College Biology - Cell Unit
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Types of Cells
Prokaryote (bacteria)
Eukaryote (plant and animal)
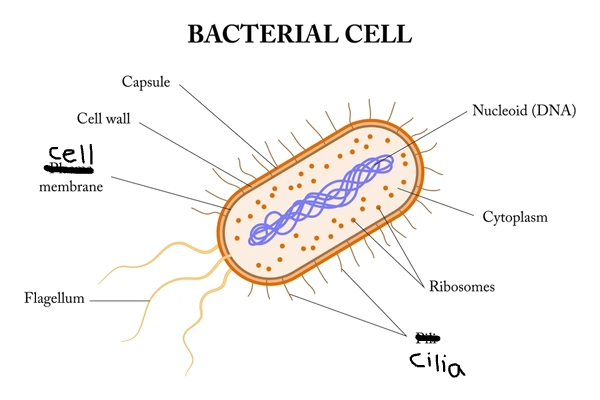
How many layers in a bacteria cell?
3 layers
Cell membrane
Cell wall
Capsule
Bacteria Cell Characteristics
DNA (scribble near top)
Ribosomes (dots)
Cilia (hairs)
Flagella (tail)
How many layers in a plant cell?
2 layers
Cell membrane
Cell wall
Plant Cell Characteristics
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Chloroplasts (plants)
Central Vacuole (plants)
Golgi
ER (SER and RER)
Vesicles (bubbles)

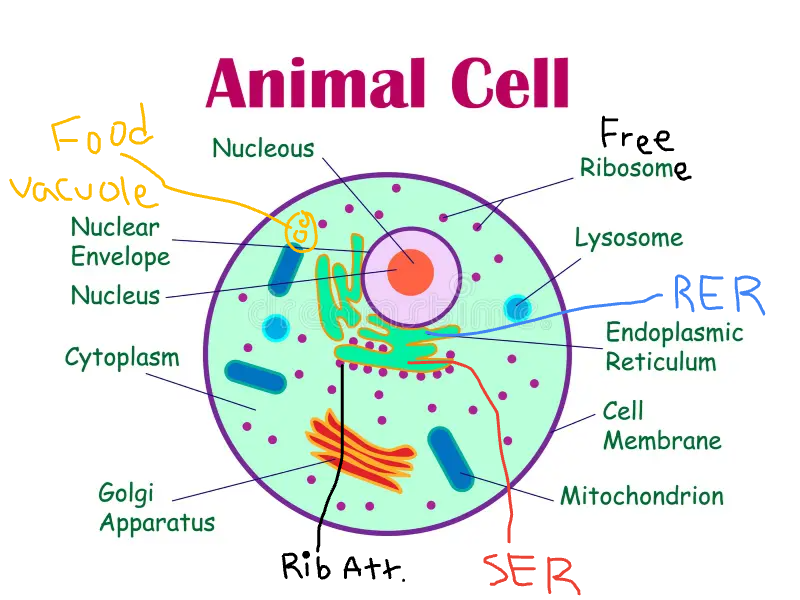
How many layers in a animal cell?
1 layer
Cell membrane
Animal Cell Characteristics
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Lysosomes (animals)
Food Vacuole (animals)
Golgi
ER (SER and RER)
Vesicles (bubbles)
Organelles
Have specialized structures
Special functions
Containers
Different local environments
Separate cells into compartments
Membranes as sites for chemical reactions
Unique combo of lipids and protein
Jobs of the Cell
Make Proteins - proteins control EVERY cell function
Make Energy - for daily life; for repair
Make More Cells - growth, repair
Protein Assembly Line
Nucleus that has DNA ) - Ribosome - RER - Vesicle - Golgi - Vesicle - Cell Membrane
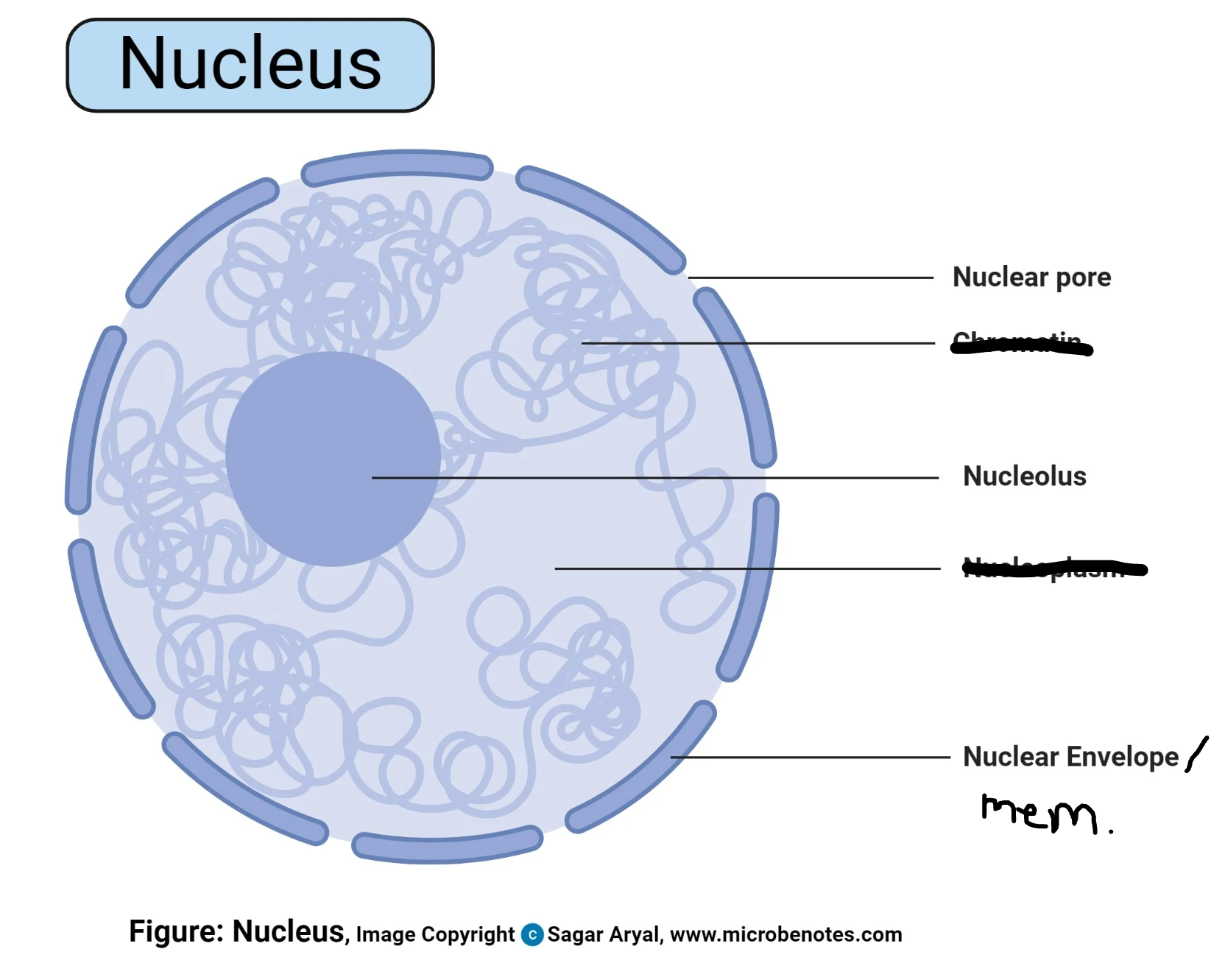
Nucleus Function
Protects DNA
Nucleus Structure
Note: allows large macromolecules to pass through
Nucleolus (creates ribosomes)
Nuclear Envelope / Membrane
Nuclear pore
The Messenger
Instructions for a protein are copied from DNA by mRNA
mRNA carries message to the cytoplasm through a nuclear pore
Ribosome Function
Protein Production
Ribosome Structure
rRNA and Protein
two subunits combine (large and small)
Types of Ribosomes
Free
In cytoplasm
Makes protein for cytoplasm
Attached
Attached to ER
Makes proteins for export
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Function
Passes proteins (RER)
Makes membranes (SER)
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Structure
Membrane of ER is connected to the nuclear membrane
Types of ER: Smooth ER
Membrane production
Many metabolic processes - build or break
Types of ER: Smooth ER
Synthesis
Makes lipids (oils, steroids, phospholipids)
Types of ER: Smooth ER
Hydrolysis
Glycogen hydrolyzes into glucose
Detoxifies drugs - most in liver
Types of ER: Rough ER
Produce proteins for exporting out of cell
Protein secreting cells
Package into transport vesicles for export
REVIEW: Steps in making a protein
The DNA in the nucleus holds the instructions for a protein
mRNA in nucleus copies instructions
mRNA moves out of the nucleus through a nuclear pore
mRNA goes to a ribosome to make a protein
Ribosome and amino acids go in correct order
RER folds the protein
Travels through vesicle to Golgi
Golgi finishes the protein
Travels through vesicle to cell membrane
Leaves out cell membrane
Cells making energy overview
Take in food and digest it
Take in oxygen
Make ATP
Remove waste
What is ATP?
ENERGY
Lysosomes [only in animal cells] Function
Note: found in white blood cells
Little stomach of the cell
Digests macromolecules
Clean up crew
Cleans up broken down organelles
Lysosomes [only in animal cells] Structure
Vesicle of digestive enzymes
Lysosome Digestion: How it works
Lysosomes fuse with food vacuole
polymer: digested into monomers then passed to cytoplasm to become nutrients
Works at pH 5
Cytosol (cytoplasm) has pH 7
Means: it will not break down in another pH
Lysosome Failure: When things go wrong
Digestive enzymes do not work on lysosome
Diseases of lysosomes are often fatal
Example: Krabbes diseases
Lysosome Failure: Steps
Picks up biomolecules but cannot digest one
Fills up with undigested material
Grow larger until disrupts cell and organ function
When cells need to die…
Apoptosis - Lysosomes can be used to kill cells when they are supposed to be destroyed
Auto-destruct process
Lysosomes break open and kill cells
How do cells make energy?
Cells convert energy into forms they can use
Mitochondria (how it makes energy) - animals and plants
Food / Nutrients make a large amount of ATP
Chloroplast (how it makes energy) - plants
Sunlight makes a small amount of ATP
Transformed into food
Goes up to Mitochondria
Large amount of ATP produced
ATP vs Glucose
ATP: active energy
Glucose: stored energy
Mitochondria AND Chloroplast BOTH…
Have double membrane
Make ATP
Have own DNA
Move and divide
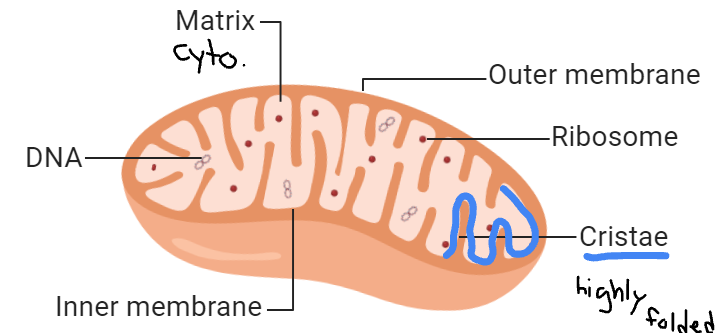
Mitochondria Function
Cellular respiration
Generate ATP
Mitochondria Structure
Note: 2 membranes add to the surface area
ATP generated along Cristae
What cells have mitochondria?
Almost all EUKARYOTIC cells have mitochondria
Either 1 very large mitochondrion or 100s to 1000s of individual mitochondria
# of mitochondria is correlated with activity
More activity = more energy needed = more mitochondria
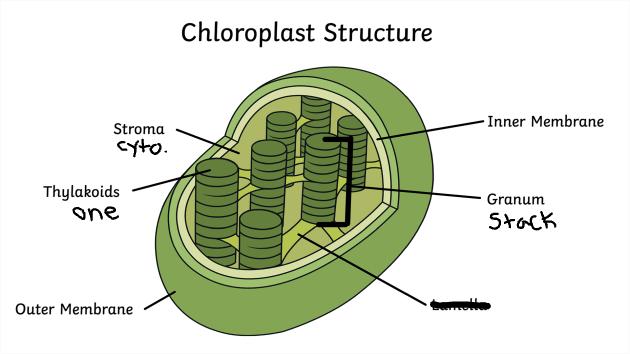
Chloroplast Function
Photosynthesis
Make ATP
Chloroplast Structure
Note: they are GREEN
Vacuoles and Vesticles Function
Little transfer ships
Think of Glinda the Good in a bubble, traveling around
Examples of Vacuoles
Food vacuole - animal
Contractile - protists
Central - plants
REVIEW: Steps in making energy
Food taken in through cell membrane into food vacuole
Food vacuole fuses with lysosome
Lysosome breaks food down into glucose
Glucose enters cytoplasm
Glucose taken in by mitochondria to make ATP
Cytoskeleton Function
Structural Support (microtubules) - bones
Maintains shape of cell
Provides anchorage for organelles
Motility (microfilaments) - muscle
Cell locomotion ~ cilia and flagella are examples
Regulation: organizes structures and activities of cell
Centrioles [animals only] Function
Cell division
Animals: pair of centrioles
Organize cytoskeleton
Guide chromosomes
REVIEW: Steps in making more cells
The cell copies its DNA and prepares for division
Centrioles organize the cytoskeleton and guide chromosomes
Centrioles move to opposite ends and form spindle fibers
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart
Microfilaments pinch the cell in two
Two identical cells are formed with the same DNA
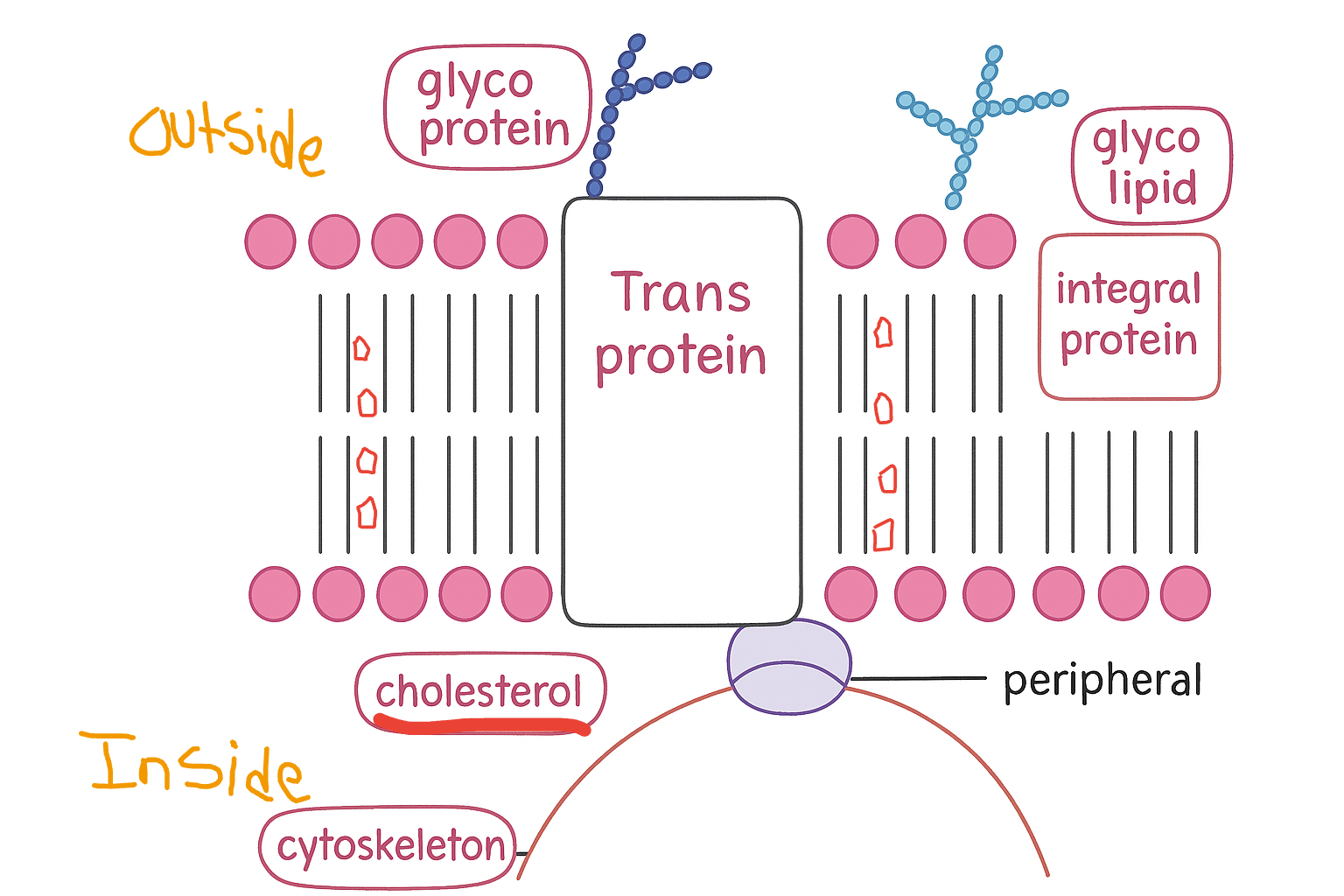
Plasma Membrane
Very thin
Fluid, fatty makeup
Very flexible, yet stable
Phospholipid Bilayer Make-Up
Lipids are hydrophobic
Phosphates are hydrophylic
Form 2 layers w/ the fatty acid tails in middle
Phosphate heads point toward watery environment
Phospholipid Bilayer Traits
Unsaturated, thus fluid-like
The only things that can get through the fatty acids are other hydrophobic substances, or small molecules
Cholesterol
Lipid
Patch the membrane, keeping some things from coming in
Keep the membrane fluid
Glycocalyx
Carbohydrate chains that extend from the outside of cell
Binding sites
Lubricate cells
Allow them to stick together
Glycocalyx Types
Glycoprotein - Protein
Glycolipid - Lipid
3 Types of Proteins
Integral: bound to the hydrophobic interior
Peripheral: are not bound to the interior, attached to trans
Trans: all the way through
Proteins: Structure
On the interior of the cell
Attached to cytoskeleton of animal cells - anchor
Proteins: Recognition
Have binding sites whose shape can be recognized by immune cells
Proteins: Communication
Cells can communicate w/ another over long distances by hormones
Hormone is received by a receptor protein at a specific bonding site
Hormone does not need to enter the cell - attach and leave a message
Proteins: Transportation
Most materials cannot pass directly through cell membrane
Proteins act as channels
Materials move in and out of cell
Fluid Mosaic Model
Refer to picture!!! (Review)
Molecular Mvmt
Has random movement
Molecules are in constant motion and spread out
Diffusion
Mvmt of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration
In diffusion, molecules move down a concentration gradient ALWAYS
Concentration Gradient
Difference between high and low
Semipermeable Membrane
Only let certain substances through it
Osmosis
The diffusion of water
Hypertonic Solution
Higher concentration of solutes outside the cell
Water goes out
Mass goes down
Hypotonic Solution
Lower concentration of solutes outside the cell
Water goes in
Mass goes up
Isotonic Solution
Solution inside cell and out have the same concentration
Water goes in and out
Mass stays the same
Molarity
How concentrated something is (Expressed with “M”)
Passive Transport - no energy
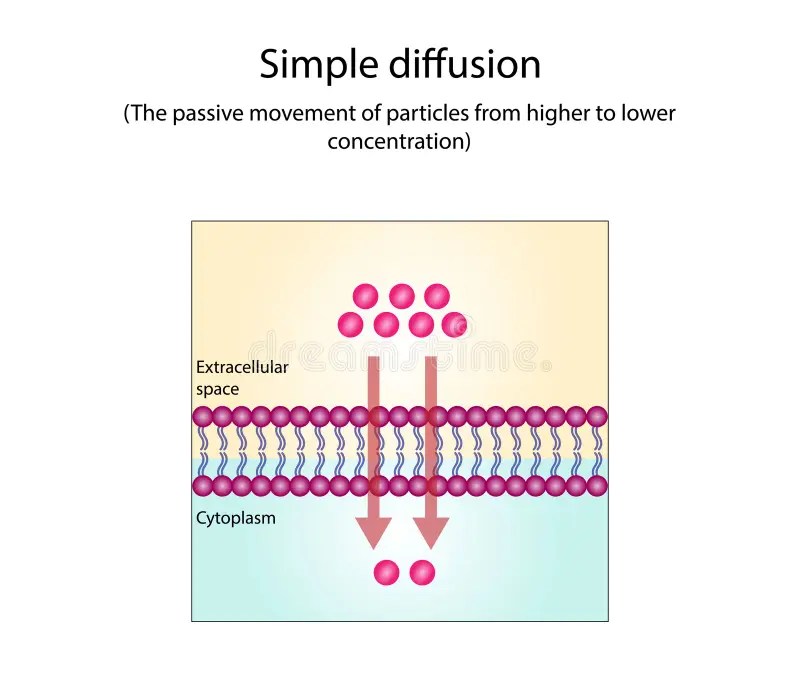
Simple Diffusion
AND
Facilitated Diffusion
Simple Diffusion
Does not require a protein channel
Examples: Carbon Dioxide, Water
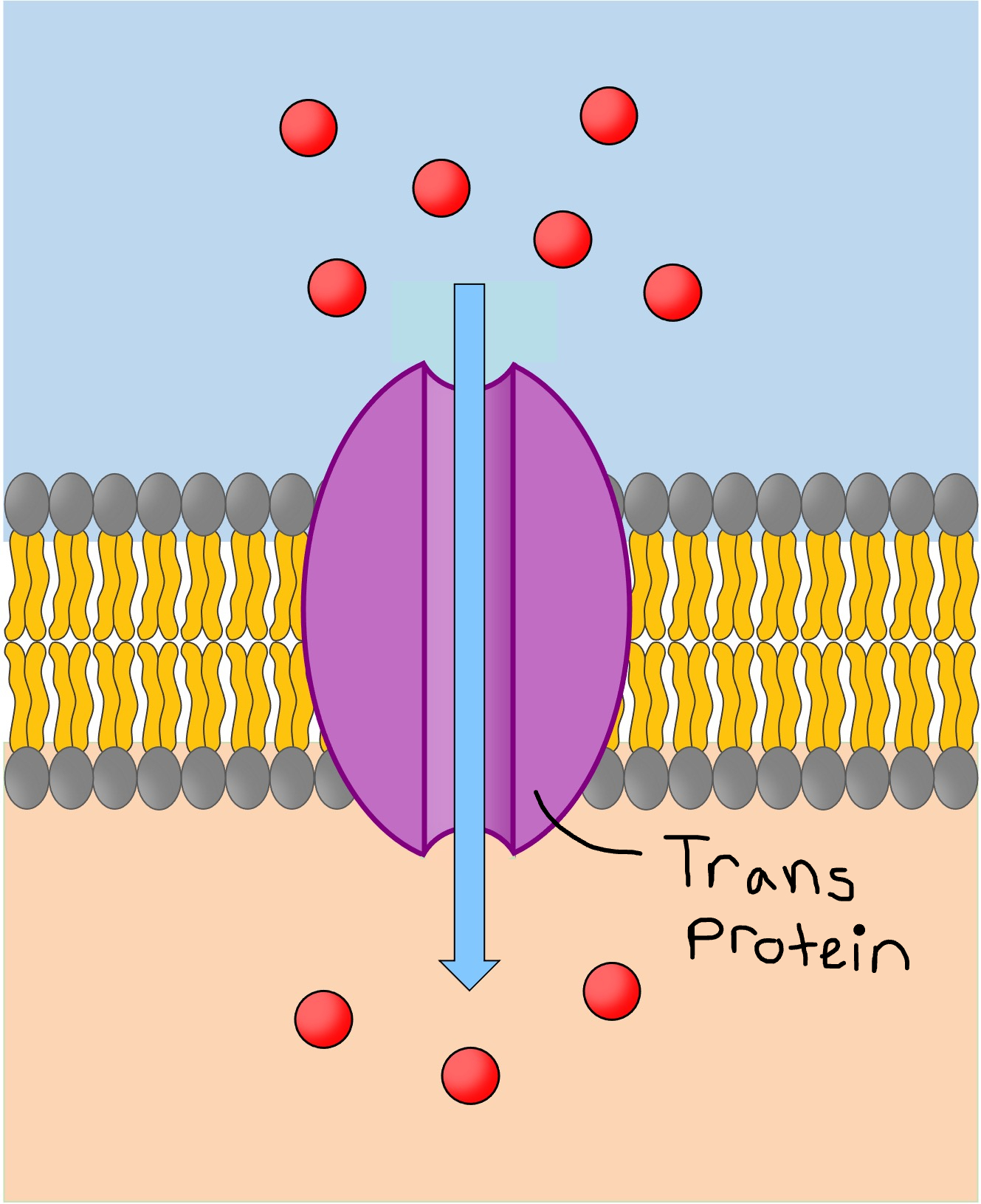
Facilitated Diffusion
Aided by a transport protein
Transport proteins are substance specific
Examples: Glucose, Amino Acids
Compare and Contrast: Simple and Fascilitated Diffusion
BOTH move from high to low
HOWEVER simple goes through the phospholipid bilayer and facilitated moves through a protein.
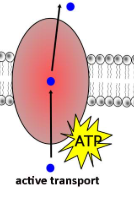
Active Transport - energy
Sometimes cells need a higher or lower concentration of substance inside the cell than outside
Moving against concentration gradient
Substance specific
Requires energy (ATP)
Exocytosis
Mvmt of large amounts of material OUT of a cell
Vesicle fuses to plasma membrane
Vesicle contents are released into the extracellular fluid
Endocytosis
Mvmt of materials INTO the cell
Endocytosis - Pinocytosis
“Cell drinking”
Endocytosis - Phagocytosis
“Cell eating”
Water Potential
Water Potential = Solutle Potential + Pressure Potential
Water will flow from a high water potential to a low water potential