Human Anatomy/Physiology Unit 1 Part 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/116
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam 9/14-9/15
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
1
New cards
Physiology
The study of body functions
2
New cards
Anatomy
The study of body structure
3
New cards
Atoms
All matter is made up of these tiny molecules
4
New cards
Molecules
A chemical substance formed by the linking of atoms; the smallest unit of a given chemical substance
5
New cards
Cells
The smallest unit capable of carrying out the processes associated with life; the basic unit of both structure and function in living organisms
6
New cards
Plasma Membrane
A protein-studded lipid bilayer that encloses each cell, separating it from the extracellular fluid
7
New cards
Tissues
A functional aggregation of cells of a single specialized type, such as nerve cells forming nervous ____. Also the aggregate of various cellular and extracellular components that make up a particular organ such as lung _____.
8
New cards
Muscle Tissue
A functional grouping of cells specialized for contraction and force generation
9
New cards
Nervous Tissue
A functional grouping of cells specialized for initiation and transmission of electrical signals
10
New cards
Epithelial Tissue
A functional grouping of cells specialized in the exchange of materials between the cells and its environment; lines and covers various body surfaces and cavities and forms secretory glands
11
New cards
Connective Tissue
______ that serves to connect, support, and anchor various body parts; distinguished by relatively few cells dispersed within an abundance of extracellular material
12
New cards
Organ
A distinct structural unit composed of two or more types of primary tissue organized to perform one or more particular functions (ex: stomach)
13
New cards
Body System
A collection of organs that perform related functions and interact to accomplish a common activity that is essential for survival of the whole body (ex: Digestive system)
14
New cards
External Environment
The environment surrounding the environment
15
New cards
Internal Environment
The body’s aqueous extracellular environment, which consists of the plasma and interstitial fluid which must be homeostatically maintained for the cells to make life-sustaining exchanges with it.
16
New cards
Intracellular Fluid (ICF)
The fluid collectively contained within all the body cells
17
New cards
Extracellular Fluid (ECF)
All the fluid outside the cells of the body consists of interstitial fluid and plasma
18
New cards
Plasma
The liquid portion of the blood
19
New cards
Interstitial Fluid
The portion of the extracellular fluid that surrounds and bathes all the body cells
20
New cards
Homeostasis
The ability for the body to maintain an ever-changing internal environment, yet keep change within tightly regulated ranges; many cells, organs, body systems involved in maintenance of homeostasis
21
New cards
Dynamic Steady State
Changes that occur are minimized by compensatory physiological responses. The term ______ *refers to each homeostatically regulated factor being marked by continuous change, whereas _________ ________* implies that these changes do not deviate far from a constant, or steady, level.
22
New cards
Homeostatic Control System
A regulatory system that includes a sensor, integrator, and effectors that work together to bring about a corrective adjustment that opposes and original deviation from a normal set point
23
New cards
Negative Feedback
A regulatory mechanism in which a change in a controlled variable triggers a response that opposes the change, thus maintaining a relatively steady set point for the regulated factor (ex: thermostat)
Common regulatory mechanism in body for maintaining homeostasis
Common regulatory mechanism in body for maintaining homeostasis
24
New cards
Controlled Variable
Some factor that can vary but is held within a narrow range by a control system
25
New cards
Sensor
The component of a control system that monitors the magnitude of the controlled variable (thermometer, senses that the room decreased in temp)
26
New cards
Set Point
The desired level at which homeostatic control mechanisms maintain a controlled variable (temp thermostat is supposed to be at)
27
New cards
Integrator
A region that determines efferent output based on processing of afferent input; also called a control center (Thermostat)
28
New cards
Effector
The component of a control system that accomplishes the output commanded by the integrator (Furnace, which then leads to increase in room temp)
29
New cards
Positive Feedback
A regulatory mechanism in which the input and the output in a control system continue to enhance each other so that the controlled variable is progressively moved further from a steady rate (ex: birth)
30
New cards
Phospholipid
These have a polar head containing a negatively charged phosphate group and two non polar fatty acid chain tails
31
New cards
Amphipathic
2 Domains
32
New cards
Cholesterol
Essential for the most common way to adjust fluidity
A type of fat molecule that serves as a precursor for steroid hormones and bile salts and is a stabilizing component of the plasma membrane
A type of fat molecule that serves as a precursor for steroid hormones and bile salts and is a stabilizing component of the plasma membrane
33
New cards
Hydrophilic
“Water-Loving”; can interact with water molecule
34
New cards
Hydrophobic
“Water-Hating”; does not mix with water
35
New cards
Lipid Bilayer
Basic structure, structural backbone, barrier to water soluble substances, fluidity
Phospholipids assemble themselves into these double layers of lipid molecules. Hydrophobic tails bury themselves into this away from the water and the hydrophilic heads line up on both sides in contact with the water. This is more fluid than rigid with the consistency of oil.
Phospholipids assemble themselves into these double layers of lipid molecules. Hydrophobic tails bury themselves into this away from the water and the hydrophilic heads line up on both sides in contact with the water. This is more fluid than rigid with the consistency of oil.
36
New cards
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
One or more double-bond
Has the cis-double bond (increases bilayer fluidity)
Has the cis-double bond (increases bilayer fluidity)
37
New cards
Saturated Fatty Acid
Only contain one single bond
38
New cards
Flippase
Transmembrane transporter enzymes responsible for asymmetric phospholipid bilayer
39
New cards
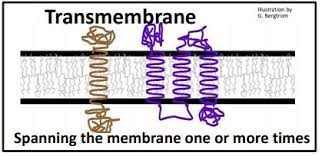
Transmembrane Proteins
EMBEDDED through the entire thickness of the lipid bilayer membrane.
Integral membrane proteins
More than one membrane spanning domains (non-polar amino acids)
Move lipophobic molecules across cell membrane (selectively permeable) through channels and carriers
Integral membrane proteins
More than one membrane spanning domains (non-polar amino acids)
Move lipophobic molecules across cell membrane (selectively permeable) through channels and carriers
40
New cards
Peripheral Membrane Proteins
Exposed to only one side of the membrane; anchored to cytosolic side or extracellular fluid side in a variety of ways.
ONLY ON ONE SIDE AND ATTACHED TO TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEIN
Polar molecules that do not penetrate the membrane. A plasma-membrane protein that studs the surface instead of penetrating the membrane.
ONLY ON ONE SIDE AND ATTACHED TO TRANSMEMBRANE PROTEIN
Polar molecules that do not penetrate the membrane. A plasma-membrane protein that studs the surface instead of penetrating the membrane.
41
New cards
Fluid Mosaic Model
The view of membrane structure. This is in reference to the membrane fluidity and the ever-changing ______ pattern of the proteins embedded in the lipid bilayer.
LIPID BILAYER WITH INSERTED PROTEINS
LIPID BILAYER WITH INSERTED PROTEINS
42
New cards
Glycocalyx
Outer surface of membrane covered with a dense carbohydrate coat
43
New cards
Leak Channels
Unregulated, undated channels that are open all the time
44
New cards
Gated Channels
May be open or closed to their specific ion as a result of changes in channel shape in response to controlling mechanisms
45
New cards
Membrane Bound Enzymes
Proteins located on either the inner or the outer cell surface function as this which controls specific chemical reactions
46
New cards
Receptors
Recognize and bind specific molecules in the environment of cell
Binding initiates series of membrane and intracellular events that alter activity of the cell
Membrane protein that binds with specific extracellular chemical messenger, bringing about membrane and intracellular events that alter the activity of the particular cell
Binding initiates series of membrane and intracellular events that alter activity of the cell
Membrane protein that binds with specific extracellular chemical messenger, bringing about membrane and intracellular events that alter the activity of the particular cell
47
New cards
Cell Adhesions Molecules (CAMs)
Proteins that protrude from the surface of the plasma membrane and form loops or other appendages that the cells use to grip one another and surrounding connective tissue fibers
Interact with cadherins and interns
Interact with cadherins and interns
48
New cards
Cadherins
Interaction with ECM and other cells
49
New cards
Desmosomes
Anchor adjacent cells together-confer stability to cell layers (cell adhesion cells)
Present in skin, cardiac muscle, uterus - where integrity of layers important
Major structural elements of these are plaque, glycoproteins filaments extracellularly, and intermediate filament scaffolding
An adhering junction between two adjacent but non touching cells formed by the extension of filaments between the cells’ plasma membranes; most abundant in tissues that are subject to considerable stretching
Present in skin, cardiac muscle, uterus - where integrity of layers important
Major structural elements of these are plaque, glycoproteins filaments extracellularly, and intermediate filament scaffolding
An adhering junction between two adjacent but non touching cells formed by the extension of filaments between the cells’ plasma membranes; most abundant in tissues that are subject to considerable stretching
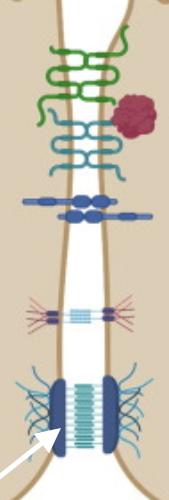
50
New cards
Plaques
A deposit of cholesterol and other lipids, perhaps calcified, and thickened, abnormal smooth-muscle cells within blood vessel walls as a result of atherosclerosis
51
New cards
Tight Junctions
Adjacent cells firmly adhere to each other by fusion of junctional proteins on outer surfaces of adjacent plasma membranes
Present in sheets of epithelial tissue (intestinal epithelium, vascular endothelium)
Form highly selective cellular barriers to macromolecule movement - very dynamic
Maintain apical/basal cell membrane asymmetry
Present in sheets of epithelial tissue (intestinal epithelium, vascular endothelium)
Form highly selective cellular barriers to macromolecule movement - very dynamic
Maintain apical/basal cell membrane asymmetry
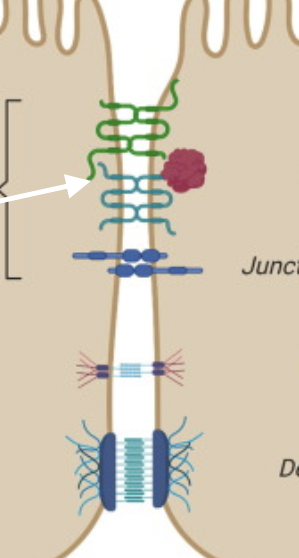
52
New cards
Gap Junctions
Protein channels between adjacent cells that allow passage of small water-soluble particles between cells
Formed by complex of cylindrically-arranged connexion subunits
Present in tissues where synchronized activity of cells is very important - cardiac and smooth muscle - functional syncctium
A communicating junction formed between adjacent cells by small connecting tunnels that permit passage of charge-carrying ions between the cells so that electrical activity in one cell is spread to the adjacent cell
Formed by complex of cylindrically-arranged connexion subunits
Present in tissues where synchronized activity of cells is very important - cardiac and smooth muscle - functional syncctium
A communicating junction formed between adjacent cells by small connecting tunnels that permit passage of charge-carrying ions between the cells so that electrical activity in one cell is spread to the adjacent cell
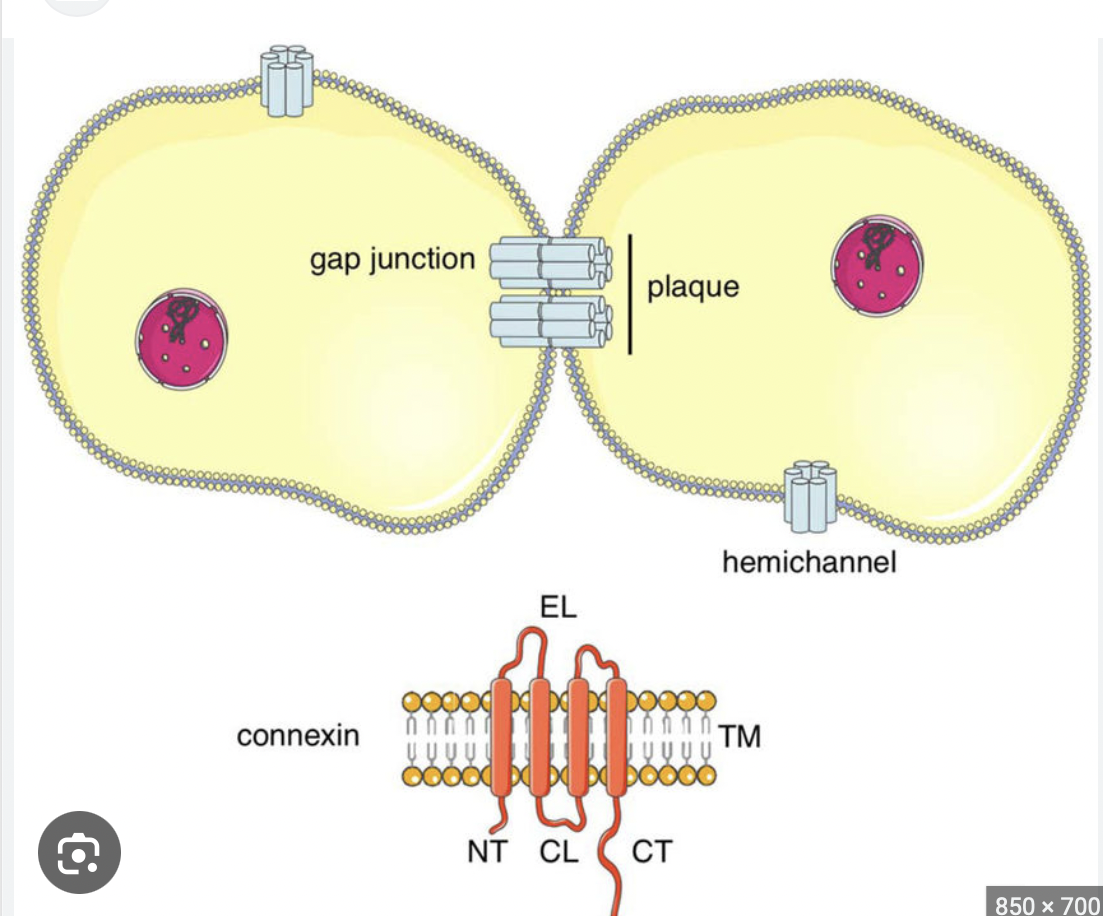
53
New cards
Connexons
Made up of 6 protein subunits arranged in a hollow, tubelike structure that extends though the thickness of the plasma membrane
54
New cards
Anatomy vs. Physiology
Relationship of form (structure) and function
ALWAYS A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
ALWAYS A RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
55
New cards
Small Intestine Anatomy/Physiology Relationship
Foldings (structure) = increased SA
Increased SA = Increased Absorption (Function)
Increased SA = Increased Absorption (Function)
56
New cards
Chemical Level of Organization
A molecule in the membrane that encloses a cell is an example of…
57
New cards
Cellular Level of Organization
A cell in the stomach lining is an example of…
58
New cards
Tissue Level of Organization
Layers of tissue in the stomach wall is an example of…
59
New cards
Organ Level of Organization
The stomach is an example of…
60
New cards
Body System Level of Organization
The digestive system is an example of…
61
New cards
Organism Level of Organization
The whole body is an example of…
62
New cards
Molecules > Cells > Tissues > Organs > Systems > Organism
Levels of organization in the body
63
New cards
Equilibrium
Interstitial Fluid and Plasma are…
64
New cards
Interstitial Fluid
Homeostasis regulates plasma which then regulates…
65
New cards
Homeostasis
Essential for survival of each cell
66
New cards
Deviation in controlled variable > detected by the sensor > Informs the integrator > sends instructions to the effector(s) > Brings about compensatory response > results in controlled variable being restored to normal
What are the components of a negative feedback control system
67
New cards
Fall in Room Temp > Thermometer senses and informs > Thermostat receives information and sends instructions > Furnace brings about what the thermostat informed > resulting in increase heat output
Describe how a thermostat is like a negative feedback example
68
New cards
Negative Feedback
The most common form of homeostatic regulator
69
New cards
Positive Feedback
Gets things done quickly and increases change
70
New cards
Uterus (smooth muscle has oxytocin receptors)
Increase in estrogen
Increase # of oxytocin receptors
Increase uterus sensitivity
Increase contractions
Increase cervix pressure
Increase serotonin oxytocin
Increase contraction
Increase Oxytocin
Leading to BIRTH (Climatic Event)
Increase in estrogen
Increase # of oxytocin receptors
Increase uterus sensitivity
Increase contractions
Increase cervix pressure
Increase serotonin oxytocin
Increase contraction
Increase Oxytocin
Leading to BIRTH (Climatic Event)
How is pregnancy similar to a positive feedback example
71
New cards
The 5 general functions of biological membrane
1. Physical Isolation (separation/creates compartments)
2. Regulation of exchange with the environment
3. Resting membrane potential - electrochemical gradient (voltage; block of material)
4. Communication between cell and environment (signaling)
5. Structural Support (connected to cytoskeleton)
72
New cards
Proteins and Lipids and a small amount of Carbs
Biological membranes are predominantly…
73
New cards
30-50%
Typical amount of protein in a biological membrane
74
New cards
40-60%
Typical amount of lipids in a biological membrane
75
New cards
10%
Typical amount of Carbohydrates in a biological membrane
76
New cards
Protein molecules
Embedded in the lipid bilayer and mediate most other functions of membrane
77
New cards
ECF side
Carbs are attached to which side? aka being attached to lipids and proteins (glycolipids)
78
New cards
Trilaminar Structure
The lipid bilayer is a _____________ structure due to the arrangement of membrane lipids
79
New cards
Membrane lipids
1. Amphipathic Lipids (2 domains; head and tail)
2. Phospholipids predominate
3. Glycerol Backbone
4. Polar head - glycerol phosphate head group
5. Non-polar tails - Hydrocarbon chains
80
New cards
Lipid Heads
Negatively charged
Polar
Hydrophilic
Lipophobic
Polar
Hydrophilic
Lipophobic
81
New cards
Lipid Tails
Positively Charged
Non-Polar
Hydrophobic
Lipophilic
Non-Polar
Hydrophobic
Lipophilic
82
New cards
VaryP
Phospholipids _____ in composition
Phosphate head group
Fatty acid makeup
Phosphate head group
Fatty acid makeup
83
New cards
Phospholipid Bilayer
\
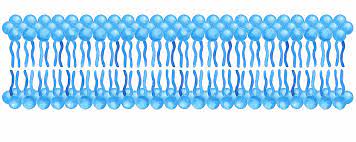
84
New cards
Micelle
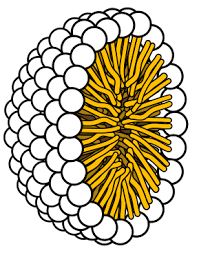
85
New cards
Liposome
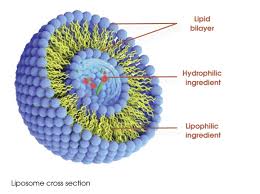
86
New cards
1. Bilayer
2. Micelle
3. Liposome
Phospholipids spontaneously assemble into what three different possibilities when in contact with water
87
New cards
Factors that influence bilayer structure
1. bilayer is very dynamic
2. fluidity depends on temperature
3. fluidity depends on composition (hydrocarbon chain size/cis double bonds; cholesterol)
88
New cards
Dynamic Two Dimensional Fluid
A lipid bilayer is a….
* Lateral diffusion is very rapid (average lipid molecule diffuses length of an average bacterial cell in about one second)
* Flip-Flop rarely occurs and only does if flippase enzyme catalyzes (once a month for individual molecule)
* Lateral diffusion is very rapid (average lipid molecule diffuses length of an average bacterial cell in about one second)
* Flip-Flop rarely occurs and only does if flippase enzyme catalyzes (once a month for individual molecule)
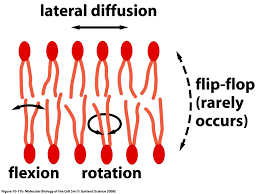
89
New cards
Bad rep for cholesterol?
This gets a bad rep because the body struggles to dispose of it because its only way to do so is for liver to turn it into bile and put it into the digestive tract
90
New cards
1. polar domain - OH group
2. Planar steroid rings - rigid
3. Nonpolar tail
What 3 main things does cholesterol have?
91
New cards
Cholesterol in Membranes
1. Inserts into bilayer between phospholipid molecules
2. Orients in bilayer with -OH groups close to polar heads. of phospholipids
3. Plate-like steroid rings interact with and immobilize first - CH2 groups of phospholipid hydrocarbons (decreases fluidity of bilayer)
4. Decreases bilayer permeability to water and small water soluble molecules (Blocks openings between phospholipid tails)
92
New cards
Reduces Molecular Movement -- RIGID
Inserting itself into bilayer between phospholipid molecules
93
New cards
Decreases fluidity of bilayer
Plate-like steroid rings interact with and immobilize first -CH2 groups of phospholipid hydrocarbons
94
New cards
Blocks openings between phospholipid tails
Decreases bilayer permeability to water and small water soluble molecules
95
New cards
1. Vary Composition of Phospholipid
2. Vary Cholesterol
How can you change bilayer
96
New cards
Diverse and Asymmetrical
Lipid Bilayer composition is…
97
New cards
Membrane function
Why is there a different # of lipids in membranes
98
New cards
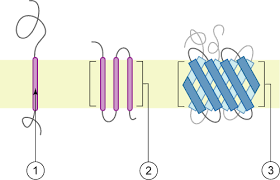
1. Amphipathic
2. Single Pass
3. Multipass
What are the three transmembrane protein spanning domains?
99
New cards
Cytoplasmic and Extracellular Domains
What 2 domains are polar in transmembrane proteins
100
New cards
Alpha-helix
Membrane spanning domain forms….
(peptide bonds form H-bonds with one another, at least 20 a.a for 1 pass)
* Single pass and multipass membrane proteins
(peptide bonds form H-bonds with one another, at least 20 a.a for 1 pass)
* Single pass and multipass membrane proteins