Normocytic Anemia II (IntraVascular Hemolysis)
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
G6PD Deficiency
Intravascular Hemolysis
X Linked Recessive
Defect in HMP shunt → which helps protect RBCs from oxidation
Found in 12% of male African Americans and in Mediterranean region
Symptoms of G6PD Deficiency Comes As A Result Of:
1. Infection
2. Ingestion of an oxidizing drug (antimalarial, sulfonamides)
3. Fava beans
Acute self-limited hemolytic anemia with hemoglobinemia and hemoglobinuria
Deficiency of G6PD Leads To
Reduced NADPH → Reduced Glutathione
→ RBC hemolysis
→ Hemoglobin denaturation
→ Heinz bodies (precipitates)
Recognize hematuria after starting drug - especially antimalarial (military)
What are the Variants of G6PD Deficiency
African variant: mild variant (mild reduction in half-life of G6PD) Mediterranean: severe variant (severe reduction in half-life)
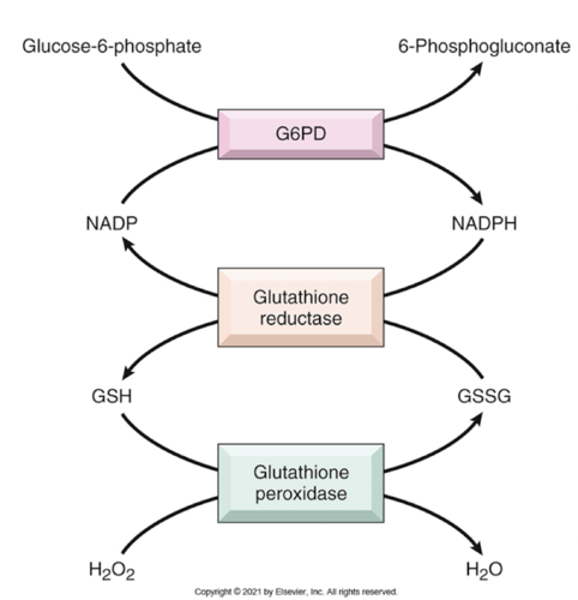
Role of G6PD In Defense Against Oxidant Injury
Reduced G6PD makes cells susceptible to oxidative stress
RBCs are normally protected from H2O2 by Glutathione (antioxidant, which becomes oxidized)
H2O2 is one of the major oxidative stressors → Becomes water with Glutathione
Deficiency of G6PD → Low NADPH → Low Glutathione → Increased Oxidative Stress → Hemolysis
Presents as → hemoglobinuria and back pain hours after exposure to oxidative stress
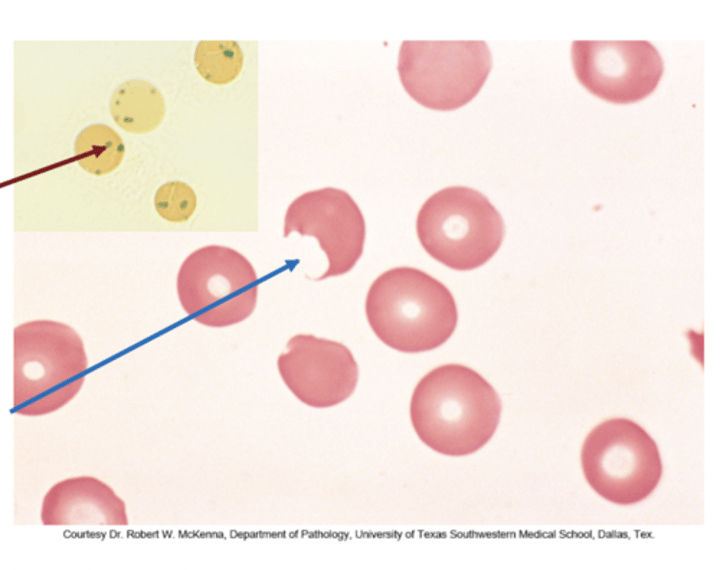
Describe Heinz Bodies from G6PD Deficiency
Oxidative stress precipitates Hgb as Heinz bodies
(inclusions within red blood cells composed of denatured hemoglobin)
Used for screening: using special Heinz stain
Heinz bodies are removed (cut) from RBCs by macrophages → resulting in bite cells
What studies confirm of G6PD?
Measurement of enzyme levels (Performed ONLY weeks after hemolytic episode resolves, as the defective RBCs are already hemolyzed and what is left during the episode are the non- defective ones)
Bite Cells (G6PD Deficiency)
Effects of oxidant drug exposure (peripheral blood smear)
"Bite cells" - splenic macrophages remove the Heinz body inclusions
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Acquired defect in RBCs, WBCs, and platelets
Absent defense mechanism on the surface of the cells → Makes cells susceptible to destruction by complement
Mutation of PIG-A gene that codes for (GPI) anchor
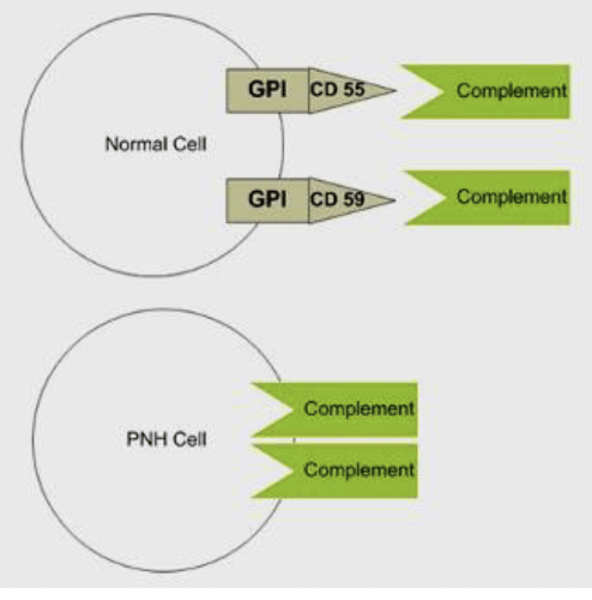
Describe the mechanism of the GPI anchor protecting RBCs
Normally, the cell is protected by a surface factor DAF (CD55, CD59 and C8 protein) which is anchoring on the surface membrane by GPI
Normally DAF (CD55/CD59) - GPI linked proteins help inactivate complement
Deficiency of (DAF) - GPI (CD55/CD59) → increased complement lysis
Features of PNH
1. Complement activation occurs episodically, often at night → shallow breathing, increased CO2, mild respiratory acidosis
2. Hemolysis at night (lysis of RBCs, WBCs, and platelets) → dark urine in the morning due to hemoglobinuria
3. Hemosiderinuria is seen days after hemolysis → can cause pancytopenia
Also increase venous thrombosis
Tests for PNH
Coombs negative hemolytic anemia Ham’s test: complement induced hemolysis in acidified serum (in vitro)
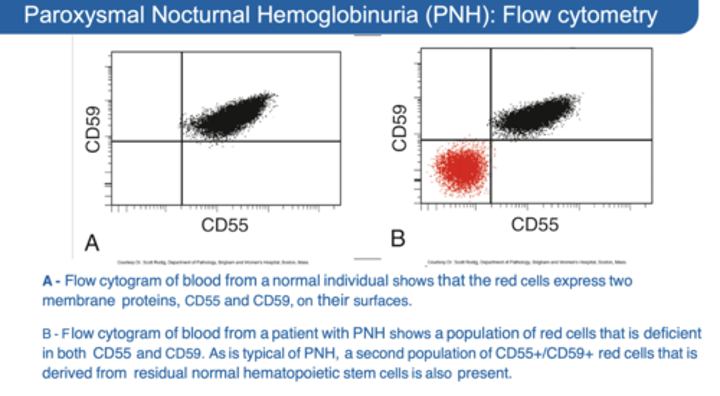
CD55/CD59 Found on the surface of RBCs prevent what?
CD55/CD59 on surface of RBCs, Platelets, and leukocytes prevent complement lysis
Screening and Dx of PNH
Sucrose test to screen (sucrose activates complement)
Hams test → Serum acidification for confirmation
Lack of CD55/CD59 (DAF) → detection by flow cytometry
Complications of PNH
1. Iron deficiency anemia
2. Aplastic Anemia
3. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) which develop in 10%
Main Cause of Death of PNH
Thrombosis of the hepatic, portal, or cerebral veins → due to release of products from the lysed platelets
Malaria
RBCs are part of the life cycle of Plasmodium and they rupture during the cycle causing intravascular hemolysis
(RBCs assume different morphologic changes during the cycle)
Spleen also destroys some infected RBCs causing mild extravascular hemolysis and splenomegaly
*KNOW WHAT IT LOOKS LIKE ON A BLOOD SMEAR*
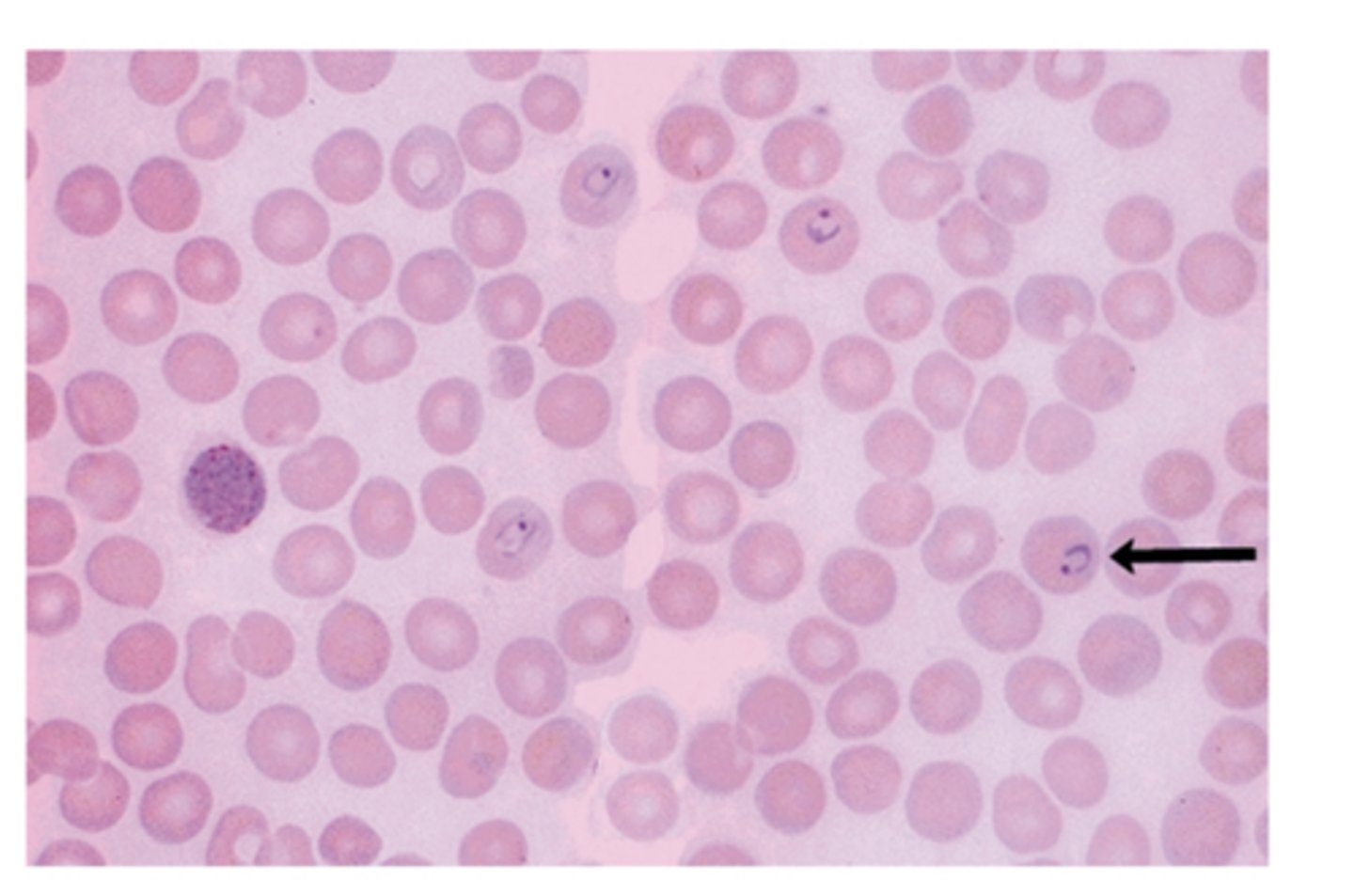
What is the name of the parasite that causes malaria? What transmits malaria?
Plasmodium is the parasite causing Malaria, transmitted by female Anopheles mosquito
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn - Erythroblastosis Fetalis
Maternal antibodies cross the placenta and react with fetal red cells
Need to have prior delivery with maternal exposure to fetal blood
→ Causes fetal hemolytic anemia
→ Causes maternal alloimmunization to fetal RBC antigens
Usually maternal antibodies to D antigen of Rh blood group
Mother usually type d and baby type D
How can ABO incompatibility cause Hemolytic Disease of Newborn
Mother group O → child A or B
Mother A → child B or AB
Mother B → child A or AB
Less severe than Rh cases (mild)
1. Fetal A and B antigens not well developed
2. Antigens are expressed on lots of other tissues to “absorb” antibodies
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn can cause
Kernicterus = staining of basal ganglia and other CNS system structures with unconjugated bilirubin
Neurologic damage
Stillbirths
Hydrops fetalis = fetal heart failure with massive edema
How can you treat Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
Give anti-D IgG antiserum (RhoGAM) to D negative mothers at 28 weeks and at delivery of D+ child
This removes fetal red blood cells from maternal circulation (through antibody removal) and prevents alloimmunization
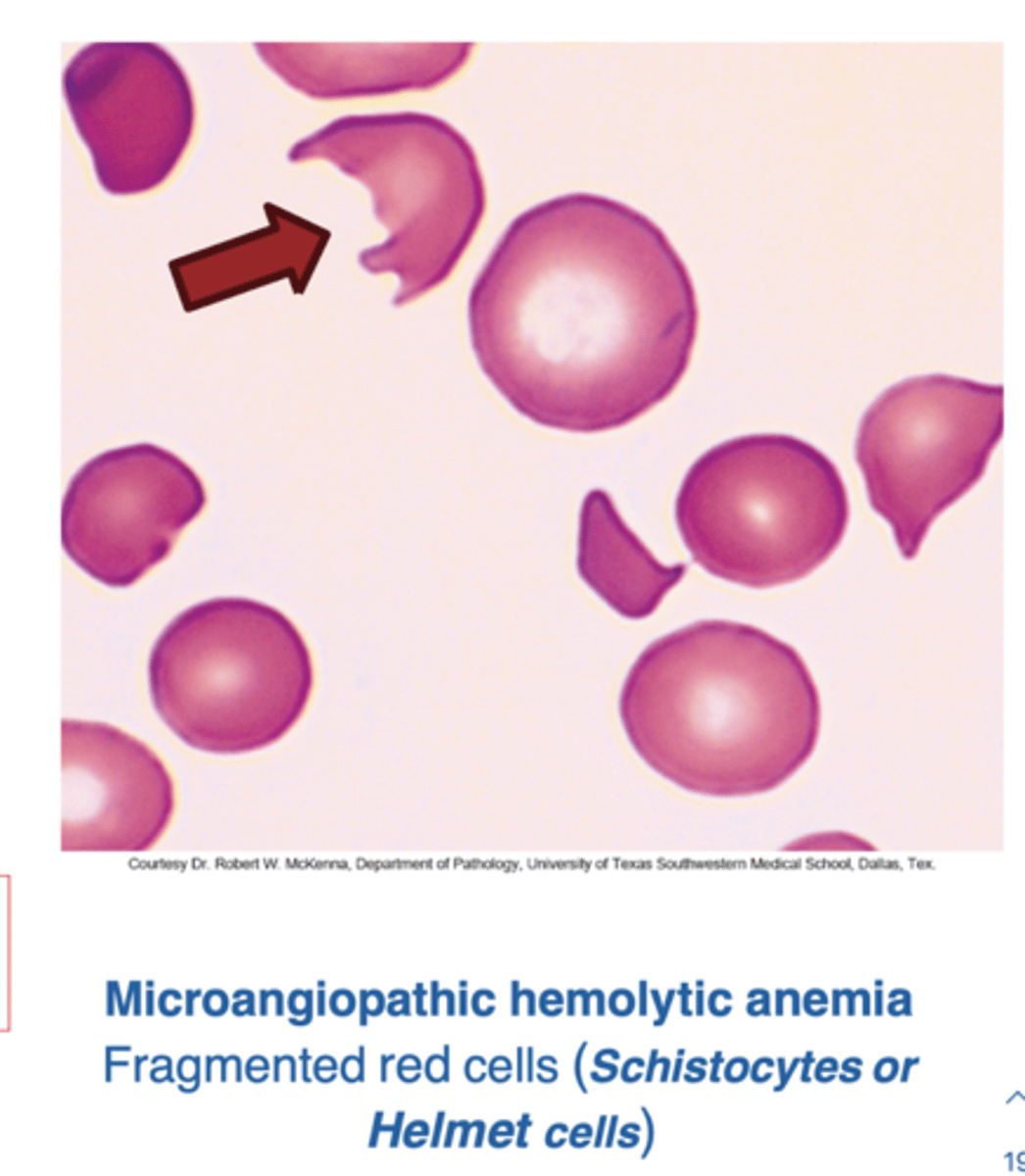
Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia
Mechanical Destruction of RBCs
Damage or destruction of the RBCs as they pass through the circulation → leading to intravascular hemolysis
Damage from:
Microthrombi
Prosthetic heart valves
Aortic stenosis
DIC/TTP/HUS
The damage produces…
Schistocytes and helmet cells on blood smear
Decreased production of Normocytic Anemia can cause:
1. Aplastic anemia*
2. Myelophthisic*
3. Anemia of chronic disease
4. Renal Failure
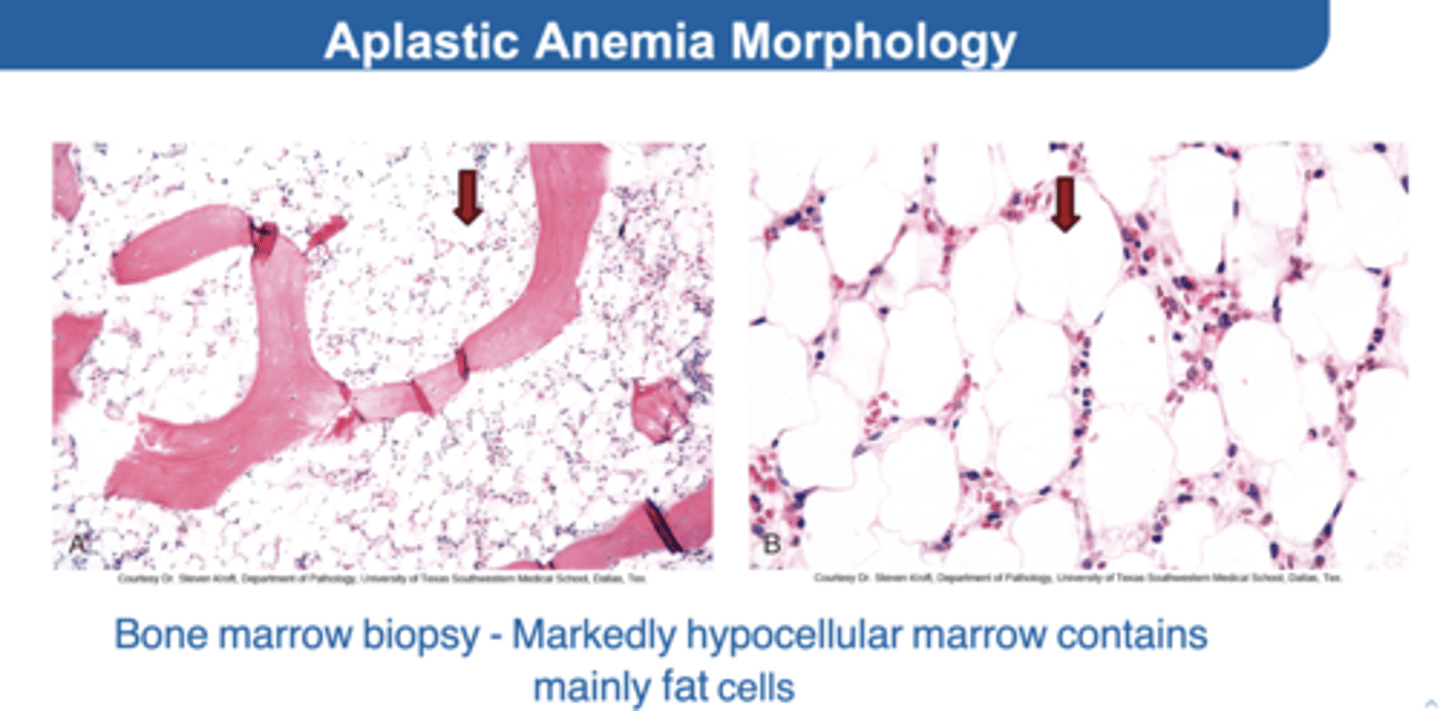
1. Aplastic Anemia
Rare, serious bone marrow failure
HOW? → Suppression or injury to the hematopoietic stem cell
You'll find→ Hypocellular marrow, pancytopenia, and no abnormal cells in blood or bone marrow
What causes damage to hematopoietic stem cells?
*KNOW THESE*
1. Chemicals - Benzene
2. Viral infections – Parvovirus B19, EBV, HIV
3. Drugs→ Chloramphenicol, sulfas, antimalarial, chemotherapeutic
4. Autoimmune damage – cytotoxic T cells
5. Radiation
What would be the result of a biopsy with Aplastic Anemia?
Almost empty bone marrow with predominantly fat and few bone spicules
Etiology of Aplastic Anemia
*Don’t forget about drugs, drugs, drugs*
1. Parvovirus B19
2. Fanconi anemia
3. Fanconi syndrome
Parvovirus B19
Viral infection resolving in a week or two in normal individuals
Happens in the presence of preexisting marrow stress (Sickle cell anemia)
→ Infects the BM progenitor cells →ineffective erythropoiesis → severe anemia
Fanconi anemia
Rare genetic disease
Causes bone marrow failure → all cell types → aplastic anemia
Fanconi syndrome
Rare kidney disorder
Inadequate reabsorption in the proximal renal tubules of the kidney
Caused by congenital or acquired diseases → toxic heavy metals or adverse drug
Aplastic Anemia Morphology
Symptoms of Aplastic Anemia
Fatigue
Malaise
Pallor
Purpura
Mucosal bleeding
Petechiae
Infection
Low reticulocyte count
Increased EPO to try to compensate Pancytopenia – decreased all cell lines (RBC, WBC and platelets)
*Note: Aplastic crises is anemia (RBC) only*
Treatment of Aplastic Anemia
1. Cessation of causative drug
2. Treatment of chemical effect
3. Immunosuppression → Cases caused by activation of T cells with cytokines
4. Bone marrow transplant
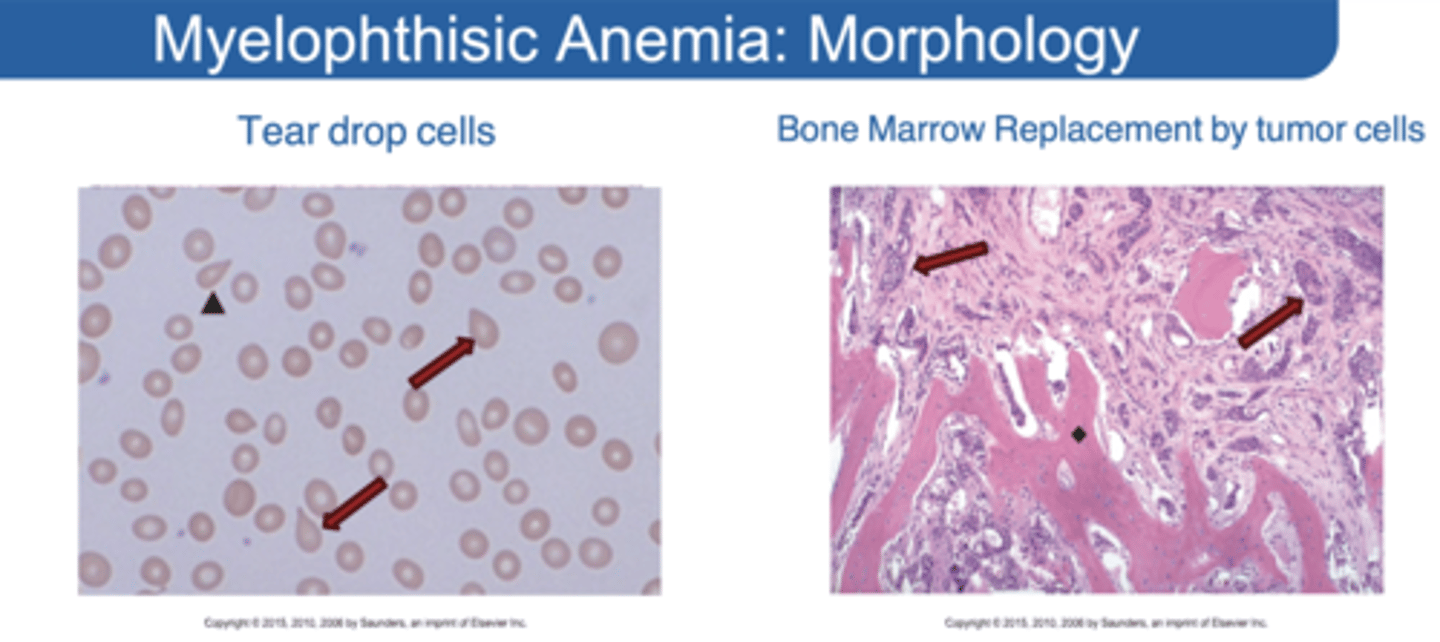
Myelophthisic Anemia
Replacement of bone marrow space with non hematopoietic tissue
Myelophthisic Anemia Can Be Caused By
1. Cancer
2. Marrow fibrosis
Impairment of hematopoiesis → pancytopenia
What indications in blood smear can show Myelophthisic Anemia?
Tear drop cells in smear = bone marrow fibrosis Peripheral blood: small numbers of nucleated red cells and immature granulocyte precursors
Morphology of Myelophthisic Anemia
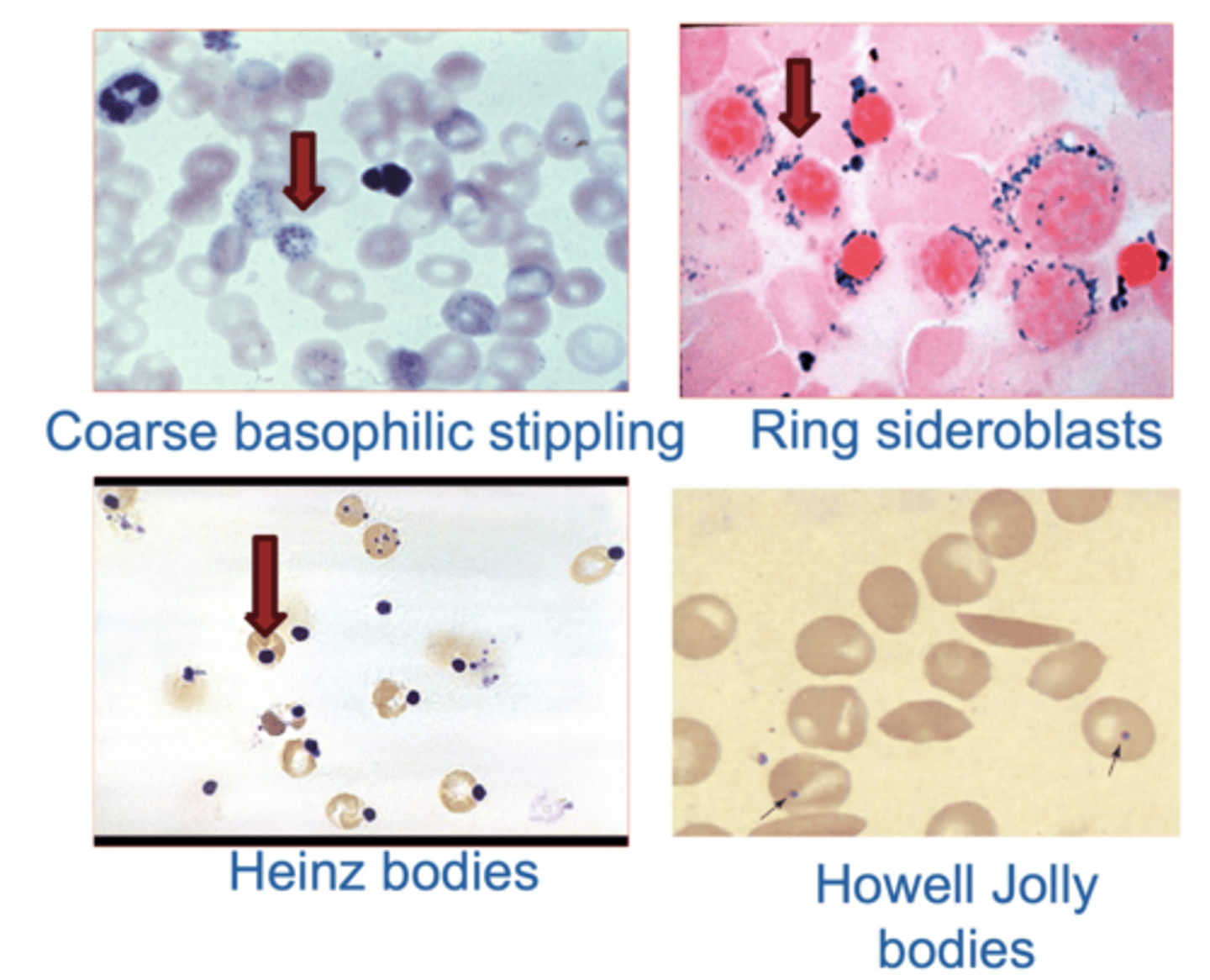
Red Cell Inclusions
1. Coarse basophilic stippling: persistent ribosomes. Indicates Pb poisoning
2. Heinz bodies: result from denatured hemoglobin → Can be seen in G6PD deficiency.
3. Howell Jolly bodies: are remnants of
nuclear chromatin. Indicates non functional / absent spleen (Sickle cell anemia/splenectomy)
4. Ring sideroblasts: have iron trapped abnormally in mitochondria forming a ring around nucleus → Seen in sideroblastic anemia (in the bone marrow).
Causes of Acquired Hemolytic Anemia
1. Infection
2. Drugs
3. Burns
4. Thrombotic microangiopathies
5. Hypersplenism
6. Vasculitis
7. Severe HTN