OB Female Physiology : The Menstrual Cycle
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Dysfunctional Uterine Bleeding (DUB)
Vaginal bleeding not related to menses or endometrial pathology
Amenorrhea
Absence or menstruation
primary amenorrhea
Menarche is delayed beyond 18 years of age
Secondary amenorrhea
cessation of uterine bleeding occurs in women who previously menstruated
Mittelschmerz
Dull ache mid cycle on either side of lower abdomen
Memometrorrhagia
Bleeding that irregular in both frequency and volume
Metorrhagia
Irregular frequent bleeding
Hypomenorrhea
Abnormally small amounts of menstrual bleeding
Hypermenorrhea
excessive volume during cyclic menstrual bleeding
Dysmenorrhea
Painful periods often associated with endometriosis
Menorrhagia
Abnormally heavy or long periods often associated with fibroids
Oligomenorrhea
Prolonged periods over 35 days, associated with PCOS
Polymenorrhea
Period cycles less than 21 days
Tamoxifen
Hormone replacement therapy drug
Less than 5mm
Post menopausal patients not on HRT should have this endometrial thickness
Postmenopausal patients on HRT should have a normal endometrial thickness of up to
8mm
1-5
Day of cycle for menses
1-5
Day of cycle for follicular phase
FSH and Estrogen
Dominant hormones in menses and follicular phase
6-14
Day of cycle for proliferative
FSH and Estrogen
Dominant hormones in proliferative phase
14
Day of ovulation
LH
Dominant hormone for ovulation
15-28
Average length of the secretory and Luteal phase
Homogenous hyperechoic
Appearance of uterine in secretory phase
Hypoechoic
Early proliferative appearance
Tri layered
Late proliferative appearance
Thin
Menses sono appearance
1-4 mm
Endo thickness in menses
4-8 mm
Endo thickness in proliferative
8-16 mm
Endo thickness in secretory phase
Menses
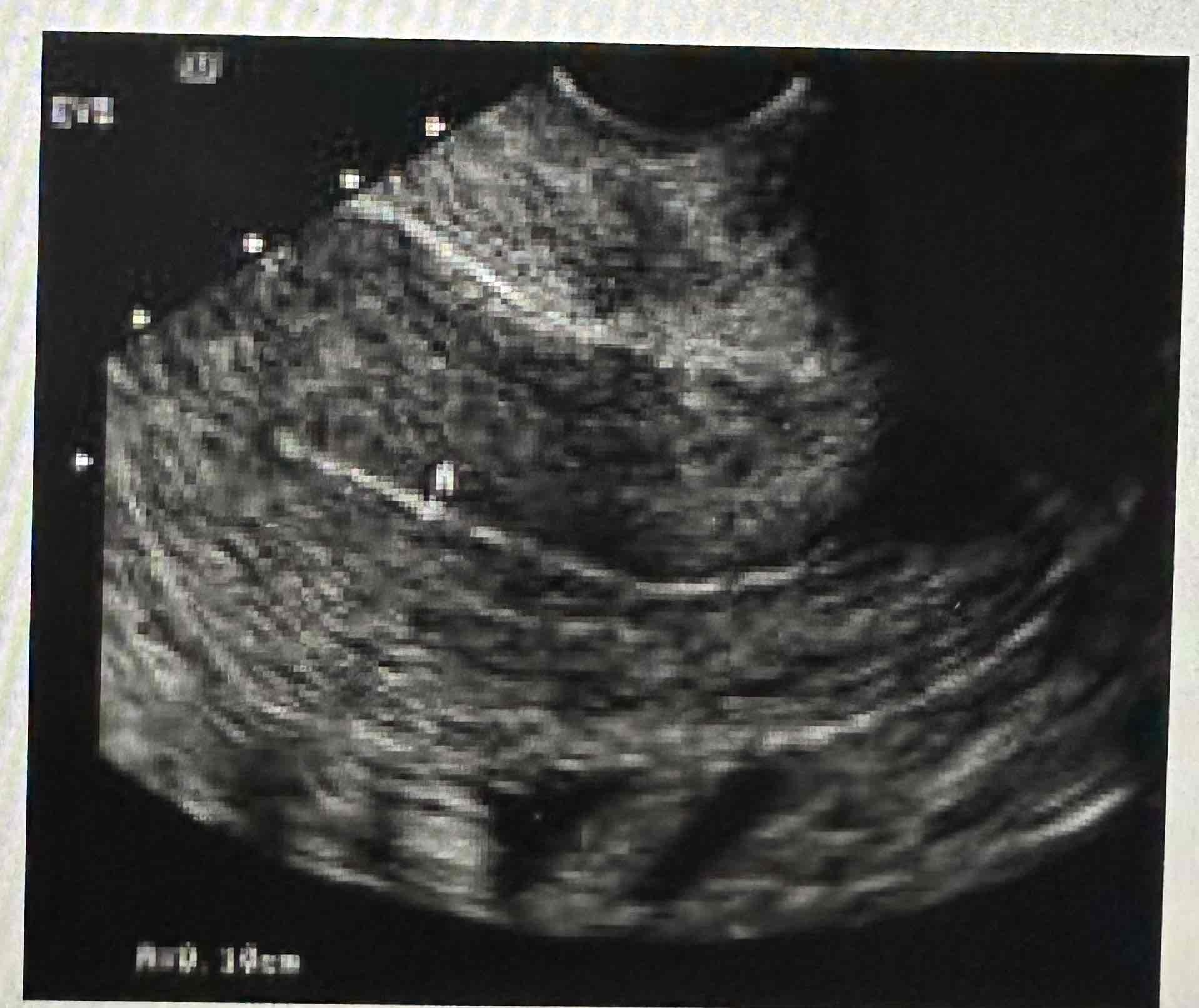
Late proliferative
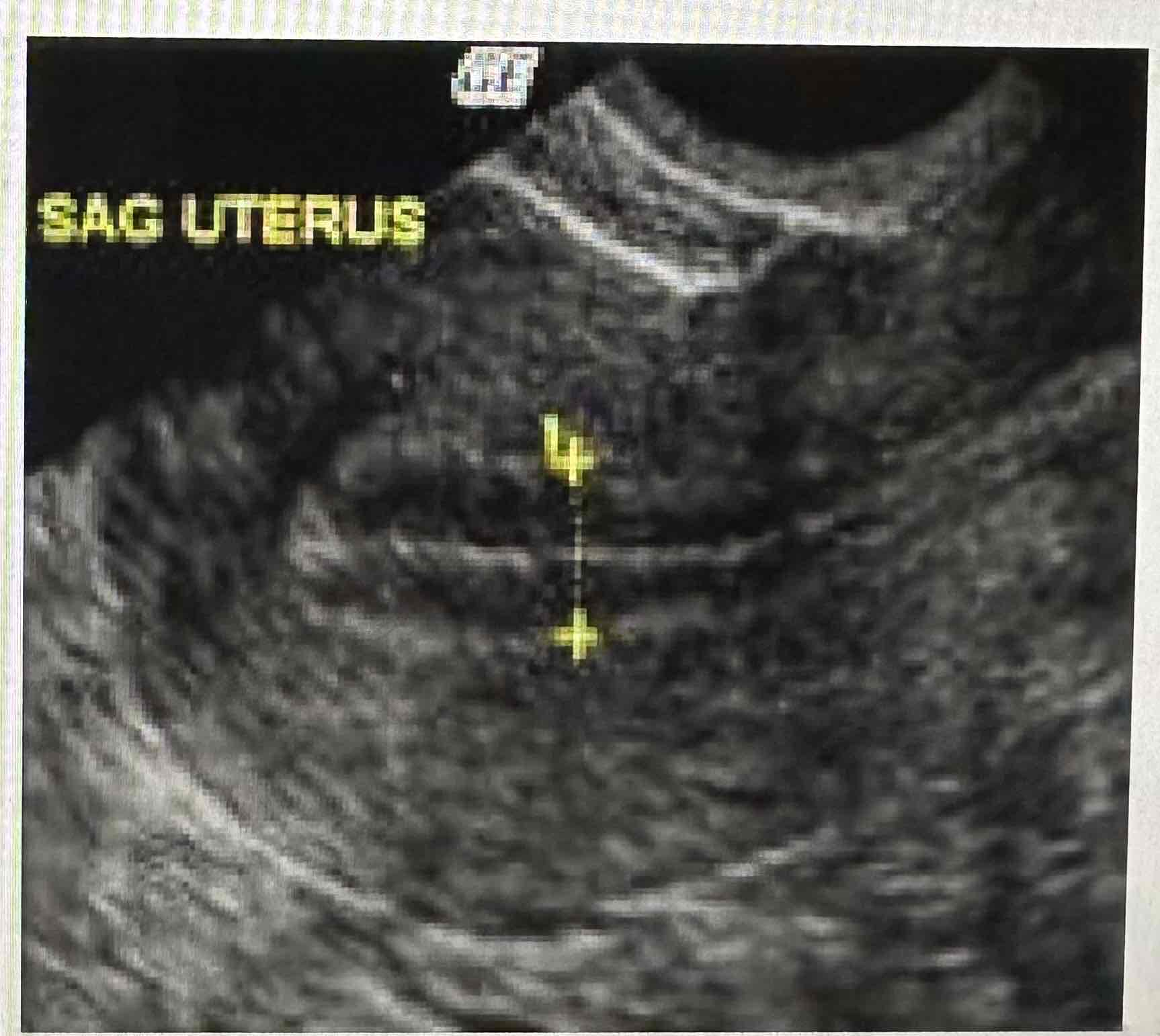
Secretory phase
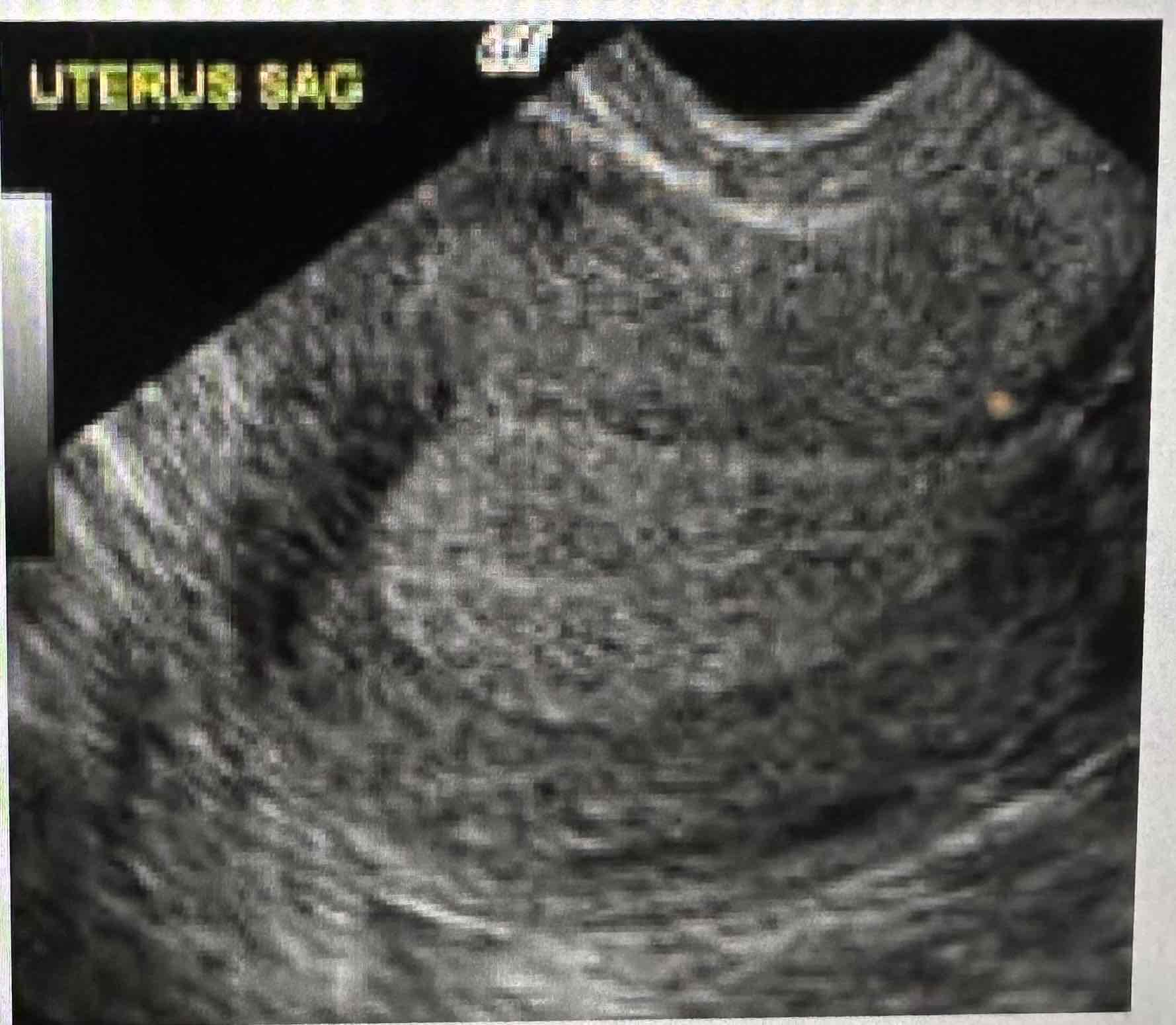
Secretory
Endometrium is thickest in what phase
Menses, Proliferative,Secretory
Order of Uterine Phase
Follicular, Ovulation, Luteal
Order of Ovarian Phase
Ovulation
Proliferative phase ends at
10 days
Proliferative phase lasts about
Proliferative
Regeneration and proliferation of endometrium stimulated by estrogen
The superficial layer
What layer is shed during menstruation
Catabolic
Menstruation can be described as this process if implantation has not occurred
Progesterone
Corpus Luteum secretes
Ovulation
Theca Cells peak during this phase with the LH
Corpus Luteum
Also described as the ring of fire
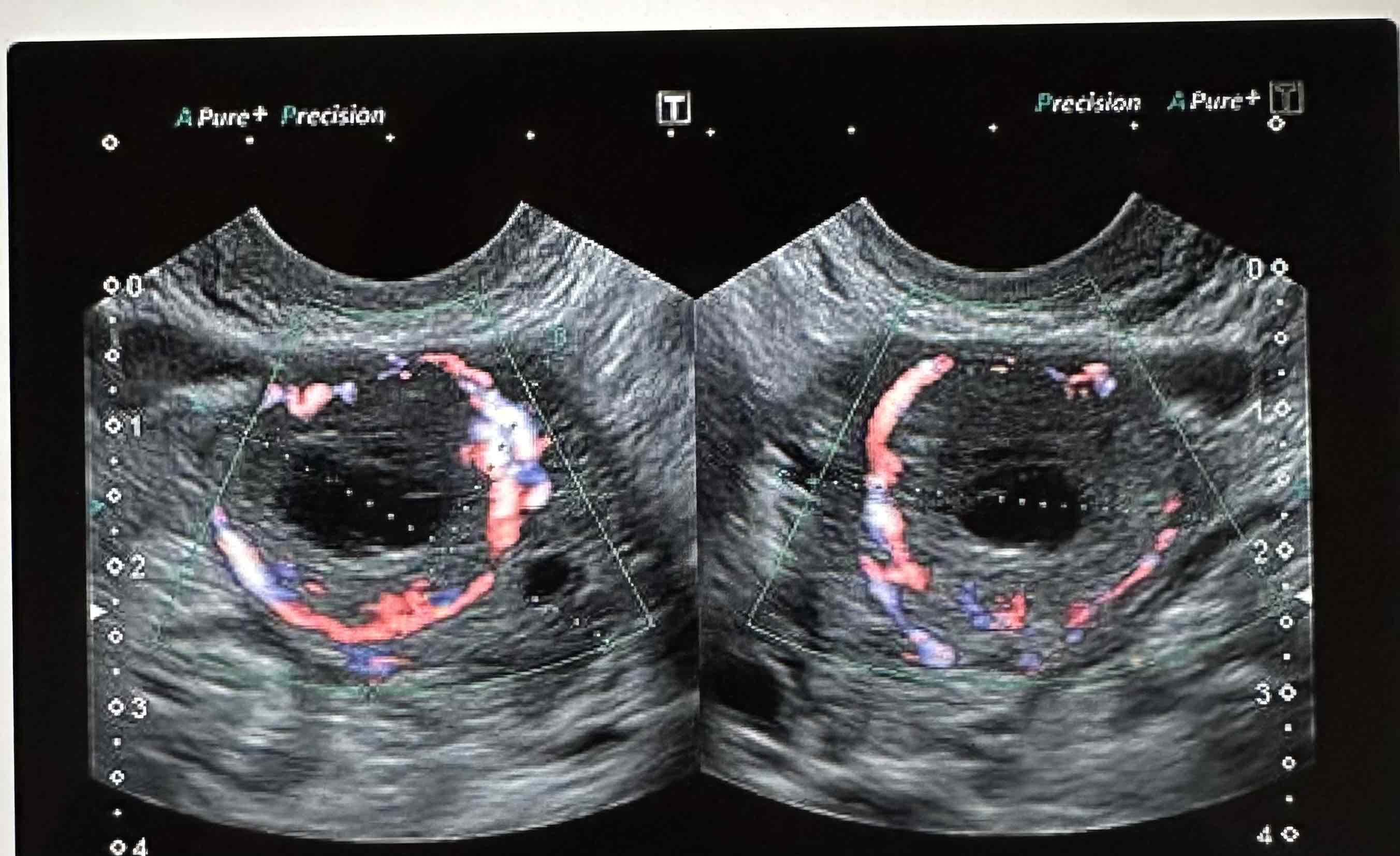
Low resistive flow
The corpus Luteum is vital and therefore has
hCG
The corpus Luteum atrophies/ regresses and becomes the corpus Albicans with the absence of
Corpus Luteum
Fatty yellowish cell type
Ovulation
Free fluid in the posterior cup de sac is normal during what phase
24-36 hours after surge
Surge of LH causes rupture of follicular membrane within
11mm or 1.1cm
Ovulation typically occurs with follicles greater than
Greater than 3cm
Considered a cyst
Graafian
Dominant follicle measuring up to 10 mm during the follicular phase
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
Stimulates maturation of follicle and is responsible for Graafian rupture
Estrogen
Theca Cells produce
Infundibulum, Ampulla, Isthmus, Interstitial
Outer to inner
28 days
Average menstrual cycle
Come from the ovary
FSH affects the ovary but does NOT
Hypothalamus
Produces gonadotropic releasing hormone (GnRH)
FSH and LH
The process of the hypothalamus producing GnRH allows the Pituitary Gland to secrete what