Inflation and deflation
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Inflation - definitiion
The rate of change in the average price level over time.
OR.. The sustained increase in the cost of living/ fall in purchasing power of money.
Why does inflation matter?
If wages and earnings remain constant, then as prices rise consumers are worse off in real terms, as their disposable income will buy less goods and services than before.
It erodes the value of money.
What is the BofE’s inflation target?
A main focus of macroeconomic policy, with target of 2% ± 1%.
Two measures of inflation
Consumer price index (CPI) - preferred by Bank of England, excludes house prices and other fluctuating markets
Retail Price Index (RPI) - includes these markets
How does CPI work?
Its based upon a basket of 700 goods and services representing typical purchases of consumers
These are weighted based upon their relative importance, i.e. petrol has a high weighting
Its updated every year to reflect changes in spending patterns.
2 causes/ types of inflation
Demand-pull
Cost-push
Demand pull inflation - what is it?
Caused by excessive demand in the economy - too much money for too few goods and services
Consumption is the largest component of AD, although any stimulant to AD will create demand-push inflation pressure if supply remains unchanged.
Causes of demand-pull inflation (6)
Reduced taxation → increases disposable income
Lower interest rates → makes borrowing more attractive than saving.
General rise in consumer spending → perhaps from higher incomes or increased confidence
Improved availability of credit
Weak exchange rate and high growth in other countries → boost export growth
Rise in consumer confidence/ growth expectations.
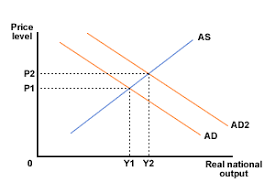
Demand pull inflation - diagram
- Any component of AD rising causes a shift right.
- In short run, factor resources remain unchanged, therefore cannot create enough additional supply, so prices pulled upwards.
Cost push inflation - what is it?
Firms respond to rising costs of production by increasing prices in order to protect profit margins.
However, firms may be able to absorb some extent in rise in costs, but can’t do this indefinitely.
Causes of cost push inflation (5)
- Wage increases - Workers will demand higher pay if prices are rising, but this causes firms to increase prices more (wage-price spiral)
- Higher raw material costs - when they become scarcer
- Higher taxes - gov may impose corporation taxes
- Higher import prices - may be due to a weaker currency
- Natural disasters - disrupt supply chains, causing rising costs
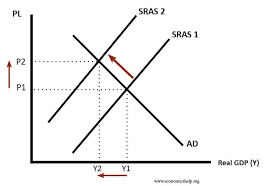
Cost push inflation diagram
- Increase in costs of production will reduce SRAS, shift leftward.
- Firms will reduce supply or exit the industry
- Prices pushed to P2
Deflation - definition
Decrease in the general price level, negative inflation
Disinflation - definition
Inflation falling, still positive - prices are still rising but at a slower rate, e.g. a fall in inflation from 2.7% to 2.3%
Causes of deflation
Occurs during periods of very low or stagnant growth
Despite the value of money rising, deflation indicates that demand is very low or suppressed.
Problems with deflation
As prices are falling, consumers tend to delay pruchases, as they believe it will be cheaper in the future
Consumption slows and firms lose confidence to invest, further harming AD.
How do world commodity prices affect domestic inflation?
Oil and food make up a large proportion of UK imports
This has a significant impact on price level, as these products are necessities so generally price inelastic - prices feed through to UK inflation.
How do changes in other economies potentially decrease inflation in UK?
Development worlwide increases their productive capacity, leading to lower cost products on UK markets.
How do changes in other economies potentially increase inflation in UK?
Demand pull: emerging markets create a growing demand for goods and services, increasing AD.
Economic performance of major trading partners like EU and USA will impact on demand.
What is the old quantity theory of prices?
Assumes that inflation is caused by a prior increase in the money supply. This is a special case of demand-pull inflation.
The source is monetary rather than real forces, where too much money is chasing too few goods.
Fisher equation of Exchange
MV = PQ
Money supply x the velocity of circulation of money = price level x quantity of output
or MV = PT
“ “= average price of transactions x total no. of transactions
or MV = PY, Y = national output
What are assumptions of fishers theory of money/exchange?
That velocity is constant and Q is independent of money supply as only affected by supply-side factors. Therefore a change in M is responsible for inflation.
Keynesian demand-pull theory of inflation - how similar to theory of money?
Also a demand based theory
Demand-pull theory - how different?
Source is from the planned expenditure of individuals, firms and households exceeding the quantity of output the economy is capable of producing.
Inflation is explained by behaviour, not money
How do keynesians vs monetarists believe a budget deficit causes inflation?
Monetarists: budget deficit → monetary expansion → demand-pull inflation
Keynesians: budget deficit → injection into circular flow of income → excess AD if near full capacity → demand pull inflation
Keynesian cost-push theory of inflation: definition
A rising price level caused by an increase in the costs of production, shown by an SRAS shift leftward
Wage-push theory of inflation
Trade unions could bargain for money wage increases in excess of any rise in labour productivity. This is due to the govt’s push for full employment + firms’ monopoly power who can pass price onto consumers.
Why are inflationary expectations important?
If inflation had been stable at 2%, agents will factor this into their future plans.
But, if inflation is volatile, then it is unanticipated, disrupting decisions and increasing volatility
Important so all agents can accurately plan their future choices.
7 consequences of inflation
Wage-price spirals
Shoe leather costs
Menu costs
International competitiveness
Investment
Savings
Income redistribution
Wage price spirals - definitom
Higher inflation will increase wage demands from workers to maintain real incomes which may cause further inflationary pressure and strain industrial relations
Shoe leather costs - definition
A lack of certainty over price levels increases the search costs, predominantly time, of making price comparisons in finding the best deal
Menu costs - definition
The costs to a firm of changing price information
International competitiveness - definition
If inflation is higher than our main international competitiors, demages export ability
Investment - definition
Inflation erodes the value of money over time, so will erode value of investments in the future. If firms are uncertain about future inflation it may disrupt long term business planning.
Savings - definition
If interest rates on savings are lower than inflation rate, this will erode its real value so will reduce incentive to save. Conversely, real value of debt will fall.
Income redistribution - definition
High inflation has a regressive effect on low and or fixed income families who suffer disproportionately the higher burden of rising energy or food prices.
Consequences of deflation
Delayed purchases and spending
Wages and unemployment
Debts
Confidence
International competitiveness
Delayed purchases and consumer spending - definition
Consumers may rationally delay their purchases of certain items in the knowledge that they will be cheaper in the future. this affects luxury purchases especially.
As consumption is a large component of AD, deflation leads to lower growth and more deflationary pressure.
Wages and unemployment - definition
Makes it difficult for workers to bargain for higher wages, and with lower prices leading to lower revenues and profits for firms, businesses may lay off workers to reduce costs and restores profit margins
Wages tend to be sticky thus workers will resists wage cuts which may lead to a rise in real wage unemployment
Debts - definition
If inflation can reduce the real value of debt then by definition deflation will increase it
Confidence - definition
Its also likely that asset prices will decline during periods of deflation which is likely to impact consumer confidence and feed through to lower consumption, AD and growth
International competitiveness - definition
It improves competitiveness if other countries experience inflation, increasing exports