BIOLOGY LAB MIDTERM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
Eyepiece
The part of a compound light microscope through which the viewer looks to see the magnified image.

2
New cards
Objective lenses
Lenses that are closest to the specimen and provide different levels of magnification.

3
New cards
Stage
The flat platform where the slide with the specimen is placed in a microscope.

4
New cards
Light source
The part of a compound light microscope that illuminates the specimen for better visibility.

5
New cards
Focus knobs
Controls that adjust the focus of the microscope to clarify the image.

6
New cards
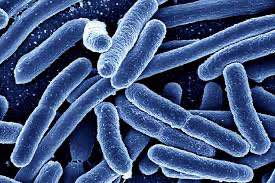
Bacilli
Rod-shaped bacteria.
7
New cards
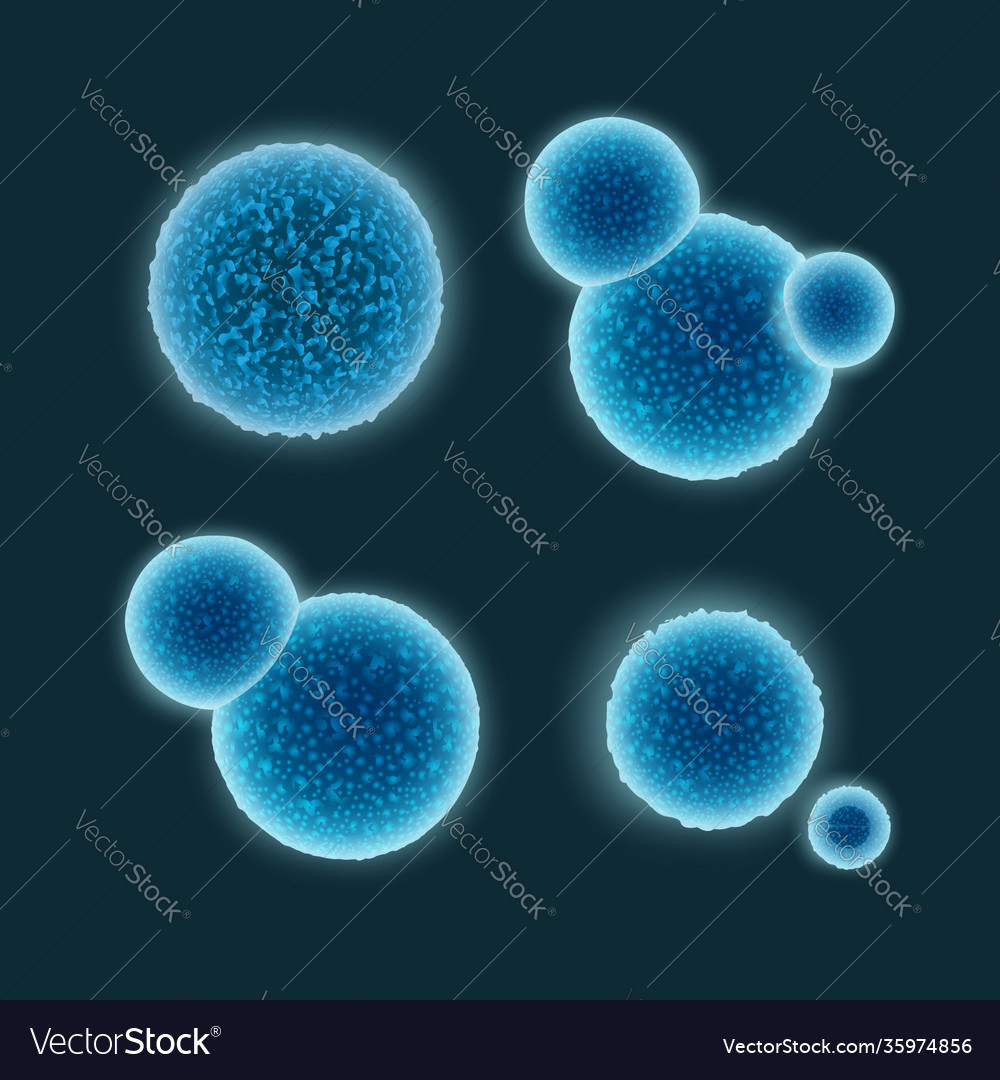
Cocci
Round-shaped bacteria.
8
New cards
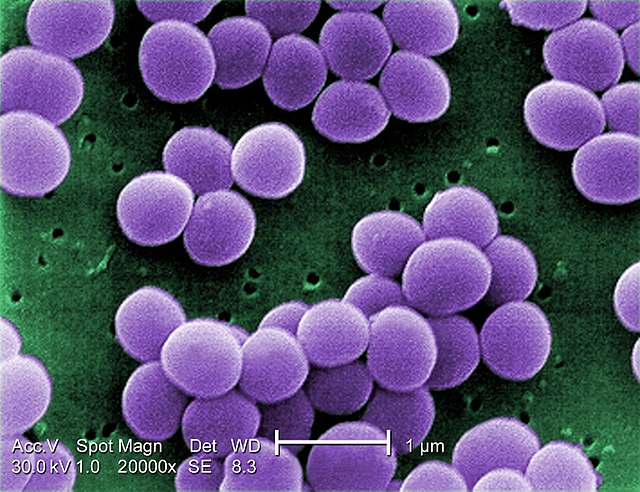
Staphylococcus
Clustered cocci that form grape-like structures.
9
New cards
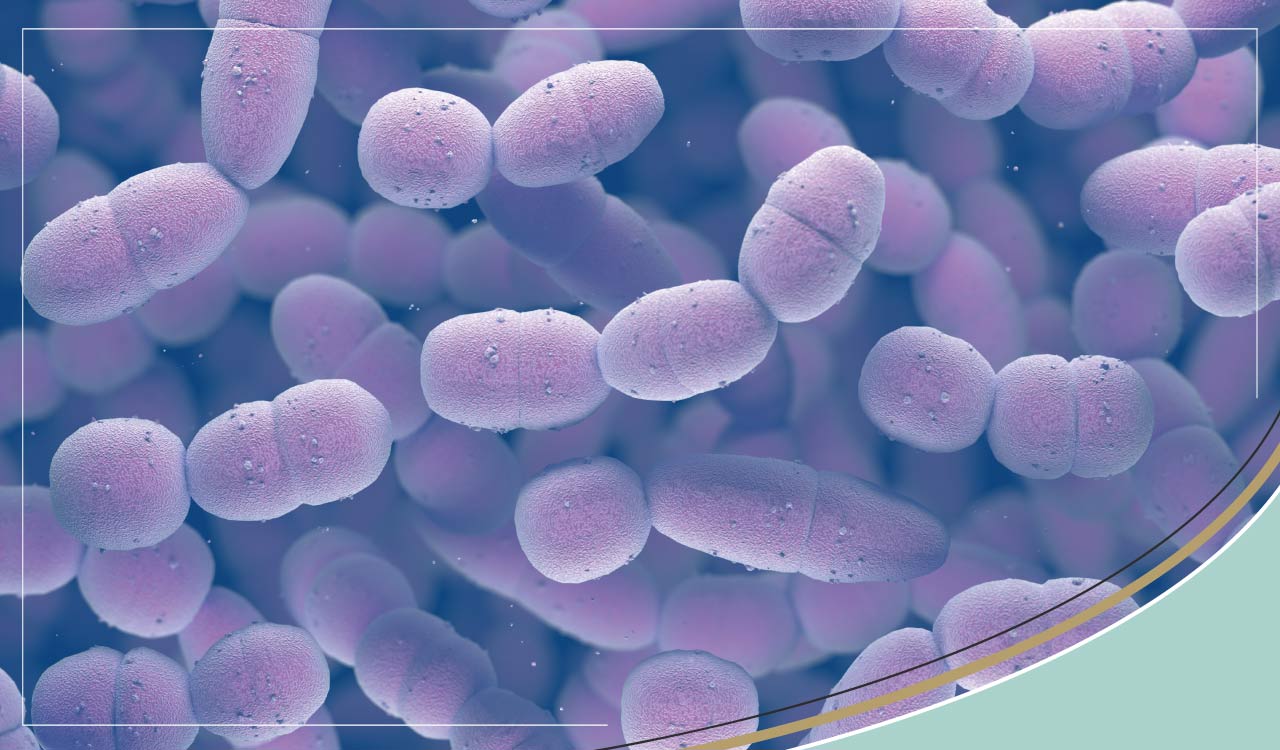
Streptococcus
Chain of cocci, resembling a string of beads.
10
New cards
Spirilla
Spiral-shaped bacteria.
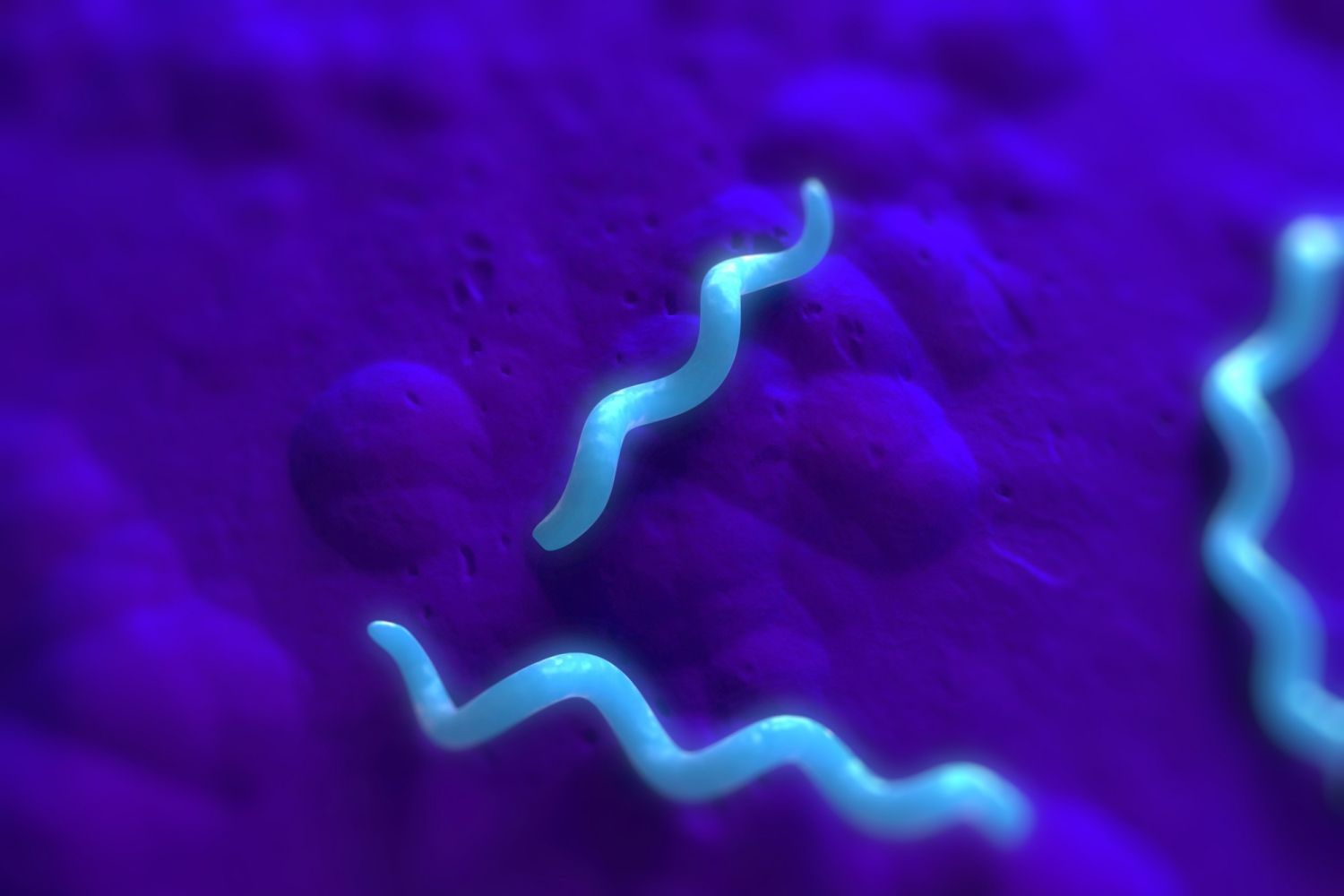
11
New cards
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells that are smaller and have a single-loop chromosome.
12
New cards
Eukaryotic Cells
Larger cells that contain linear chromosomes.
13
New cards
Glycolysis
The metabolic process in which glucose is split into pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP.
14
New cards
Preparatory reaction
The process in the middle of mitochondria where pyruvate is converted to acetyl-CoA and CO2.
15
New cards
Citric acid cycle
The process in the matrix of the mitochondria where acetyl-CoA is completely broken down to CO2, producing a small amount of ATP.
16
New cards
Electron transport chain
The final step of cellular respiration occurring in the inner membrane of mitochondria that requires O2, producing H2O as a byproduct.
17
New cards
Compound Light Microscope
A type of microscope that uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small samples.
18
New cards
Pathogens
Microbes that cause disease.
19
New cards
Opportunistic Pathogens
Microbes that may cause disease only when the host's immune system is compromised.
20
New cards
Communicable Disease
A disease that can be spread from person to person.
21
New cards
Non-communicable Disease
A disease that is not spread from person to person.
22
New cards
Cellular Respiration
The process of breaking down glucose to produce ATP.
23
New cards
Denaturation of Enzymes
A process where enzymes lose their structure due to factors like high temperature, pH, or salinity.
24
New cards
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important energy source during cellular respiration.
25
New cards
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants convert carbon dioxide and sunlight into glucose and oxygen.
26
New cards
Carbon Sink
A natural environment that absorbs more carbon dioxide than it releases.
27
New cards
Chlorophyll a
The main photosynthetic pigment that absorbs blue and red light.
28
New cards
Chlorophyll b
A photosynthetic pigment that absorbs light in the yellow/green spectrum.
29
New cards
Carotenoids
Pigments that are red, orange, or yellow and assist in photosynthesis.
30
New cards
Stomata
Small openings on the surface of leaves that allow gas exchange.
31
New cards
Xylem
Vascular tissue in plants that transports water and minerals from the roots.
32
New cards
Phloem
Vascular tissue in plants that transports sugars and nutrients.
33
New cards
Isotonic Solution
A solution with the same solute concentration as the cell.
34
New cards
Hypotonic Solution
A solution with a lower solute concentration than the cell, causing the cell to swell.
35
New cards
Hypertonic Solution
A solution with a higher solute concentration than the cell, causing the cell to shrink.
36
New cards
Biologically Important Molecules
Molecules essential for life, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and nucleic acids.
37
New cards
ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate)
The primary energy currency of the cell, produced during cellular respiration.
38
New cards
Photosynthesis Components
Key elements include sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and chlorophyll.
39
New cards
Starch Test
A test using iodine to show if starch is present, turning black/blue if present.
40
New cards
Protein Test
A test where biuret solution turns purple if protein is present.
41
New cards
Fat Test
A test using Sudan IV powder which shows red if fat is present.