ACTIVITY 4 - THE FUNGI
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/90
Earn XP
Last updated 5:13 PM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
1
New cards
absorptive heterotrophs
Mode of Nutrition of Fungi
2
New cards
Eukaryotes
Eukaryotes or Prokaryotes
3
New cards
Extracellular
where does digestion of food take place at for fungi
4
New cards
ranges from yeasts to filamentous molds to complex mushrooms
Range of
size and complexity of fungi
size and complexity of fungi
5
New cards
chytridiomycetes
Which phylum does not develop
motile cells
motile cells
6
New cards
sexual or asexual,
mainly by spores
mainly by spores
Mode of reproduction for the Kingdom Fungi
7
New cards
compatible mating strains
Although sexual reproduction occurs in fungi, the terms “male” and “female” are not applicable. Instead they are called
8
New cards
zygote
All fungal nuclei are haploid except
9
New cards
cells with two nuclei
What is dikaryotic
10
New cards
nuclear envelope does not breakdown and reform
How is mitosis in fungi different from others
11
New cards
hyphae
slender filaments in which the fungi body exist as
12
New cards
bubddles/ collection of hypha
mycelium
13
New cards
mycelium is loosely knit
What causes for a fungus to have a
fuzzy appearance
fuzzy appearance
14
New cards
the mycelium consists of tightly packed hyphae
What causes for a mushroom to have a fleshy form or structure
15
New cards
septate and aseptate hyphae
Two types of hypha/ fungal filaments
16
New cards
have cross-walls called septa (sing. septum)
septate hyphae
17
New cards
coenocytic, no cross walls
aseptate hyphae
18
New cards
polysaccharides and chitin, not cellulose as in plants and many protists.
Composition of Cell walls of hyphae
19
New cards
breaking down complex compounds and making elements available for synthetic activities of other organisms
Importance of fungi as decomposers
20
New cards
approximately 600 described species
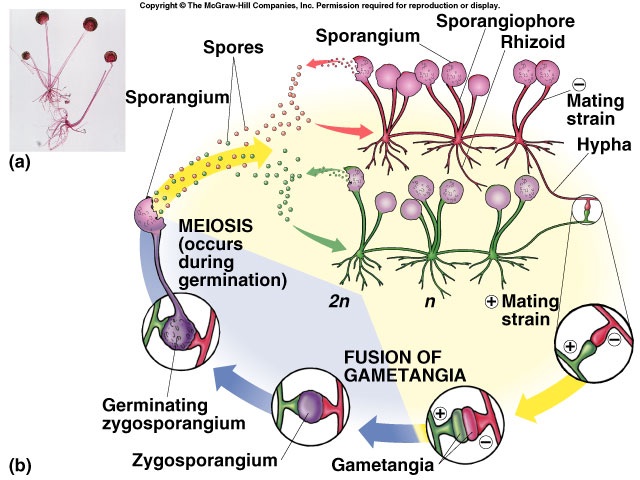
How many described species are in
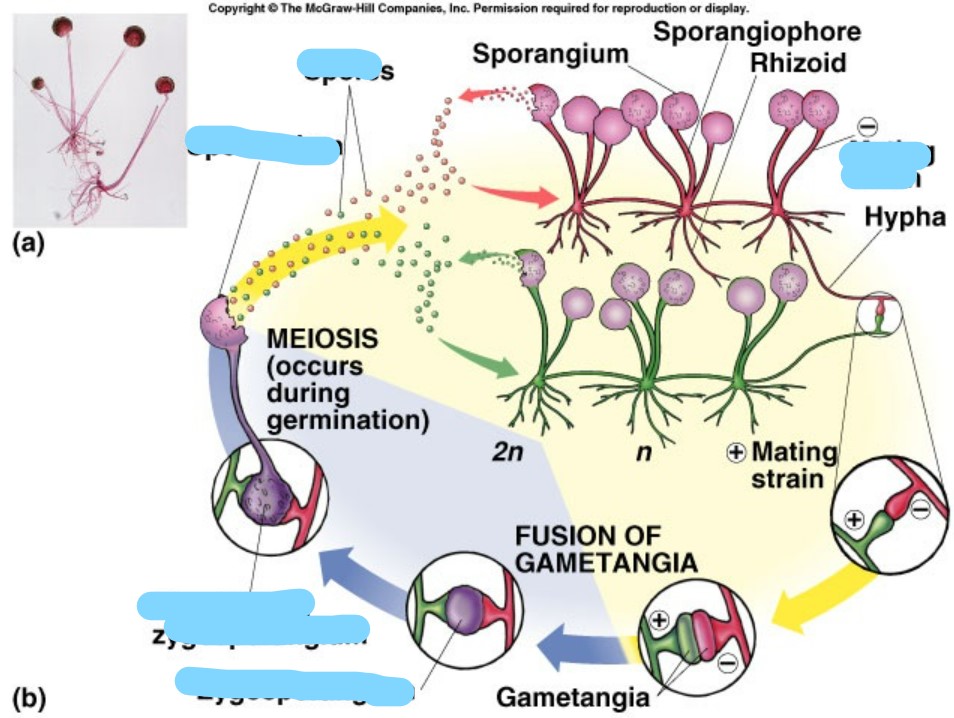
DIVISION ZYGOMYCOTA
DIVISION ZYGOMYCOTA
21
New cards
mostly terrestrial fungi living in decaying plant and animal matter in soil or forest litter
Where does ZYGOMYCOTA live
22
New cards
DIVISION ZYGOMYCOTA
Division wherein these fungi have
coenocytic hyphae and do not form complex fruiting bodies.
coenocytic hyphae and do not form complex fruiting bodies.
23
New cards
DIVISION ZYGOMYCOTA
What division is
Rhizopus stolonifer
Rhizopus stolonifer
24
New cards
Rhizopus stolonifer
the most common zygomycetous fungus of Division Zygomycota
25
New cards
DIVISION ZYGOMYCOTA
What division are
animal traps and fly fungi
animal traps and fly fungi
26
New cards
mass of thread-like structures growing at right angles to the hyphae.
rhizoids
27
New cards
cases or sporangia at their tips.
bear spherical spore
bear spherical spore
sporangiophores
28
New cards
produce asexual nonmotile spores
When some of these spores are blown far, they may initiate new distant colonies.
When some of these spores are blown far, they may initiate new distant colonies.
sporangia
29
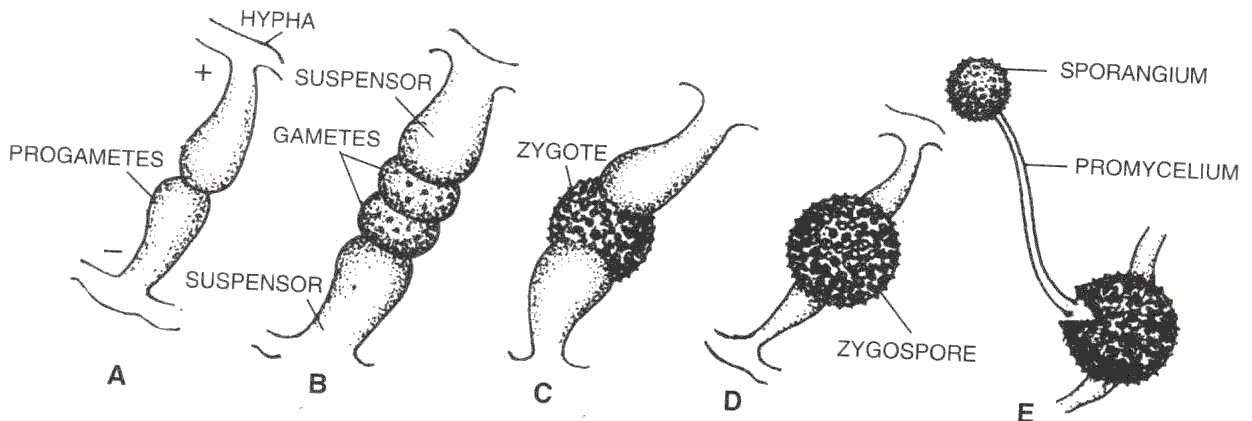
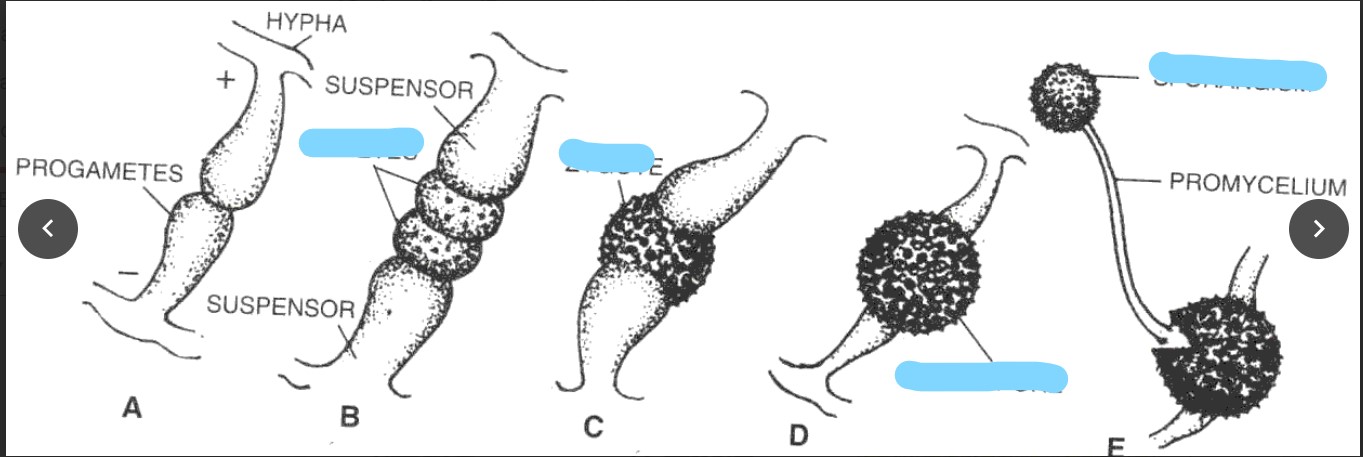
New cards
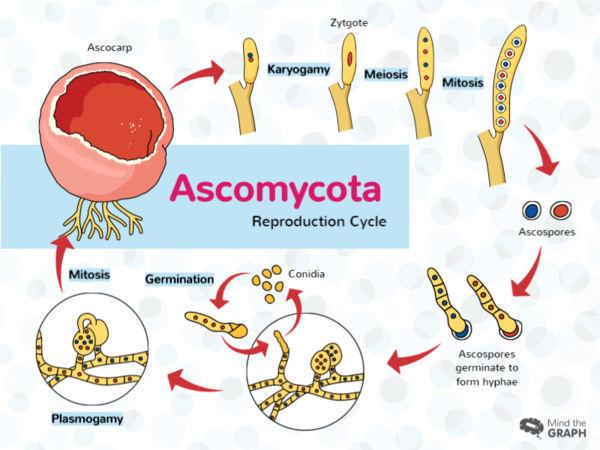
fusion of cytoplasm
plasmogamy
30
New cards
nuclei pair and fuse
karyogamy
31
New cards
formed after the karyogamy which becomes inactive for moths
zygosporangium
32
New cards
resistant sporangium, hindi pa siya spore
zygospores
33
New cards
1. finding of compatible mating straining (closing of two hypha)
2. mycelium produces short multinucleate branches growing toward equivalent branches on the other mycelium
3. plasmogamy
4. karyogamy
5. zygosporangium
6. germination -→ meosis
7. zygospores
blown away and germinate into new individuals
Process of LIFE CYCLE OF ZYGOMYCOTA
34
New cards
the sac fungi
The phylum termed as
35
New cards
a large sac-like cell
characterizes the division of ascomycota
characterizes the division of ascomycota
ascus
36
New cards
during germination ascus entering meiosis
how are ascospores formed
37
New cards
unicellular, filamentous, and thalloid (not multicellular)
Cell composition of Ascomycota
38
New cards
unicellular members of Division Ascomycota
Yeasts
39
New cards
used in bread making and in the alcoholic fermentation of beverage
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
40
New cards
beneficial and harmful to man
Ascomycetous mold fungi
41
New cards
desirable flavors to certain cheeses, produce high quality citric and other organic acids, and are the source of such antibiotics
Penicillium and Aspergillus
42
New cards
can cause a serious lung disease called aspergillosis.
Aspergillus,
43
New cards
major spoilers of stored food, leather, cloth, painted surfaces, etc
Others are destructive parasites of plants
Others are destructive parasites of plants
Molds
44
New cards
1. Yeasts
2. Saccharomyces cerevisiae
3. Ascomycetous mold fungi
4. Penicillium and Aspergillus
5. Aspergillus
6. Molds
Examples of Ascomycota
45
New cards
reproductive branch of ascomycota
conidiophore
46
New cards
Asexual nonmotile spores
• produced by the conidiophore
• produced by the conidiophore
conidia
47
New cards
The fruiting body produced by ascomycetes
• Eg, apothecium
• Eg, apothecium
ascocarp.
48
New cards
two to eight ascospores, depending on the species of ascomycete
how many ascospores do ascus contain
49
New cards
apothecium.
What kind os ascocarp does the cookeina fungi posses
50
New cards
fertile layer with in the apothecium wher the asci develops
hymenium,
51
New cards
Interspersed among the asci are sterile filaments
paraphyses
52
New cards
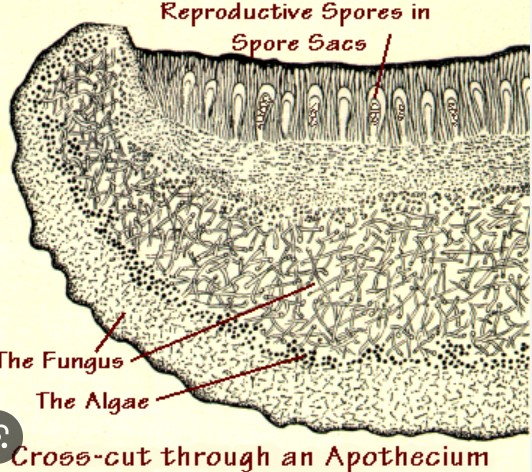
STRUCUTRE OF APOTHECIUM \[INFORMATIVE SLIDE\]
53
New cards
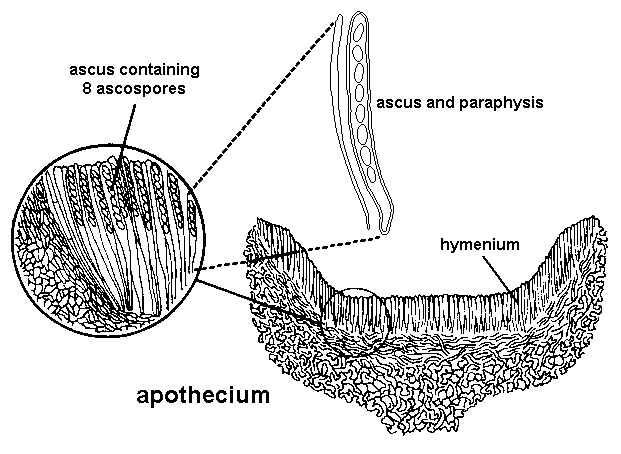
TRY TO IDENTIFY THE PARTS
54
New cards
ascogonium or antheridium
rp Two types of ascocarp
55
New cards
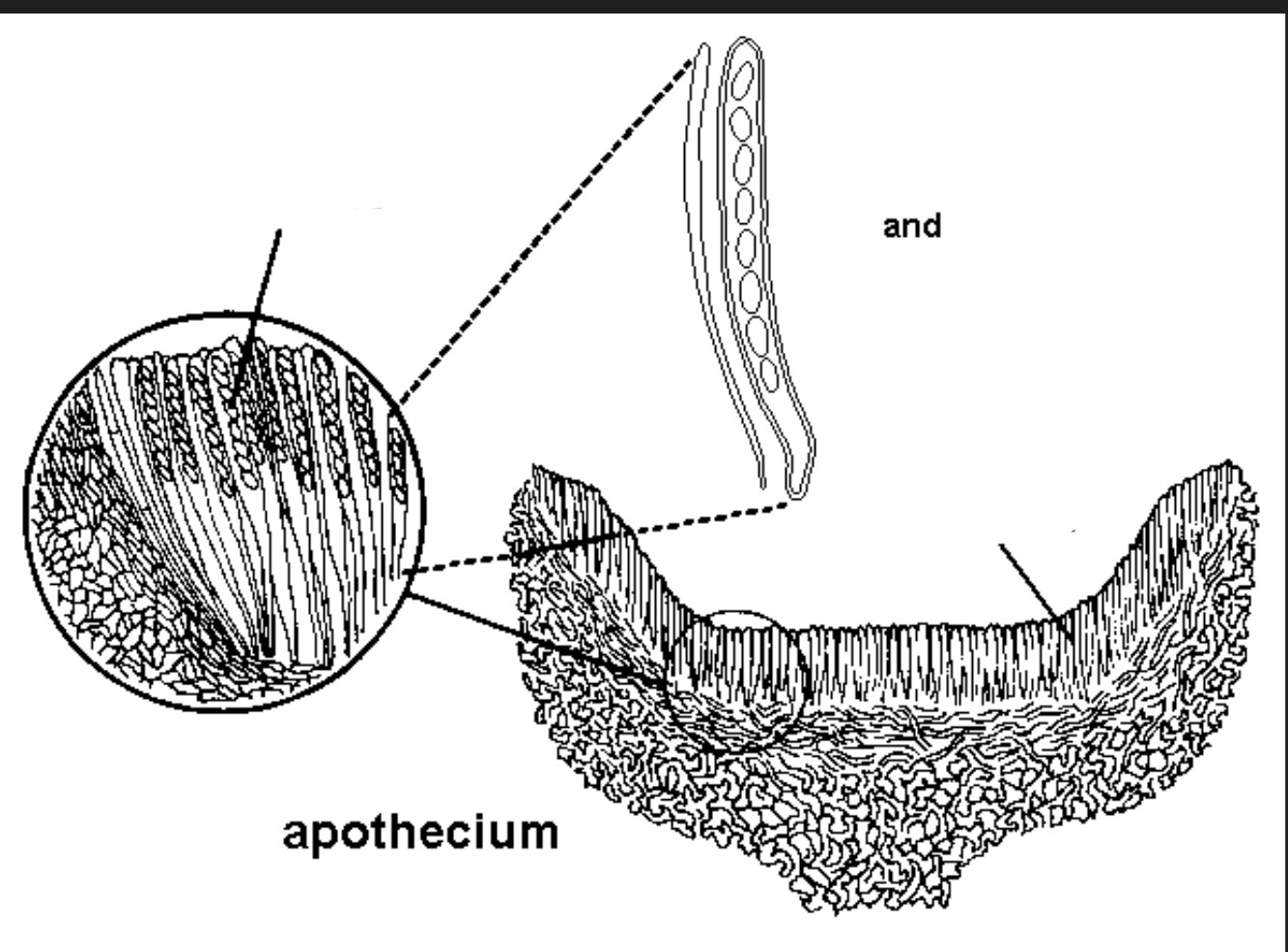
from the subterminal cell (where karyogamy occurs, thus, forming the zygote) of each hypha in the hymenium.
\
see attached image for visualization
\
see attached image for visualization
how are asci formed
56
New cards
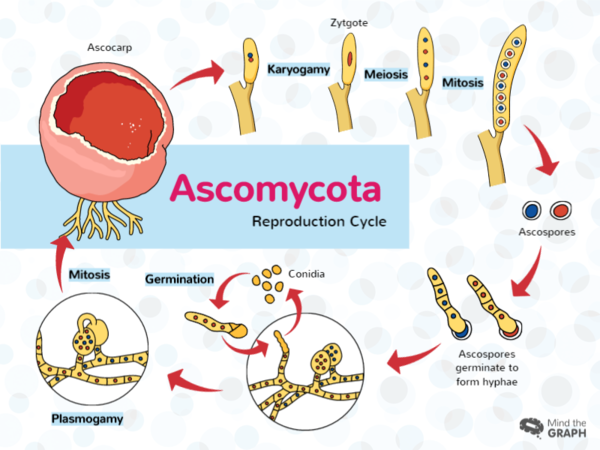
57
New cards
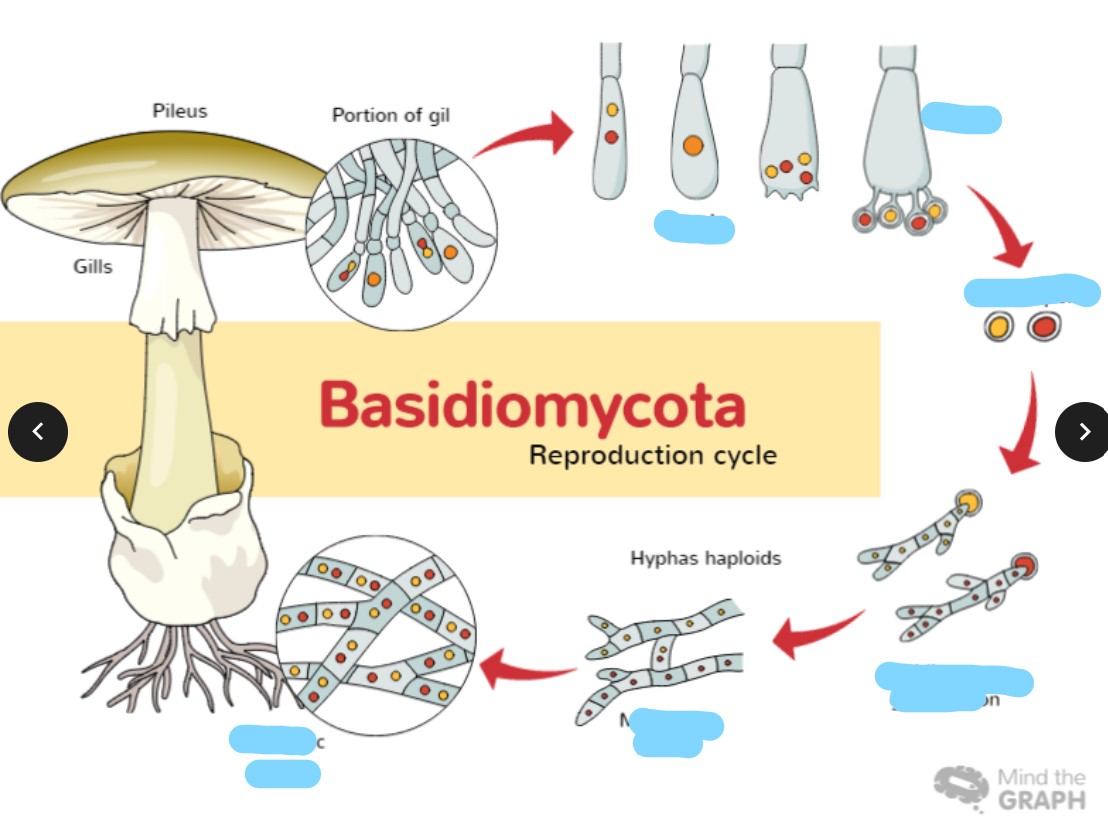
DIVISION Basidiomycota
from what division are the following:
bird’s nest fungi.
mushrooms,
tooth fungi, coral fungi
bird’s nest fungi.
mushrooms,
tooth fungi, coral fungi
58
New cards
basidiocarp
macroscopic fruiting bodies of DIVISION Basidiomycota
59
New cards
club-shaped basidia
What is the shape of the spores produced by the
basidiocarp
basidiocarp
60
New cards
saprophytically
Mode of nutrition of Basidiomycota
61
New cards
DIVISION Basidiomycota
major wood decay organisms
62
New cards
DIVISION Basidiomycota
what division form
mycorrhizal relationships with the roots of trees
mycorrhizal relationships with the roots of trees
63
New cards
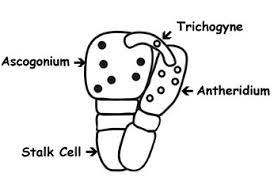
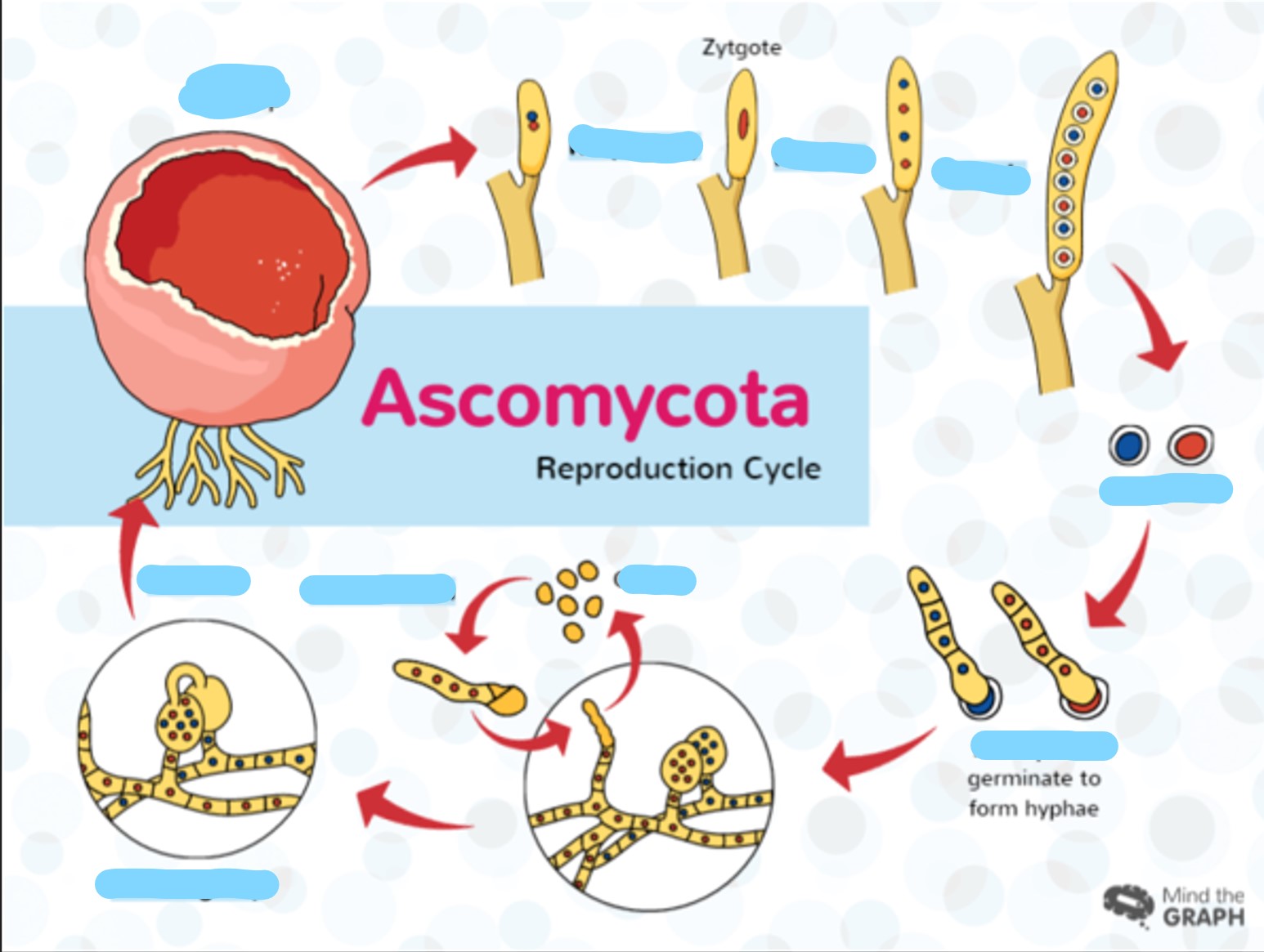
ascogonium which is the female strain
\
see imagae as reference
\
antheridium is male counter strain
\
see imagae as reference
\
antheridium is male counter strain
between the ascogium and antheridium, which gives rise to a new hyphae
64
New cards
cap-like structure of Basidiomycota
pileus
65
New cards
membranous sheets under the cap
gills
66
New cards
stalk supporting the pileus
stipe
67
New cards
form in each basidium
• Four tiny projections
• one haploid nucleus is squeezed out through each sterigma. This results to externally located spores called basidiospores
• Four tiny projections
• one haploid nucleus is squeezed out through each sterigma. This results to externally located spores called basidiospores
sterigmata
68
New cards
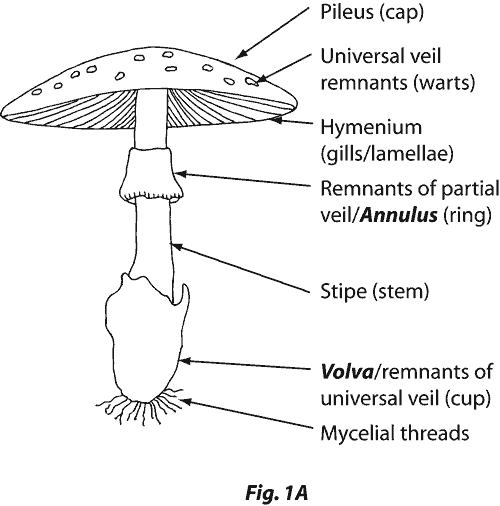
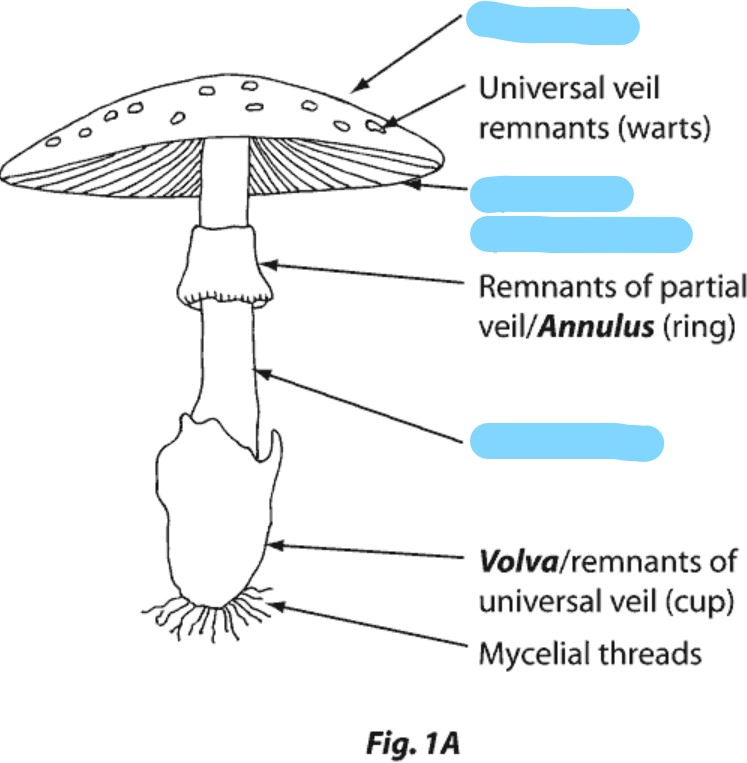
69
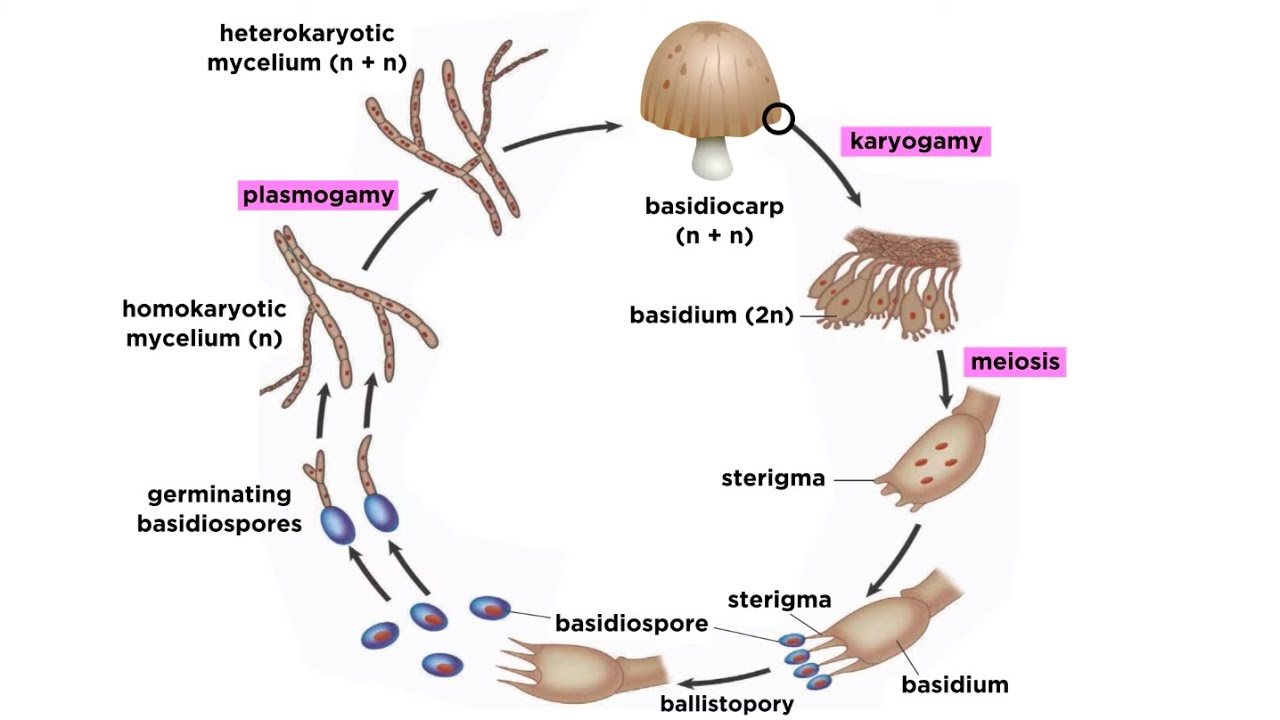
New cards
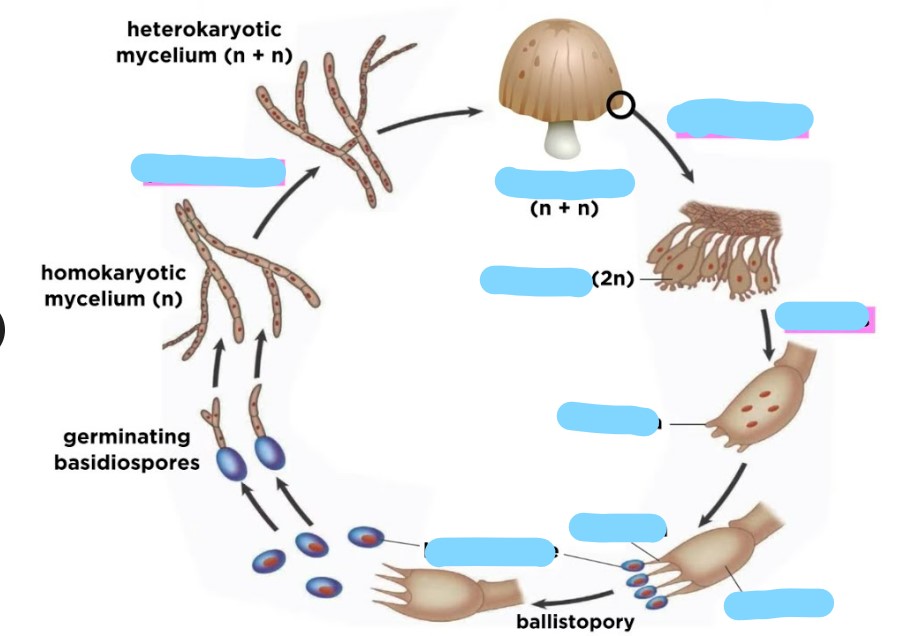
70
New cards
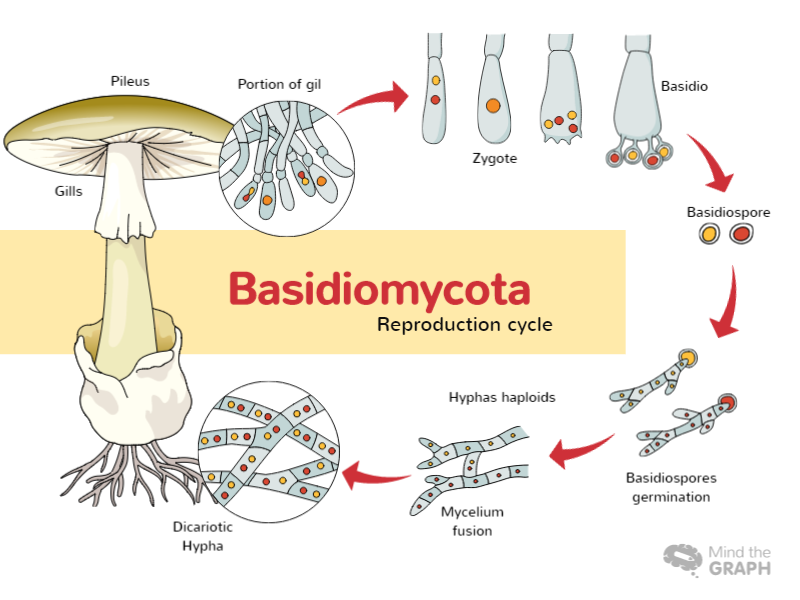
71
New cards
symbiotic relationship between a fungus (mycobiont) and an alga (phycobiont).
Lichens
72
New cards
soredia
dispersal unit of lichens is called
73
New cards
clump of a few algal cells closely enveloped by fungal hyphae.
soredia
74
New cards
either an ascomycete or a basidiomycete
mycobiont is either what divisions
75
New cards
any of the various types of free-living algae
phycobiont are what kind of algae
76
New cards
lichen growth type
intimate contact with the substrate making the lichen hard to separate from it
intimate contact with the substrate making the lichen hard to separate from it
crustose
77
New cards
lichen growth type
leafy with a distinct lower cortex and rhizinal attachment to the substrate
leafy with a distinct lower cortex and rhizinal attachment to the substrate
foliose
78
New cards
lichen growth type
hair-like, shrubby, finger-like, or strap-shaped
hair-like, shrubby, finger-like, or strap-shaped
fruticose
79
New cards
80
New cards
81
New cards
COOKEINA APOTHERA
82
New cards


83
New cards


84
New cards


85
New cards
86
New cards


87
New cards
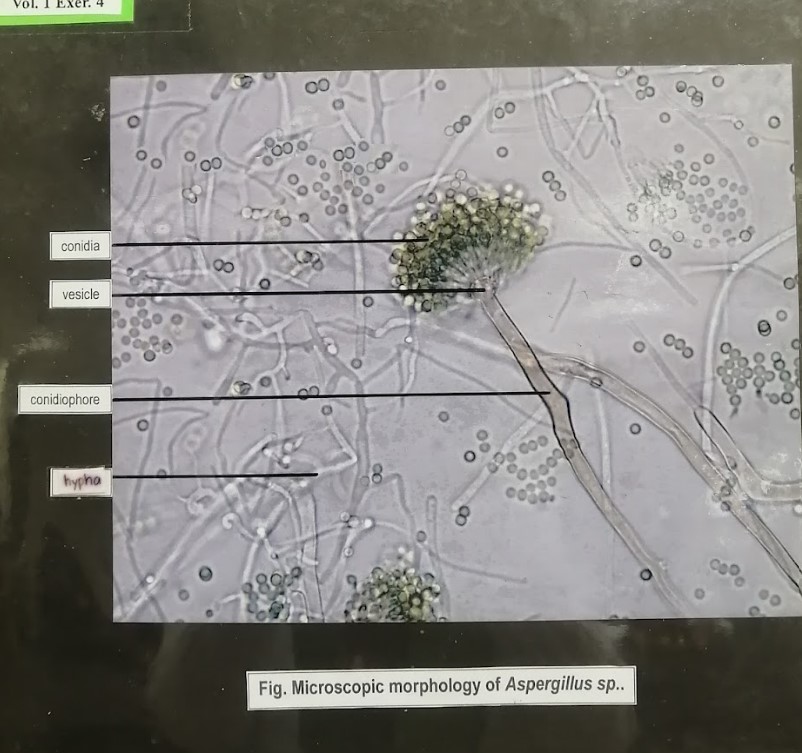
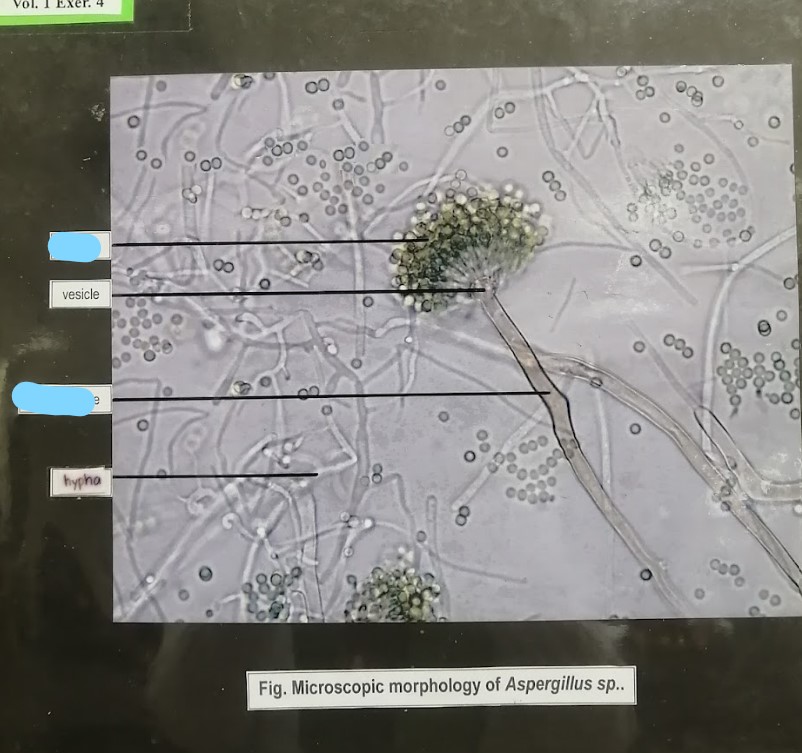
88
New cards


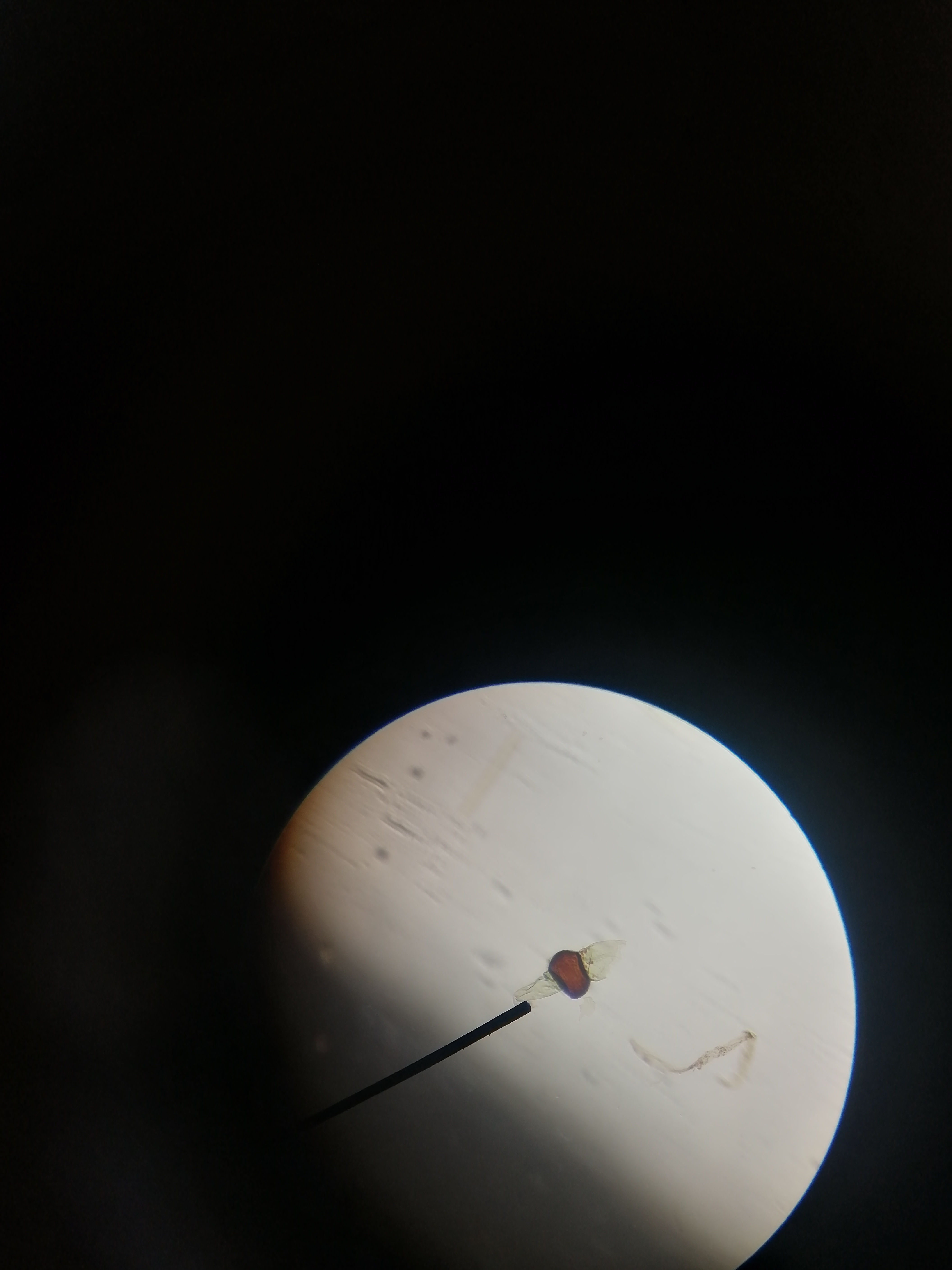
89
New cards
penicillium
Ascomycota
Ascomycota
what specimen and what division
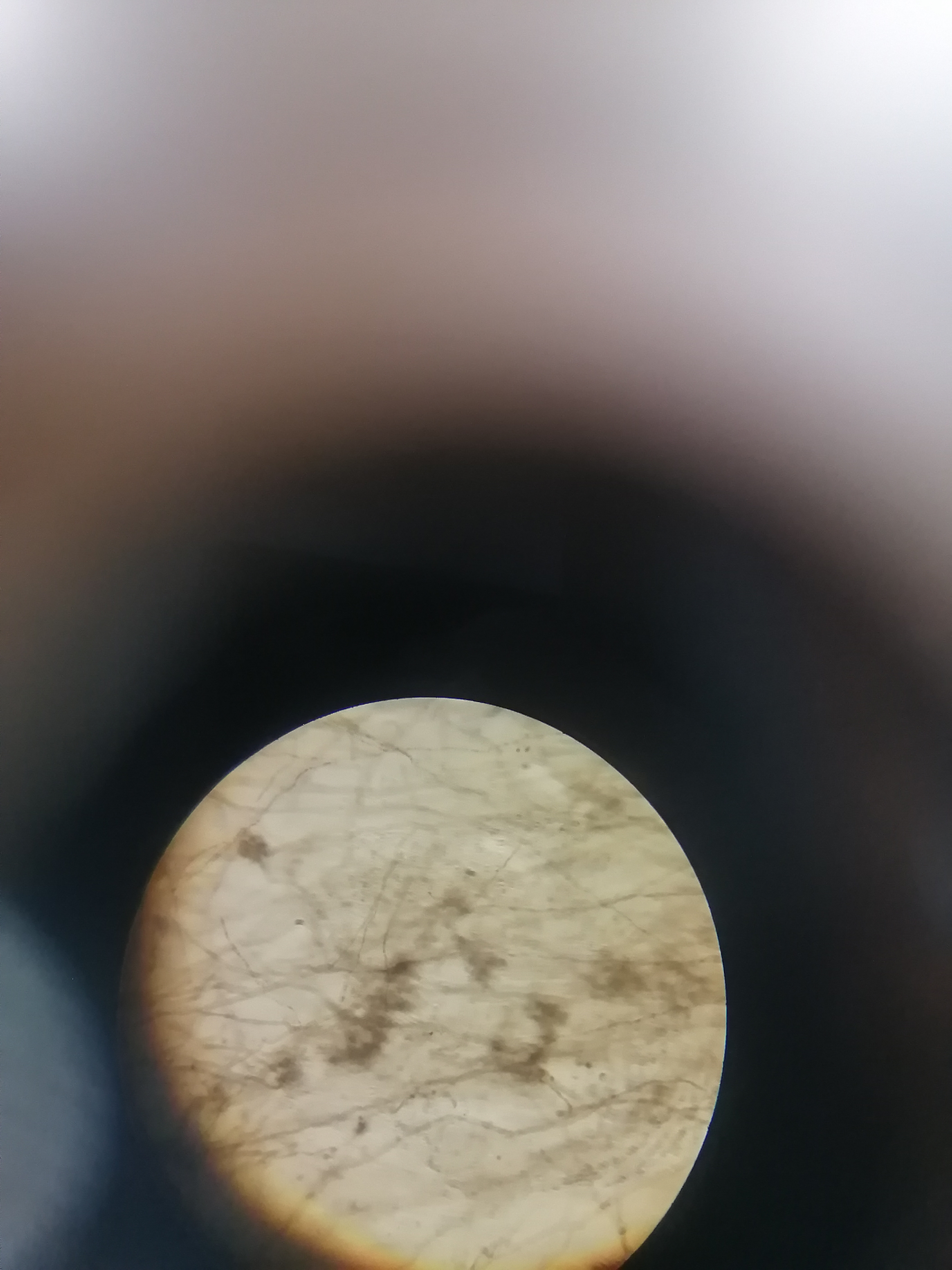

90
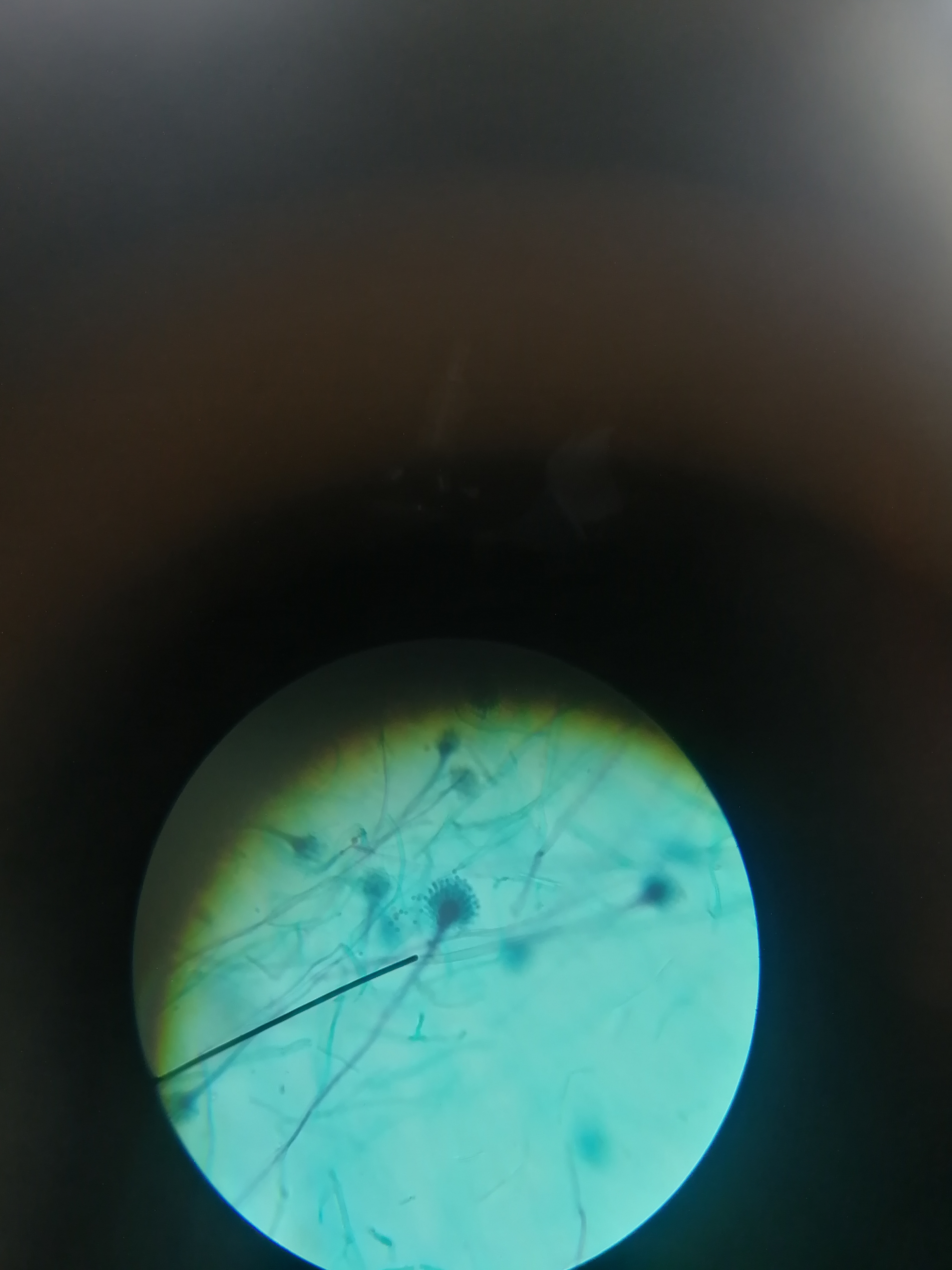
New cards
Aspergillus
Asco
Asco
what specimen and what division
91
New cards
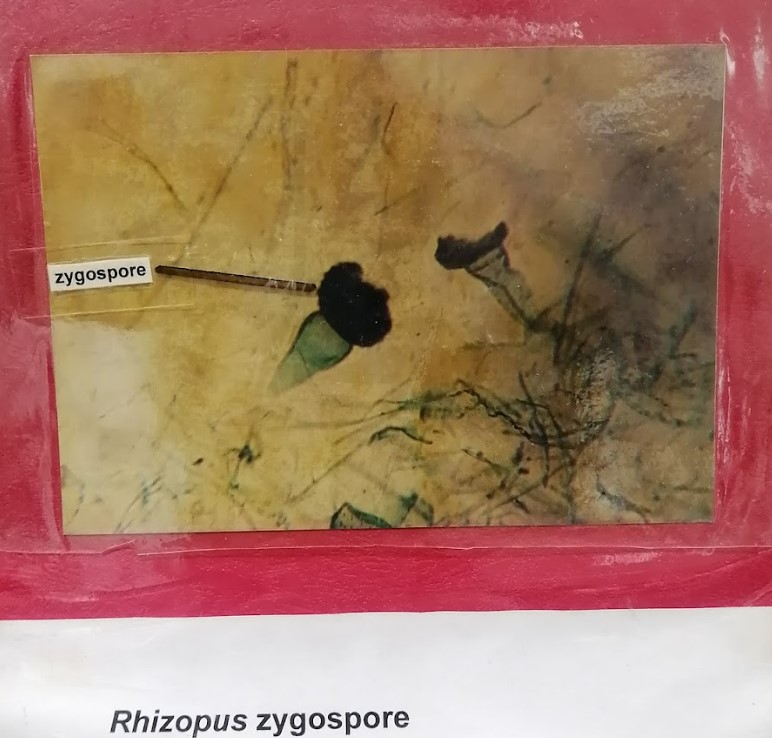
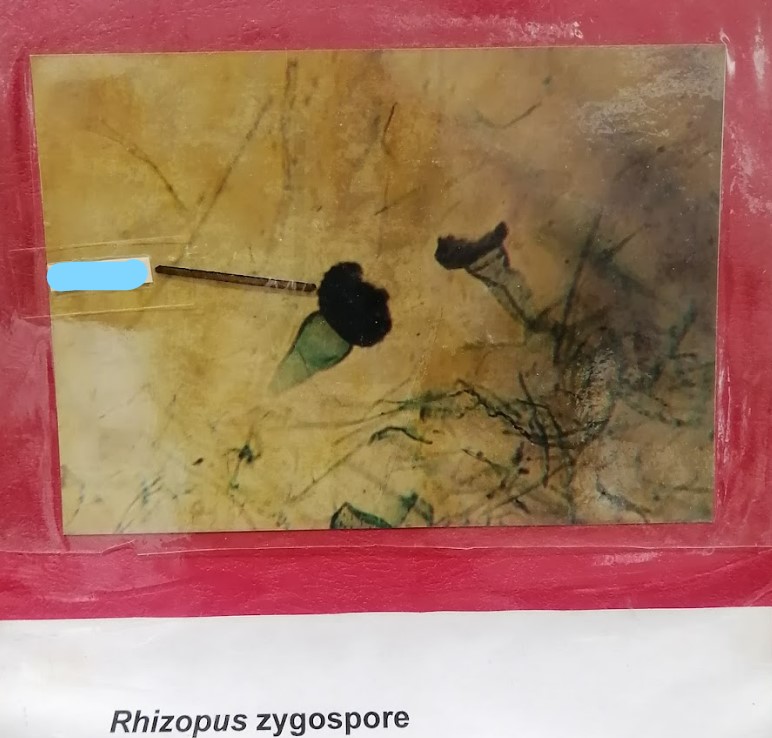
Rhizopous Zygospore
zygomycota
zygomycota
