotic: slightly movable -> vertebrae
-Diarthrotic (synovial joint): movable joint -> knees, elbows, wrist, shoulder
-Amphiarthrotic: slightly movable -> vertebrae
-Diarthrotic (synovial joint): movable joint -> knees, elbows, wrist, shoulder
32
New cards
Name the types of diarthrotic joints
-Ball & Socket joint (shoulder, hip)
-Hinge (elbow, knee)
-Pivot (lower arm)
-Saddle (thumb)
-Hinge (elbow, knee)
-Pivot (lower arm)
-Saddle (thumb)
33
New cards
Frontal bone
Anterior portion (forehead)
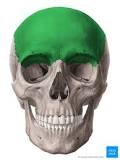
34
New cards
Parietal bone
On each side of the top of skull
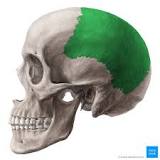
35
New cards
Temporal bone
Side, above ear
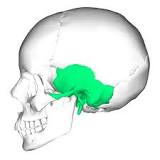
36
New cards
Occipital bone
Forms the back of the skull
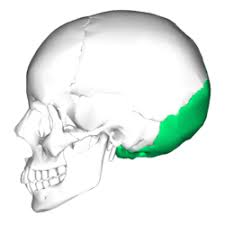
37
New cards
Sphenoid bone
Within the cranium, party visible in
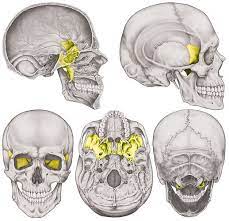
38
New cards
Ethmoid bone
Nasal cavity, visible in eye socket
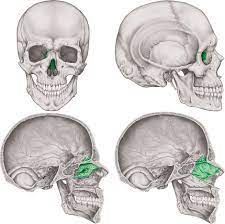
39
New cards
Maxilla bone
Forms upper jaws
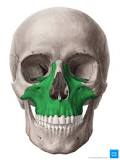
40
New cards
Mandible bone
Lower jaws, only movable bone of the skull
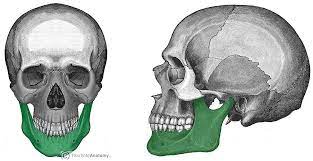
41
New cards
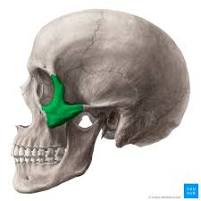
Zygomatic bone
Cheek bone
42
New cards
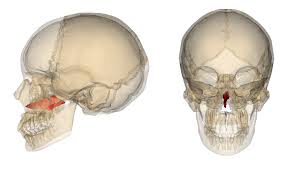
Vomer bone
Small, thin, plow-shaped, midline bone that occupies and divides the nasal cavity
43
New cards
Define sutures
Connection points between skull bones
44
New cards
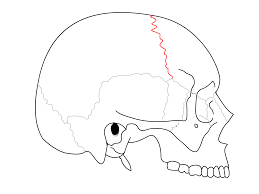
Coronal suture
Between frontal and parietal bones
45
New cards
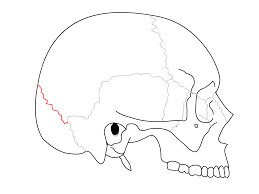
Lambdoidal suture
Between occipital and parietal bones
46
New cards
Squamosal (squamous) suture
Between temporal and parietal
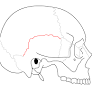
47
New cards
Sagittal suture
Between parietal bones

48
New cards
What are fontanels?
"Soft spots" of an infants skull, these form sutures as you age, top spot is the anterior fontanel
49
New cards
What is the mental foramen?
An opening on the chin that allows nerves and blood vessels to come through to supply face
50
New cards
What is the foramen magnum?
Large opening through bottom of skull, where the spinal cord enters skull
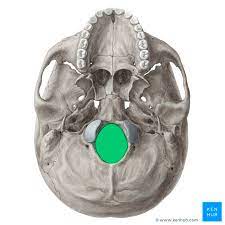
51
New cards
Name the vertebrae
-Cervical (C1-C7) -> neck
-Thoracic (T1-T12) -> middle back
-Lumbar (L1-L5) -> lower back
-Sacrum & Coccyx (fused bone)
-Thoracic (T1-T12) -> middle back
-Lumbar (L1-L5) -> lower back
-Sacrum & Coccyx (fused bone)
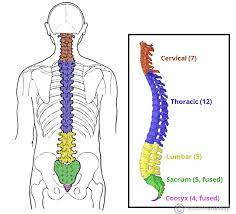
52
New cards
True ribs ->
First seven pairs, attach directly to sternum
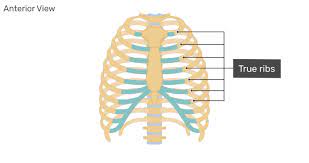
53
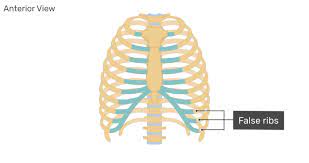
New cards
False ribs ->
Last five pairs
54
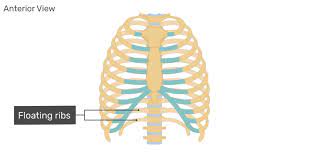
New cards
Floating ribs ->
Last two pairs (floating ribs are a part of false ribs)
55
New cards
The pectoral gridle consist of...
-Shoulder
-Two clavicles (collar bones)
-Two scapulas (shoulder blades)
-Two clavicles (collar bones)
-Two scapulas (shoulder blades)
56
New cards
The pelvic gridle consist of...
-Hips
-Two large bones called coxal bones
-Two large bones called coxal bones
57
New cards
Upper leg ->
Femur
58
New cards
Kneecap ->
Patella
59
New cards
Lower leg ->
-Tibia (shin)
-Fibula (bone that connect to side of ankle)
-Fibula (bone that connect to side of ankle)
60
New cards
Ankle and upper foot - 7 bones ->
Tarsal
61
New cards
Heel bone (largest) ->
Calcaneus
62
New cards
Foot ->
Metatarsals
63
New cards
Toes ->
Phalanges
64
New cards
What are your carpals?
Wrist bones
65
New cards
What are your tarsals?
Ankle bones
66
New cards
Upper arm ->
Humerus
67
New cards
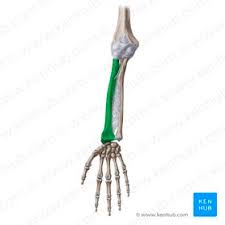
Lower arm ->
-Ulna (pinky)
-Radius (thumb)
-Radius (thumb)
68
New cards
Wrist ->
Carpals (8 small bones)
69
New cards
Hand ->
Metacarpals
70
New cards
Fingers ->
Phalanges
71
New cards
Tranverse break

72
New cards
Linear break

73
New cards
Oblique, nondisplaced break

74
New cards
Oblique, displaced break

75
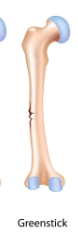
New cards
Greenstick break
76
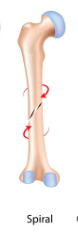
New cards
Spiral break
77
New cards
Comminuted break

78
New cards
What are bone spurs?
Also known as osteophytes
Occurs when the body grows small projections on the edges of bones
Occurs when the body grows small projections on the edges of bones
79
New cards
What is plantar fasciitis?
-Common cause of heel pain
-Inflammation of the plantar fascia
-Walking can be painful
-Inflammation of the plantar fascia
-Walking can be painful
80
New cards
What is osteoporosis?
-Increased activity of osteoclasts cause a break down of bone.
-Bones become more fragile
-The spongy bone becomes more porous
-Bones become more fragile
-The spongy bone becomes more porous
81
New cards
What are the causes of osteoporasis?
-Lack of exercise
-Poor diet
-Genetics
-Ethnicity
-Gender
-Poor diet
-Genetics
-Ethnicity
-Gender
82
New cards
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
An autoimmune disease which causes joint stiffness and bone deformity
83
New cards
What is rickets?
-Vitamin D deficiency
-Causes weak, brittle bones that fracture easily and affect growth
-Causes weak, brittle bones that fracture easily and affect growth
84
New cards
Nasal bone
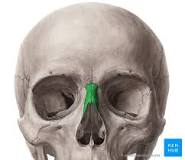
85
New cards
Lacrimal bone
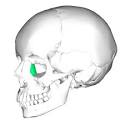
86
New cards
Mastoid Process
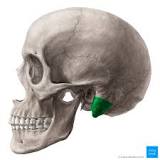
87
New cards
What is osteosarcoma?
Bone cancer
88
New cards
What are the abonormalities of the spine?
-Kyphosis: hunchback curve
-Lordosis: swayback in lower region
-Ankylosis: severe arthritis in the spine
-Scoliosis: curve of the spine
-Lordosis: swayback in lower region
-Ankylosis: severe arthritis in the spine
-Scoliosis: curve of the spine
89
New cards
Talus
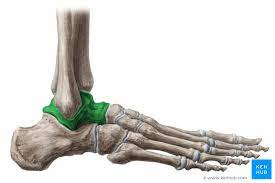
90
New cards
Calcaneus
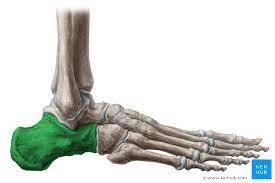
91
New cards
Navicular
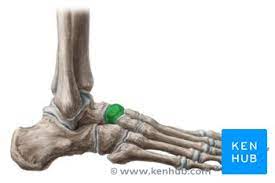
92
New cards
Cuboid
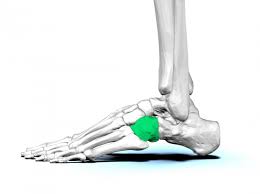
93
New cards
Medial Cuneiform
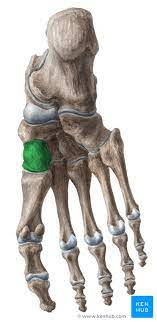
94
New cards
Intermediate Cuneiform
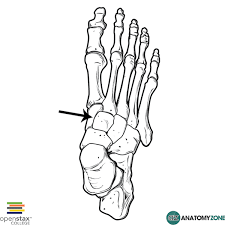
95
New cards
Lateral Cuneiform
96
New cards
Metatarsals (foot)
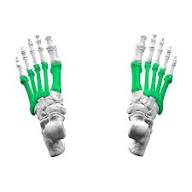
97
New cards
Proximal Phalanx
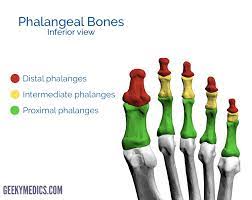
98
New cards
Middle Phalanx (Foot)
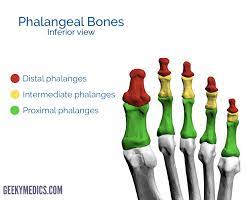
99
New cards
Distal Phalanx (Foot)
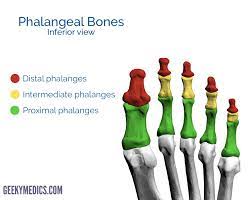
100
New cards
Radius