Child Development Exam 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
Development
continuity and change that happens over time (in people, children)
5 age periods
Prenatal, infancy & toddlerhood(0-3), early childhood(3-6), middle childhood(6-11), adolescence(11-20)
3 aspects of development for each age group
physical, cognitive, psychosocial
Heredity
nature; in born traits we inherit from our parents, genetics
Environment
nurture; persons situational experiences
Maturation
unfolding of a natural sequence of physical and behavioral changes, natural order children follow aka biological sequence
Nuclear family
two generational kinship, parents and children
extended family
multigenerational network
culture
customs, traditions, values of a society
ethnic group
(race and ethnic gloss) people who are tied by a culture in ancestry or religion
NOT race- race is complicated and hard to define
ethnic gloss
assume everyone in ethnic group is the same
socioeconomic status (SES)
strongly related to income but tied into education and occupation
Normative events
experienced the same by most people in the group
Normative age-graded influences
tied to age(kids of the same age group) ex. puberty, baby teeth falling out
normative history-graded influences
tied to specific historical point ex. people who all experienced the great depression and are older
nonnormative events
unusual experience that has a major impact on a childs development
Critical period vs. sensitive period
critical- specific time when a certain event has its greates impact; physiological aka it needs to happen or it will never happen
sensitive- ideal time for things to happen but can still happen if it does not; not physiological
ex. Genie
Nature vs. Nutrue
influence of heredity vs environement, scientists agree both play a role
active vs. passive
both are at play in development. childrens influence on their own development vs the influence of their environment (like a sponge)
continuity vs. discontinuity
both are at play,
continutiy emphasizes development as a gradual contiunual process (quantitative)
discontinuity is dramatic radical changes(qualitative)
all domains are interrelated
consensus by scientists; physical, cognitive, psychosocial
wide range of developmental differences
motor physical milestones there is a lot of variability
children shape…
their own development
ex. difficult temporment babies vs easy temporment babies
Historical and cultural contexts
where/how a baby is raised varies
early experience is important
early experiences (age 0-3) are critical but kids are resilient and have more flexible brains
Psychosexual theory (Freud)
Id (devil basic insticts; sex and aggression)
Ego (decision maker focuses on reality but not necessarily moral)
Superego (moral conscience, be a good person)
Oral Stage
First of Freuds psychosexual stages; birth to 12 mo, all pleasure comes from the mouth and fixation would be smoking, being sassy
Psychosexual stages
libido (free floating sexual energy) and fixation (the libido moves around during development) different stages; oral anal phallic latency genital
anal stage
Freuds psychosexual stages 12-18 mo; toilet training and gratification from bowel or bladder training; fixation really messy or really neat
phallic stage
Freud psychosexual stages 3-6 years; symbolism of genitals, boys wanna have sex w mom but realizes he cant and is besties w dad, girls jealous theyre not dudes and wanna w dad and cant so become like mom
latency stage
Freud psychosexual stages 6-12 years
genital stage
Freuds psychosexual stages adolesence; mature sexual expression
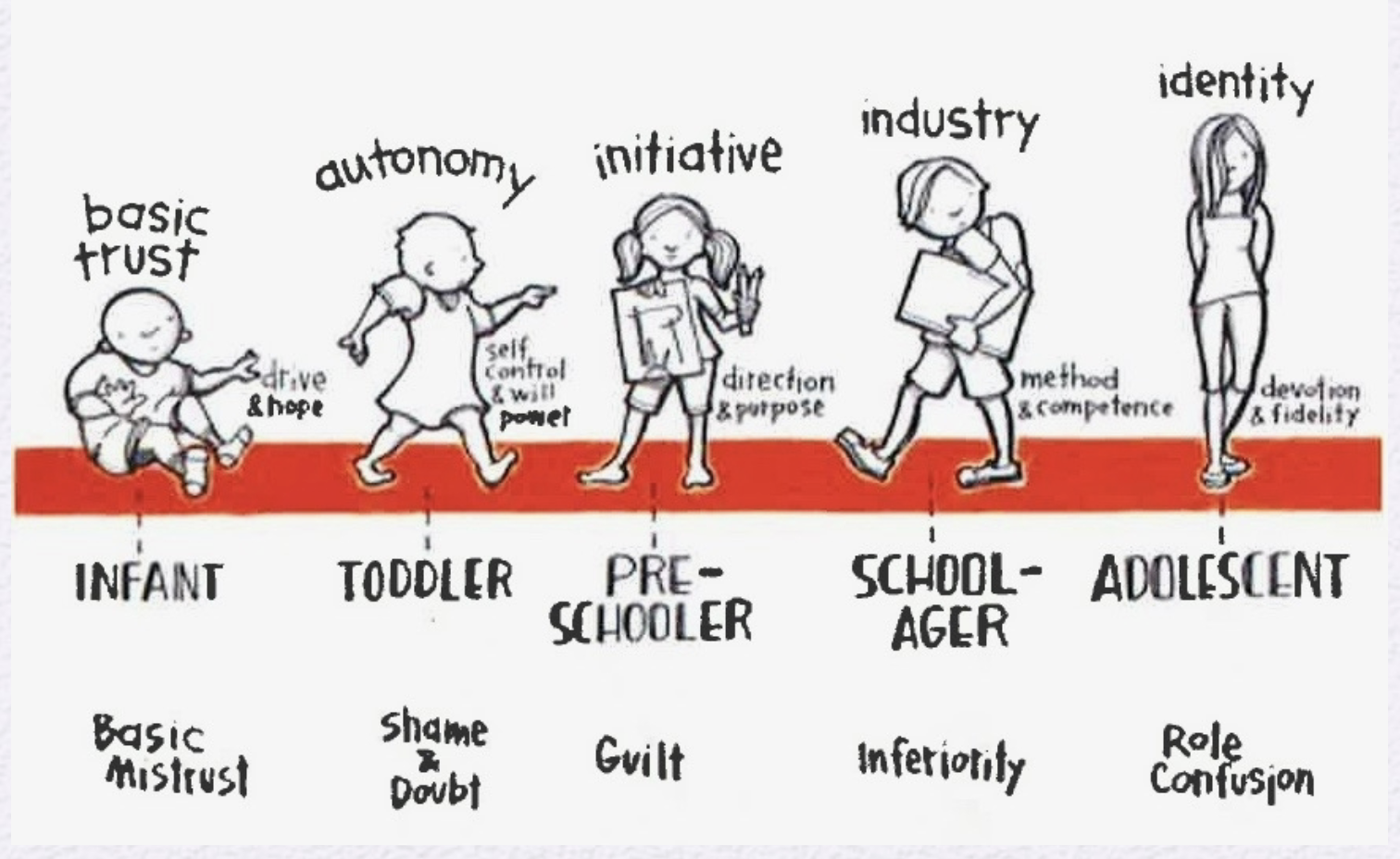
psychosocial theory
Erikson; critical stages for social relationships (but you can learn it later too)
behaviorism
study specific associations regarding learning
Classical conditioning
type of behaviorism; pavlov how we learn to make connections between things in environment (associate two events in environment) child as passive learner
operant conditioning
child as passive learner, respondign to environment ex. jason smiles on accident, gets picked up, smiles on purpose to get picked up
social learning theory
kid as active learner; reciprocal determinism and observational learning
reciprocal determinism
social learning theory; cause of learning is bidirectional, environment and child both impact each other
observational learning
social learning theory; learning by observing and imitating in a social context
cognitive stage theory
Piaget; kids as active learners: schemes (concept, form these) and adaptations (how we handle information and fit it into schemes)
assimilation
cog stage theory; interpret info and fit it into what you already know
accomodation
cog stage theory; change cognitive structure to include new info
equilibration
balance between accomodation and assimilation
information processing approach
break down mind into component parts, research style
contexual perspective
impact of social context on kids development
bioecological theory
all environments affect child
microsystem
bioecological theory; day to day environment aka home and school for kid
mesosystem
bioecological theory; link between microsystems
exosystem
bioecological theory; linking of 2 or more systems at least 1 of which does not directly impact child (ex. parent having bad day at work and in bad mood at home)
macrosystem
bioecological theory; big overarching influences (culture, education, famine)
Sociocultural theory
how children interact w environment to shape cognitive development (zone of proximal development and scaffolding)
zone of proximal development
Sociocultural theory; level at which child can almost master a task on their own (need new learning to occur)
scaffolding
Sociocultural theory; temporary support given by teachers and parents while child is mastering a task
evolutionary/sociobiological perspective
evolutionary basis of behaviors, humans born with innate behaviors, eating (sucking, swallowing), hearing a baby cry and thinking its a terrible noise so picking up baby
fertilization
conception, ovum and sperm form single cell
zygote
the one cell created by fertilization
dizygotic twins
two zygotes, fraternal
monozygotic twins
one zygote, identical
ART
Assisted Reproductive Technology
Infertility
Inability to concieve for 12 months, affects 15% of couples worldwide
Causes of infertility
age(fertility declines in late 20s for women and later for men (only 1/3 of issues are men))
increasing rates of STIs like gonorrhea
ART Techniques are…
expensive, not usually covered by insurance and only work 24% of the time
artificial insemination
injection of sperm (husbands or donors) into cervix
In Vitro Fertilization
fertilization outside the womens body, adverage cost $72000, top method used
Ovum transfer
eggs donated by another woman and fertilized through IVF, donors paid more
Surrogate motherhood
woman gets pregnant through IVF or artif. insemination, usually for women struggling w miscarraiges
adoption
usually done thorugh attorney hard to do domestically
chromosomes
coils of DNA that carry different genes each cell has 23 pairs
gametes
sperm and egg, each has 23 individual chromosomes
genes
Specific codes for traits on specific chromosomes
DNA
enable formation and function of cells
sex chromosomes are not ______
binary, there are weird variations that can happen
sex hormones
SRY genes cause release of testosterone at 6-8 weeks for males, Wnt-4 for female characteristics
Alleles
pair of genes that determine a trait
homozygous
both alleles the same
heterozygous
get both but dominant shows
genotype
the genes and their form (pattern of alleles)
phenotype
trait and how it shows
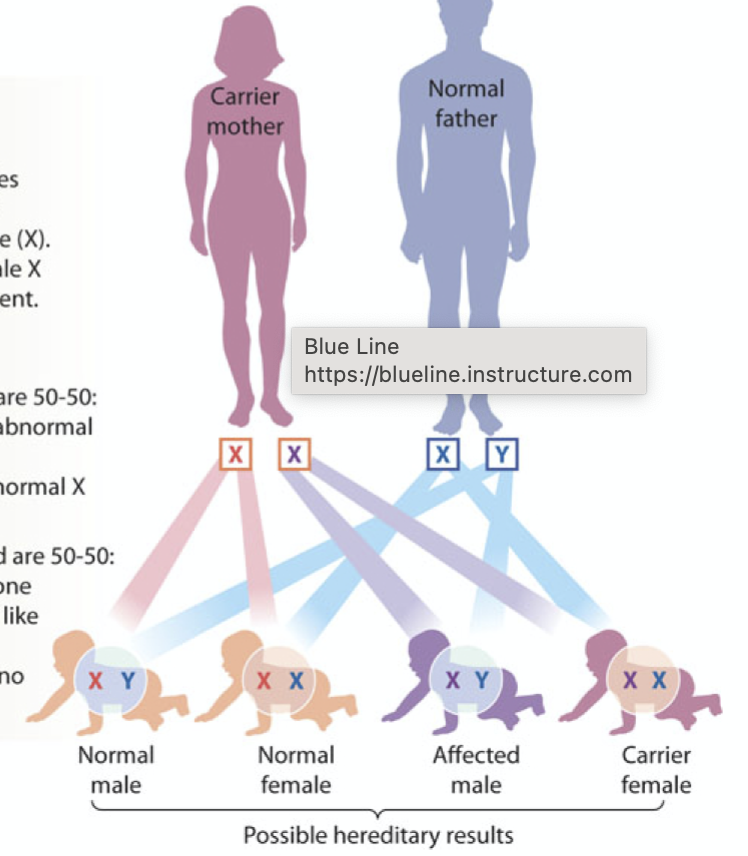
sex-linked inheritance
inherited differently between men and women
incomplete dominance
blood type
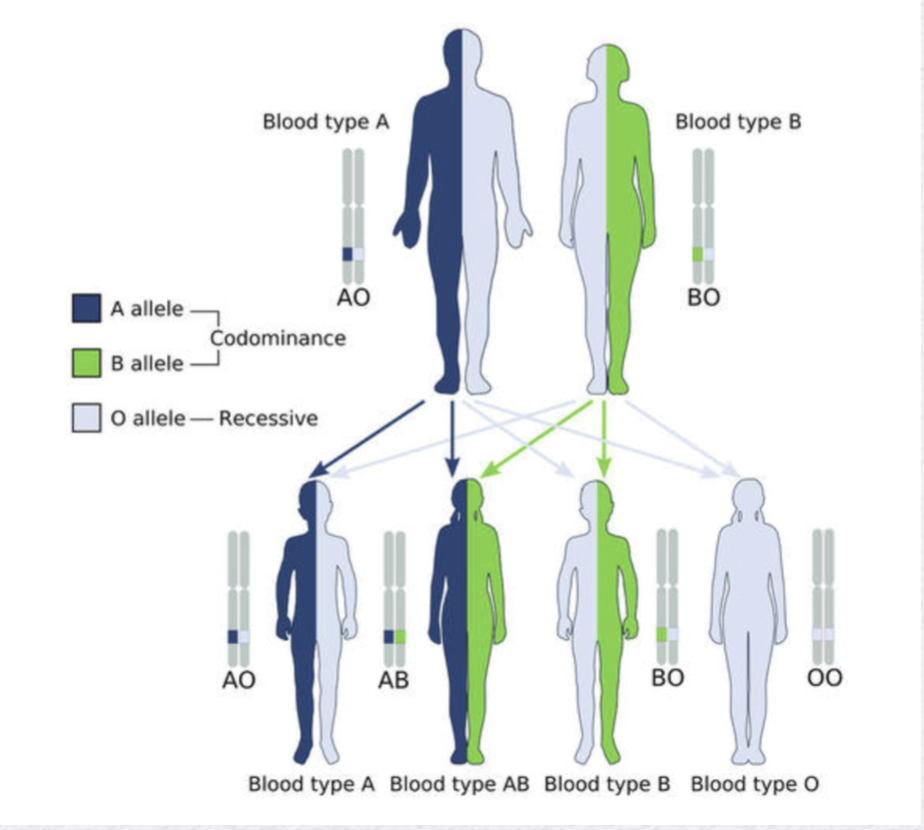
polygenic inheritance
interaction of a number of genes to produce a complex trait ex. skin color
multifactorial transmission
interaction between genes and environment to produce a factor (nature/nuture)
epigenesis
mechanism that controls functioning of the genes by turning them on and off without affecting their DNA structure; explains why identical twins are different
genetic and chromosomal abnormalities usually happen
during formation of egg and sperm
down syndrome
trisomy 21; 3 chromosomes on 21 pair
genetic counseling
help parents figure out chances of having a kid with particular disorders
heritability
statistical estimate of the contribution of heredity to individual differences on a specific trait within a given population, not between population
reaction range
potential variability of a trait genetics/heredity limit range of a trait but where a person develops in that range depends on environment
canalization
describe a trait that has very strong genetic component to the point where environment doesnt matter very much
siblings
share 50% of genetic material; theres enough differences that kids grow up in different environments
family studies
look at a trait across family relationship and resemblances to see if theres a pattern
adoption studies
child whos adopted (genetically unrelated) and relation to adoptive parents vs. biological
twin studies
show nature vs. nuture
cephalocaudal principle
development of embryo from head to tail
proximodistal principle
development starts at center and works its way outward
germinal stage
prenatal stages; conception until 2 weeks, by 2 weeks it will have formed
embryonic stage
prenatal stages; 2-8 weeks all major organs, body system will develop- embryo is very vulnerable to environment most birth defects here
fetal stage
8-40 weeks; finishing touches, growth, fetus is very active, hearing develops
fetal hearing
respond to sound and vibration, prefer what they are familiar with, cna distinguish between mothers voice, fathers voice and find them soothing
fetal “learning”
can recognize rhythm and sounds of certain books, songs and the rhythm of languages