Common Bacterial Infections
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MRSA, STDs, Rheumatic Fever, Cat Scratch Fever, Chancroid
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
MRSA (Methicllin-Resistant Staph Aureus)
A gram positive cocci that is resistant to beta-lactams coming both outpatient and inpatient settings
healthy people in close contact (sports teams, military, prisons)
Community Acquired MRSA is common in
long-term care, recent hospitalization, surgery (5% of hospitalized patients are colonized)
Hospital Acquired MRSA is common in
prior antibiotics, indwelling devices (CAUTI), immunosuppression
Risk factors for MRSA
SSTIs that fail to respond to beta-lactams (often has a spider bite appearance), can cause systemic infections such as pneumonia (usually post-flu), bacteremia, osteomyelitis, endocarditis
Presentation of MRSA
Severe or recurrent infections, failure of initial therapy, systemic symptoms, immunocompromised host
MRSA is a clinical diagnosis, when is a culture and sensitivity recommended?
Wound cultures, Blood cultures (sepsis signs), U/S (abscess vs cellulitis), Nasal screening (colonization in inpatient settings)
Other Diagnostics for MRSA
multiple lesions, systemic symptoms, comorbidities, lack of clinical response post I and D
Antibiotics are indicated for MRSA (textbook answer - tbh its all the time)
TMP-SMX, doxy, minocycline, clindamycin (check coverage), IV vanc, linezolid, daptomycine, nasal mupirocin or CHG washes (colonization)
Antibiotics for MRSA (I swear to GOD if you pick a beta-lactam)

local tissue destruction, delayed wound healing, septic joints, bacteremia, sepsis, endocarditis/osteomyelitis (IV drug users, prosthetic valves)
Complications of MRSA
Hand Hygiene, PPE, decolonization, education on wound care
Prevention Strategies for MRSA
Most reported bacterial STI (🥇), Highest in females 👩
Stats for Chlamydia
Multiple partners, inconsistent condom use, prior STI, under 25; MSM (Gonorrhea only)
Risk Factors for Chlamydia and Gonorrhea
Chlamydia trachomatis (intracellular) incubates in 7-21 days; vaginal, anal, oral sex and perinatal
Etiology and transmission of Chlamydia
Asymptomatic, rectal discomfort 🍑, Urethritis (clear/mucoid discharge, dysuria) 👨🦰, Cervicitis (discharge, friability (bleeds on contact)) 👩🦰
Presentation for Chlamydia
PID, infertility, ectopic pregnancy, neonatal conjunctivitis, neonatal pneumonia, increased HIV transmission rate
Complications of Chlamydia
2nd most reported bacterial STI 🥈, highest in males 👨🦰
Stats for Gonorrhea
Neisseria Gonorrhoeae (gram neg diplococcus - resistance increasing) incubates in 2-7 days, vaginal, anal, oral sex and perinatal
Etiology and transmission of Gonorrhea
Urethritis (dysuria, COPIOUS purulent discharge 💧), epididymitis 👨🦰; Cervicitis (thick, yellow/green discharge, bleeding 🩸), pelvic pain 👩🦰; Rectal pain, tenesmus 🍑; sore throat
Presentation for Gonorrhea
PID, infertility, ectopic pregnancy, Disseminated Gonococcal infection (DGI - rash, arthritis, tenosynovitis), neonatal conjunctivitis, Reactive Arthritis, ophthalmia neonatorum, increased HIV transmission rate
Complications of Gonorrhea
NAAT 🏆 (sample from urine, vaginal/cervical, urethral, rectal, pharyngeal), 1st void urine, Only culture if treatment fails
Diagnostics for Chlamydia and Gonorrhea - test for both they are buddies
Doxy 🥇, Azithromycin (or amoxicillin) 🤰
Treatment plan for Chlamydia - avoid sex for 7 days afterward
Ceftriaxone
Treatment plan for Gonorrhea - treat partners from the past 60 days, avoid sex for 7 days afterward
Annually screen sexually active females under 25, MSM, HIV +, pregnancy; Use EPT for chlamydia, Retest in 3 months (reinfection is common)
Prevention plan for Chlamydia and Gonorrhea
Unprotected sex, multiple partners, history of other STIs, Substance use, 20-34 y/o, high burden in the SOUTH
Risk factors for Syphilis
Treponema Pallidum (spirochetes); Requires direct contact with syphilitic lesion or vertical transmission
Etiology and transmission Syphilis

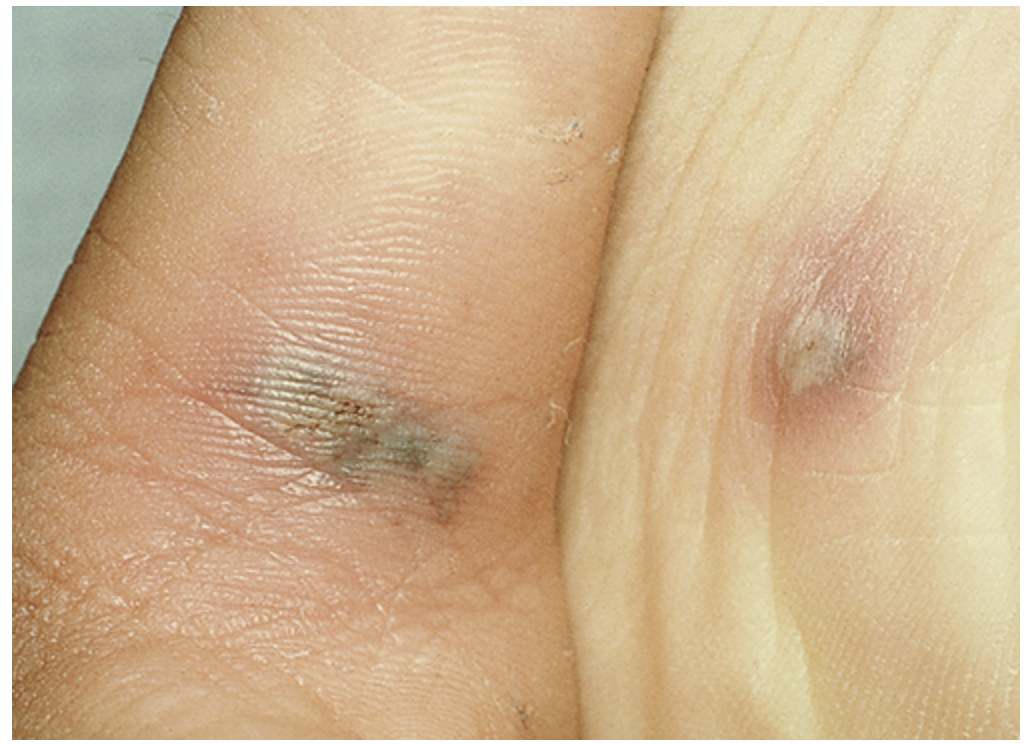
Painless chancre at site of inoculation (genital, anal, oral - resolves on its own)
Primary stage of Syphilis
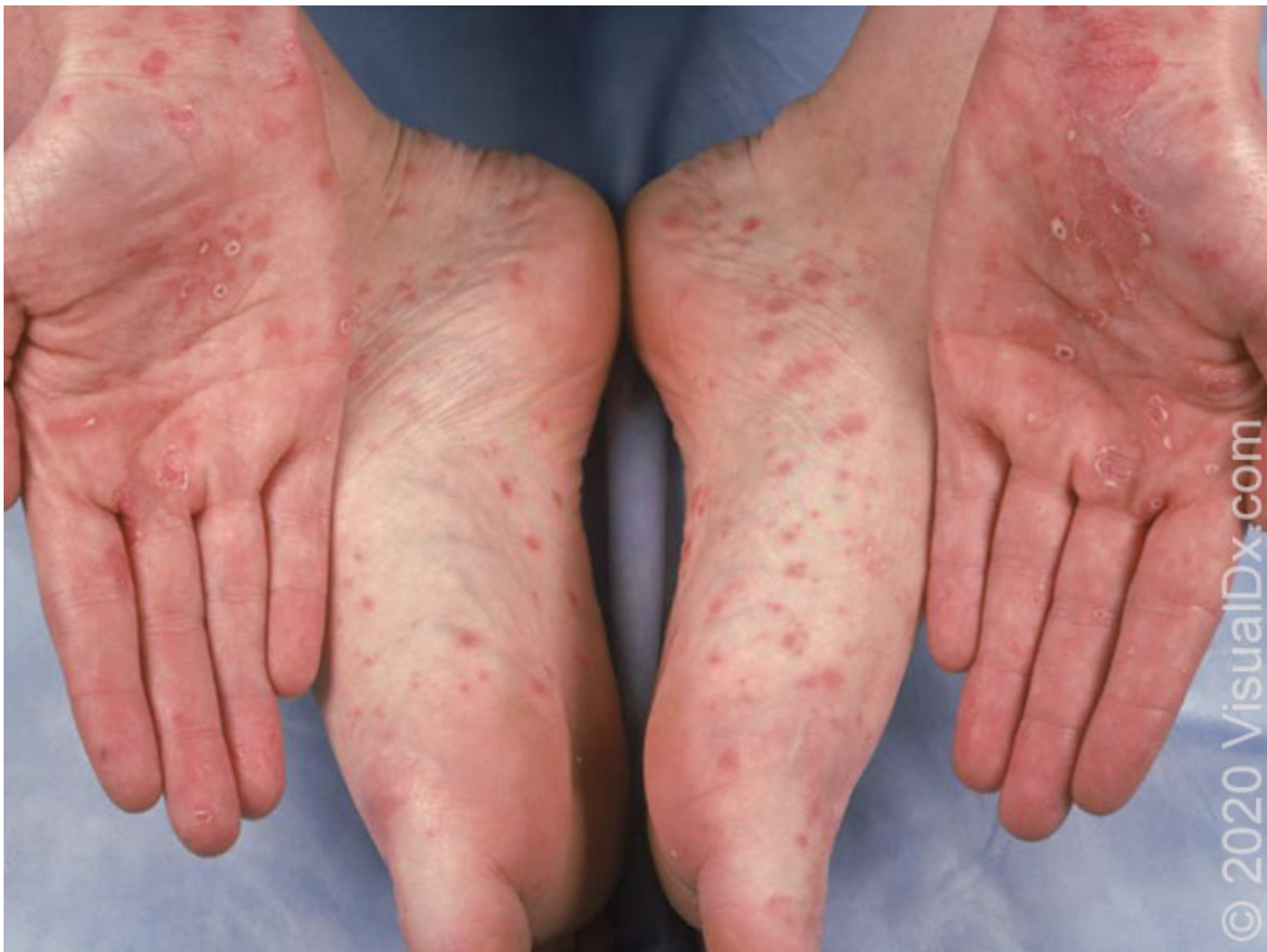
Diffuse rash (palms and soles), mucous patches, Lymphadenopathy
Secondary stage of Syphilis
Dormant (seropositive)
Latent stage of syphilis
Gummas, aortitis, neurosyphilis
Tertiary stage of Syphilis
Snuffles, rash, bone deformities, hepatosplenomegaly
Congenital Syphilis signs and symptoms
Nontreponemal (RPR) for screening → Treponemal (FTA-ABS, TP-PA) to confirm; CSF testing for neuro, ophthalmic or otic, test for HIV
Note: if you switch the order its reverse sequence screening
Work-up for Syphilis
Benzathine Penicillin G (primary, secondary, or early latent -1x; Latent or unknown - 3x); Aqueous Crystalline Penicillin (Neurosyphilis or ocular/otic syphilis); Penicillin ONLY 🤰 (desensitize if allergic); Test for HIV and Retest RPR at 6, 12, 24 months; treat partners from the last 90
Management for Syphilis
Screening if pregnant (1st trimester, repeat in 3rd if at risk), MSM, people with HIV, multiple partners
Prevention and Public Health for Syphilis
Group A strep infection, overcrowding, low-resource settings, lack of secondary prophylaxis
Risk factors for Rheumatic Fever - most common in children aged 5-15
Molecular mimicry leads to an autoimmune reaction 2-4 weeks after initial strep
Pathogenesis for Rheumatic fever
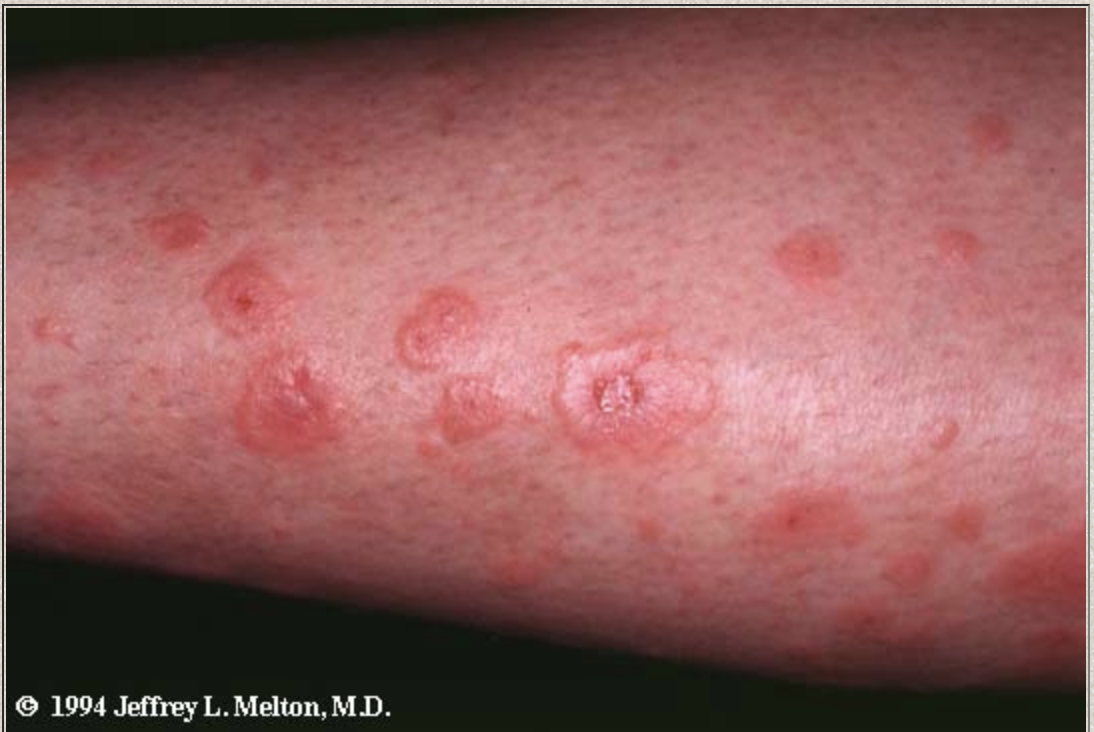
Migratory polyarthritis, Carditis, sydenham chorea, erythema marginatum, subcutaneous nodules
Major manifestations of the Jones Criteria (Rheumatic Fever)
Fever, arthralgia, elevated ESR/CRP, 1st degree AV Block (prolonged PR)
Minor Criteria (jones) for Rheumatic Fever
2 major OR 1 major + 2 minor; MUST SHOW EVIDENCE OF STREP INFECTION (rising ASO or anti-DNase B), echocardiogram (for subclinical carditis)
Diagnosis of rheumatic fever requires
Pen VK 🥇 (eradicate gas - azithromycin, cephalexin, benzathine G), ASA/NSAIDs (arthritis), Diuretics and ACE inhibitors (Heart Failure management), Monthly Pen G for secondary prophylaxis (5 yrs or until 21 for w/o carditis; 10 yrs or until 40 for w/)
Management plan for Rheumatic Fever
Carditis and valvular damage (mitral most common), Chronic rheumatic heart disease (RHD), Heart failure, Arrhythmias (A.fib), Recurrent rheumatic fever
Complications of Rheumatic Fever
Take your full antibiotic treatment for GAS
Prevention measures for Rheumatic Fever
Bartonella (cat scratch fever)
A common cause of lymphadenopathy in children that is spread via kitten scratches or bites that affects immunocompetent patients

Bartonella henselae (gram neg)
Etiology of cat scratch fever
Azithromycin shortens duration, Doxy for systemic diseases
7 y/o male presents to the ED for a painful, swollen lymph node in his armpit. On physical exam you note a scratch on his upper arm that his mother states is from their new kitten. Vitals are stable with an exception of a 99.9 temp. What is your management plan?
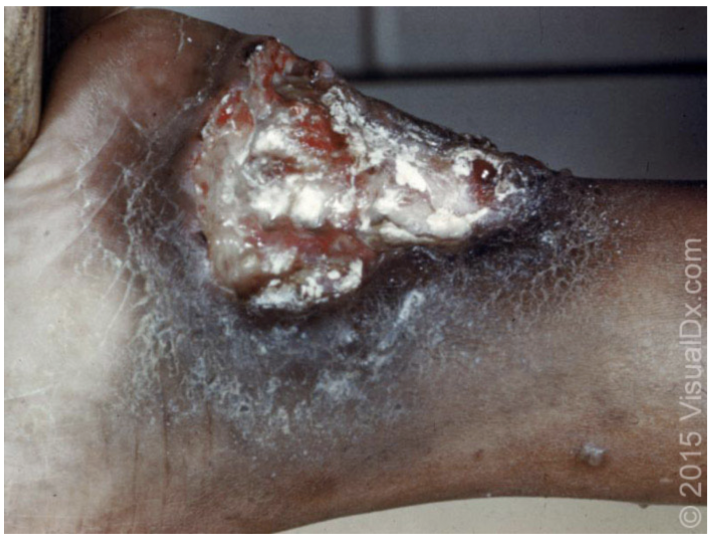
Chancroid
A painful genital ulcer that is endemic in some tropical regions and is sexually transmitted
Haemophilus ducreyi (gram neg rod)
Etiology of Chancroid
Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone
45 y/o male reports to the ED for a painful genital ulcer. Social hx is positive for a trip to the Bahamas. On physical exam your note tender unilateral inguinal lymph nodes that are draining. You’ve rule out syphilis and HSV, what is your management plan?