Module 5: IB-300
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Strategic Trade Policy: National Asset or Liability?
Strategic Trade Policy: Use of trade policy instruments, including tariffs, subsidies, or quotas, to shape companies’ strategic interactions
Nationalization
The process of taking privately owned property and converting it to a publicly owned asset (gov steps in and takes private property for itself)
motivated by the belief that government can manage a public good or necessity better than the private, profit-driven sector
2 approaches: communist and European approach
Nationalization: Communistic
The state owns and directly controls major industries (or all industries, depending on how far the system goes)
aims to prevent exploitation by private industries and provide universal access to essentials
Nationalization: European approach
does not aim to eliminate private ownership, rather, they selectively nationalized key industries while leaving most of the economy in private hands
can provide stable, affordable public services and reduce inequality without centralizingthe entire economy
Privatization
The government sells a full organization or part to the open market in order to privatize the company
to gain more efficiency in business operations, raise money, or reduce the government’s bureaucracy
Money can be invested, for example education or things that benefit society
Reasons why governments restrict trade
protect infant industries, national security reasons, and promote fair competition
Reasons why governments restrict trade: Protect National Defense
Governments may restrict or regulate trade in specific industries (e.g., defense, technology, energy) to protect national security
Economists say this is a weak argument and is used to gain an emotional advantage
Reasons why governments restrict trade: Impose sanctions
inflict economic damage, punish, or encourage change of behavior
seldom achieve their goal
product collateral economic damage
Reasons why governments restrict trade: protect an infant or dying industry
give infant industries chance to grow and build comparative advantage
without this lower-cost imports will underprice in local market
slow down impact of dying industry—move capital into other sectors
Reasons why governments restrict trade: Protect Domestic Jobs
“Cheap foreign labor” argument does not hold up, wages don’t account for all production costs
argument has strong emotional appeal
Reasons why governments restrict trade: Ensure Fair Competition
import duty to bring the cost of imports up to the cost of domestic goods
Don’t ban imports, but equalize them
Consumer impact: Import duty increases the price they pay
Reasons why governments restrict trade: Protect consumers
Governments limit importation of counterfeit goods and any good or services that may threaten physical, mental or social well-being
Different types of tariff barriers
What is meant by government stability?
maintains itself in power
fiscal, monetary, and political policies predictable and and not subject to sudden, radical changes
protection from unfair competition
protection from terrorism, cyber crime, and other threats
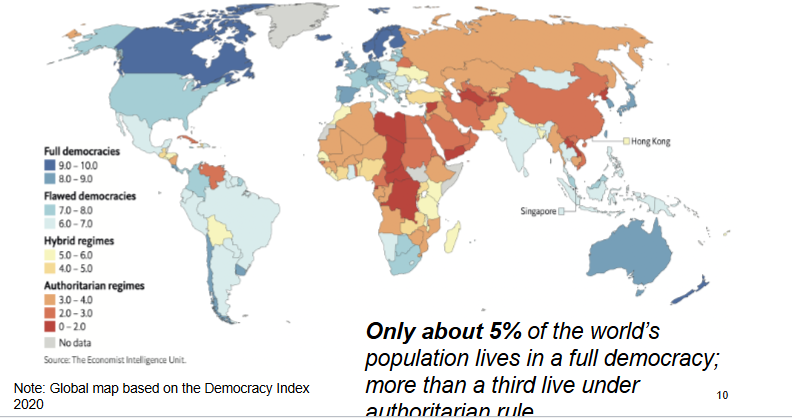
Democracy practices and % of the world that live in a full democracy?
power comes from the people
strong protection for civil liberties
5% of the world live in a full democracy
Authoritarian practices and % of the world is under authoritarian rule?
power is concentrated in one leader, party, or small elite
civil liberties are restricted; dissent is discourages or punished
1/3 of the world live in an authoritarian regime
Democracy Index
offers a global snapshot of the state of democracy, measuring political freedoms, civil liberties, and how power is exercised in practice
Different types of tariff barriers
import tariffs and export tariffs
Import tariffs
taxes on imported goods for the purpose of raising their price to reduce competition for local producers or stimulate local production
Export tariffs
taxes on exported goods for the purpose of restricting exports of certain items (maintain domestic supply or national security)