sharp force trauma SFT
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
sharp force trauma (SFT)
impact from narrow-edged implement that results in cutting of skin/incised damaged underlying to bone, narrowly focused, dynamic, slow-loaded. compressive force with sharp object that produce damage to hard tissue in form of an incision (broad/narrow)
basic criteria
first criteria for recognition is tool has edge bevel — defined as border that is acute angle, bevel is created in blade to prevent splintering of material being cut, sharpened and rounded or sheared off to help in incision
SFT patterns
trauma patterns associated with square-edged instruments is more consistent with blunt force trauma then SFT — often get both together, if there are fractures it has to be BFT as well as blunt force sharp force trauma
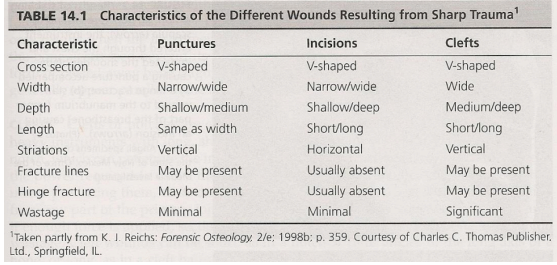
puncture
penetrating wound from tip/point of sharp instrument that impacts bone will result in compression of outer table of bone to produce gouge impact (certain bones, like cranial vault, may capture rather accurate replica of knife tip)

incisions
causes horizontal striations (can be very thin lines), usually dont see evidence of this on bone only on skin — longer than wide, result from force applied across bone surface from slashing/stabbing

clefts
(chopping wounds) some instances force of blow can result in fracturing of bone, in order to be classified as SFT instrument must have edge sharp enough to incise bone, fractures associated with sharp injuries are result of blunt force failure, impact from sharp object with excessive force begins with incised wound and may end in tension/compression force
knives
narrow blades, leave corresponding narrow ‘V’-shaped trough in bone, single/double-bladed — double-bladed can leave opposite ‘V’-shaped trough in bone, tend to leave behind only microscopic striations
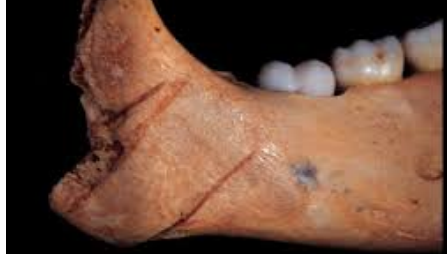
saws
defines as blade with teeth, working edge of saw blade contains projections (teeth) that acts like chisels, produce slicing/shaving actions

ax, hatchet marks
ax has a wedge shaped blade — very wide, v-shaped cross section, smooth, significant chipping
SFT wound characteristics
SFT analysis - steps
determine whether implementing tool is knife, saw,/other type of tool
once general class of tool is diagnosed, more detailed characteristics may be available
defect analysis
thorough description of wound that includes type, fractures, delamination of bone, location, size
description of possible instrument that includes, type, blade length, width, serrations, etc.
direction of force
number of traumatic events
sequence of events