Elasticity of Demand
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Price elasticity of demand formula
PED = New - Original
———————
Original
PED definition
Measures the responsiveness quantity demanded to a change in price for a good or service
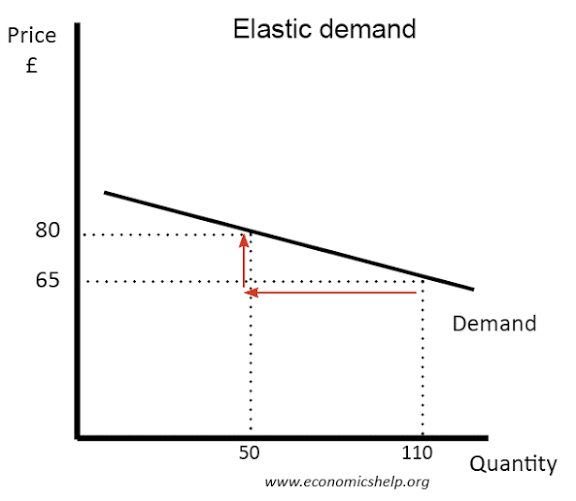
Elastic goods
Elastic goods - demand changes a lot when price changes
PED value greater than 1
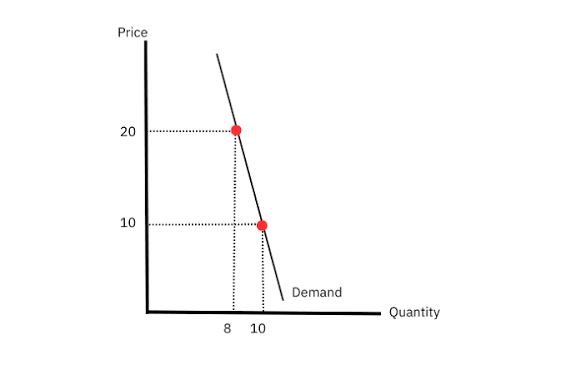
Inelastic goods
Demand changes a little when price changes
Value less than 1
Elastic demand diagram
Inelastic demand diagram
Factors that influence Elasticity
Essential - essential goods are inelastic
Substitutes - the more substitutes the more elastic
Percentage of income - if the price increases by a small bit, demand will be elastic as it doesn’t have a significant change like 10% increase in coffee price
Perfectly inelastic demand
PED = 0
Essential goods like water and electricity
Perfectly elastic demand
PED = infinity
Price of good is always the same, demand is infinite
Good, oil
When the good is elastic:
increasing price will decrease total revenue
decreasing price will increase total revenue
When the good is inelastic:
increasing price will increase total revenue
decreasing price will decrease total revenue
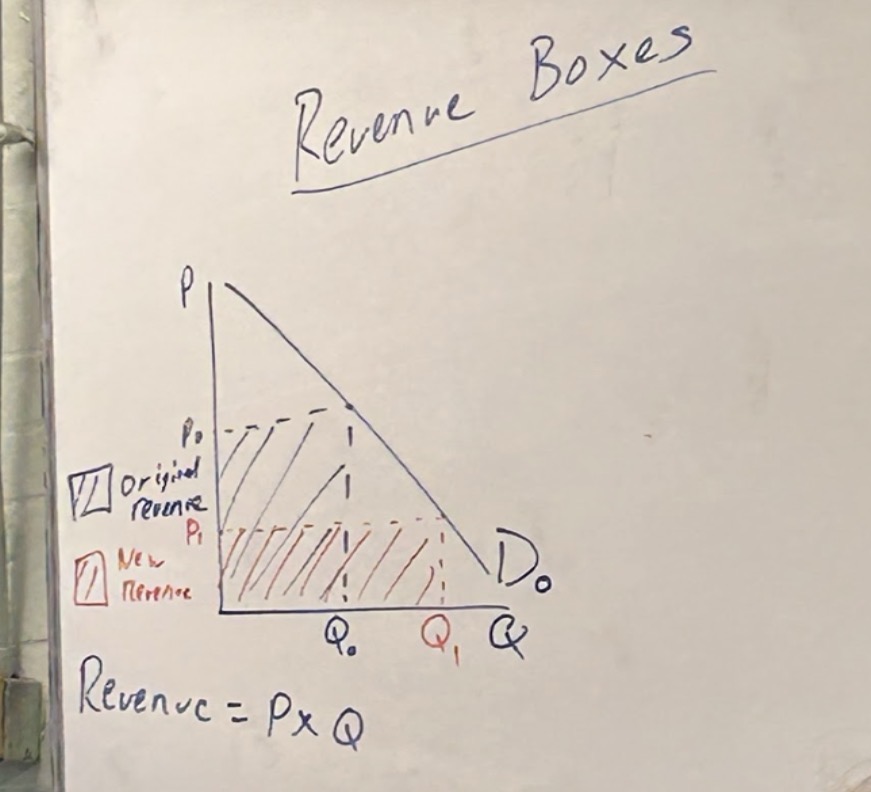
Revenue boxes
used to work out revenue at price points
price x quantity
Why is PED important?
Firms will know how to maximise revenue
Governments know which goods to tax
Taxes on inelastic goods won’t change consumption, but will increase tax revenue
Taxes on elastic goods will reduce consumption and lead to structural unemployment
PED for primary vs manufactured goods
Primary - inelastic goods as they are necessities, no substitutes
Manufactured - elastic demand, lots of substitutes,
Income elasticity of demand
A measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in consumer income
YED formula
YED = percentage change in Qd
———————————-
Percentage change in income
Luxury goods
Goods which have a high income elasticity of demand
YED > 1
Necessity good
Goods which have a low income elasticity of demand
-1<YED<1
YED a positive value
Normal good
YED a negative value
Inferior good
Why is YED important for firms?
During a recession:
incomes typically fall
demand for inferior goods increase
firms will increase production of inferior goods
During a boom:
incomes typically rise
demand for luxury and normal goods increase
firms will increase production of luxury and normal goods
Sectoral changes in structure of economy:
As incomes rise proportion of GDP from primary sector decreases, so firms will produce tertiary services as they have a higher proportion of GDP coming from them
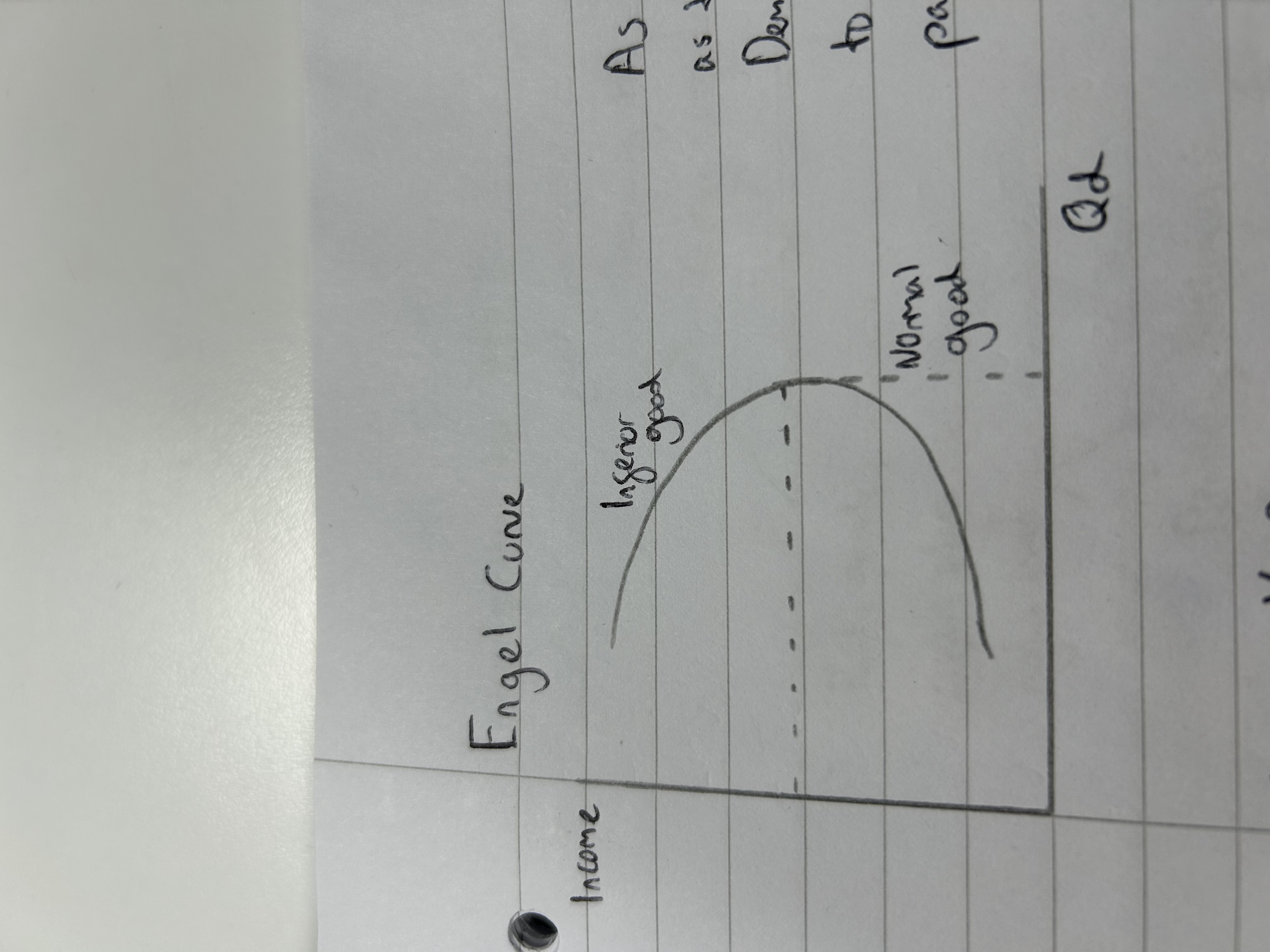
Engel curve
As incomes rise, people buy more potatoes so demand for them increases. Demand then falls as people begin to buy superior goods, therefore potatoes become inferior