BSCI 170 - Molecular Inheritance
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Start of Unit 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
When was the structure of DNA discovered? By who?
1953
Watson, Crick, Franklin
What is genetic material?
material used to store information necessary for a cell, an organelle, or a virus to carry out all physiological activities and to replicate itself
When cells maintain a genetic program directing faithful reproduction, what does one cell become?
two
What are three things that must happen to genetic information during faithful reproduction?
stored and protected
read out in a way that cells can understand
transferred unchanged to the next generation
What does it mean that the transfer of proteins is irreversible?
DNA becomes RNA and vice versa. However, RNA is only used to create a protein which is not reversible
Was the identification of DNA as the genetic material a single or multistep process?
multistep
Who identified the genetic material?
What did they work with?
What did they discover about inheritance?
How do traits behave?
Traits can be either…
Gregor Mendel
Garden peas
Traits can be inherited independently
Traits behave as discrete units
Dominant or recessive
By the early 1900s, a few things were known.
When do chromosomes segregate?
When is the number of chromosomes halved?
Where are genes located?
during cell division
germ cell formation
on chromosomes
Who developed drosophila as a model organism for genetics?
What did they prove?
T.H. Morgan
Proved that genes are located on chromosomes and mapped them
What do we know by about 1940?
What do genes code for?
Where are genes located?
What are chromosomes composed of?
recognizable traits
on chromosomes
protein and DNA and RNA
Protein, DNA, and RNA: Which of these is the gene?
Most scientists focused on proteins
What are some key characteristics of proteins?
What was DNA believed to be?
What was RNA believed to be?
What was more known about?
structurally and functionally diverse and complex
too simple and too small
too unstable
proteins
Who is Frederic Griffith?
What did he discover?
How many strains are there?
a Britsh edical microbiologist
Streptococcus pneumoniae
two
What are the two strains (varieties) of streptococcus pneumoniae?
R strain (benign) which lacks a protective coat, so it is recognized by host’s immune system
S strain (virulent) which has a polysaccharide coat that prevents detection by host’s immune system
Transformation
What is this in terms of R and S cells?
What occurs during transformation?
What did this initiate?
R cells were converted into S cells
something “passed” from nonliving cells to living cells
changed nonpathogenic cells into being pathogenic
Heritable and permanent
Changed the genetic material
This initiated a 14-year search for the transforming principle
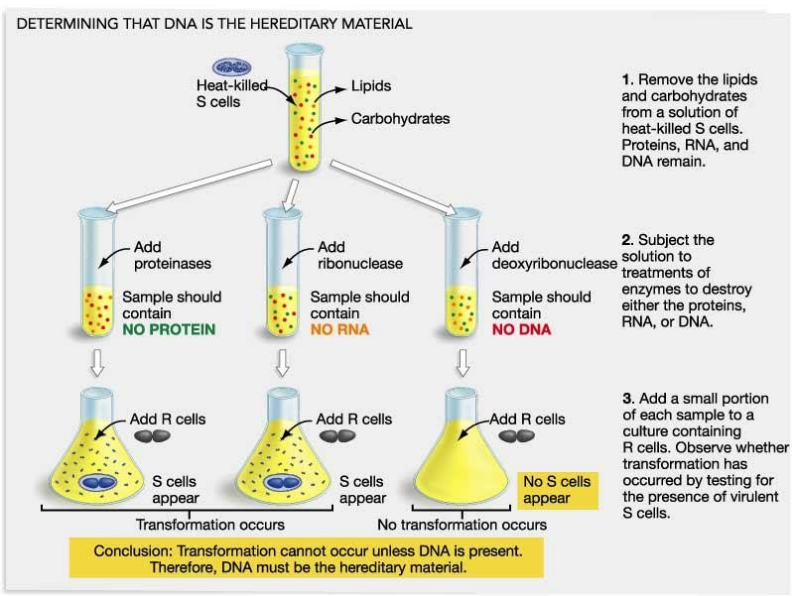
for your reference
N/A
What are bacteriophages?
bacteria eaters
viruses that infect bacteria
take over cell metabolism to make more phage particles
composed of DNA and protein only
T/F: Nucleic acids contain phosphorus but not sulfur
true
T/F: Protein contains both sulfur and phosphorus
false; only contains sulfur
Which two amino acids have sulfur in the side chain?
cysteine and methionine
What are isotopes?
element with same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons
What are the most common isotopes that are stable?
Sulfur-32: 16 protons/16 neutrons
Phosphorus-31: 15 protons/16 neutrons
Some isotopes are unstable and lose energy to regain stability, how is this energy loss detected?
as radioactivity
What are some useful radioactive isotopes? What do they do?
Sulfur-35: 16 protons/19 neutrons
labels proteins; not nucleic acids
Phosphorus-32: 15 protons/17 neutrons
labels nucleic acids; not proteins
What were some conclusions of the experiment with the bacteriophages?
genes are transferred during phage infection
DNA, not protein, is transferred during infection
genes are composed of DNA
conclusions accepted with little controversy
Before the bacteriophage experiment, what was thought of DNA?
DNA was believed to be too simple to store information
What are Chargaff’s Rules?
In any given organism:
[A] = [T] and [G] = [C]
Ratio of A:T = 1 and Ratio of G:C = 1
The concentrations of the nucleotides are different in different organisms
The concentrations of the nucleotides are the same in different tissues in the same organism
What are the different forms of DNA? What do these result in?
A form of DNA (reduced hydration), B form of DNA (highly hydrated)
these result in very different x-ray diffraction patterns
Which form of DNA makes better crystals than the other?
A form makes better crystals than the B form
Rosalind Franklin was able to capture of the B form of DNA, what was determined from this?
DNA is a helix
width and density of diffraction lines in the crystal suggested two strands not three
How are bases in DNA arranged? What principle was used to determine this?
Since two purines together would be too wide and two pyrimidines together would be too narrow, a purine and pyrimidine together would be consistent with x-ray data
This is the Goldilocks Principle
Watson-Crick Base Pairing
When polymer strands are antiparallel, how do stabilitizing hydrogren bonds form?
when purines pair with pyrimidines