IV : Adaptive Immunity
1/89
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Adaptive Immunity
- Is specific to each pathogen/microbial agent
Adaptive Immunity
- Increases response to a pathogen upon repeated exposure
Adaptive Immunity
- Takes longer to become activated but is longer lasting
• T lymphocytes
• B lymphocytes
Adaptive Immunity involves lymphocytes:
Double-Negative Stage
Double-Positive Stage
Mature T Cells
T-Cell Differentiation
Double-Negative Stage
- Chemokines drive differentiation process
Double-Negative Stage
- Thymocytes undergo rearrangement of genes coding for T-cell receptors (TCRs) (CD4 & 8)
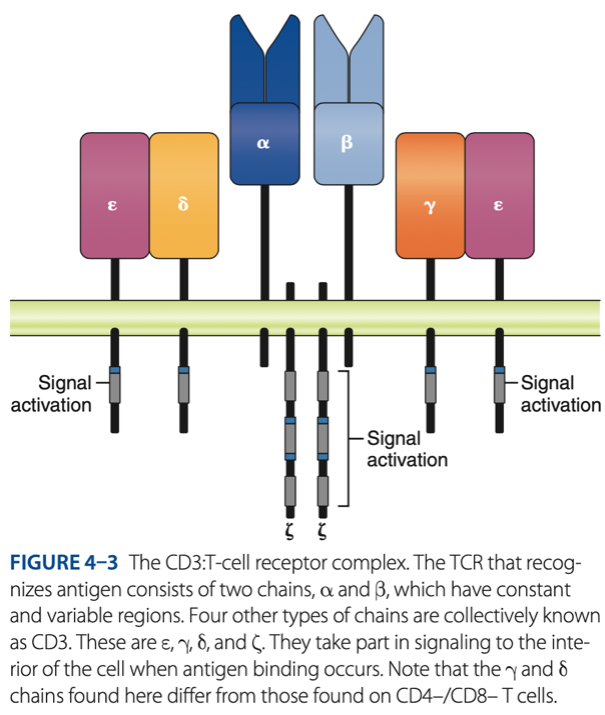
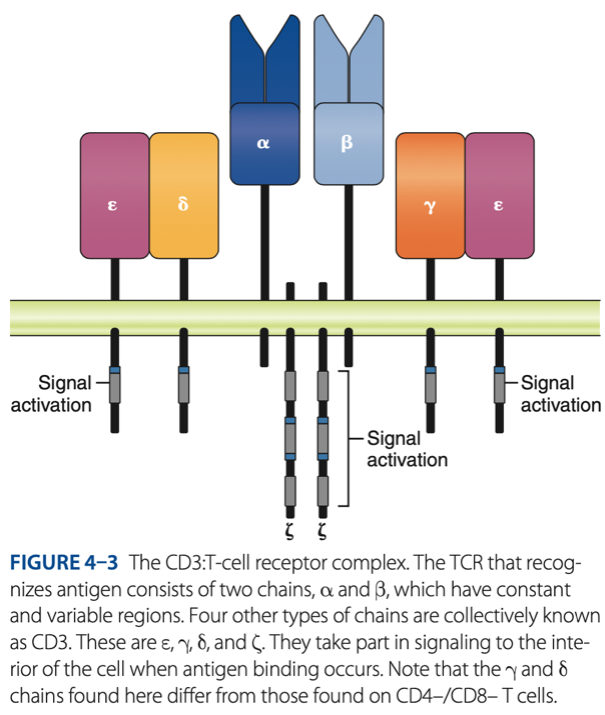
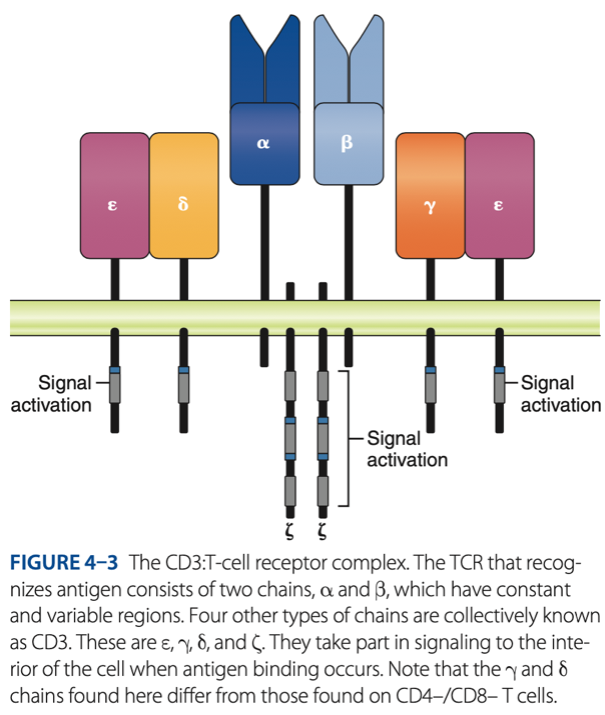
CD3 / TCR Complex
Double-Negative Stage
alpha & beta chains that recognize antigen
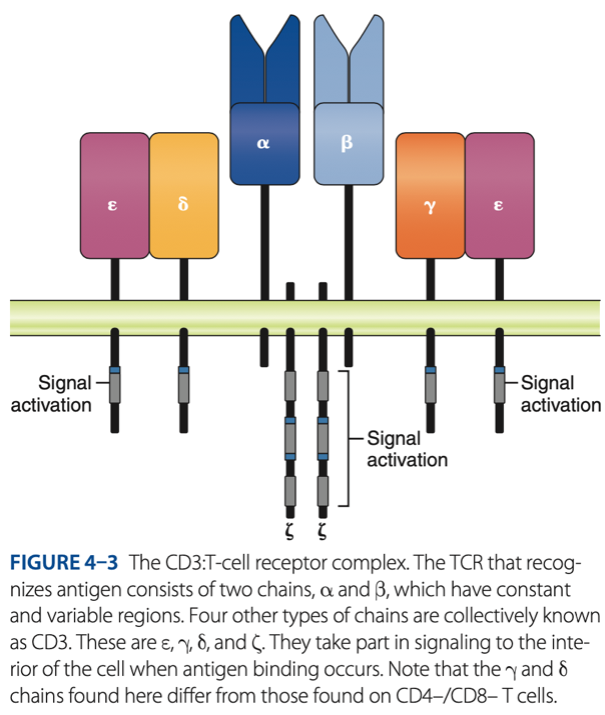
CD3 / TCR Complex
Double-Negative Stage
- 6 other chains in 3 pairs that assist with signaling (alerts) when antigen binds to T cells (CYTOKINES)
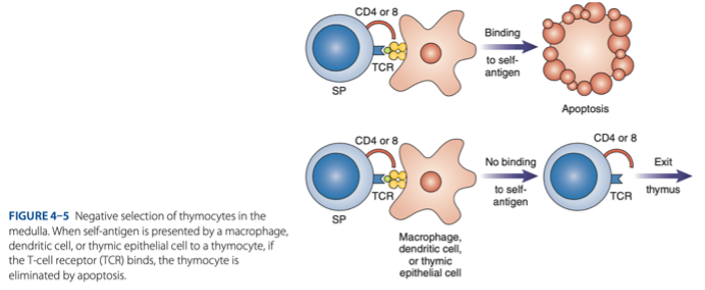
Double-Positive Stage
- Thymocytes express CD4 & CD8 & rearrange gene coding for the alpha chain.
Double-Positive Stage
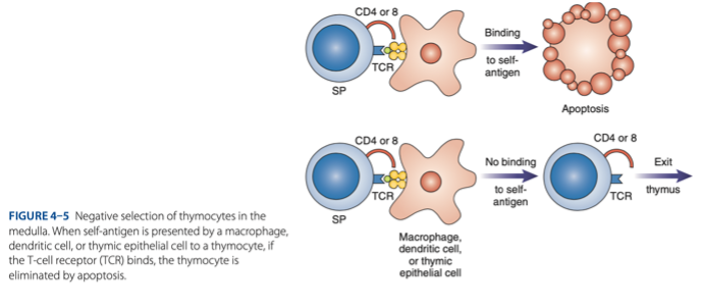
- Positive selection of functional TCR
Double-Positive Stage
must undergo + selection bc not all produced lymphocytes are qualified thus results to apoptosis
survive
Double-Positive Stage
- MHC Restriction: Only cells that react with host MHC -
destroyed
Double-Positive Stage
- Negative Selection: Cells that react with self-antigen are - .
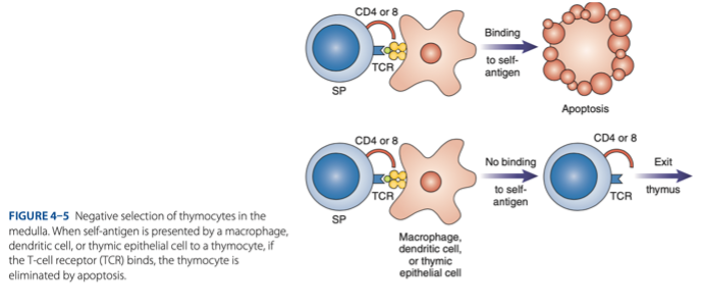
Mature T Cells
Survivors of positive & negative selection exhibit either CD4 / CD8
CD4 T Cells
Mature T Cells
are helper T cells that assist in antibody production
CD4 T Cells
reacts with class II MHC (plasma cells)
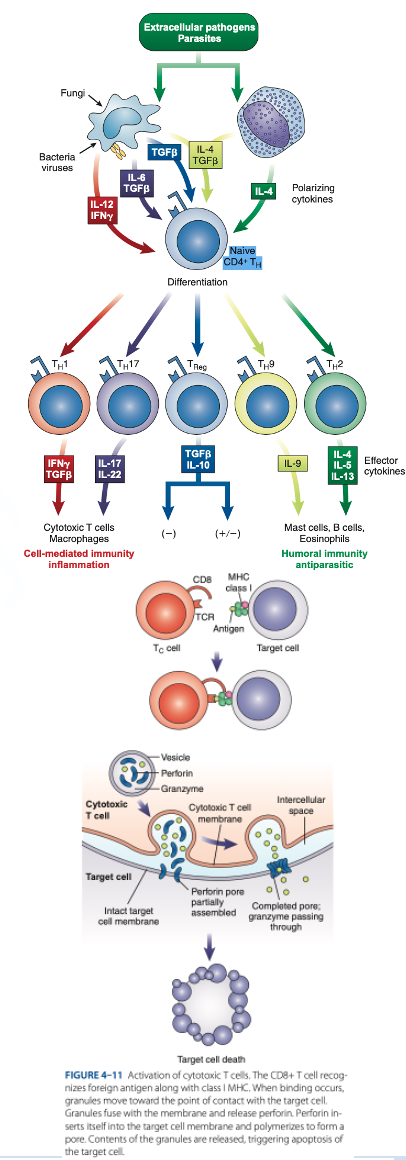
CD8 T Cells
Mature T Cells
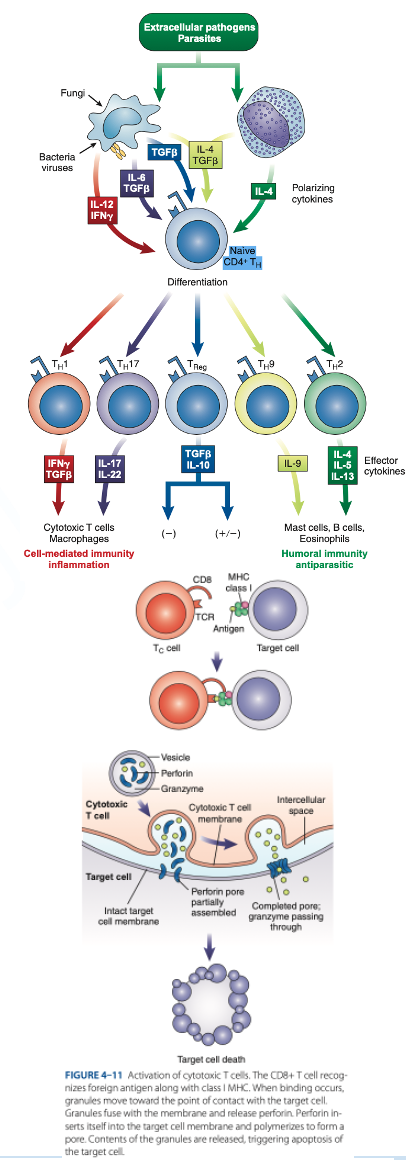
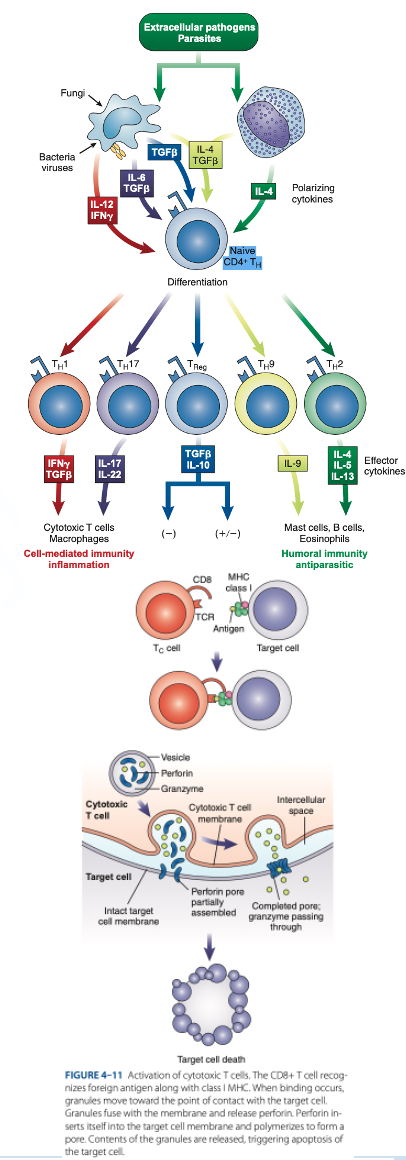
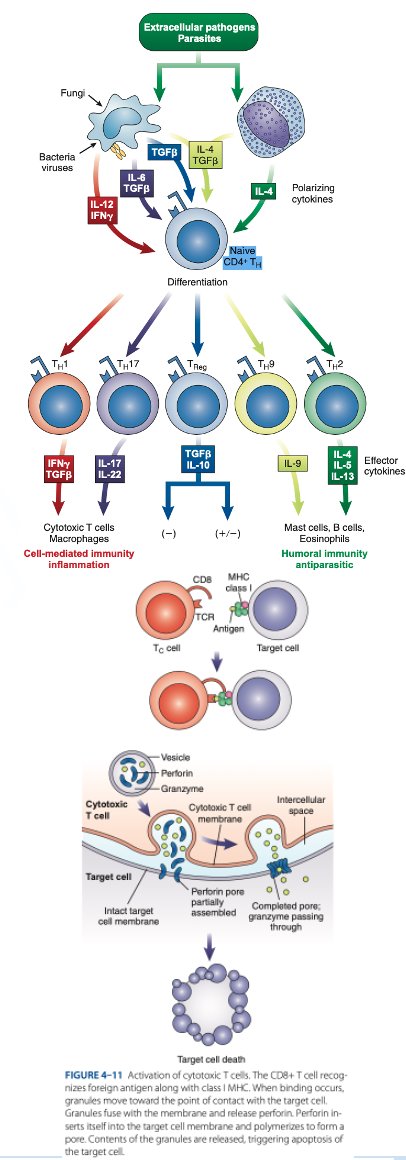
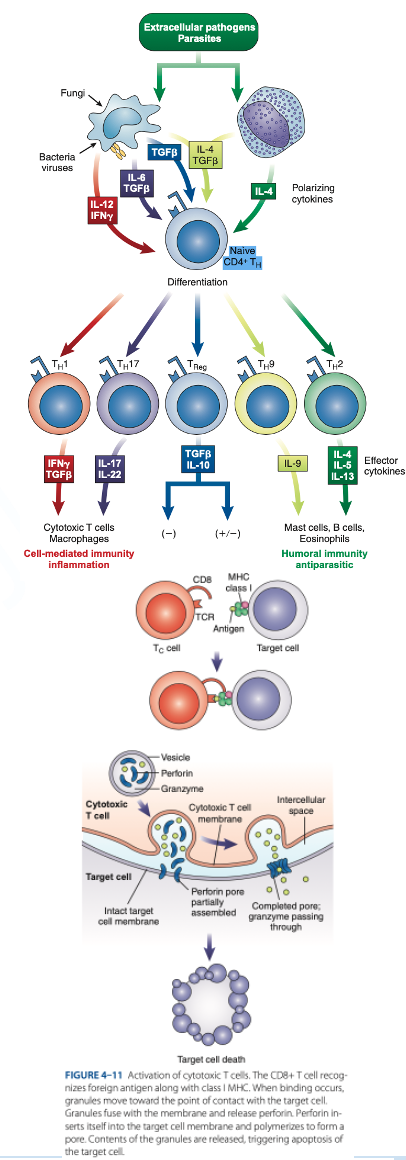
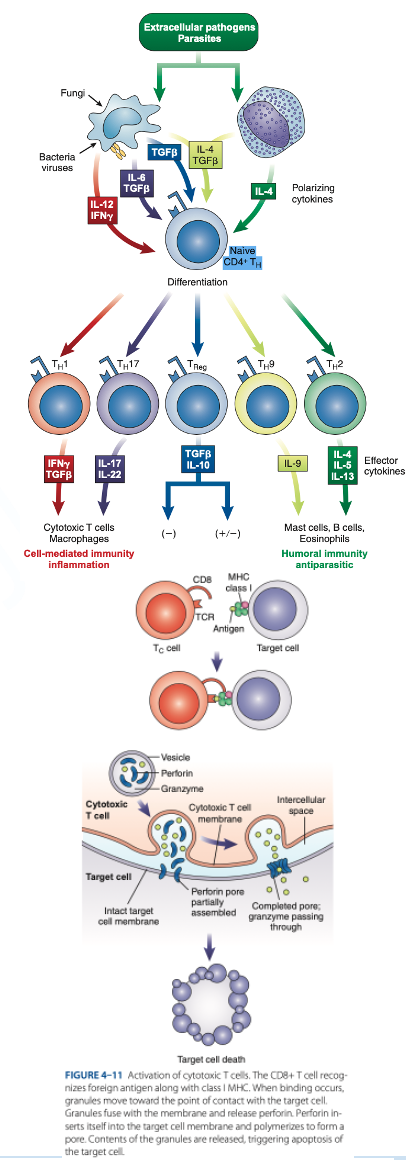
are cytotoxic T cells that kill target cells (tumor cells, cancer cells & cells infected with parasites, viruses & bacteria).
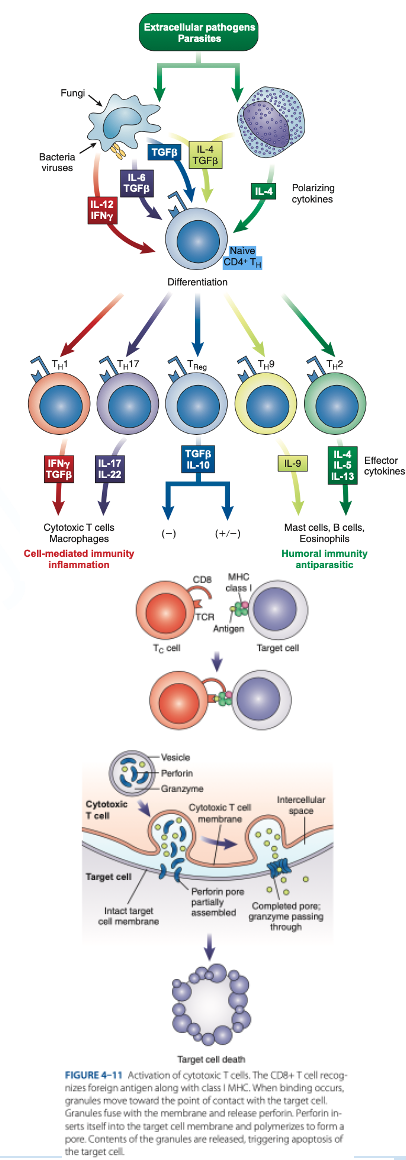
CD8 T Cells
reacts with Class I MHC (nucleated cells such as neutrophils, monocytes)
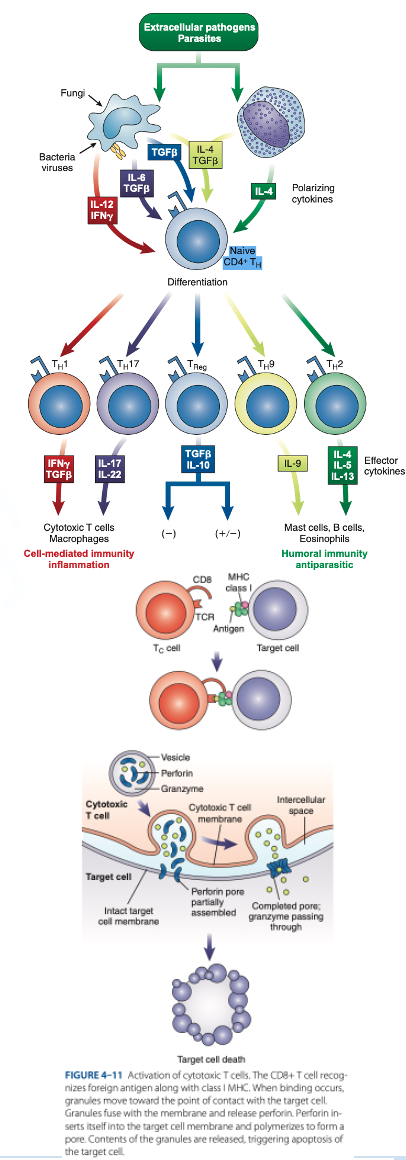
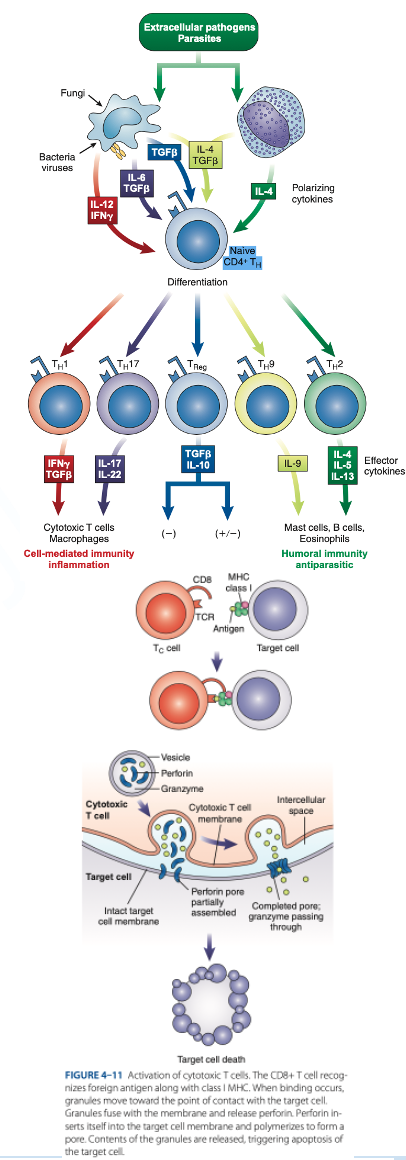
Th1 Cells
Th2 Cells
T Regulatory (Treg) Cells
What are the T helper (Th Cells)
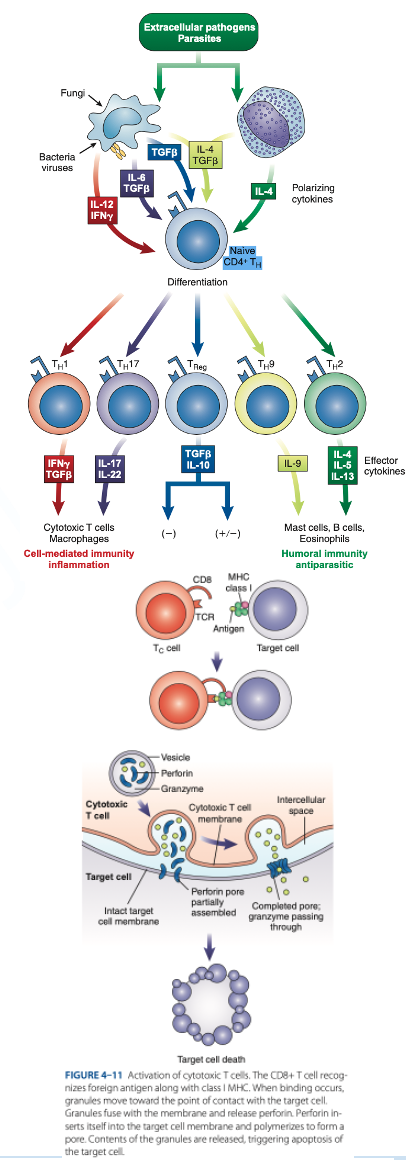
T helper (Th Cells)
- Have CD4 receptor
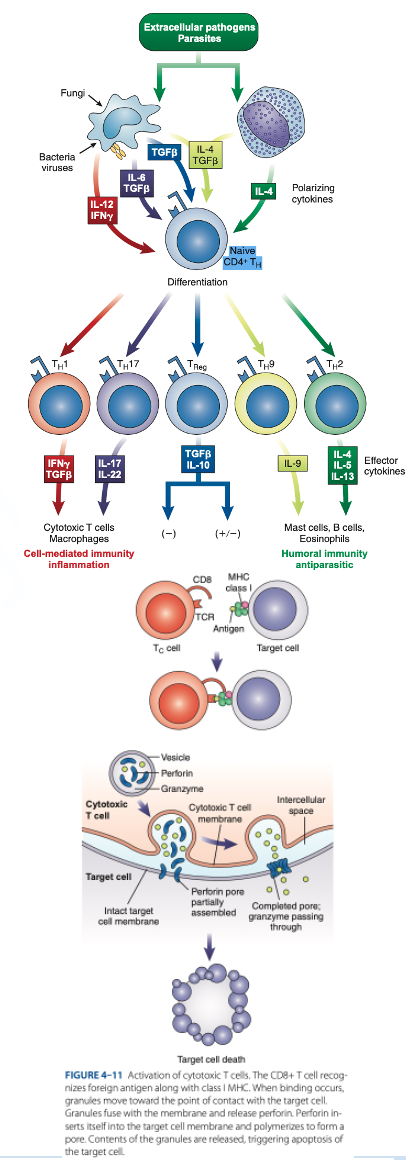
T helper (Th Cells)
- Recognize antigen & Class II MHC protein
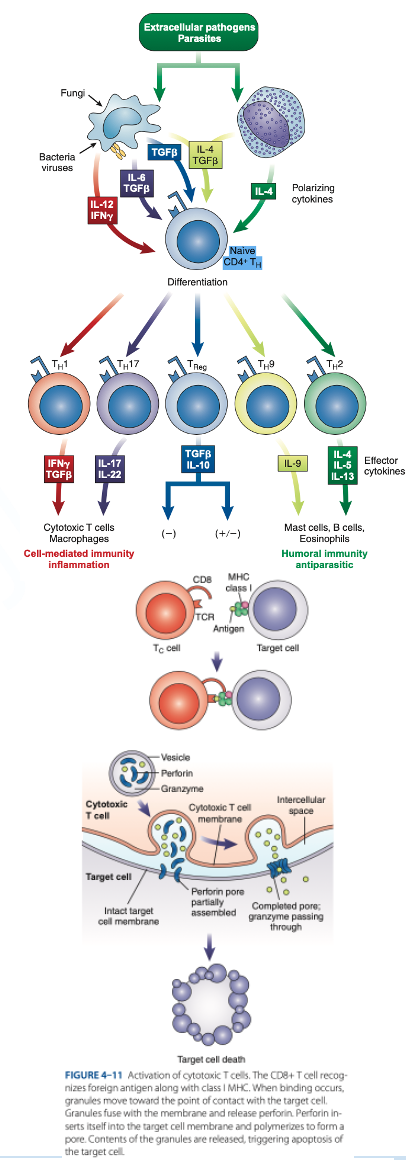
T helper (Th Cells)
- Accounts for 2/3 of peripheral T cells
Th1 Cells
- Produce interferon gamma, interleukin-2, tumor necrosis factor-β
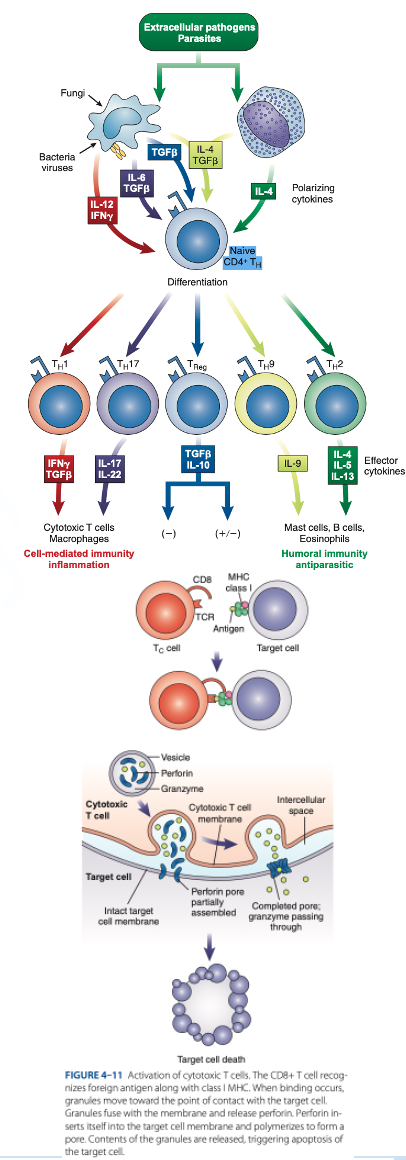
Th1 Cells
- Activate cytotoxic lymphocytes & macrophages

Th2 Cells
- Produce interleukins 4, 5, 6, 9, 10, 13
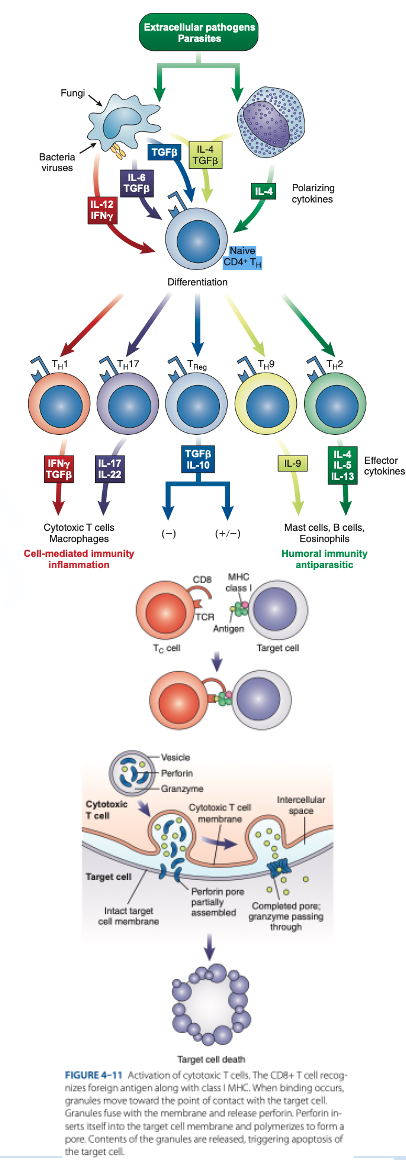
Th2 Cells
- Help B cells produce antibodies

Th2 Cells
- Regulate B-cells activity.
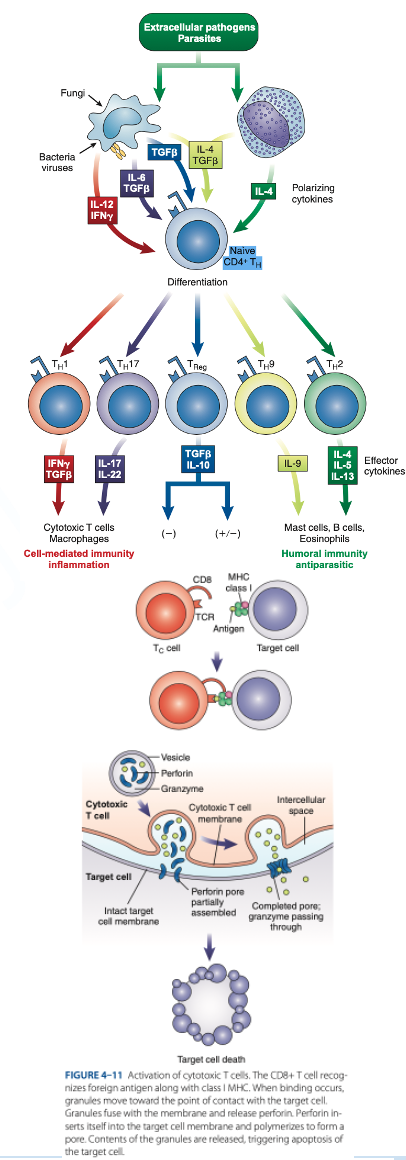
T Regulatory (Treg) Cells
- Have CD4 & CD25
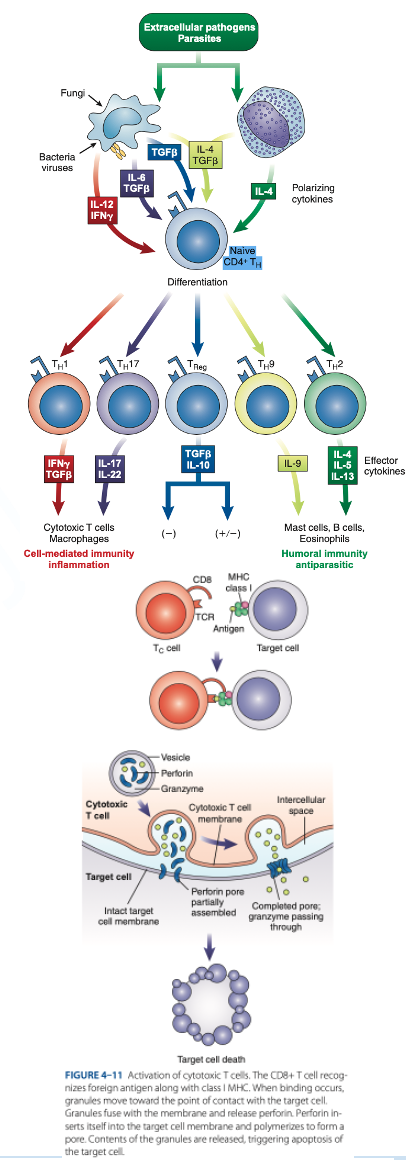
T Regulatory (Treg) Cells
- Suppress the immune response to self-antigens.
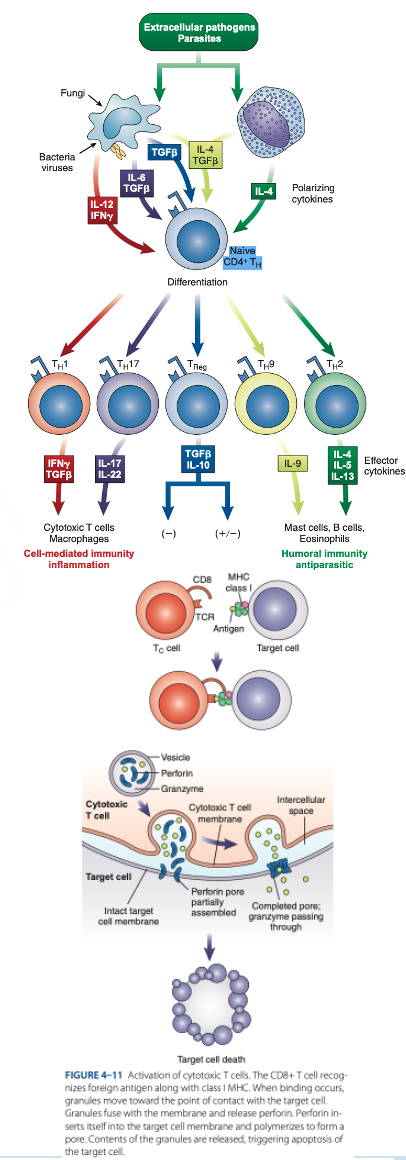
T Regulatory (Treg) Cells
- Secrete inhibitory cytokines to inhibit proliferation of other T-cell populations.
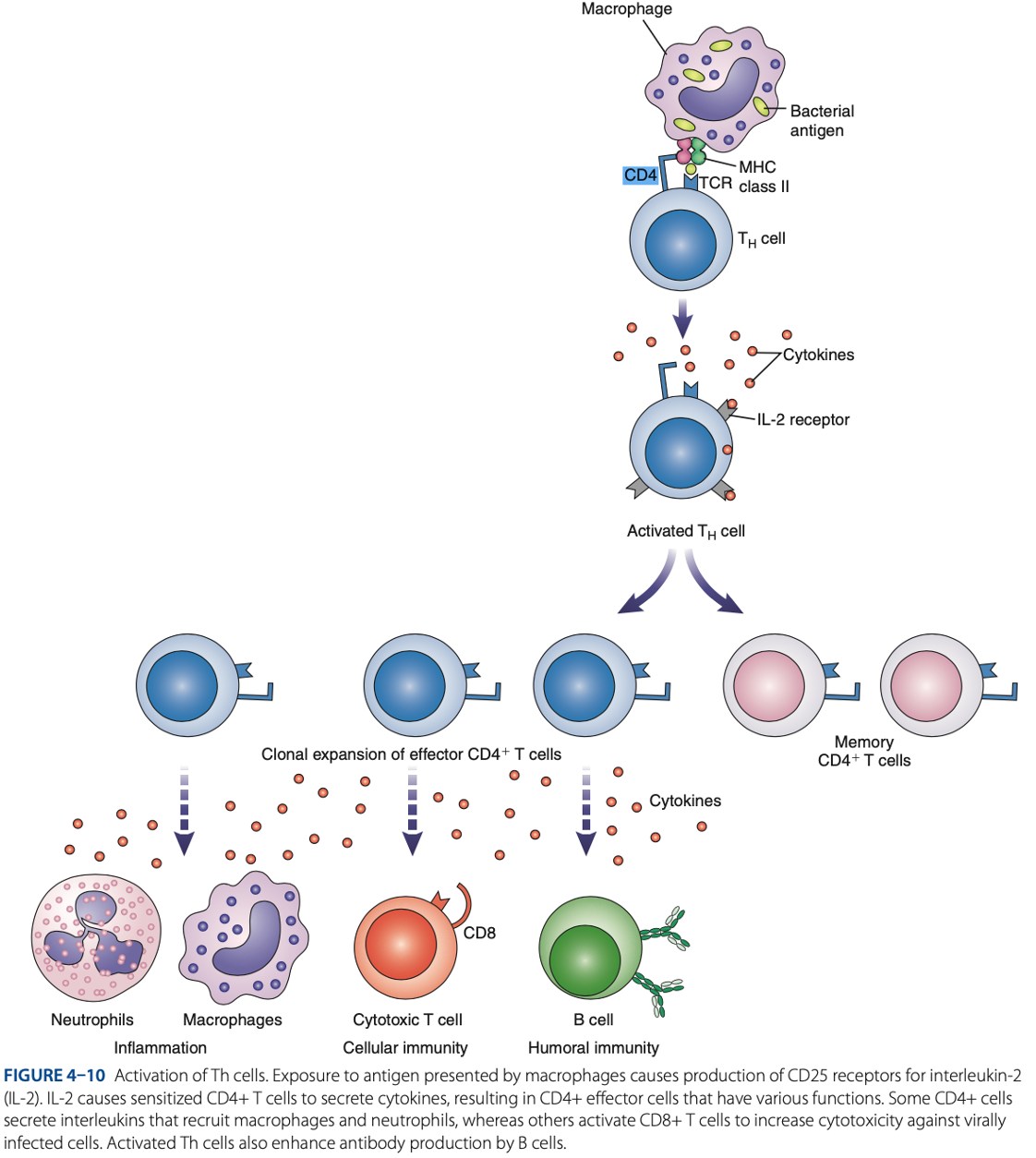
Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs)
Role of T Cells In Adaptive Immune Response
what are activated during innate immune response.
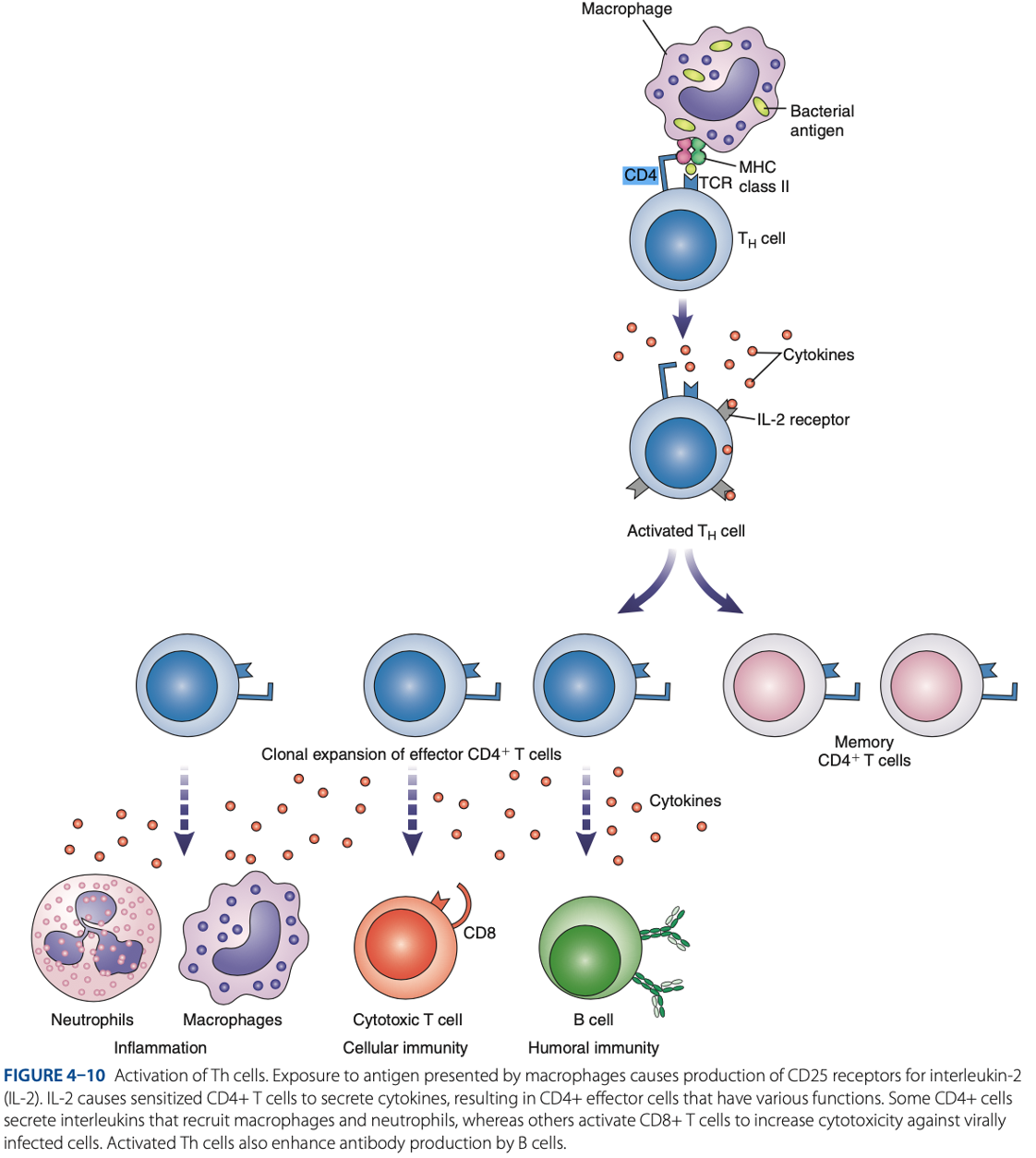
T Cells
Role of T Cells In Adaptive Immune Response
what interact with APCs to initiate adaptive immune response.
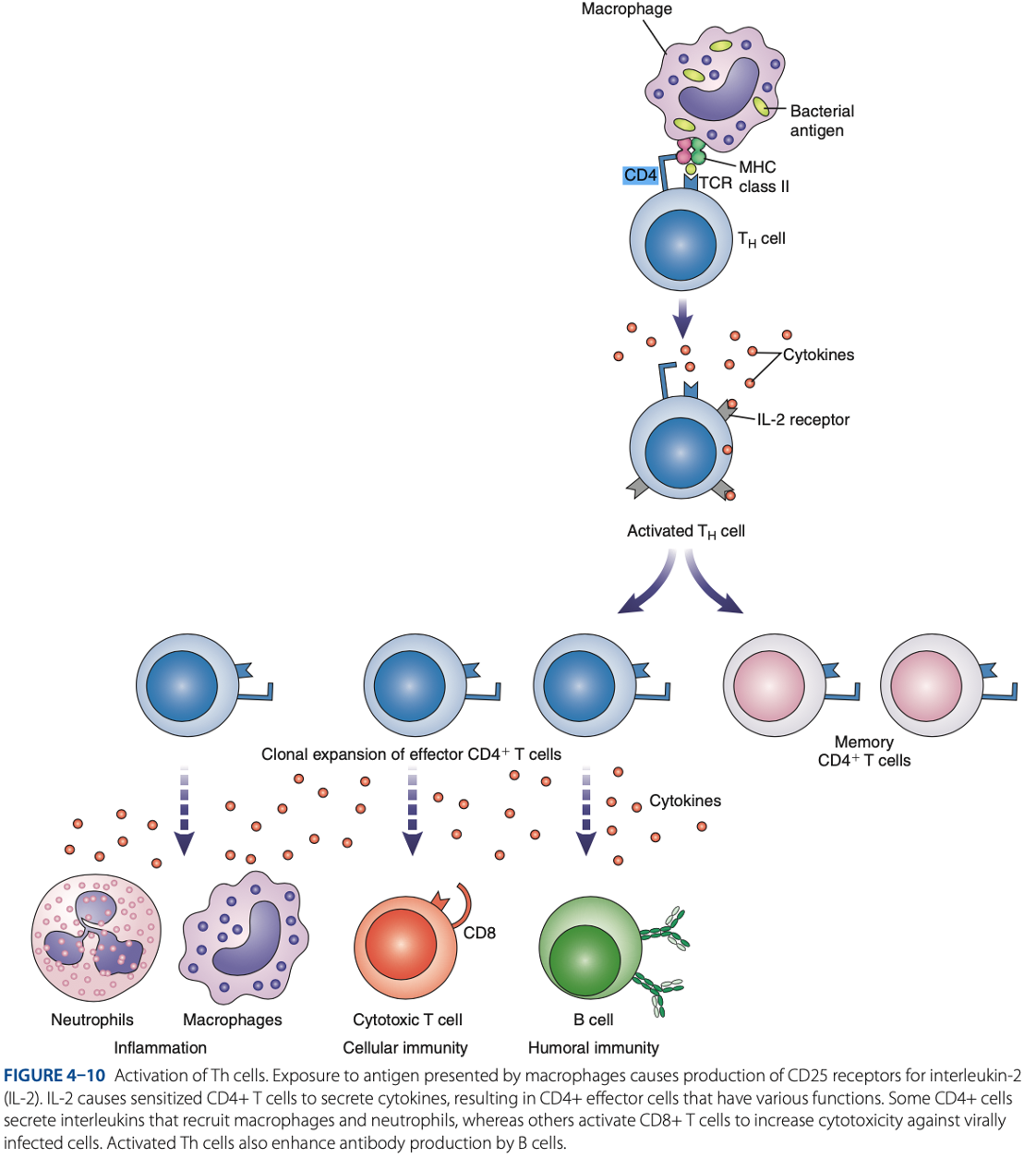
T Cells
Role of T Cells In Adaptive Immune Response
what circulate throughout the bloodstream, lymph nodes, & secondary lymphoid tissue, looking for antigens.
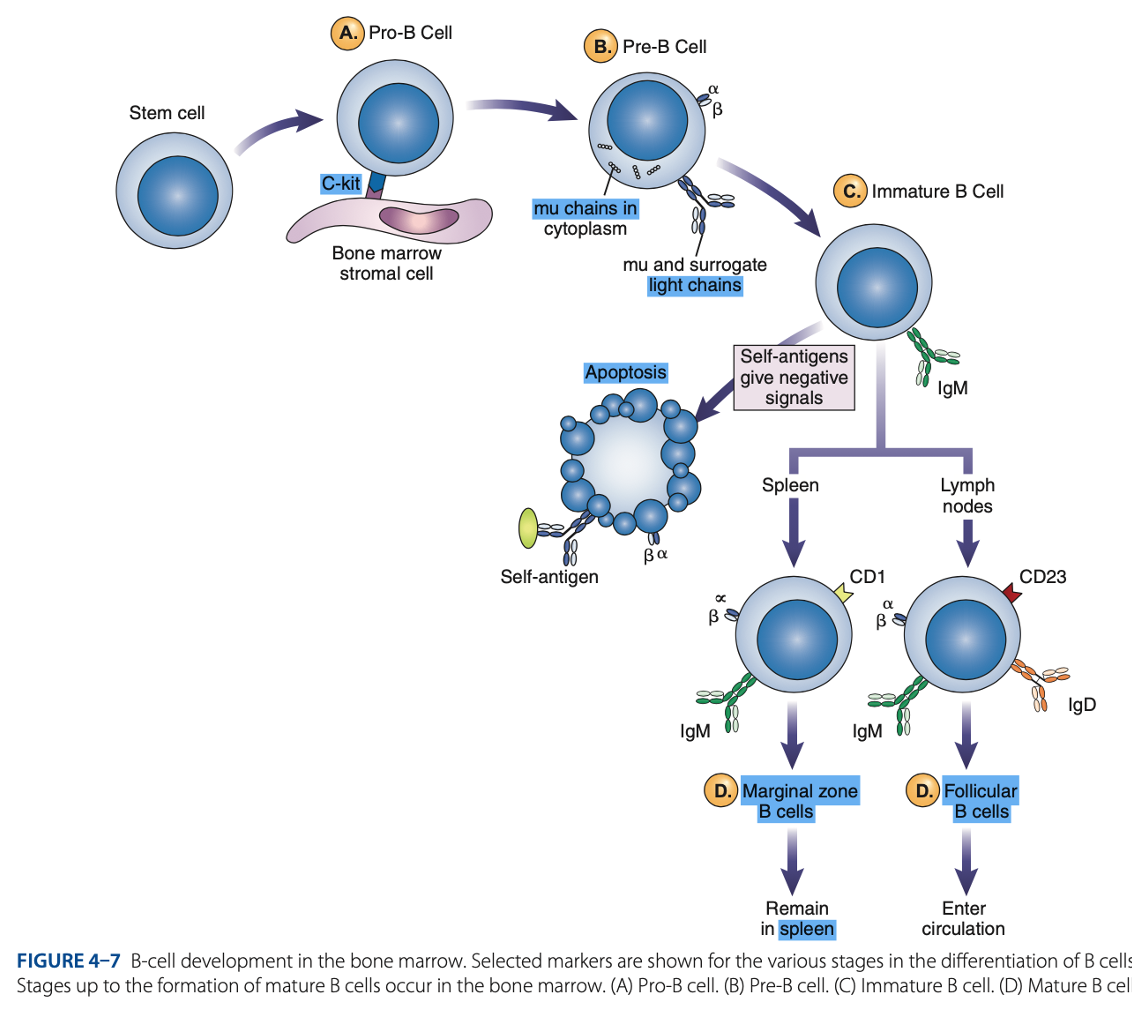
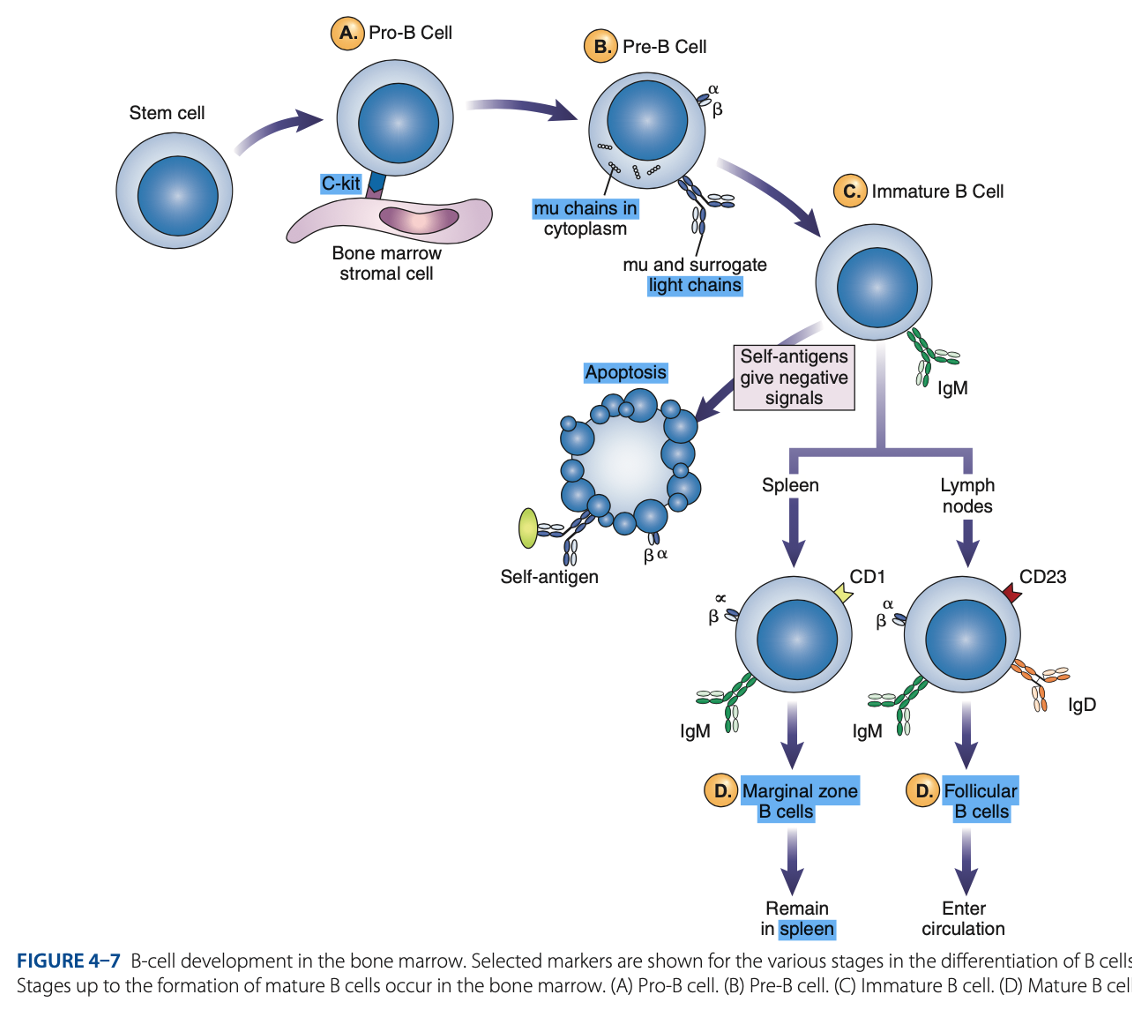
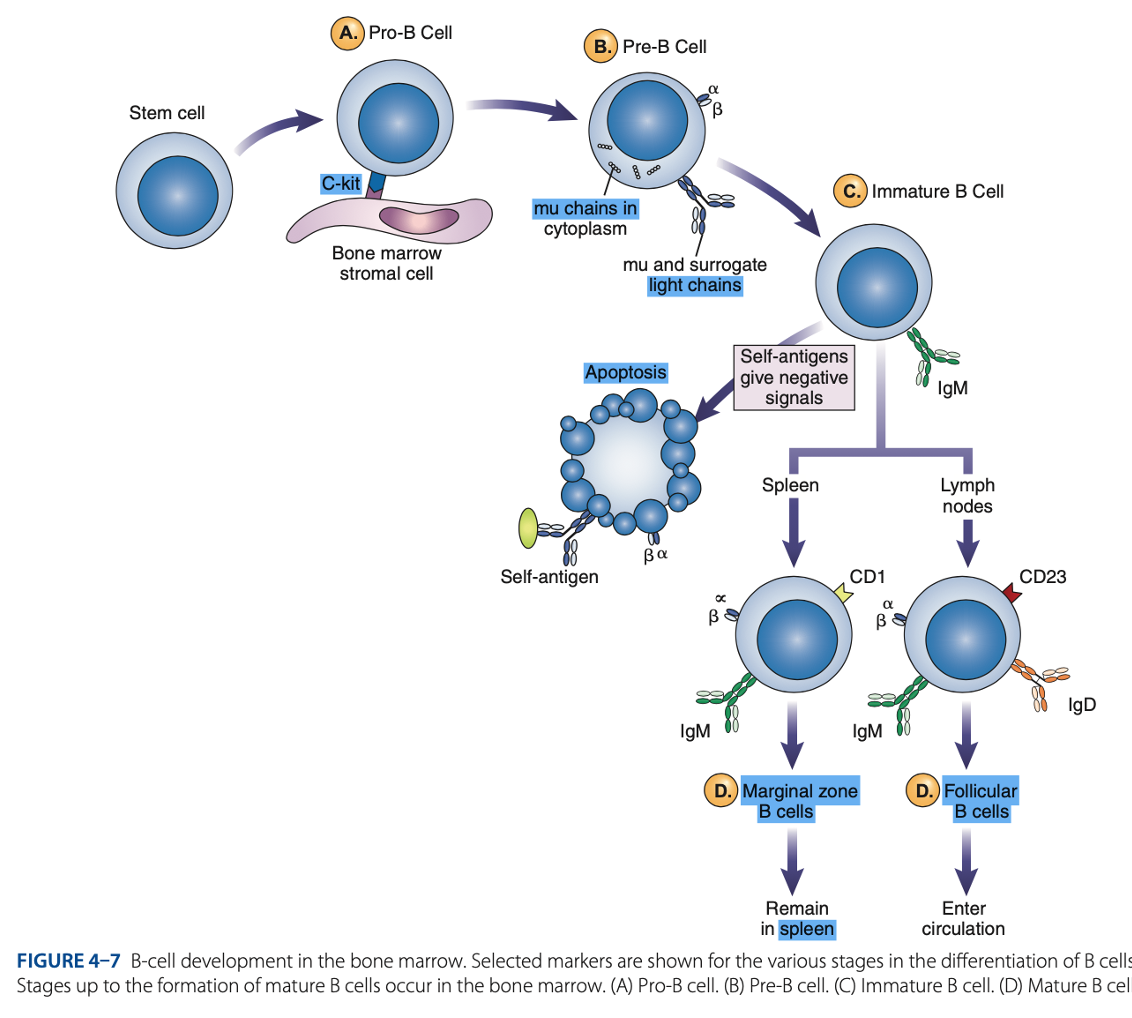
bone marrow
B-Cell Differentiation occurs in
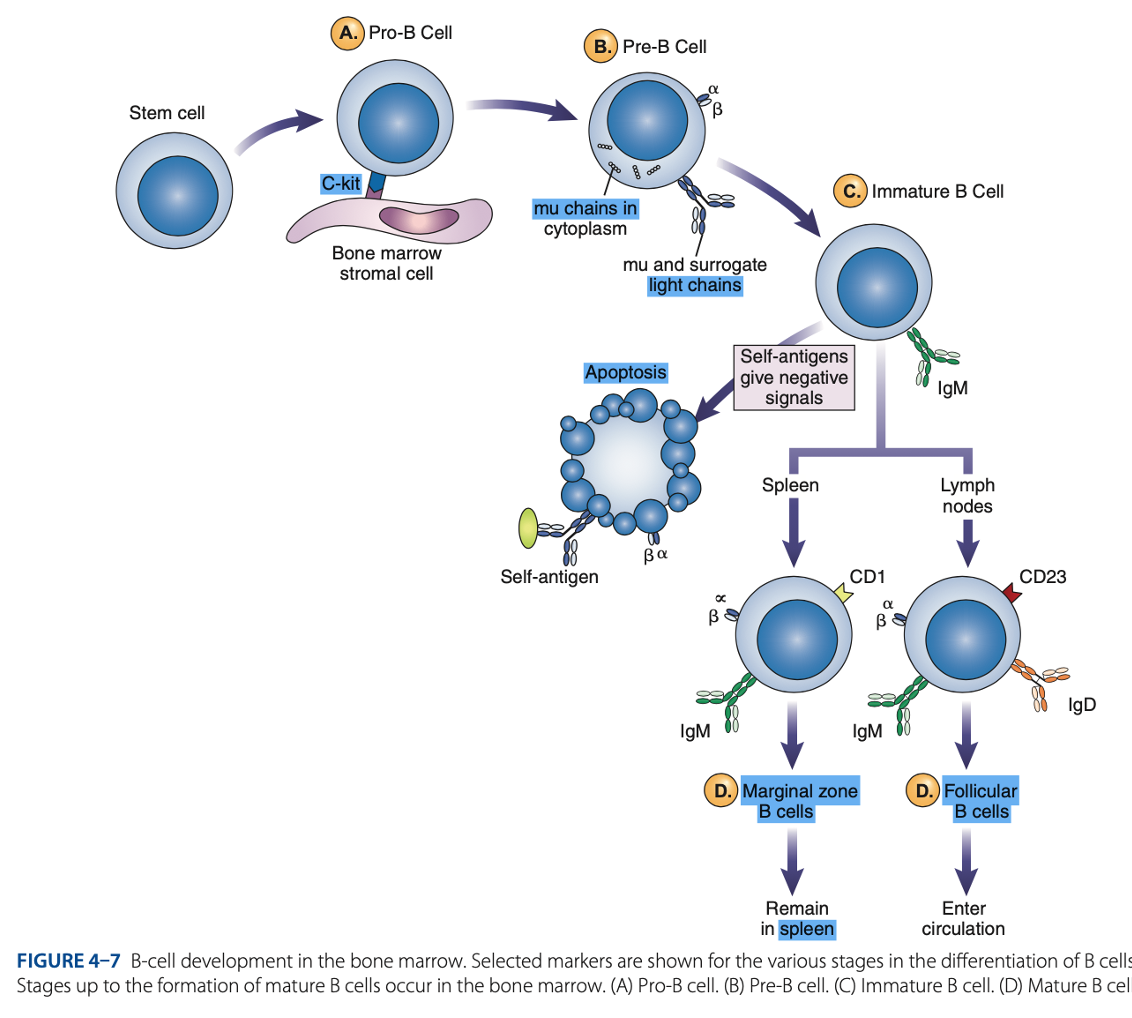
hematopoietic stem cell
B-Cell Differentiation starts with a - that develops into an early lymphocyte progenitor
• Development of mature immunocompetent B cells
• Activation of B cells by antigen
• Differentiation of activated B cells into antibody-producing plasma cell
B Cell differentiation involves:
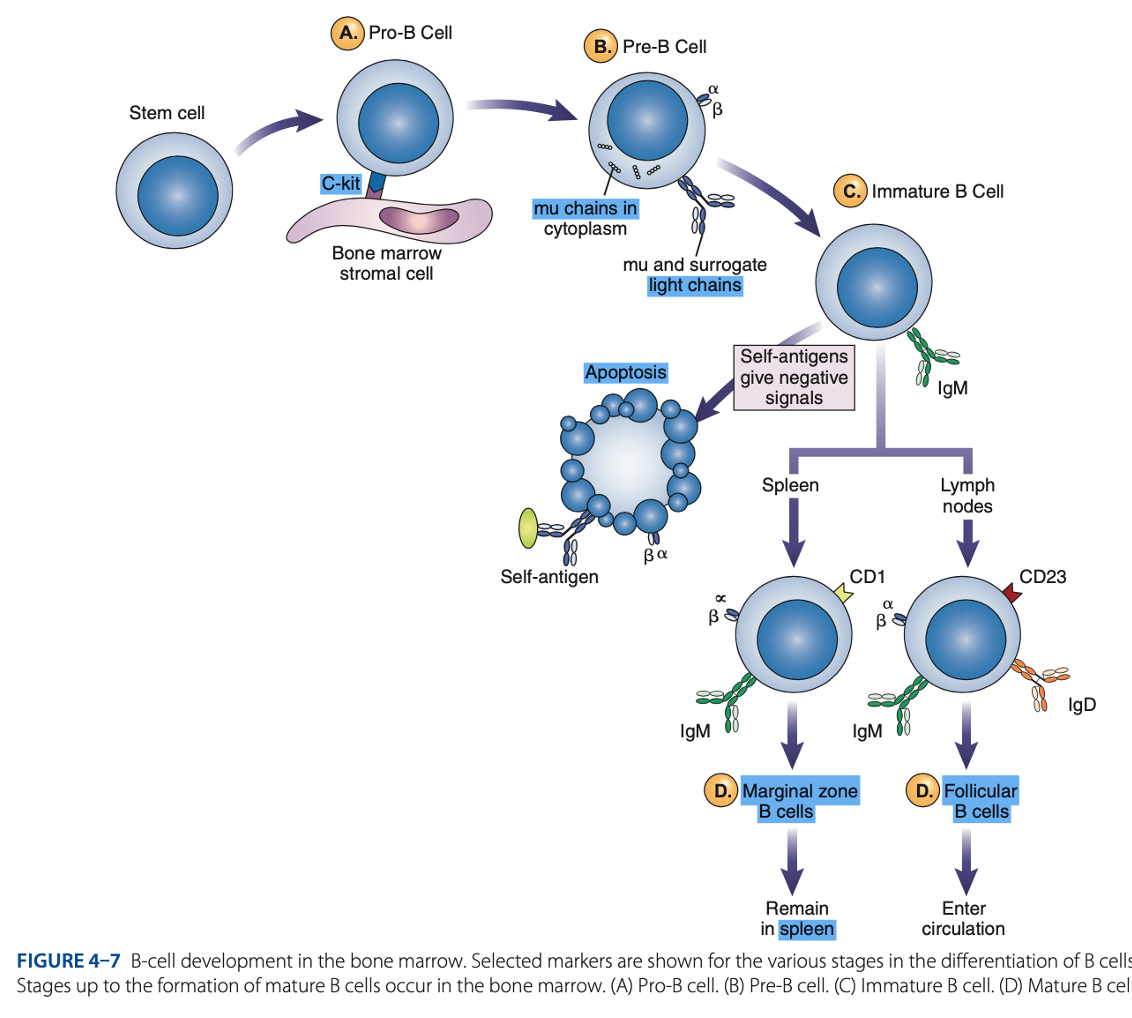
• Pro-B cells
• Pre-B cells
• Immature B cells
• Mature B cells
Antigen-independent Phase
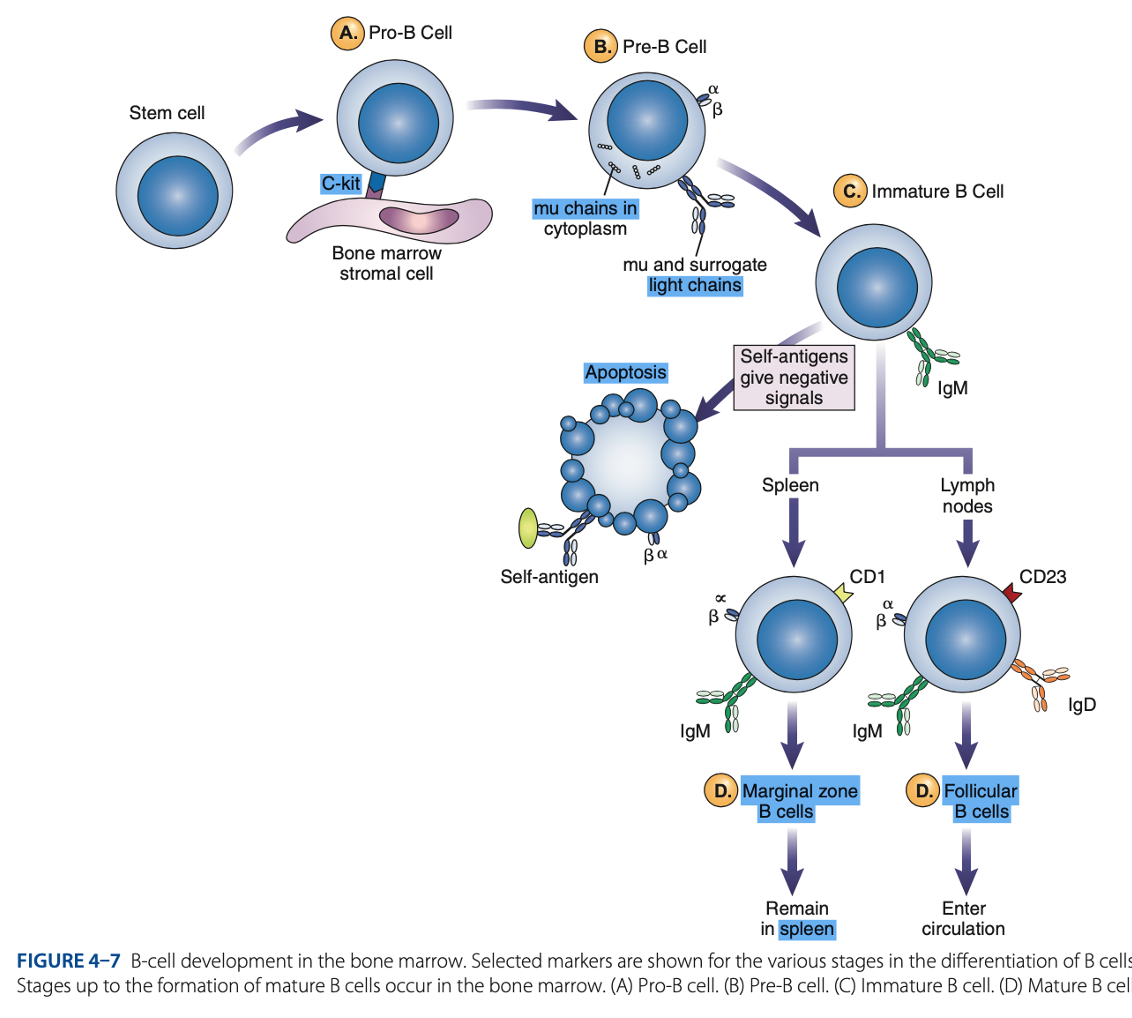
Pro-B Cells
- Develop from rearrangement of genes that code for heavy & light chains of antibody molecules.
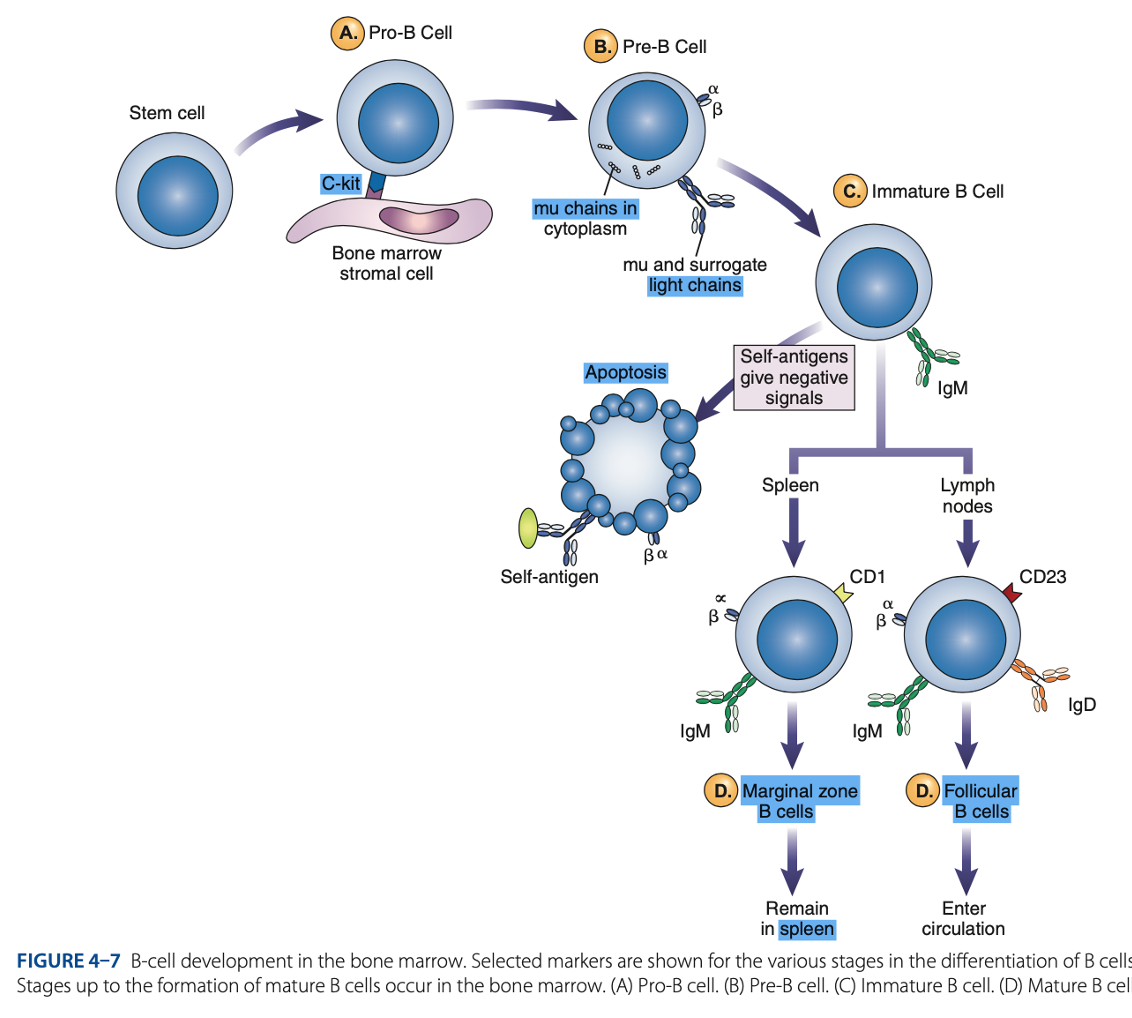
Pro-B Cells
- Made specific for certain antigens by variable regions
Pro-B Cells
- Must successfully rearrange one set of heavy-chain genes to become pre-B cells.
IgM Class
What are the Heavy µ Chains in Pre-B Cells
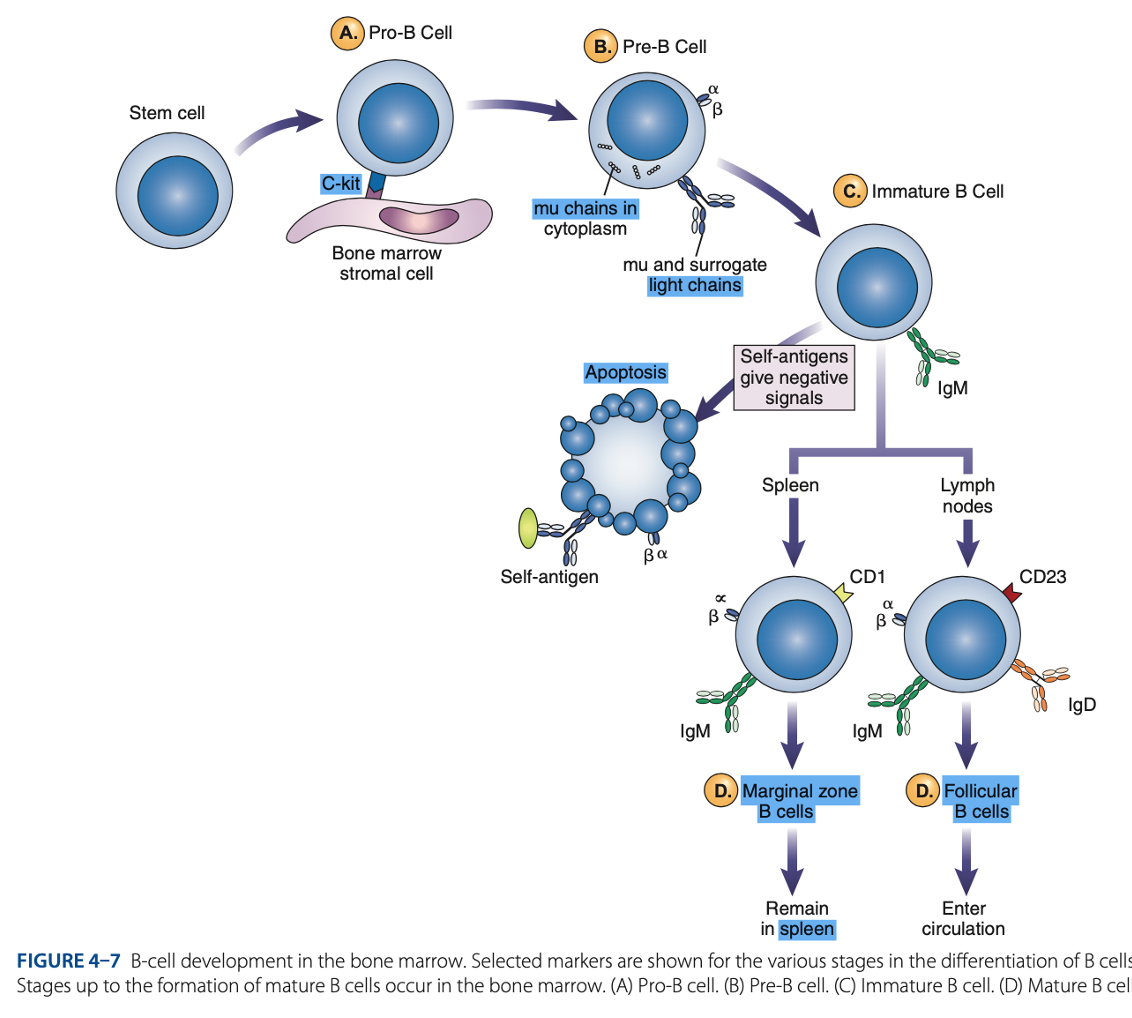
Heavy µ Chains of IgM Class
accumulate in cytoplasm & can express on cell surface with a surrogate light chain.
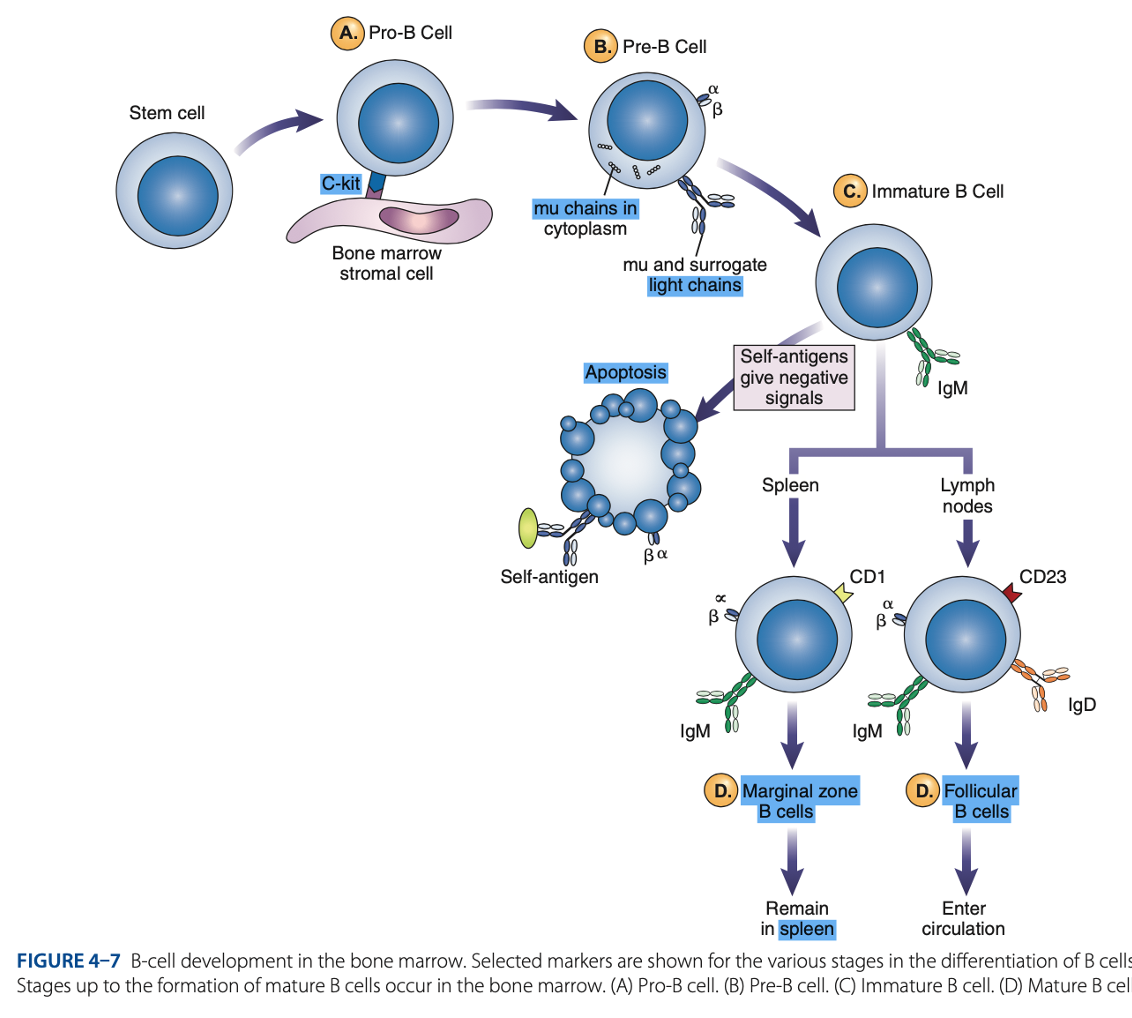
Ig-α & Ig-β
What are the short chains in Pre-B Cells
Immature B Cells
- Have complete IgM antibody molecules on cell surfaces that serve as antigen receptors

central tolerance
Immature B Cells
- The process of - involves elimination of B cells that have self-reactive receptors
spleen
Immature B Cells
- If immature B cells survive central tolerance, they move to the -
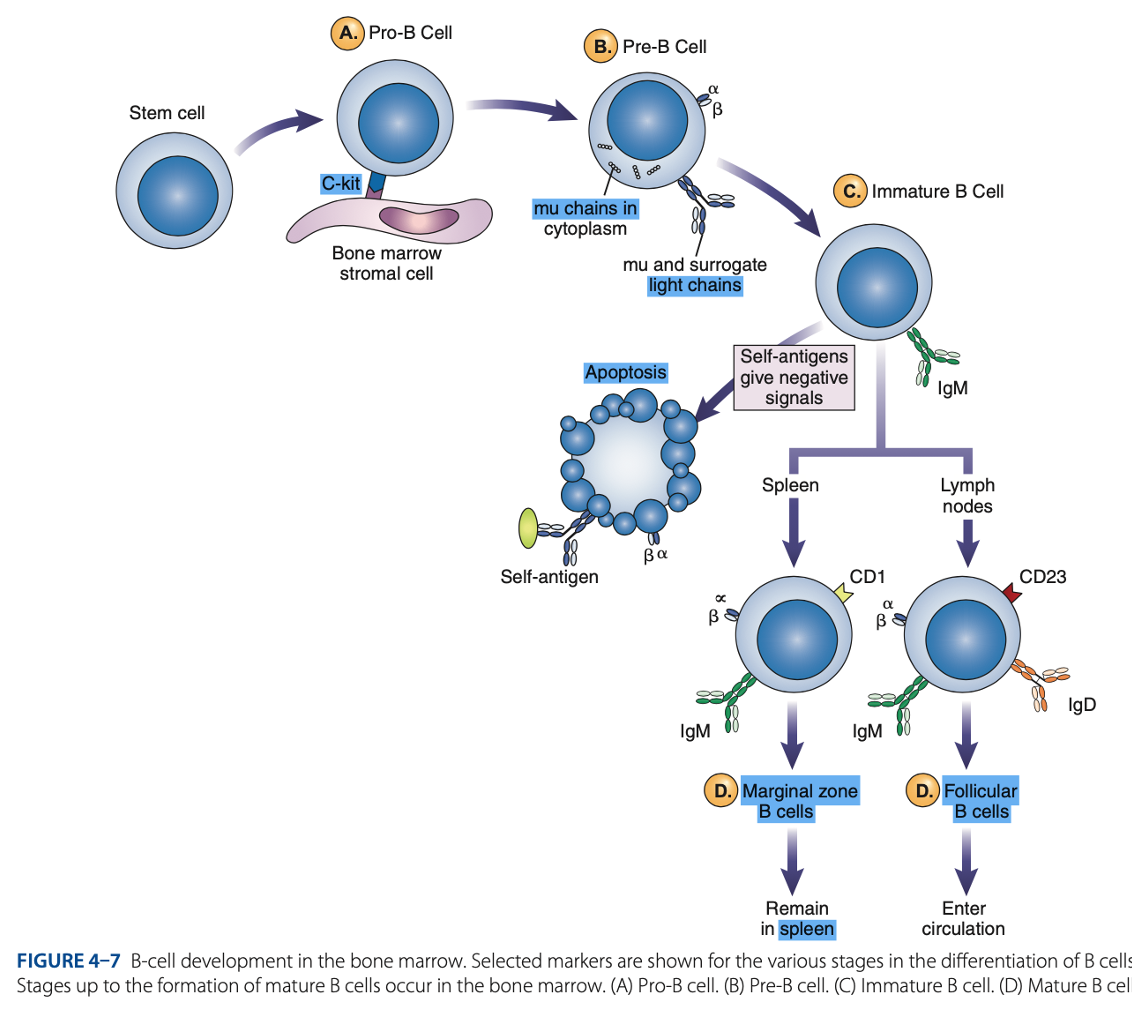
Immature B Cells
- Have variable regions that determine specificity for antigen
• CD21
• CD40
• Class II MHC Molecules
Immature B Cells
- Include other surface proteins:
CD21
Immature B Cells
what acts as a receptor for a breakdown product of the complement component C3, known as C3d
CD40 & Class II MHC Molecules
Immature B Cells
are important for interaction of B cells with T cells.
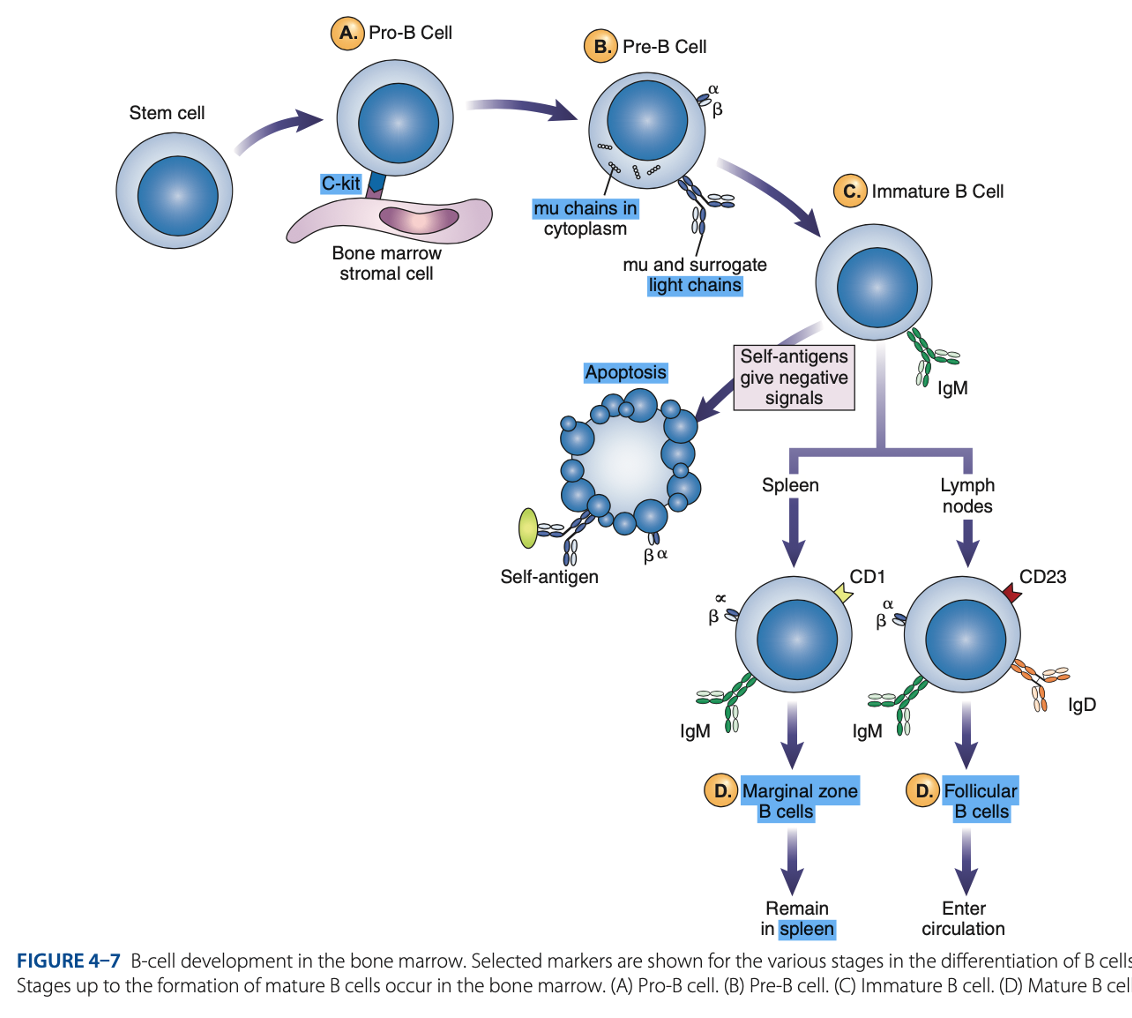
Spleen
Mature B cells develop in the
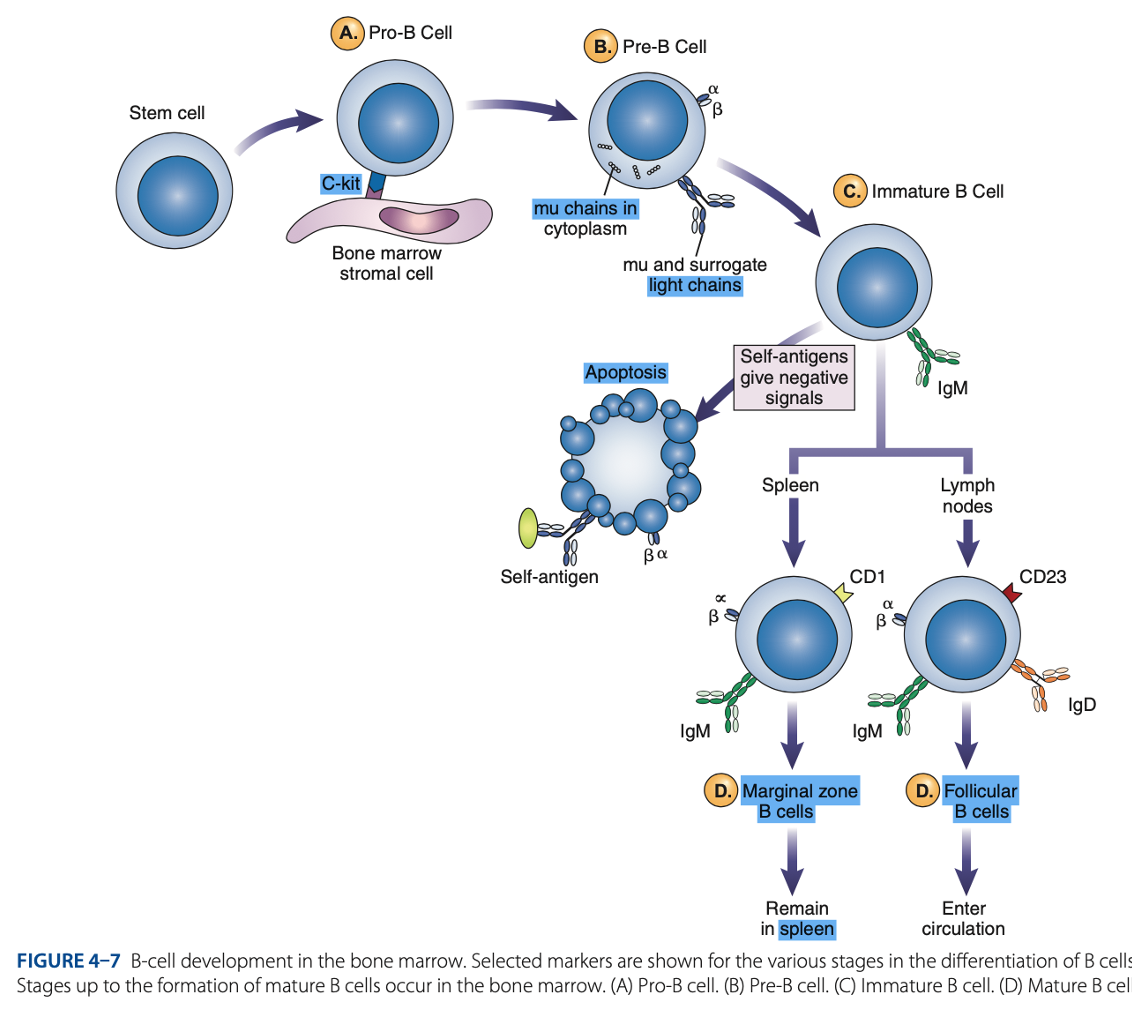
Marginal B cells
Mature B Cells
– remain in spleen & respond quickly to bloodborne pathogens.
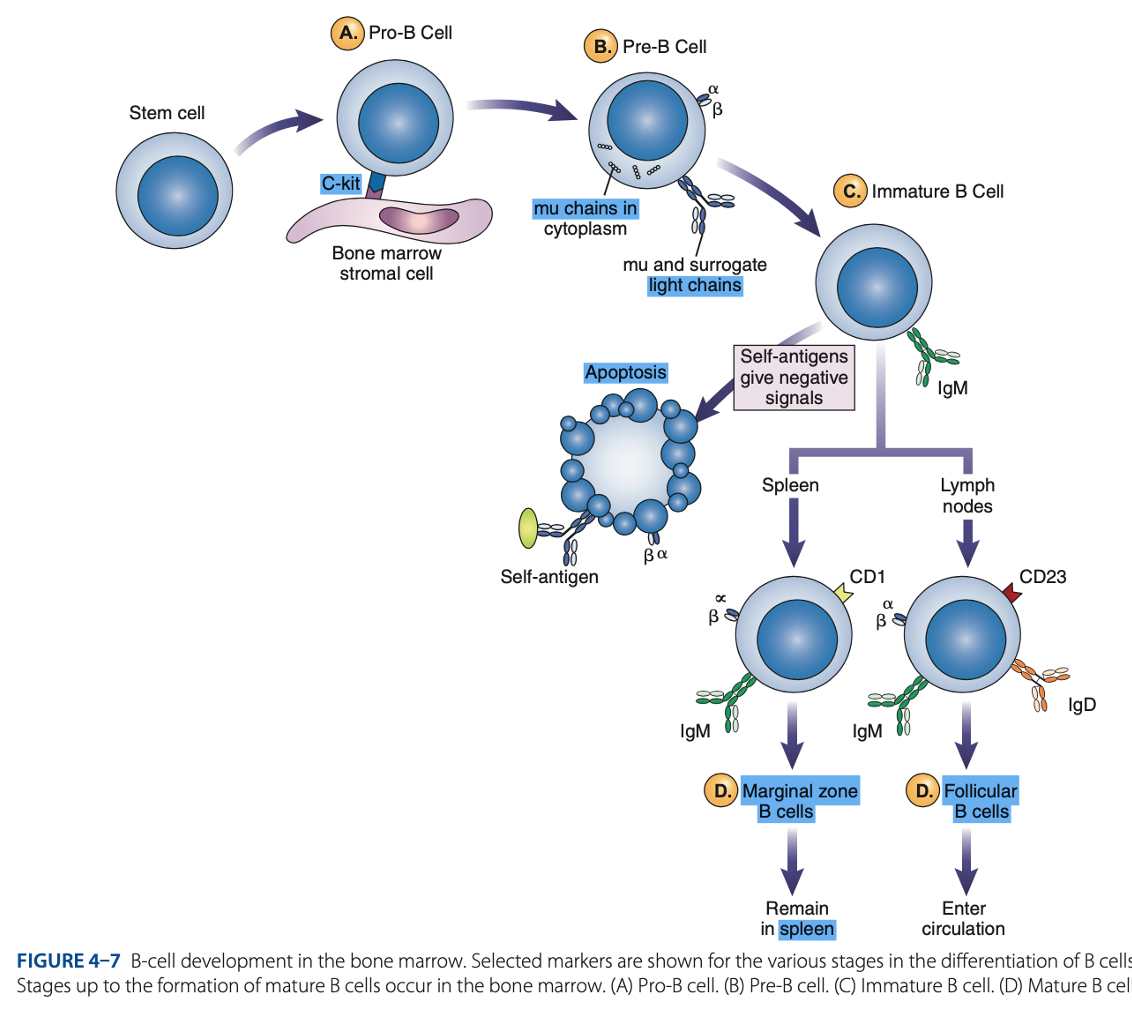
Follicular B Cells
Mature B Cells
– migrate to lymph nodes & other secondary organs.
- Recirculates
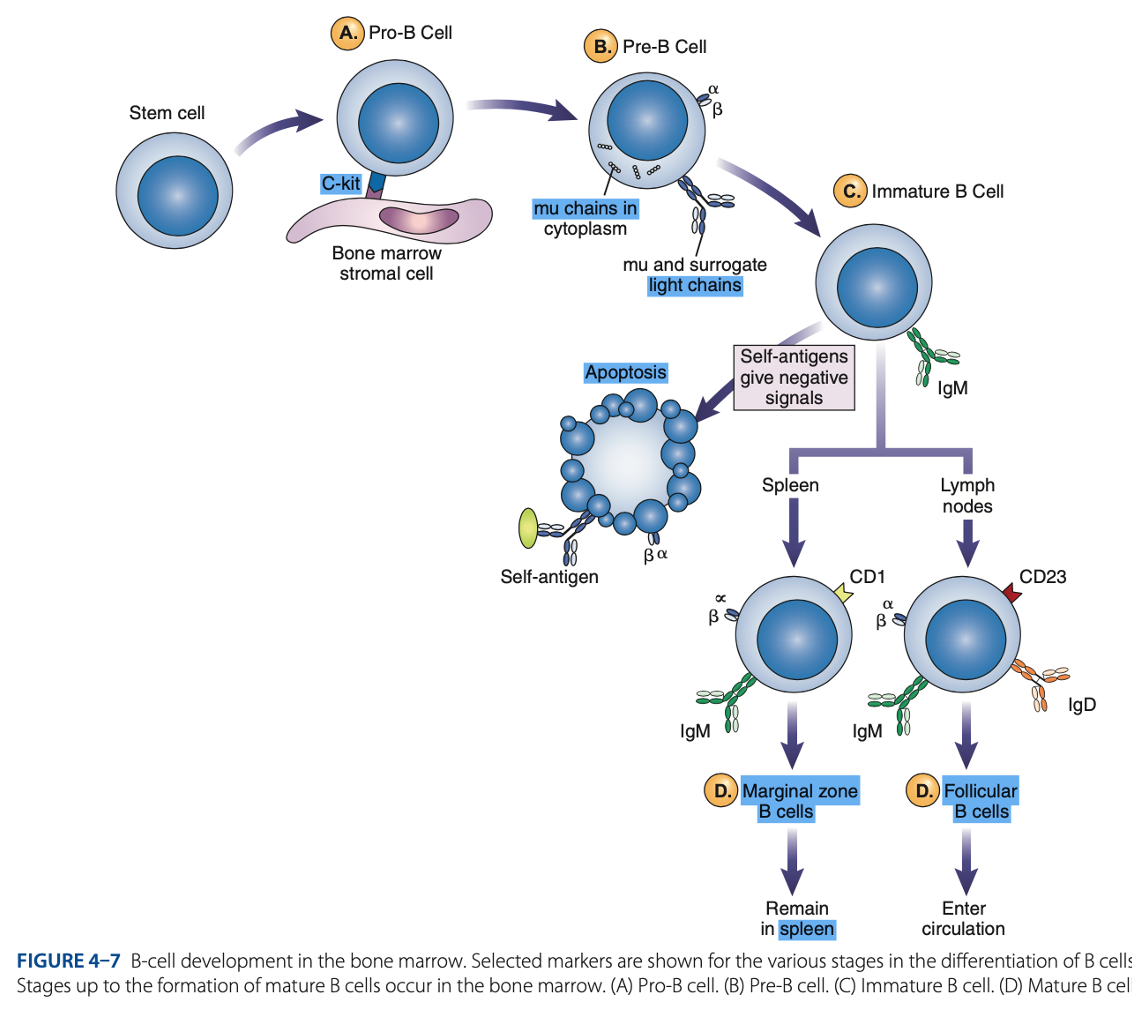
Mature B Cells
- Exhibit IgM & IgD
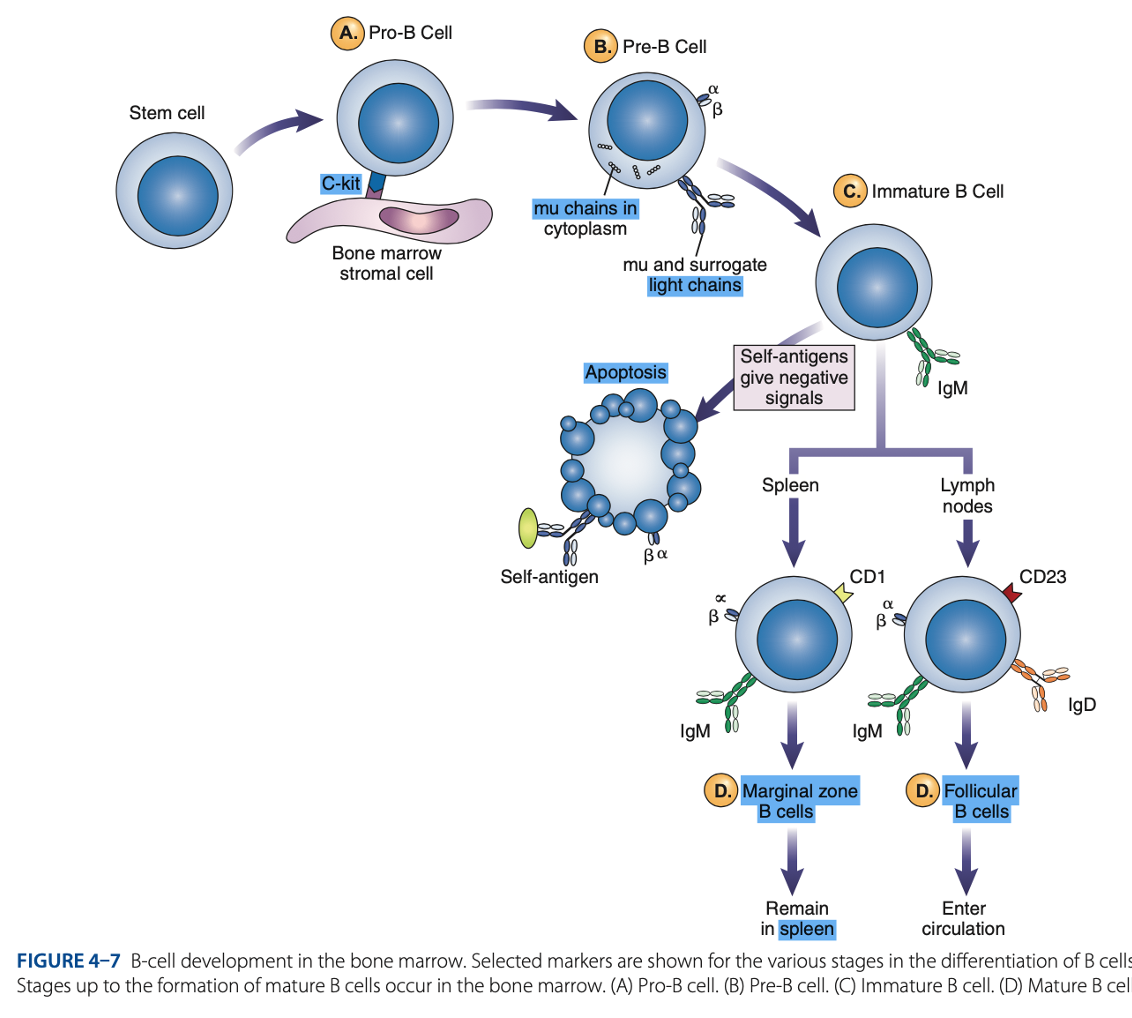
Mature B Cells
- Surface immunoglobulins provide activating signal to B Cells when contact with antigen occurs.
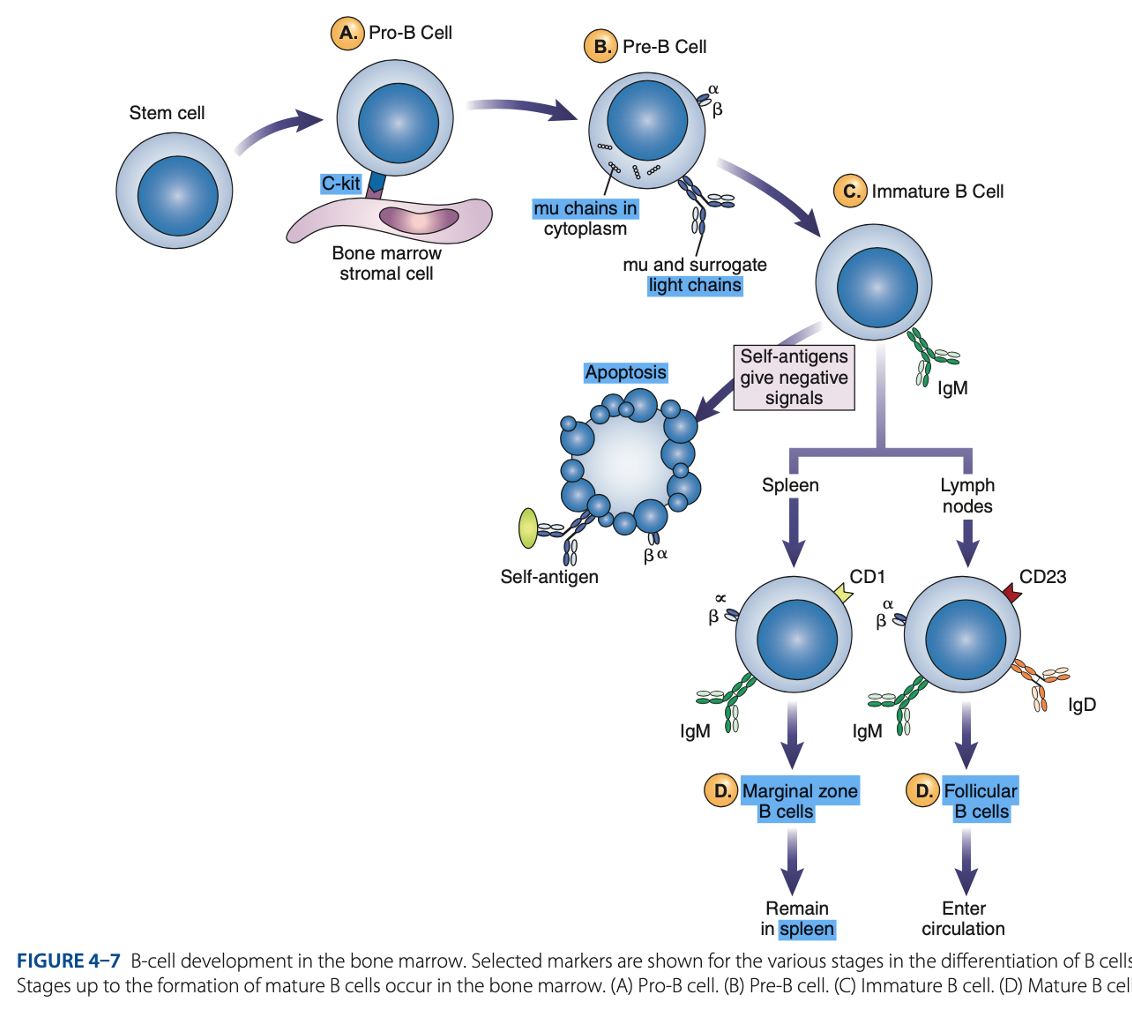
• Memory Cells
• Antibody-secreting Plasma Cells
Mature B Cells
- When stimulated, enter antigen-dependent phase, forming:
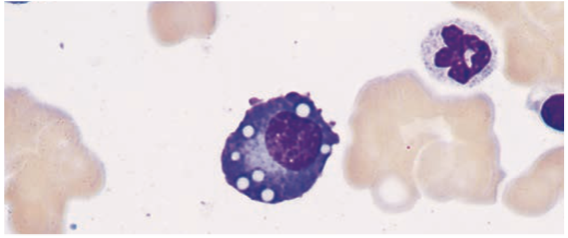
Plasma Cells
End product of B cell differentiation
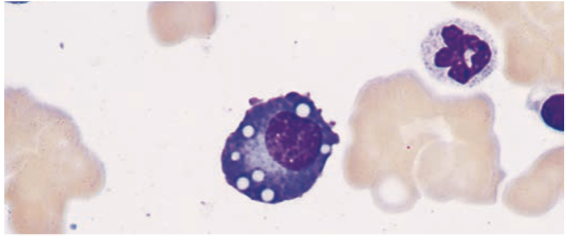
peripheral lymphoid organs & bone marrow
Plasma Cells is found in the
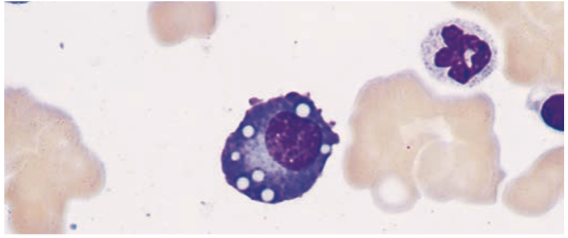
Plasma Cells
- Have a lot of cytoplasmic immunoglobulin but little or no surface immunoglobulin.
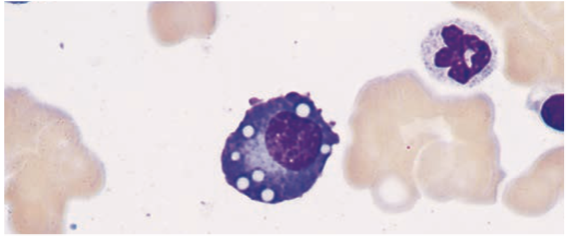
Plasma Cells
- Produce antibodies
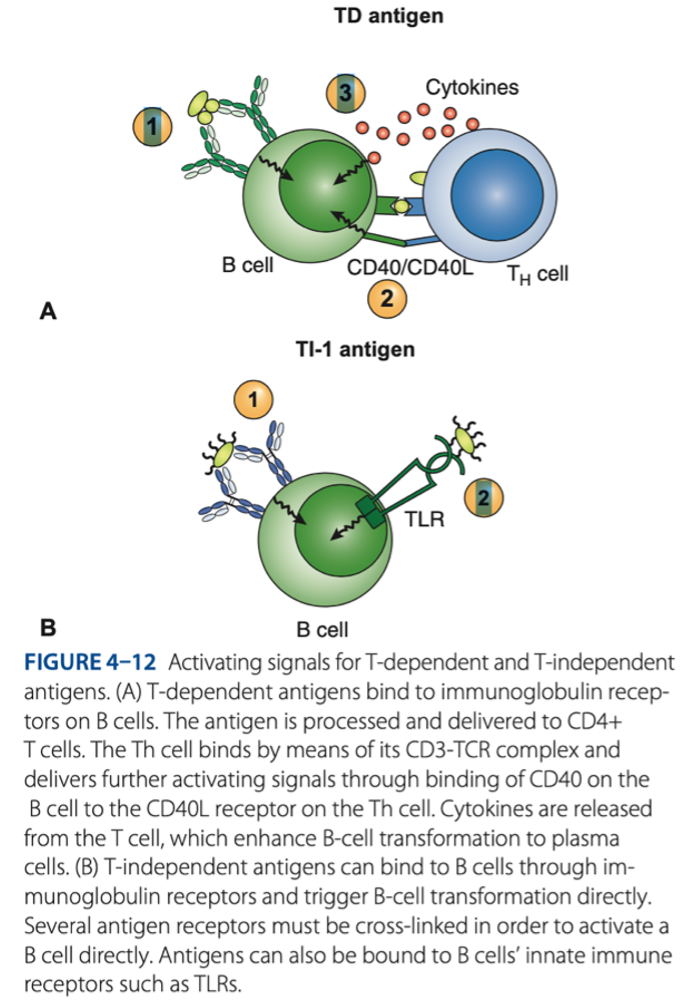
• Response to T-dependent antigens
• Response to T-independent antigens
Role of B Cells In Adaptive Immune Response
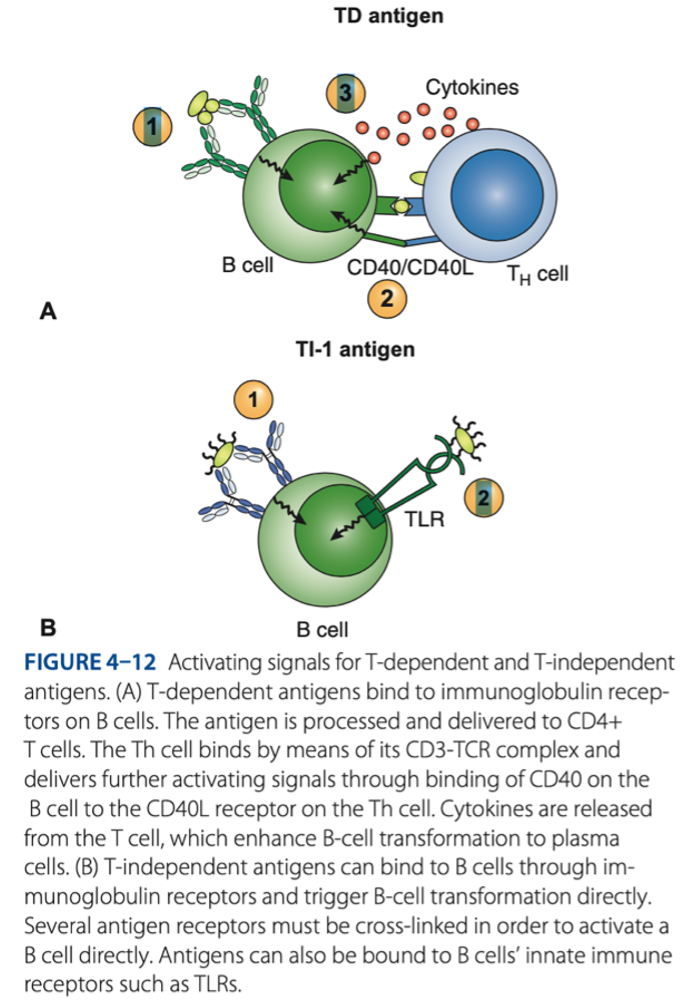
MHC CLASS II - plasma cells = produce antigen & antobody
T-dependent antigens is presented by
gram -
T-independent antigens is specific for what bacteria
• Malignancies
• Immunodeficiency diseases
• AIDS
Laboratory Identification of Lymphocytes
• Helps diagnose:
• Segregates lymphocytes into subsets
• Uses monoclonal antibodies
Laboratory Identification of Lymphocytes
• Uses cell flow cytometry:
Adaptive immunity
is characterized by specificity, ability to remember a prior exposure to an antigen, & an increased response upon exposure to that same antigen.
B cells
mature in bone marrow during the antigen-independent stage & in secondary lymphoid organs during the antigen-dependent phase.
B cells
can be recognized by the presence of surface antigens, or CDs, that are detected by monoclonal antibodies. B-cell markers include CD19, class II MHC proteins, and surface immunoglobulins.
T cells
are responsible for cell-mediated immunity, which involves production of cytokines that serve as regulatory factors for the immune response.
monoclonal antibodies
Lymphocytes are identified using - directed against specific surface antigens. They are enumerated through the use of cell flow cytometry, which categorizes cells on the basis of light scattering.
cell flow cytometry
Lymphocytes are identified using monoclonal antibodies directed against specific surface antigens. They are enumerated through the use of - , which categorizes cells on the basis of light scattering.
a. Class I
1. Which MHC molecule is necessary for antigen recognition by CD4+ T cells?
a. Class I
b. Class II
c. Class III
d. No MHC molecule is necessary.
d. It consists of a limited number of repeating determinants.
Which would be characteristic of a T-independent antigen?
a. The IgG antibody is produced exclusively.
b. A large number of memory cells are produced.
c. Antigens bind only one receptor on B cells.
d. It consists of a limited number of repeating determinants.
a. Production of antibody by plasma cells
Humoral immunity refers to which of the following?
a. Production of antibody by plasma cells
b. Production of cytokines by T cells
c. Elimination of virally infected cells by cytotoxic cells
d. Downregulation of the immune response
a. Bone marrow
Where does antigen-independent maturation of B lymphocytes take place?
a. Bone marrow
b. Thymus
c. Spleen
d. Lymph nodes
c. MHC antigens
In the thymus, positive selection of immature T cells is based upon recognition of which of the following?
a. Self-antigens
b. Stress proteins
c. MHC antigens
d. μ chains
b. IgM and IgD
Which of these are found on a mature B cell?
a. IgG and IgD
b. IgM and IgD
c. Alpha and beta chains
d. CD3
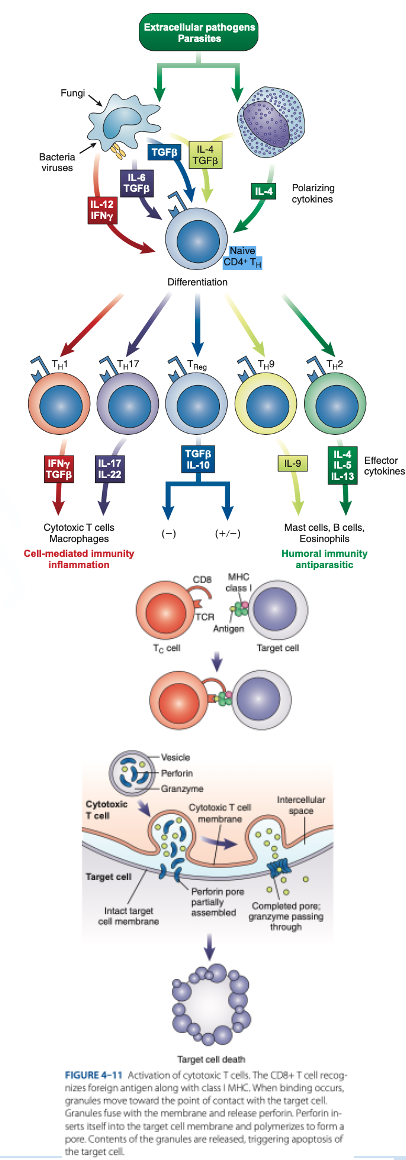
d. They produce granzymes that stimulate apoptosis.
How do cytotoxic T cells kill target cells?
a. They produce antibodies that bind to the cell.
b. They engulf the cell by phagocytosis.
c. They stop protein synthesis in the target cell.
d. They produce granzymes that stimulate apoptosis.
c. Cytokines
Which of the following can be attributed to antigen-stimulated T cells?
a. Humoral response
b. Plasma cells
c. Cytokines
d. Antibody
a. μ chains in the cytoplasm
Which is a distinguishing feature of a pre-B cell?
a. μ chains in the cytoplasm
b. Complete IgM on the surface
c. Presence of CD21 antigen
d. Presence of CD25 antigen
b. As the cell becomes an immature B cell
When does genetic rearrangement for coding of antibody light chains take place during B-cell development?
a. Before the pre-B cell stage
b. As the cell becomes an immature B cell
c. Not until the cell becomes a mature B cell
d. When the B cell becomes a plasma cell
b. CD4
Which of the following antigens are found on the T-cell subset known as helper/inducers?
a. CD3
b. CD4
c. CD8
d. CD11
d. Lymph nodes
Where does the major portion of antibody production occur?
a. Peripheral blood
b. Bone marrow
c. Thymus
d. Lymph nodes
c. CD2+CD3+CD4-CD8-
Which of the following would represent a double- negative thymocyte?
a. CD2-CD3+CD4-CD8+
b. CD2-CD3-CD4+CD8-
c. CD2+CD3+CD4-CD8-
d. CD2-CD3-CD4+CD8-
d. Alpha and beta chains are unique for each antigen.
Which of the following best describes the T-cell receptor for antigen?
a. It consists of IgM and IgD molecules.
b. It is the same for all T cells.
c. It is present in the double-negative stage.
d. Alpha and beta chains are unique for each antigen.
c. Elimination of virally infected cells
A cell flow cytometry pattern belonging to a 3-year- old patient showed the following: normal CD4+ T-cell count, normal CD19+ B-cell count, low CD8+ T-cell count. Which type of immunity would be affected?
a. Production of antibody
b. Formation of plasma cells
c. Elimination of virally infected cells
d. Downregulation of the immune response
b. Ability to remember a prior exposure to a pathogen
Which of the following is a unique characteristic of adaptive immunity?
a. Ability to fight infection
b. Ability to remember a prior exposure to a pathogen
c. A similar response to all pathogens encountered
d. Process of phagocytosis to destroy a pathogen
a. Elimination of autoimmune responses
Clonal deletion of T cells as they mature is important in which of the following processes?
a. Elimination of autoimmune responses
b. Positive selection of CD3/TCR receptors
c. Allelic exclusion of chromosomes
d. Elimination of cells unable to bind to MHC
antigens
d. In lymph nodes
Where do germinal centers occur?
a. In the thymus
b. In the bone marrow
c. In peripheral blood
d. In lymph nodes