Week 2 - ANHB3323 (3) - Microscopy and the Cell Cycle
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Cell size
Cell size = 5-100um
Nucleus = 5um
Red Blood Cell = 8um
- cellular ruler
Light vs Electron Microscope visibility (vs human eye)
Light = down to 0.2um
Electron = down to 0.2nm
Human Eye = down to 0.2mm
Electron microscope
done in a vacuum
therefore cant do live cells
Fixation
immediate stop of living processes in cells/tissues
to preserve structure
Fixation will block...
degradation of enzymes such as: DNAses, RNAses, and proteases
and
Prevent 'rotting' in bacteria
Methods/Reagents used for Fixation of Cells (5)
1. Physical (heat/freezing etc.)
2. Solvents
3. Acids
4. Chemical
5. Metal Salts
What do you do to a Fixed Tissue Sample after Fixation? (roughly)
Process it to make it harder
Cut it to make it transparent (thinner)
Sectioning as Fixed Tissue (2 methods)
1. Cryostat:
- cuts frozen sections:
- 5 to 20um
2. Parafin/wax embedding:
- 3 to 10um sections
- permanent archival block
Immuno-staining
antibody to recognise specific antigen
antibody is visualised with fluorescent secondary antibody/conjugate
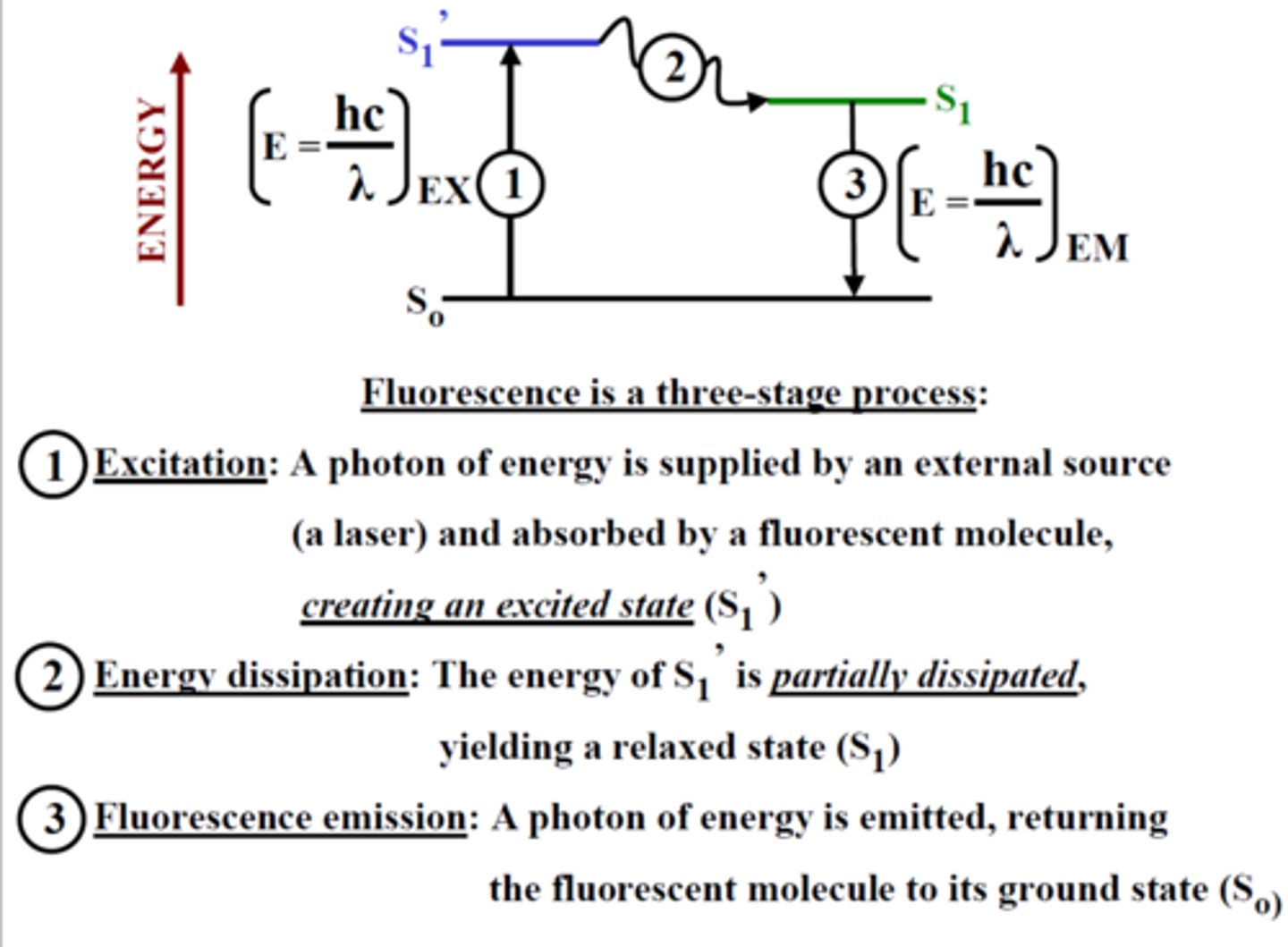
Fluorescence (3 stage process)
1. Excitation Photon of energy (hvEX)
2. Excitation-state Lifetime
3. Emission Photon of energy (hvEM)
Electron Microscopy Types (2)
Transmission EM (TEM):
- information of internal structure
- electron beam enters specimen
Surface Scanning EM (SEM):
- information of surface structure
- electron beam bounces off surface
Transmission Electron Microscope Sample Preperation
1. Fixation:
- Glutaraldehyde
- Paraformaldehyde
2. Post-Fixation:
- Osmium (secondary fixative)
Surface Scannaing Microscope Sample Preperation
1. Fixation:
- Glutaraldehyde
- Paraformaldehyde
2. Post-fixation:
- Osmium
- Tannic acid
[only difference with TEM = tannic acid]
Cell cycel phases
Interphase:
1. G1 = growth
2. S = DNA replication
3. G2 = final prep
Mitosis:
1. Prophase
2. Metaphase
3. Anaphase
4. Telophase
Duration of each phase in Interphase
G1 = indefinite (normal cell activity)
S-phase = 6 to 8 hours (DNA replication)
G2 = 3 to 4 hours
Cell shapes
Squamous, spheroid, polygonal, discoid, cuboidal, fusiform, columnar, fibrous and stellate
Nucleus
Control centre of cell:
Nuclear envelope with pores
chromatin (DNA wrapped around histones)
nucleolus (make ribosomes)
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Rough: studded with ribosomes, site of protein synthesis
Smooth: lipid synthesis and drug metabolism
Golgi Apparatus
Modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles.
Non-ATP diffusion
Passive diffusion: small molecules across the cell membrane
Facilitated: use a protein channel, slightly larger molecules
Types of Carrier proteins
Channel: shape is constant
Carrier: changes shape to conform to molecule (active or passive)
Receptor: required for cell signalling → receptor is specific to it’s complimentary ligand therefore not signalled unless bound by appropriate molecule.
Active diffusion
Requires ATP, moves against concentration gradient, can transport larger molecules.
Exocytosis vs endocystosis
Exo: out of the cell
Endo: Into the cell
Endocytosis Methods
Phagocytosis: ingestion of large particles or cells;
Pinocytosis: uptake of small particles or fluids.
endocrine signalling
steroid hormones: require transport protein in bloodstream, can pass through cell membrane to intracellular receptors typically on nucleus.
peptide hormone: travel freely through blood, attached to receptor on cell membrane and trigger a cascade.
Messenger types
first/primary messenger: only one, typically outside the cell
Secondary messenger: once activated there can be multiple
Signalling
Endocrine: hormones
Exocrine: secretions into ducts and outside the body.
Electrical: used by nervous system, driven by movement of positively charged ions