ENT 220 Midterm
1/280
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
281 Terms
How many segments are in the head?
6
How many segments are in the thorax?
3
Plates in thorax
Notum (dorsal), Pleuron (lateral), Sternum (ventral)
How many segments are in the abdomen?
11
Dorsal, lateral ventral plates in the abdomen
Tergum (dorsal), Pleural membrane (lateral), Sternum (ventral)
Functions of the integument/exoskeleton
Resistancetodryingout
Metamorphosis
Sensory and neuro-motor sophistication
Mobile winged adults
Layers in the Cuticle
EPIcuticle
PROcuticle
EXOcuticle
ENDOcuticle
Layers in the integument
Cuticle and epidermis
5 layers in the epicuticle
Lacks chitin
cement layer
wax layer
superficial layer
Outer epicuticle
Inner epicuticle
What is chitin made of?
Rotating bundles of N-acetyl-D-glucosamine polymers
Sclerotization
Hydrogen bonding of chitin chains, Quinones (phenolic bridges) link proteins, Dehydration of protein chains
Arthrodial membrane
Unsclerotized cuticle, in between joints, caterpillar skin
Cuticle benefits
water movement
protection
barrier to pathogens and predators
crypsis
waste products (pigment, chemicals)
attaching muscles, provides leverage
Cuticle disadvantages
specific modifications for gas exchange
specific modifications for sensory reception
restriction on growth
molting- vulnerable physically, chemically, osmotically
Energetic cost of new exoskeleton that must be larger than the old one
5 Main sclerites in the head
vertex, gena, frons, clypeus, labrum
5 main mouthparts
Labrum, Mandibles (2), Maxillae (2) Hypopharynx, Labium
Prognathous
Forward jaw
Opisthognathous
Behind jaw
Hypognathous
Under jaw
Maxillary and labial palps function
chemosensory
Parts that make up the preoral cavity
Chemosensory
Suctorial Mouthparts
nectar feeding in Lepidoptera through proboscis
Piercing-sucking mouthparts
Wide variety of distantly related insects consume liquid food: herbivores (cicada), parasites (mosquitoes), adult fleas, carnivores (assassin bugs), elongated and toothed stylets enclosed by sheath (labium)
Sponging/lapping mouthparts
modifiedmouthpartsof “higher” flies (“suborder” Brachycera)
Chewing-lapping mouthparts
occur in adult bees; mouthparts modified to consume nectar and honey
Galea
elongated maxillae held together by spines and hooks, part of the proboscis, extended by increase in hemolymph pressure, coiled due to elasticity of cuticle and contraction of muscles, nectar sucked up by Cibarium
Hemiptera piercing and sucking mouthparts adaptations
Mandibles are long stylets
Maxillae form long interlocking stylets that form anterior food canal and posterior salivary canal
Efficient muscular pumps in head
All palpi lost and labrum reduced
Labium forms long, protective sheath
Mosquito special piercing and sucking mouthparts
Labium -Labellar lobes (modified palpi) for mopping up blood
Mosquito piercing and sucking mouthparts - 6 stylets
Scissor-like mandibles (2)
Drill-like maxillae (laciniae-mesial lobe of maxillary stipes) (2)
Labrum-epipharynx long, sharp— forms food canal (1)
Hypopharynx long, sharp— contains salivary canal (1)
Tsetse fly (Glossinidae) piercing and sucking mouthparts
Mandibles and maxillae lost
Labrum, hypopharynx, labium and maxillary palpi present and similar to mosquitoes
Labium with protrusible, spiny tip (piercing)
Stablefly (Muscidae) special piercing and sucking mouthparts
Rasping labellar lobes
House fly sponging mouthparts
labellar lobes with pseudotracheae modified for sponging up liquid food
Pseudotracheae
Open tubes that funnel food to the food canal in labrum
Horse flies piercing & sponging mouthparts
Mandibles, maxillae, hypopharynx swords, Labium with pseudotracheae, food canal formed by labrum-epipharynx & hypopharynx
Honeybees and bumblebees chewing-lapping mouthparts
“Tongue”: glossae (labium)
Surrounded by tube formed by galea (maxillae) and labial palp
Sucking pump and tongue draw up nectar
Mandibles not directly used in feeding
Maggot rasping mouthparts
Highly reduced, mouth hooks used for rasping, Myiasis, predation, decomposing
Odonata (dragonflies, damselflies) Seizing-Grasping mouthparts
Labium elongate, grasping and prehensile hooks, Thoracic / abdominal muscle contraction = hemolymph pressure
Neuroptera & diving beetle larvae Mandibulosuctorial mouthparts
Mandibles & maxillae form scythe-like feeding tubes, contain salivary (poison) canal
Aquatic filtering adaptations in Diptera (Fly) larvae
Labrum with brushes: feeding currents in mosquitoes
Antennae: grasping food
1st body segment name
PROthorax and FOREleg
2nd body segment name
MESOthorax, MIDleg, FOREwings
3rd body segment name
METAthorax, HINDleg, HINDwings
Thoracic sclerites
Notum (dorsal); Pleuron (lateral); Sternum (ventral)
PTEROthorax
Consists of the MESO and METAthorax
Pleuron sclerite sections
episternum (anterior) and epimeron (posterior) by pleural suture (ridge)
Specialized legs for cursorial locomotion
elongate, more distance, less effort, well developed femora and tibiae on all legs
Specialized legs for SALTATORIAL locomotion
Located on metathorax (HINDLEG), Enlarged femora/tibiae, Legs anchored by tarsal claws/pads, stored elastic energy released
Specialized legs for NATATORIAL locomotion
mid and hind legs flattened, row of setae (tibia and/or
tarsi), anterior movement, legs rotated
Specialized legs for FOSSORIAL locomotion
forelegs modified for digging, toothed projections from femur/tibia to rake soil, tarsi reduced
Specialized legs for RAPTORIAL locomotion
generally located on prothorax, to grasp prey for feeding, metathoracic in some parasitic wasps, “hanging flies”, large depressor muscles
Function of wing remigium
power & movement
8 main veins in wings
pre costa (PC)
costa (C)
sub costa (Sc)
radius (R)
media (M)
cubitus (Cu)
anal (A)
jugal (J)
Tegmina
Thickened leathery forewing modification
Elytra
Hardened forewings in beetles (Coleoptera)
Hemelytra
Forewings have a thickened base; Apical is membranous, in Heteroptera (true bugs)
Haltere
Reduced wings that act as a stabilizer or balancer
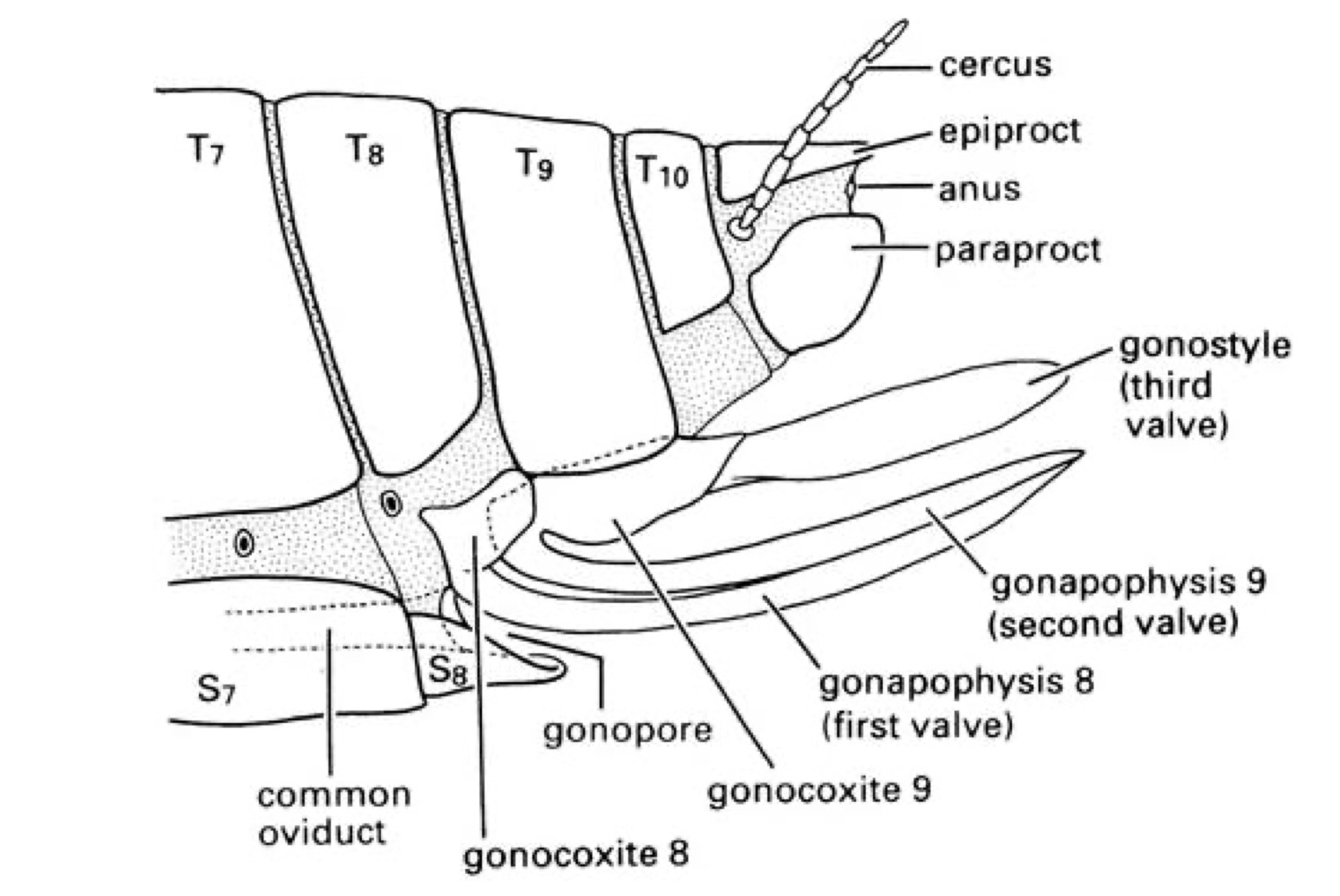
Which body segments bear genitalia?
8 and 9
How many body segments are in the abdomen?
11
Appendicular (“true”) ovipositors
Formed from appendages of A8 and A9, have 3 pairs of valves, Primitive condition, in some Odonata, Orthoptera, some Hemiptera, Hymenoptera
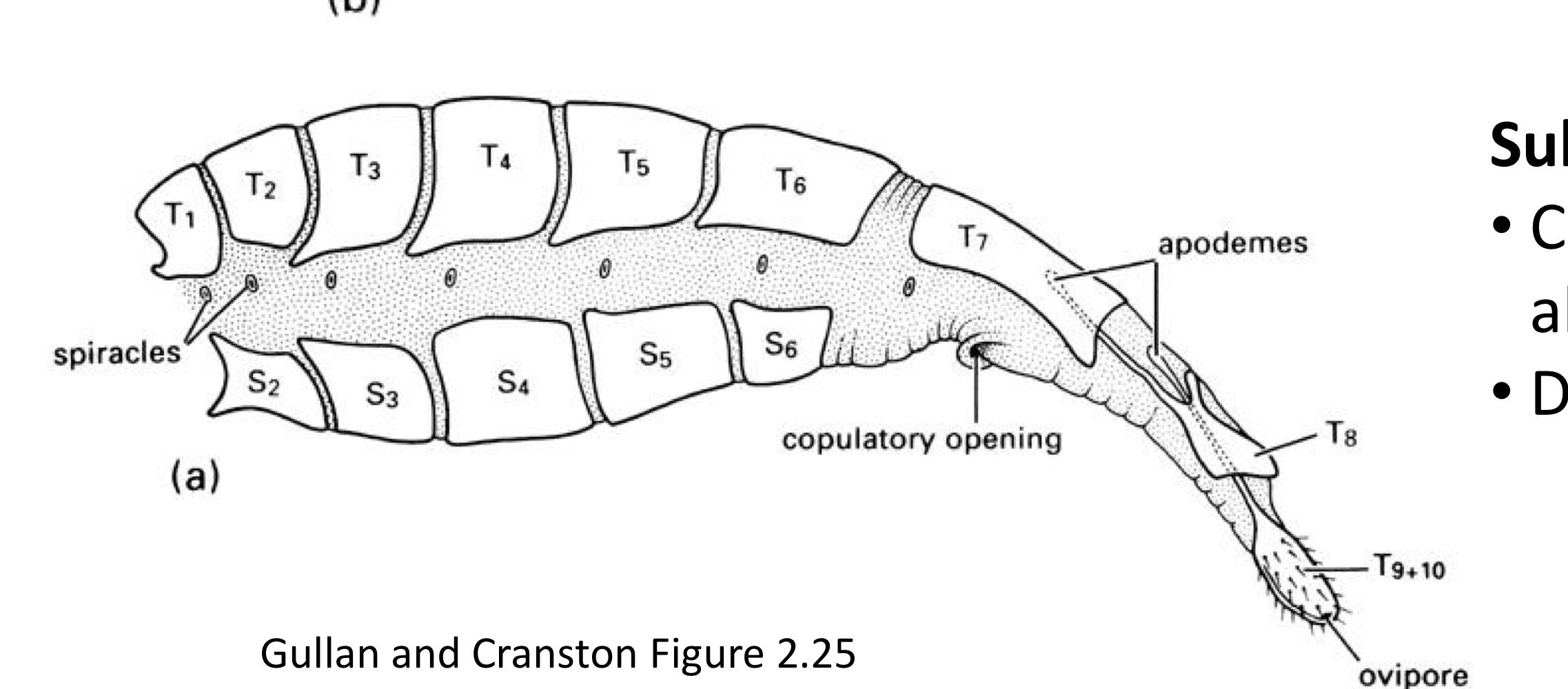
Substitutional ovipositors
Composed of extensible posterior abdominal segments, derived convergently several times, in Lepidoptera, Coleoptera, Diptera, Terminalia is telescopic, Manipulated by muscles attached to apodemes
Aedeagus
whole copulatory organ, structures of ninth abdominal segment, includes sclerotized penis
Stomodeum
Foregut, ectoderm and replaced at molt
Mesenteron
Midgut, endoderm and retained at molt
Proctodeum
Hindgut, ectoderm, replaced at molt
Digestion process
Grinding in the preoral cavity
Swallow with muscular pharynx
Food to esophagus
Crop for storage
Proventriculus to regulate food passage
Cibarium
Forms upper area of the pre-oral cavity
Salivarium
Forms lower area of the preoral cavity, connection to salivary glands
Dilator muscles
In the preoral cavity, made of pharyngeal muscles and cibarial pump
Proventriculus
Located in the preoral cavity, has grinding teeth
Peritrophic membrane
Located in the midgut, Formed by chitin, surrounds food bolus, permeable to enzymes, protects epithelial cells, compartmentalizes digestion (cyclic), secreted with feces
Structures located in the midgut
gastric caecae increase surface area for nutrient absorption
gut epithelium one cell layer thick
epithelial cells produce and secrete enzymes (lipases, amylases, proteases)
peritrophic membrane protects epithelium
after digestion pyloric valve relaxes-remaining material to hindgut
Modifications to digest liquid food
Narrowing of mouth tube to increase liquid flow
Esophageal diverticulum to store liquid
Salivary gland secrete or regurgitate ventricular fluids (Anticoagulants,toxins, histolysing)
Filter chamber
digestive specialization
Anterior and posterior section of midgut touch in enclosed membrane
water shunted to hindgut
food concentrated in midgut
In many Hemiptera
osmoregulation not disturbed
Used for sap because of low nutrients in it
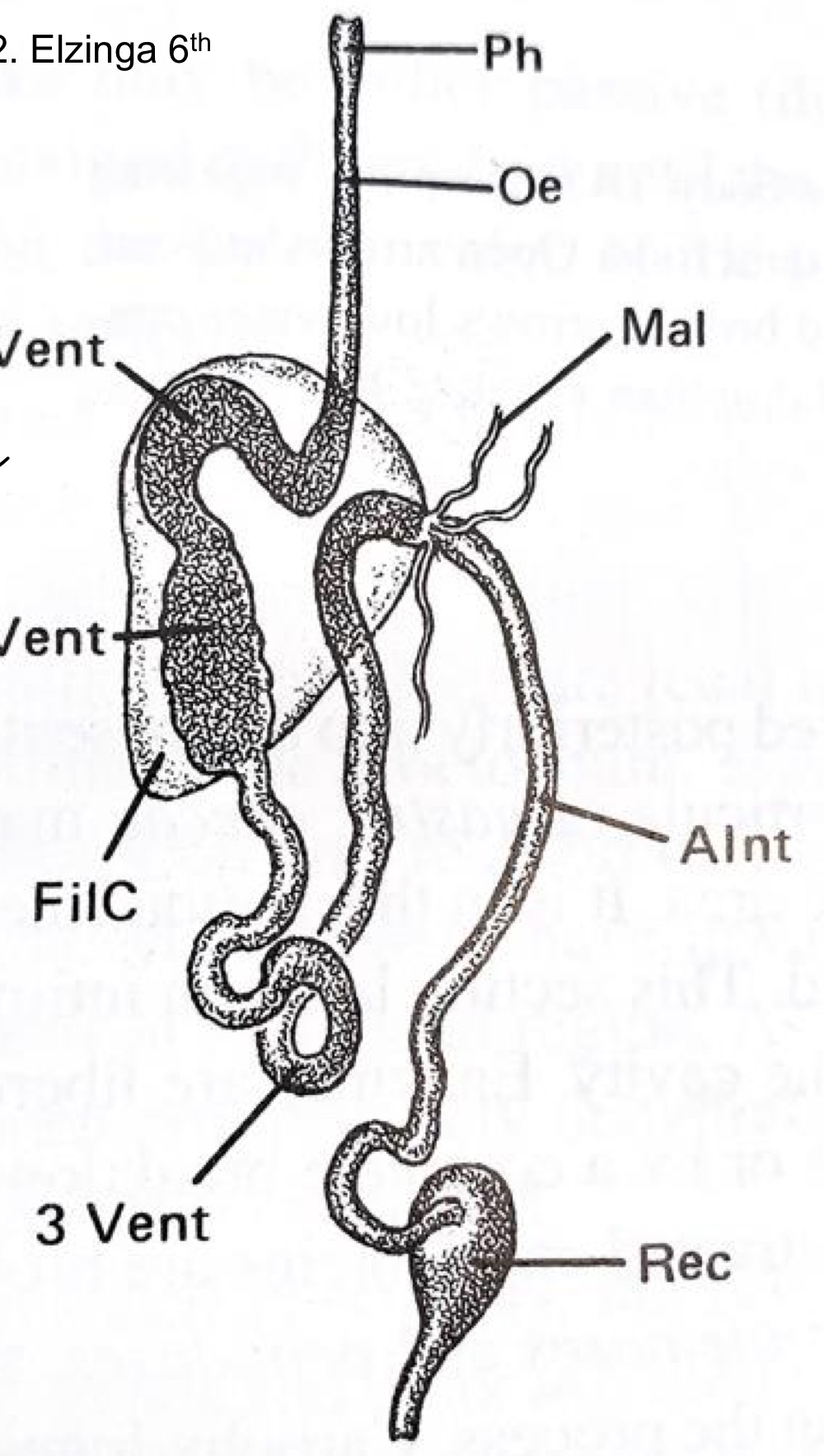
Function of the foregut
Resorption of water and ions (NA+, K+,CL–)
Defined by entry of Malpighian tubules
Rectum
Concentrates waste while avoiding toxicity (e.g. Nitrogen)
Often houses bacterial endosymbiont
Insect symbionts
Bacteria/protozoa/fungi in gut
Provide sterols for moulting and carotenoids for eyes
May have to reinoculate/relocate post-molt
Sit in midgut
Malpighian tubules
in the foregut
Outgrowth of the alimentary canal
Ends freely in the body cavity
Range 2 or > 200. Aphids only insects without them
Produce filtrate from hemolymph
Cryptonephric system
preserve water in dry habitats
distal end of the Malpighian tubules are in contact with the rectum
ex. Tenebrio molitor
Function of the rectum
reabsorb water
Rectal epithelium thickened to form rectal pads
Specialized cells in rectal pads carry out active recovery of Cl-
Pumping Cl- creates electrical and osmotic gradients for absorption of H2O, salts, sugars and amino acids
Bug nitrogenous waste types
ammonia: highly toxic
uric acid: less toxic, store N
Urea: rare
Fat body
Equivalent to vertebrate liver
Synthesizes, stores, and metabolizes fats, carbohydrates, proteins
Loose network of cells associated with connective tissues of body
site of glycogen deposition and storage
Stores insect yolk vitellogenins
Releases Trehalose (blood sugar)
Hemocoel
insect body cavity, with sinuses separated by septa, has hemolymph
Hemolymph function
Nutrient transport
Waste transport
Hormone transport
Heat transfer
Chemical defense
Hydrostatic skeleton (soft larvae)
Hatching, molting
Wing enlargement
Movement
What is Hemolymph made of?
Plasma (liquid) + Hemocytes (blood cells)
What is circulatory plasma made of?
Water (50-90%)
Inorganic ions (varies with diet)
Waste (uric acid)
Organic acids
Sugars
Mainly trehalose; (glycerol in some)
Lipids
Hexamerins→storage proteins
Lipophorin→transport lipids
JH-binding proteins (juvenile hormone)
4 main Hemocyte functions
Phagocytosis
Encapsulation of parasites and large foreign material
Hemolymph coagulation
Storage and distribution of nutrients
Does not carry oxygen
Dorsal vessel
“heart”
Simple tube of myocardial cells
Lies in pericardial sinus above dorsal diaphragm
Dorsal diaphragm
in the circulatory system
Connective tissue
Alary muscles move fluid up
Support dorsal vessel
Has septa
Ostia
Segmentally arranged openings of dorsal vessel for hemolymph, Act as one-way valves
Circulatory pathway
Enters pericardial sinus
Via dorsal diaphragm septa
Posterior end
Moves to dorsal vessel – Via ostia
Dorsal vessel contracts – Posterior to anterior
Leaves aorta
Circulates postero-ventrally – expansion of the abdomen, anterior to posterior
Ventral diaphragm
Fibromuscular septum
Aids circulation
Peristaltic contractions
Pumps hemolymph backwards & laterally in perineural sinus
No ostia
Accessory pulsatile organs
pumps blood to but not inside appendages
Pumps blood to base of antennae, wings, legs, cerci
Spiracles
External openings
Up to 10 pairs: 2 thoracic; 8 abdominal
Lack of O2 or build-up of CO2 initiates opening
Closed most of the time for water conservation
Tracheae
Develop as paired invaginations of epidermis (ectodermal origin)
Has sclerotized taenidia for support
Shed at molting
Tracheoles
Fine tubules of gas exchange system that contact cells
<1 μm diameter
Not always shed at moulting
Taenidia
Sclerotized spiral thickenings for tracheal support
Flexible but resists compression
Intima
ectodermally derived internal cuticle
inner lining of tracheae, foregut, hindgut
In tracheae: has wax, cuticulin, and chitin layers
shed during molt
helps prevent O2 absorption and H2O loss
3 phase discontinuous gas exchange
Closed spiracular phase→consume O2 from tracheae, levels drop
Flutter phase→spiracles rapidly open/close, O2 enters but CO2 keep building up
Open spiracular phase→exchange O2, CO2 and H2O
What structures aid in Diffusion & Ventilation
Air sacs
body compression→thorax & abdomen
rapid compression and expansion of trachea
coordinated opening and closing of spiracles
Hemolymph movements
Air sacs
tracheal dilations
assist in flight: increase buoyancy
reservoir for oxygen
increase tidal air flow
decrease mass of flying insects
distribution of cooler air
Forms space for molting
tympanic structures
Helps to escape pupal case
Siphon (Terminal spiracle)
helps insects to breathe in water
suspends from water meniscus
direct connection between atmosphere & spiracles in terminal respiratory siphon
water repellent hairs at tip of siphon