Bio 10 🧬🔬🧫
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
Spontaneous Generation/Abiogenesis
The belief that life could arise from non-living matter; proposed by Aristotle
Characteristics of Living Things
Made of cells
Need energy
Produce wastes
Responds and adapts to their environment
Reproduce
Grow
Biogenesis
The development of living organisms from other living organisms.
Level of organization
Cells (most basic) → Tissues →Organs → Systems (most complex)
Cell
The most basic unit of structure and function
all living things are composed of cells
cells are OPEN-SYSTEMS
Tissue
A group of similar cells that share the same structure and function
Ex: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, epithelial tissue, connective tissue (in human); vascular tissue (in plants)
Organ
A group of various types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function
Ex: brain, heart, leaf
System
A group of organs and tissues that perform a shared complex function
Ex: digestive system
Multicellularity/ Multicellular Organisms
An organism consisting of many cells of different type (ex: human)
have a larger size
have a variety of specialized cells
have an ability to thrive in a broader range of environments
Individual cells in a group organize themselves and interact with each other to function efficiently
Cell Theory
1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells
2. The cell is the smallest functional unit of life
3. All cells are produced from other cells
Francesco Redi
Italian physicist that disproved the theory of spontaneous generation
Experiment: In 1668, he placed meat in two different jars. He covered one jar with cloth and left the other open. While maggots developed in the open jar, none appeared in the covered jar.
Louis Pasteur
French scientist who was convinced spontaneous generation did not occur and disproved it by observing micro-organisms multiplying under a microscope.
-Invented pasteurization: heat is applied to kill microbes and prevent spoilage and disease.
-Proved the "active principle" in air was also an organism through the "swan-neck flasks" experiment
Rudolf Virchow
German physician who concluded that cells divide to produce more cells.
—> cell comes from other living cells
Robert Hooke
An English scientist who was the first to name the structures he saw under a microscope as "cells".
Antony van Leeuwenhoek
a Dutch tradesman and scientist became the first person to look at living cells
He increased the resolution and magnification of microscopes
Zacharias Jansen
A Dutch lens maker who was credited with forming the first compound light microscope
Matthias Jakob Schleiden + Theodor Schwann
German scientists
Schleiden concluded all plants are composed of cells and that each new cell developed from the nucleus
Schwann found that animal cells are also made up of cells
Compound Light Microscope
A microscope with two or more lenses (typically the ocular lens and objective lenses) that is used to view objects illuminated by visible light.
Most biological material is transparent, compound microscope allow for contrast by adding stain
Parts of a Compound Light Microscope
Tube, Revolving Nosepiece, Objective Lenses (low, medium, high), Stage Clips, (Iris) Diaphragm, Lamp/Light Source, Eyepiece/Ocular Lens, Arm, Stage, Coarse Adjustment Knob, Fine Adjustment Knob, Base

Tube
Connects the eyepiece to the rest of the the microscopes
Revolving Nosepiece
Rotates/ revolves to change the objective lenses
Objective Lenses
Low (4X), Medium (10X), High (40X)
Used to view objects at three different magnifications
Stage & Stage Clips
Stage: the platform that supports the slide being viewed
Stage clips: hold the slide in place
Iris Diaphragm
Adjust the amount of light entering the field of view (FOV)
Lamp/Light Source
Provides light to illuminate the object
Ocular Lens/Eyepiece (10X)
Look through this to see an object under the microscope
Arm
connects the base and the barrel
Base
support the microscopes
Fine Adjustment Knob
Moves the stage a very small amount up and down to bring the object into focus.
Used on medium and high objective lenses
Coarse adjustment Knob
Moves the stage up and down, which brings the object into focus.
Used for LOW power
Organelles
“Little organs” in a cell with a specific function
Maintain life: acquire nutrients, excrete waste, exchange matter and energy
3 main types of cells
Plant, Animal, Bacteria
Total Magnification
Tells us how magnified the object is.
Formula: Total mag. = ocular lens x objective lens
Field of View (FOV)
It's the area seen when looking in a microscope.
Formula: Mag on High/Mag on Low = Field Dia on Low/Field Dia on High
FOV can be referred to as field diameter
increase the magnification, the field of view gets smaller
Size of Specimen (Actual Size - AS)
An approximation of the size of the specimen viewed
Formula: SOS/ AS = FD x fraction of space occupied by specimen
Prokaryotes
single-celled organisms with no nucleus (prokaryotic) and no membrane-bound organelles
2 domains: archaea and bacteria
contain: ribosomes, flagella, some nuclear materials, some prokaryotes have cell walls
Ex: cyanobacteria, E. coil bacteria, thermophiles
are very small (smaller than eukaryotes)
Found almost everywhere (soil, skin, intestines,…)
Interior is entirely cytoplasm, with some ribosomes
Nucleoid is the space where ribosomes are
Chromosomes/ DNA are usually circular
Reproduce by binary fission
eukaryotes
Complex cells with an organized nucleus, many membrane-bound organelles
Can be single/ multi-celled
Ex: animals, plants, human
Systems
open system: allow the exchange of both matter and energy
closed system: allow the exchange of energy but not matter
isolated system: allow neither
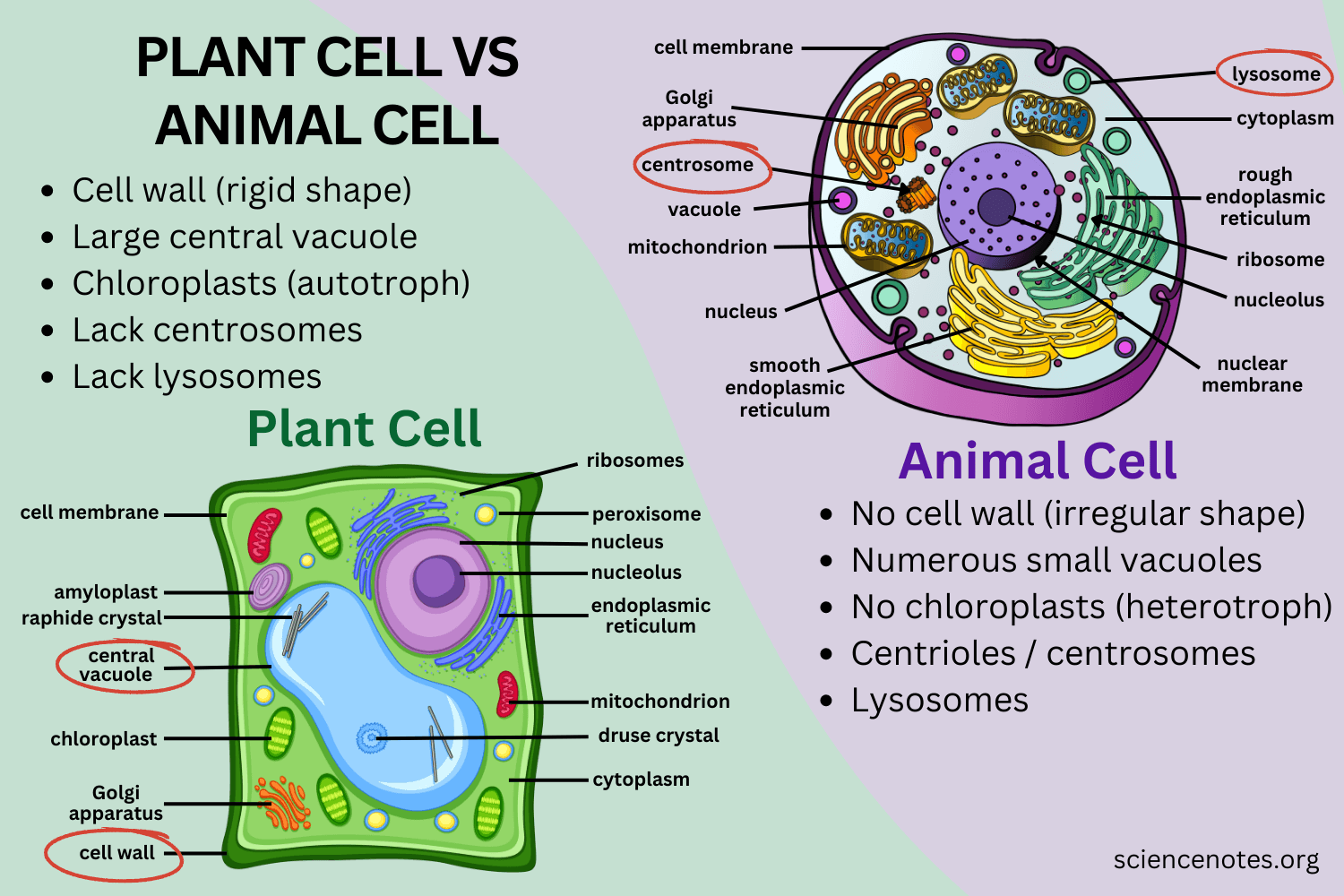
Organelles in animal cell
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus + Nucleolus
Rough/ Smooth ER
Ribosomes
Vesicles
Golgi Apparatus
Lysosomes
Centrioles
(Cytoskeleton)
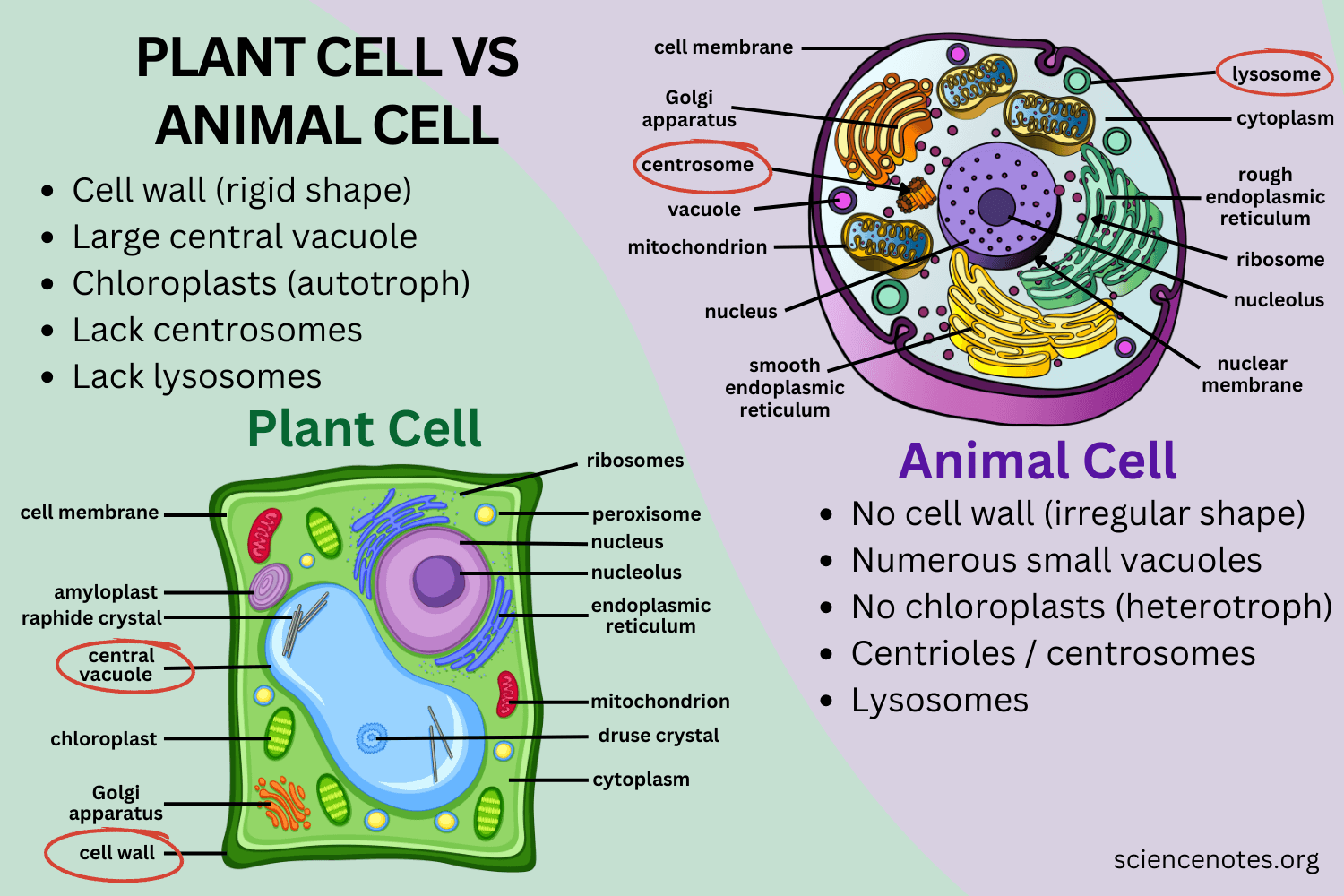
Organelles in plant cell
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Cytoplasm
Nucleus + Nucleolus
Rough/ Smooth ER
Ribosomes
Large central vacuole
Golgi Apparatus
Chloroplast (chlorophyll)
(Cytoskeleton)
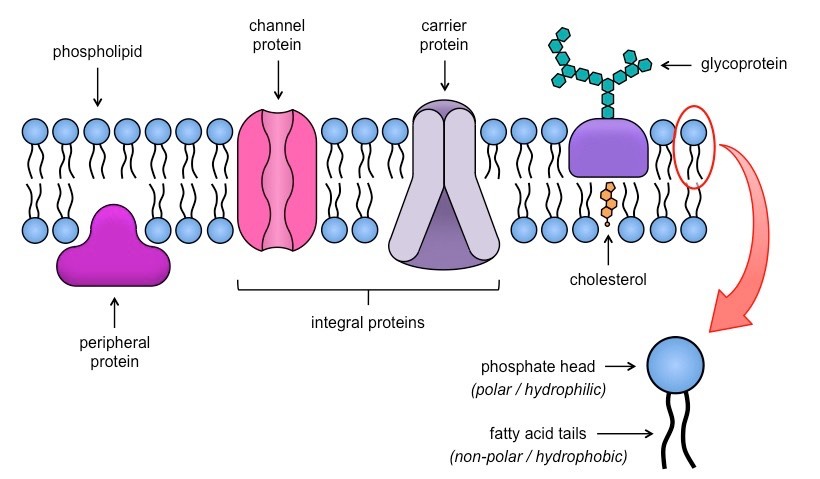
Cell Membrane (plasma membrane)
The boundary around a cell that separates the cell interior from the environment.
consists of a double membrane structure
made of phospholipids, proteins, carbs, cholesterol
control cell transport (what in + out of cell)
Semi-permeable, in both plant and animal
Cytoplasm
Jelly-like fluid inside a cell including all organelles except the nucleus
Mostly made of water + hold organelles
in both plant and animal cells
Nucleus
Acts as the "control center" in a cell
Contain nucleolus, nuclear envelope, nuclear pore, chromatin
contains genes/ genetic info
directs the structure and function/all activities of the cell.
in both plant and animal
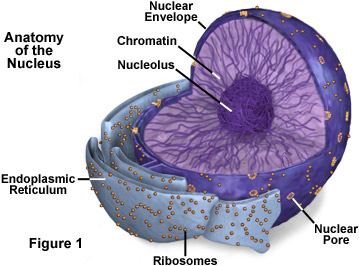
Nucleolus
The area in the nucleus of a cell where ribosomes are produced.
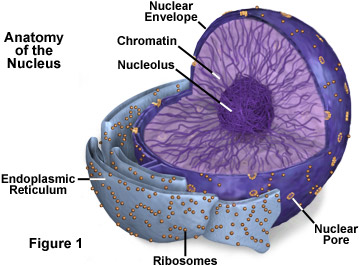
Ribosomes
The cell structure that translates genetic information sent from the nucleus into proteins
can be free floating in cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER; made of 2 subunits
Synthesizes (builds) proteins from DNA, using amino acids
In both plant and animal
Lysosomes
A vesicle containing digestive enzymes (a type of protein) where materials and old cell parts that no longer work are degraded to be recycled or used to provide energy
“clean up crew”
animal cells ONLY
The pH is generally low, helping the digestive enzymes function
Lysosomes can fuse with vesicles containing food particles
Some lysosomes protect the body by killing infectious micro-organisms
Endoplasmic Reiticulum (ER)
A network of folded membranes and tubes connected with the nucleus, where proteins and lipids are synthesized and packaged in vesicles.
Rough: attached ribosomes; transports proteins.
Smooth: without ribosomes; produce, transport, metabolize lipids and hormones (usually send to the cell membrane/ the Golgi apparatus)
Both in animal and plant
Golgi Apparatus/Body
Where proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum are modified, repackaged, and distributed to other locations in the cell
Both in animal and plant
Major role: folding and packing proteins
Also produce lysosomes
Mitochondria
the "powerhouse", where food molecules are broken down into ATP energy that can be used by the cell to carry out other activities
Converting sugar into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) = cellular respiration
in both plant and animal
Centrioles
located near the cell nucleus; helps organize genetic material during cell division
in animal cells, most plant cells don’t have them
When a cell divides, it must reproduce all of its genetic material and then divide this material between the two new cells
During cell division, centrioles help by moving genetic material correctly into each new cell
Vacuoles / vesicles
A balloon-like organelle that can store water, food, and minerals in a cell
Both in animal and plant
Animal cells have many smaller vacuoles AKA vesicles
Plant cells have a large central vacuole
store mainly water + maintain the shape of plant cell
can contain poisons to prevent animals from eating the plant
Some vacuoles contain wastes
Cell Walls
Very thick layer made of cellulose (fiber) that surrounds the cell membrane of plant cells
provide structure + support
prevent over-expansion when plants take in water
ONLY plant cells
Chloroplasts
containing chlorophyll, where photosynthesis takes place (plants making glucose)
ONLY plant cells
Have two layers of membranes: an inner layer of flattened membrane sacs enclosed by a second outer membrane
The inner membranes contain the green pigment molecule chlorophyll
Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in chloroplasts that traps light energy for photosynthesis
Glucose
A sugar that is used by cells as a source of energy
formula: C₆H₁₂O₆,
Photosynthesis
The process by which plants use light energy, water, and carbon dioxide to produce food (sugars) in the form of carbohydrates and oxygen.
carbon dioxide + water + (sunlight)→ oxygen + glucose
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + (sunlight) → 6 O2 + C6H12O6
Occurs in the chloroplasts; chlorophyll traps sunlight
Cellular Respiration
The process by which cells obtain energy by breaking down glucose in the presence of oxygen.
both plant and animal cells
requires mitochondria
sugar (glucose) + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + ATP
C6H12O6 (aq) +6 O2 (g) → 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O (l)
Surface Area-to-Volume Ratio
Cells want a high SA and low V = high SA:V ratio
skinner, flatter and smaller cells absorbs and excrete substances/ nutrients more efficient → functions better
(ex: microvilli in small intestine, cilia)
Volume increases faster than SA, as a cell grows
Large and complex organism must be MULTICELLULAR
When a cell can no longer function well → it divides
Cell differentiation
All cells in the multicellular organism have the same sets of genes
But large differences in structure and activities
Not only have genes for the instructions of their functions but also to specialize in every possible way
Nutrients that enter the cell
Glucose
Water
Hormones
Minerals (ions)
Oxygen
Wastes that cells need to remove
Urea (protein breakdown)
Excess water
Excreted hormones + enzymes
Minerals (ions)
CO2
Lactic acid
Particle Model of Matter
All substances are made out of tiny particles
All particles in a pure substances are the same
Particles are in constant, random (Brownian) motion
There are attractive forces of varying strength between particles
There are spaces between particles, which can be occupied by particles of other substances
Solute
something that dissolves in a solvent
usually a solid, grams
the lesser amount/ minor component of a solution
Solvent
substance that dissolves a solute
usually a liquid, litres
the greater amount/ major component of a solution
Solution
solute + solvent
concentration
number of molecules in a solution per litre (g/l)
concentration gradient
difference in concentration between 2 areas
Permeability
Impermeable: don’t allow any solute to pass through
Semi-permeable: allow some solutes through but block others (cell membrane)
Permeable: allow any material to pass through
Selectively permeable membrane
a barrier that allows only certain solutes, based on
size
shape
electrical charge
lipid solubility
Ex: oxygen-in, CO2-out
Fluid Mosaic Model
describe what the cell membrane looks and functions like
Mosaic: a pattern of different types of molecules put together
Fluid: the movement of the membrane, floating around not static
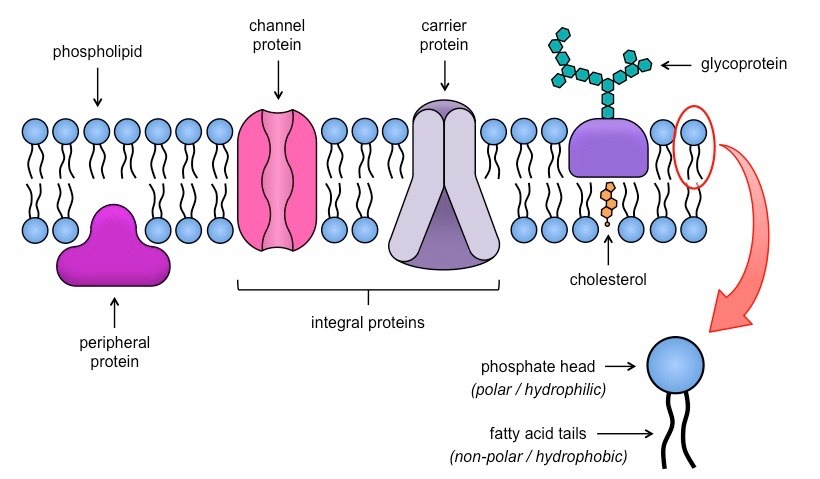
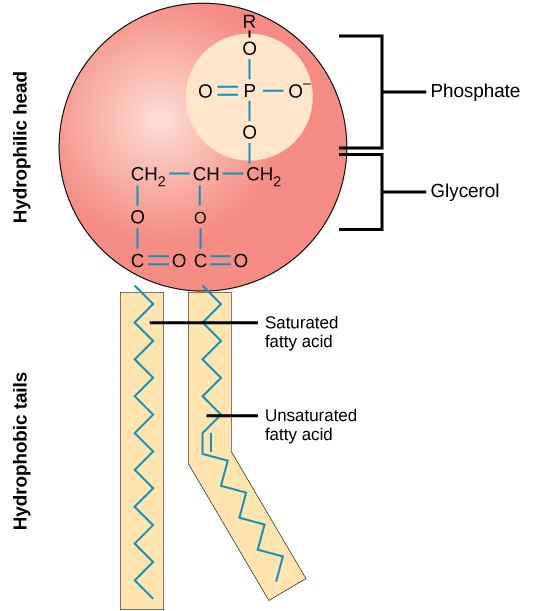
Phospholipid bilayer
phosphate heads: hydrophilic (water-loving), polar
lipid tails: hydrophobic (water-fearing), non-polar
water do not seep in and out of the cells due to water-fearing tails
lipid and lipid-soluble substances can pass through
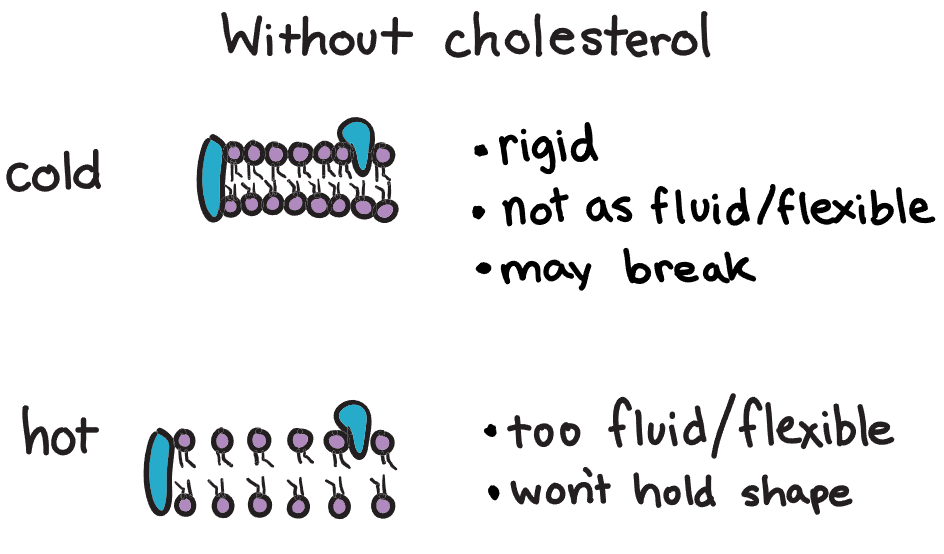
Cholesterol
controls the fluidity of cell membrane, “stabilizer”
in cold → keeps the lipids moving so that they don't freeze
in hot → it slows the lipids down, limiting their travelling
carbohydrate chains
attached to the lipids/ proteins outside of the cell membrane
act as "cell markers" or signs so that the immune system knows the condition of cells
involved in cell-to-cell communications
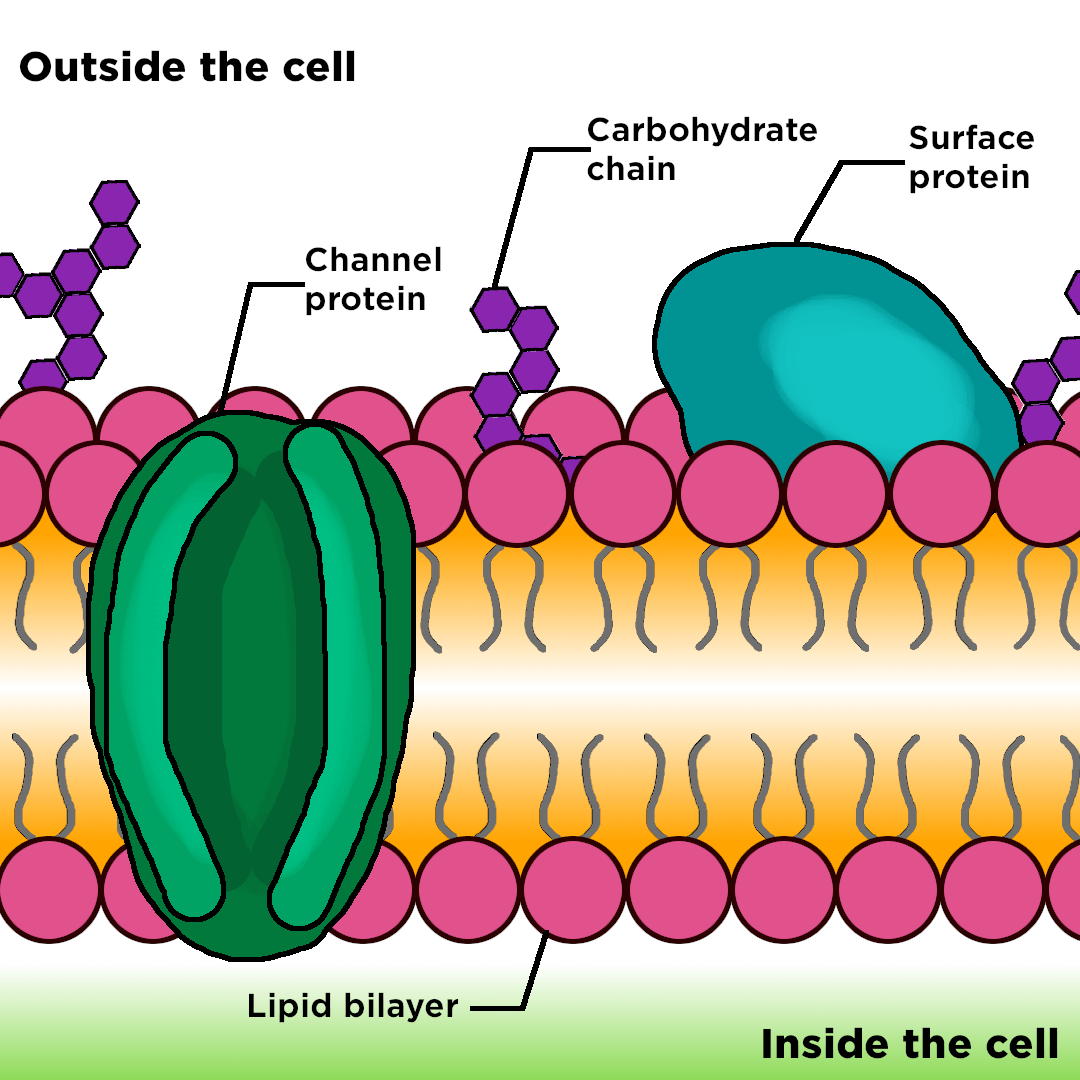
membrane proteins
Embedded in the cell membrane
transport certain substances/molecules through the membrane + carry out chemical reactions
Some have "marker" molecules on them to allow cellular recognition + protect cells from infection.
may also act as an attachment site for "messenger molecules” (hormones)
Messenger molecules
Used in cell-to-cell communication and control of cell functions (ex: hormones)
membrane proteins (positions)
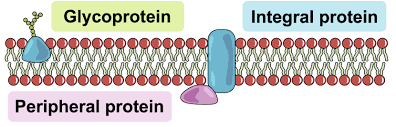
Integral proteins: go through the membrane, transport water and water soluble substances
Peripheral proteins: only one side, can have enzymes (to speed up reactions) or cytoskeleton structure (to provide strength for the cell)
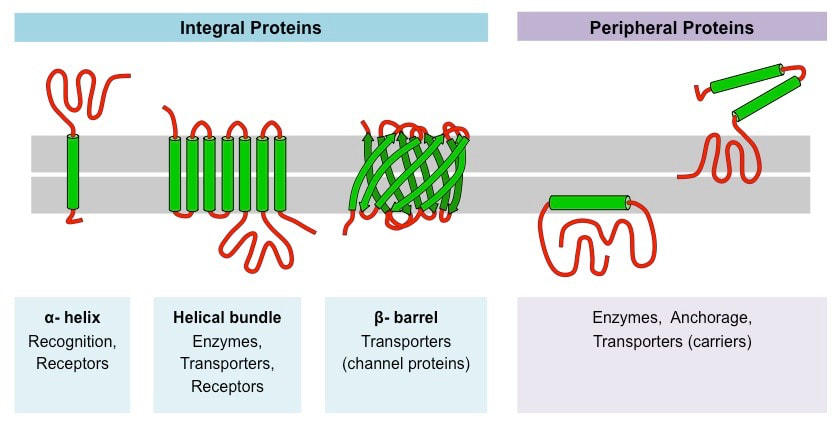
membrane proteins (functions)
transport proteins: facilitated diffusion (channel proteins, high→low), active transport (pumps, low→high)
* transmembrane/ integral protein
glycoproteins: identify cells that belong to an organism, cell recognition and signaling, have carbohydrate chains attach to them
*can be integral or peripheral
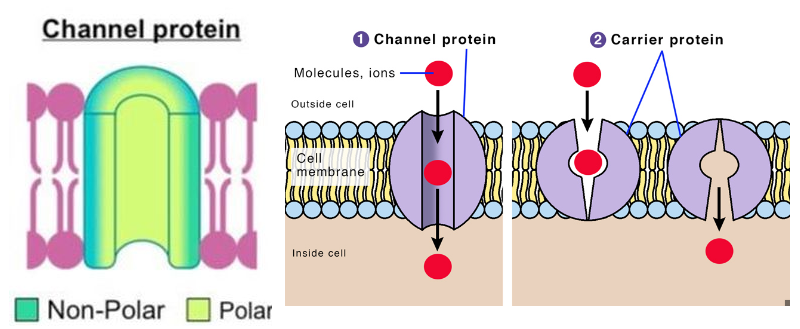
transport proteins
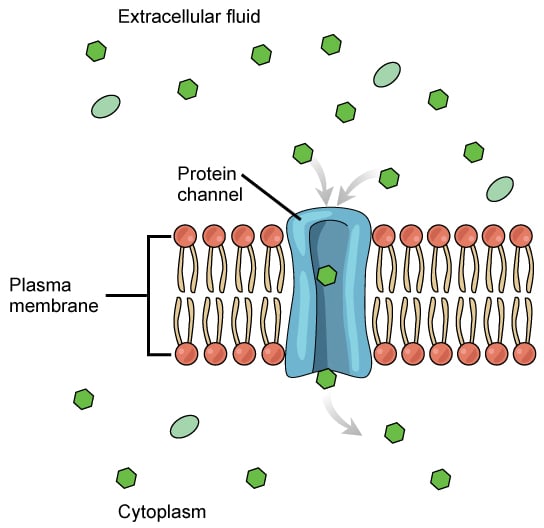
Channel protein (facilitated diffusion)
create hydrophilic holes to transport molecule, some are “gated” (can open and close)
have polar and non-polar parts
transport molecules faster
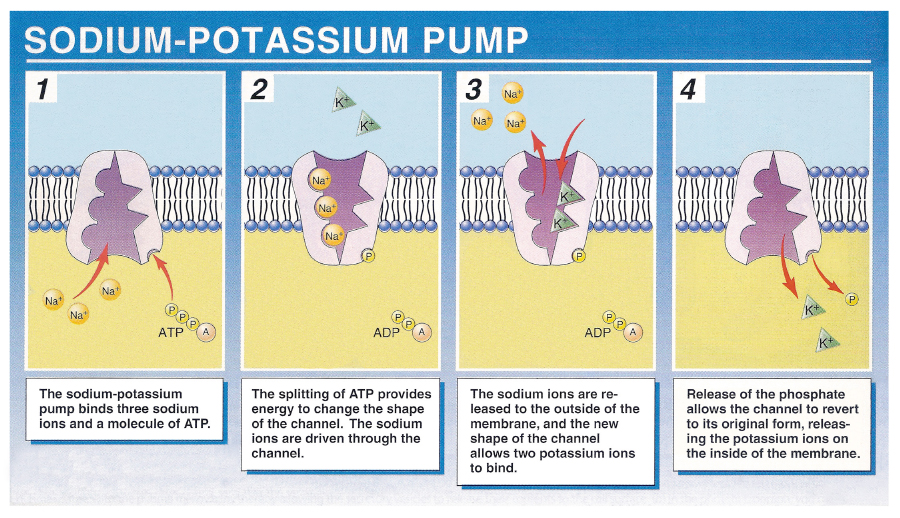
Carrier protein (facilitated diffusion/pump)
can change shape to move the molecules from one side of the membrane to another
transport slower bc have to change shape + “reset” each time
ex: glucose carrier, sodium-potassium pump
Cell transport
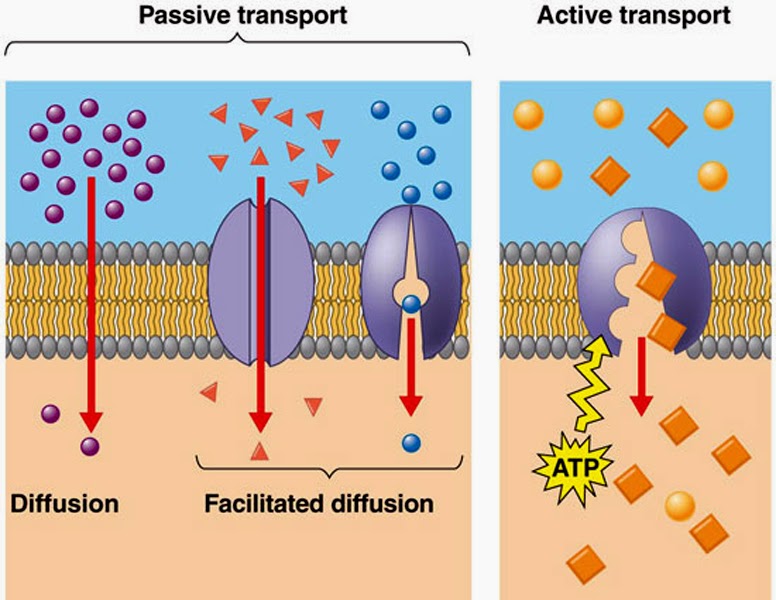
Passive transport (high→low, require no energy)
Facilitated Diffusion
Regular Diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport (low→high, require energy)
Protein pumps
endocytosis
exocytosis
toward/ up the concentration gradient
high → low
against/ down the concentration gradient
low → high
Regular/ simple Diffusion
some nonpolar molecules can pass through cell membrane by themselves (ex: oxygen, carbon dioxide)
Facilitated diffusion
for molecules that can’t pass through the cell membrane on their own
requires transport protein
ex: glucose carrier, polar molecules
Osmosis
the diffusion of water across a membrane
high solute concentration = low water concentration → solute takes up room, leaving less space for water
active pumps
a transport protein use ATP energy to move materials in/ out of cell
ex: sodium-potassium pump
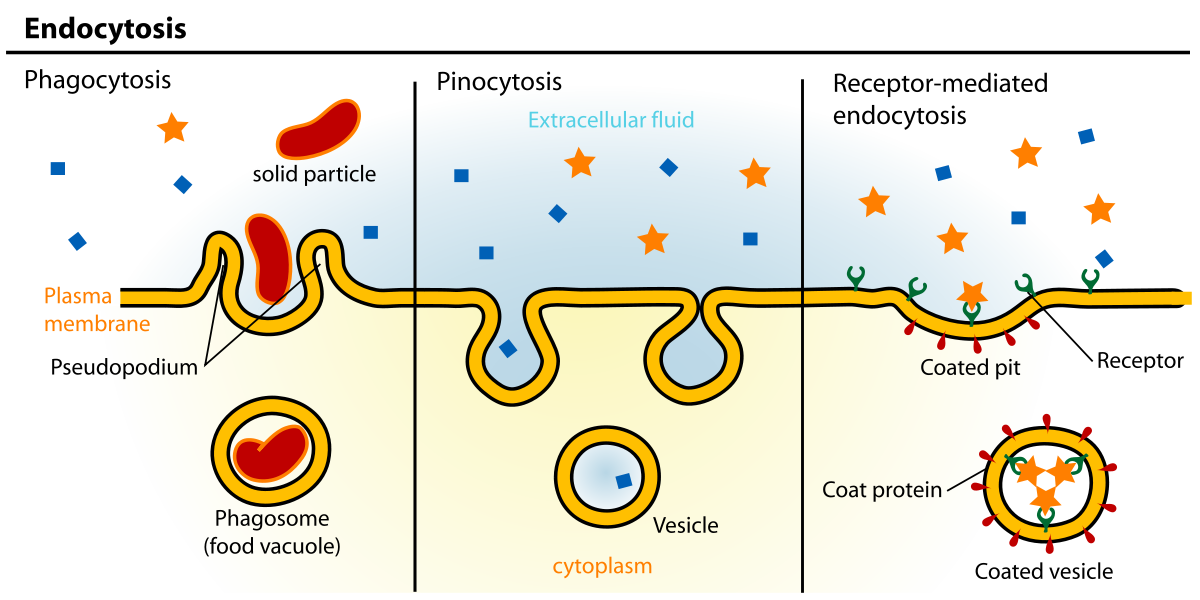
endocytosis (“endo” = in)
requires ATP energy,
cell membrane fuse with the substances → fusing substances usually will form vesicles around them → to bring them inside the cell
(vesicles are made out of the same material with the cell membrane → so it can be taken inside the cell)
Types:
pinocytosis: cell drinking (take in a fluid/ liquid)
phagocytosis: cell eating (take in a solid)
receptor-mediated endocytosis: bind to substances
Receptors
Proteins protruding from the cell membrane
detect specific compounds or cells in their environment.
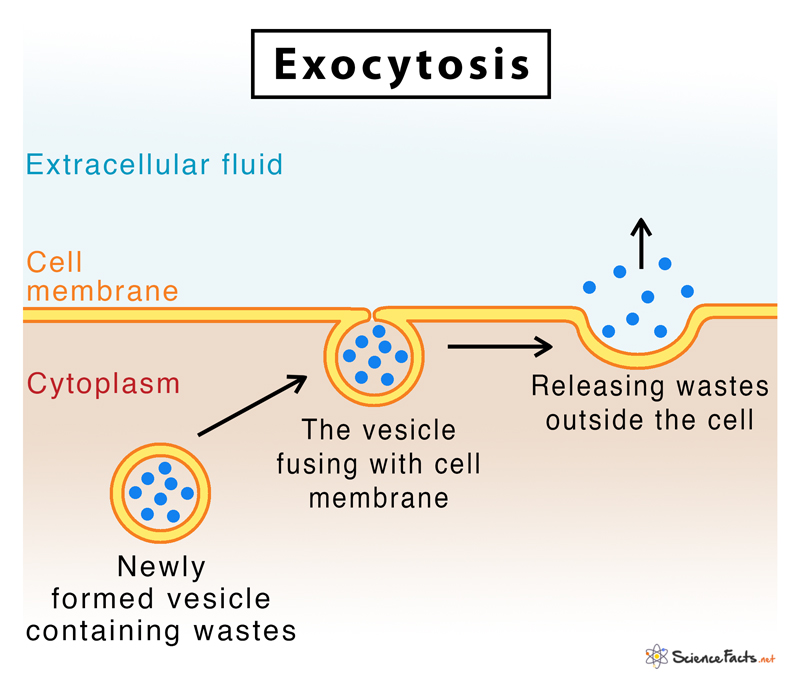
Exocytosis (“exo” = out)
requires ATP energy
allow substances to exit the cell
Golgi Apparatus (pack stuff) → vesicles → cell membrane
Factors affecting the rate of diffusion
Temp (warmer = faster)
Pressure (more particles = faster)
Agitation (Stirring)
Size of solute (smaller = travel faster)
Tonicity
describe the amount of solute in a solution
3 types of solutions
Isotonic (equal concentration)
Hypertonic (higher concentration)
Hypotonic (lower concentration)
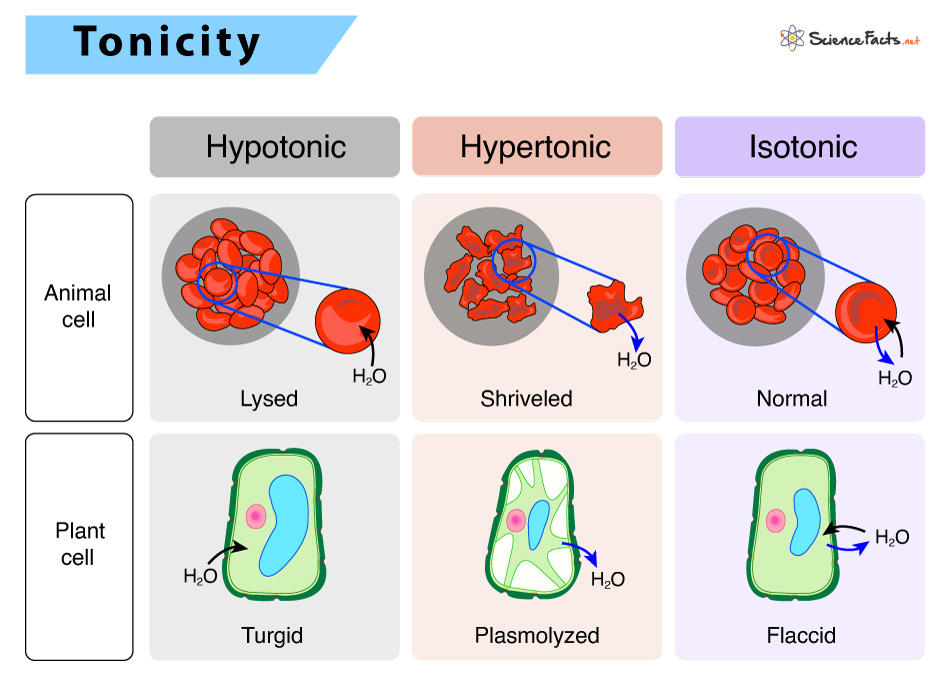
Isotonic
two solutions separated by a membrane that have equal concentration of solute
water content/ mass stays the same
hypertonic & cell shrinking
one solution has a higher concentration of solute
ex: salty water
Plasmolysis = cell shrinking (cytoplasm pull away from cell)
both plant and animal cells will lose water content/ mass → shrivel/ shrink
plant cells lose turgor pressure when placed in a hypertonic solution
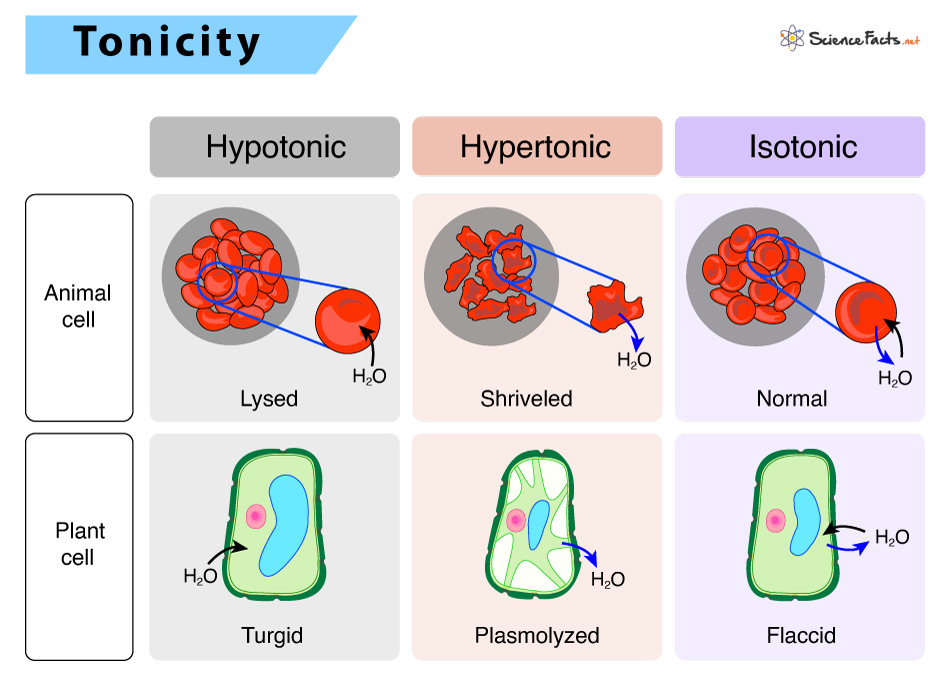
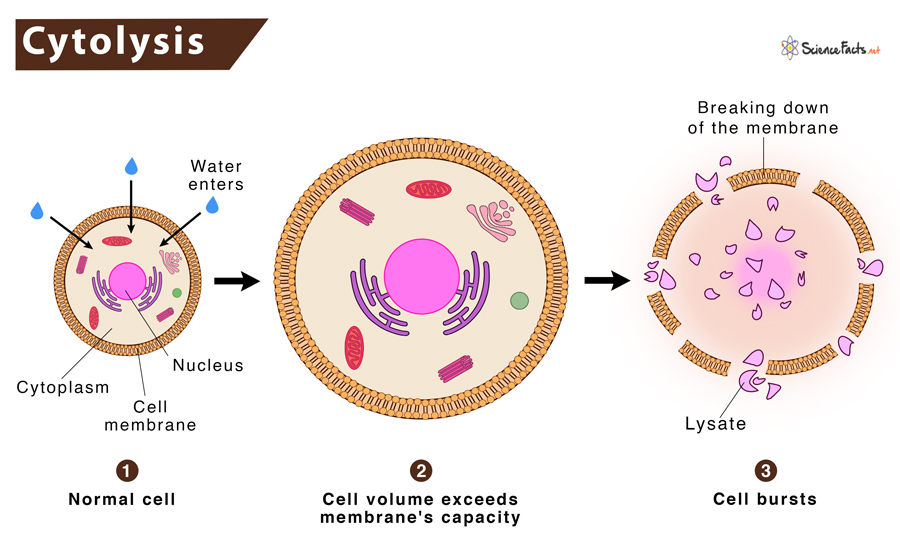
hypotonic & cell swelling
one solution has a lower concentration of solute
cell will gain water content/ mass when placed in hypotonic solution
Cytolysis = cell bursting
plant cells don’t burst bc they have cell walls → so they require hypertonic solution
animal cells can burst → so they require isotonic solution
Equilibrium
A state in an isolated chemical system in which the net flow/ overall distribution does not change
occurs once molecules are distributed evenly.
Molecules do not stop moving after reaching equilibrium
Leaf-cross structure
Mesophyll (middle layer): palisade, spongy
Upper and Lower Epidermis
Waxy Cuticle
Guard Cell
Stoma (stomata)
Veins: xylem, phloem
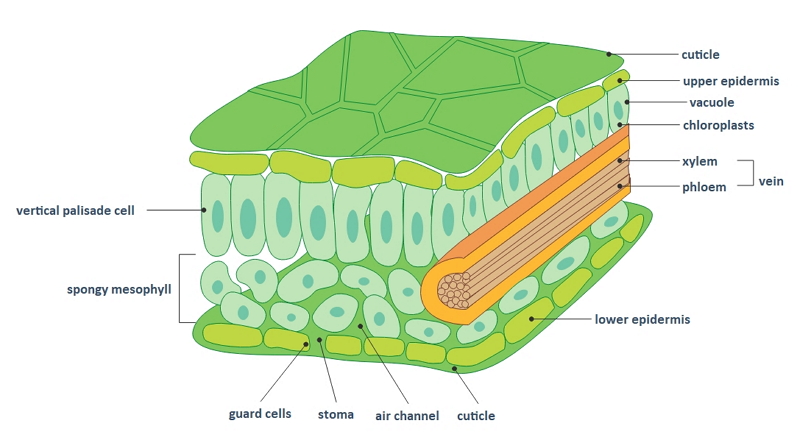
Palisade Mesophyll
long, narrow column-shaped cells packed closely together
located near the top of the leaf for max light exposure
contain the most chloroplasts
Spongy mesophyll
round cells, few chloroplasts
lots of space (air pockets) for gas exchange
Upper & Lower Epidermal Tissue
Tightly interlocked, transparent cell layer → transparent to allow light through
prevents physical damage, water loss
protects from diseases by making the cuticles
Waxy cuticle
made by epidermal cells
prevents water loss via transpiration
also acts as a defense against pathogens
hydrophobic → water droplets stay on the leaf instead of soaking in
guard cell
control the opening and closing of the stoma