OCR Biology Paper 1
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Part 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
In light microscopes we can see…
cells and their structures, such as nuclei and chloroplasts.
Magnification formula is…
Image Size
_________
Object Size
The formula for percentage change is…
(Final Value - Initial Value) / Initial Value x 100
Bacteria multiply by…
binary fission, a method of asexual reproduction. This means bacteria double every certain amount of time, e.g. 10mins.
A bacterium with a mean division time of 20 minutes is placed in a nutrient-rich environment. If you start with one cell, how many cells will there be after 2 hours?
21 = 20mins
26 = 120mins
64= 120mins
What is step 1 of the Aseptic Technique?
Open your petri dish towards a flame to push germs in the air away from the dish and prevent contamination.
What is step 2 of the Aseptic Technique?
Use sterilised (very clean) tools to make sure that there are no unwanted bacteria.
What is step 3 of the Aseptic Technique?
Gently place a tiny drop of bacteria in the middle of the dish.
What is step 4 of the Aseptic Technique?
Use a sterilised loop to spread the bacteria evenly across the agar surface.
What is step 5 of the Aseptic Technique?
Put tape around the dish, but leave space for air.
What is step 6 of the Aseptic Technique?
Put it in an incubator (a warm box) at 25 degrees - a good temperature for bacteria to grow.
What is a genome?
It is all the genetic material inside an organism.
What is a gene?
A piece of DNA that tells your body how to make a protein.
What is a genotype?
The genetic code in your DNA
What is a phenotype?
How genetic code is presented in characteristics - e.g. eye colour, hair colour…
What is DNA?
A two-stranded polymer in a double-helix shape.
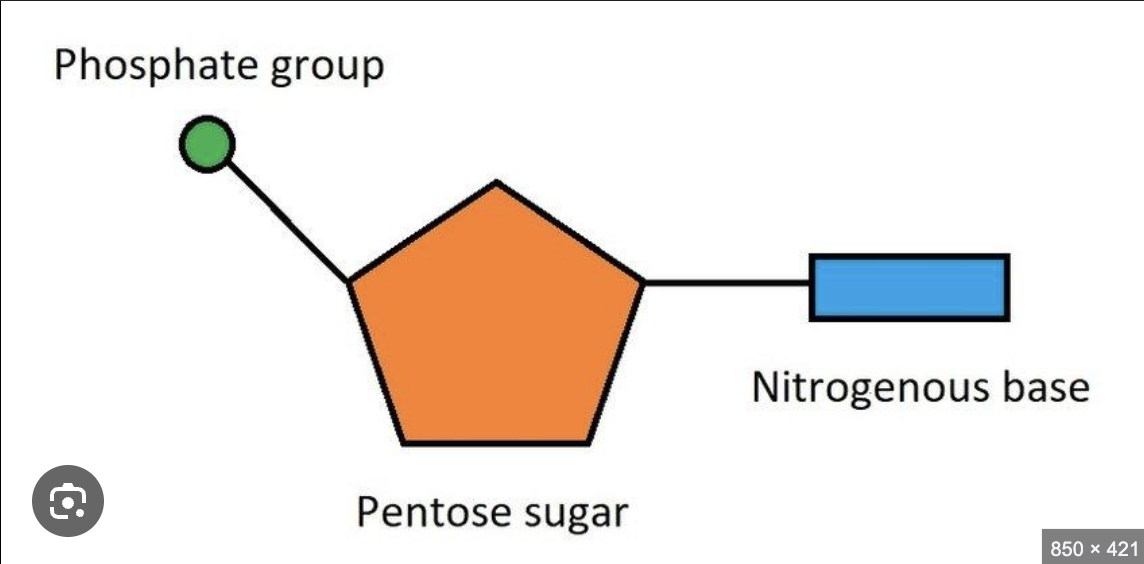
What is a nucleotide?
Monomers between the two strands, made up of a sugar, phosphate and base.
How does DNA code?
DNA gives instructions to make proteins. These instructions are read in groups of 3 (called bases).
What can harmful mutations do to a gene?
It can change a gene, meaning a protein dosen’t function efficiently.
What does epigenetics mean?
It means how your genes can change.
What are enzymes?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed reactions and break larger molecules into smaller ones.
What does the enzyme amylase do?
It breaks down starch into glucose.
What does the enzyme carbohydrase do?
It breaks down carbohydrase into sugars.
What does the enzyme protease do?
It breaks down protein.
What does the enzyme lipase do?
It breaks down fats into glycerol.