Biology - Introduction to Molecular Genetics
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
DNA → RNA →Proteins
Central Dogma of Molecular Genetics
What enzyme is used to go from RNA → DNA
Reverse Transcriptase
Nucleoside
sugar (ribose/deoxyribose) + nitrogenous base; no phosphate
Nucleotide
sugar (ribose/deoxyribose) + nitrogenous base + phosphate
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
-OH is present at 2’ and 3’
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (RNA)
-OH ONLY at 3’
Which Nucleotide is a Purine
A and G
PURe As Gold
Which Nucleotides are Pyrimidines?
T, U, and C
CUT the PYe
A pairs with
T in DNA
U in RNA
G pairs with
C
How many hydrogen bonds between C and G
3
How many hydrogen bonds between A and T (or U)
2
Nucleosome
Structures composed of DNA wrapped around a histone proteins
Chromatin
DNA packing patterns within a chromosome due to the organization of nucleosomes
Euchromatin
loosely packed
DNA is easily accessible for transcription
Heterochromatin
Tightly packed
DNA is most inaccessible for transcription
Acetylation
Addition of negatively charged acetyl group to a histone
Loosens nucleosome packing
Deacylation
Removes acetyl group; makes overall charge more positive
Tightens nucleosome making DNA less accessible for transcription
Methylation
Can tighten or loosen DNA
Usually keeps inactivated genes inactivated
Steps of DNA replication
Initiation
Elongation
Replication
Initiation
Relies on creation of the origin of replication
A special enzyme will recognize the origin of replication and begin replication
What is an Origin of Replication?; How is it formed?
The beginning point for DNA replication
Has a high density of AT bonds; AT only has 2 hydrogen bonds meaning this area has a weaker bond making it easier to pull apart
Circular DNA has 1; Linear DNA has multiple
DNA in Prokaryotes
Circular
One origin of replication
DNA in Eukaryotes
Linear DNA
Multiple origins of replication
Initiation Phase Replication Enzymes
Helicase: unzips DNA by breaking H bonds; Creates replication fork; causes supercoiling
Topoisomerase: relieves built up tension from supercoiling by nicking the DNA
Helicase
unzips DNA by breaking H bonds
Creates replication fork
causes supercoiling
Topoisomerase
relieves built up tension from supercoiling
Periodically cuts one strand to allow DNA to unwind then reattach
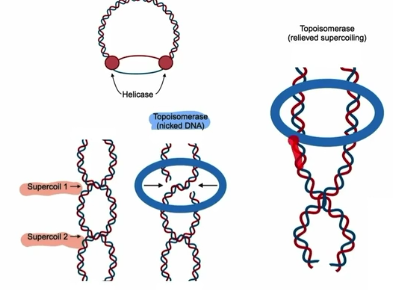
DNA Elongation Enzymes
Single Stranded Binding Proteins (Not an Enzyme)
DNA polymerase
Primase
SSBs
Prevents DNA strands from reattaching
DNA polymerase
Elongates new DNA strands by adding nucleotides
Needs a free 3’ hydroxyl group
Adds nucleotides from 5’ to 3’
Replaces RNA primers (from primase) with DNA
Primase
places an RNA primer complementary to the DNA strand
Provides free 3’OH for DNA polymerase; creates starting point for nucleotide addition
Leading strand
continuously synthesized
3’ end faces the opening of the DNA fork
Lagging strand
Synthesized not continuously
3’ end faces away from the opening of the replication fork
Okazaki Fragments
Caused by the lagging strand
Short DNA fragments that compose the growing lagging strand
Ligase
Seals together the okazaki fragments
Creates coherent complementary strands
Termination
DNA replication will terminate when the end of the chromosome is reached
Some nucleotides at the end points go unreplicated and are lost
Telomeres
Non Coding repetitive DNA segments at the end of the chromosomes
Buffer against loss of critical genetic information
Located beyond coding DNA
Telomerase
Replaces lost nucleotides with new ones maintaining the telomeres
In which direction does DNA polymerase read the template strand?
3’ to 5’ (opposite of how it adds nucleotides)
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Protein encoding RNA
RNA that is part of DNA → RNA → Protein
RNA polymerase
Enzyme responsible for reading DNA template and generating a new RNA transcript
Template DNA strand
also called the anti sense and non-coding DNA strand
strand transcribed by RNA polymerase and is complementary to the RNA transcript
Coding/Sense DNA strand
The strand not being read by the RNA polymerase
Identical to new RNA transcript except T is U
promoter sequence
where RNA polymerase binds to
Translation and Transcription in Eukaryotes
occur in different location
Transcription happens in nucleus
Translation happens in the cytoplasm
Translation and Transcription in Prokaryotes
occur in the same location
Transcription and Translation happen simultaneously in the cytoplasm
Initiation of prokaryotic transcription
RNA polymerase opens transcription bubble
Operon
Serveal genes packaged together and transcribed all at once
Controlled by one promoter
Operator region closely associated with promoter
Operon regulation
repressors bind to the operator region
promoter bind to the promoter region
lac-operon
Inactive without stimulation;must be induced to become active
Genes involved: lacZ lacY and lacA
Encodes for different proteins which are all involved in lactose metabolism
Turns on when glucose is not available as an energy source
lac repressor protein
Constitutively expressed (always produced under normal conditions)
When lactose is present it is converted into allolactose
Allolactose binds to repressor protein and activates lac-operon
Allolactose is an inducer
CAP site in prokaryotes
found upstream from RNA polymerase
cAMP activates the cap protein
Low glucose = high cAMP
cAMP presenses makes transcription go faster
trp-Operon
responsible for producing tryptophan
Default active unless repressed
Produces tryptophan synthetase which is responsible for Trp production
Repressed by product Tryptophan
Low tryptophan = allows for transcription
High tryptophan = inhibits RNA polymerase form transcription
Transcription factors (Eukaryotes)
DNA binding proteins that influence transcription
May help RNA polymerase bind to promoter regions of DNA
Includes activators and repressors
Promoter Sequences (Eukaryotic Transcription)
Site of RNA pol binding
TATA box: common DNA sequence found within promoter; may be recognized and bound by transcription factors
Enhancers (Transcription Factors < Eukaryotic Transcription)
DNA segments that bind activator proteins
When activator proteins bind this increase gene transcription
Silencers (Transcription Factors < Eukaryotic Transcription)
DNA segments that bind repressor proteins
When repressor proteins bind to there segment there is a decrease in gene transcription
Colocalization (Eukaryotic Transcription)
DNA bending protein will bend DNA to bring the promoter regions and silencers/Enhancers in close proximity to one another
Silencers/Enhancers can bind with transcription factors that can then bind with the promoter region to upregulate or downregulate the rate of transcription
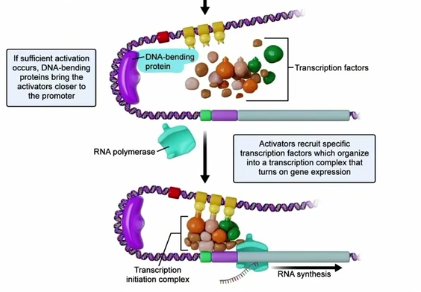
Poly-A-Signal ( Termination < Eukaryotic Transcription)
DNA sequence located within the termination sequence
Signal for transcription termination and dissociation of RNA polymerase
Sequence induces polyadenylation (the addition of many A; AAAAAAA); This will cause a weaker bond between the DNA and RNA transcript finally allowing the RNA to finally snap off
Terminator sequence
includes the Poly-A-tail signal that induces polyadenylation
transcription produces
pre-mRNA
Post-transcriptional modifications
Functional alterations to the RNA transcript post transcription
convert pre-mRNA into mRNA
mRNA
RNA used to encode for proteins in translation
Main types of post-transcriptional modifications
5’ capping
3’ polyadenylation
Splicing
5’ capping (Eukaryotic post translational modifications)
Cap is the 7-methylguanosine cap
Helps protect the mRNA transcript from enzyme degradation
Aids in ribosomal attachment to mRNA transcript
3’ poly a tail
Addition of poly-A-tail
Helps protect RNA transcription from degradation
Signals that mRNA is ready for export from the nucleus
Introns
Segments of DNA that do no code for proteins
Removed during splicing
Exons
DNA segments that encode for proteins
Spliceosome
Enzyme responsible for splicing during post transcriptional modifications
Alternative splicing
Pre-mRNA transcription containing many exons can be spliced into many mRNA variations
Resulting mRNAs will have different exon combinations
Alternative splicing allows for one pre-mRNA to encode for many proteins
miRNA
silence expression of mRNA transcripts
does this by base pairing with part of the mRNA transcript
A form of Post-transcriptional gene regulation
Silence mRNA translation
snRNA (Small nuclear RNA)
combines with proteins to make the functional portions of spliceosomes
snRNPs (Small nuclear RiboNucleoProteins)
snRNA and protein complex; spliceosome
Translation
mRNA → Proteins
Ribosomes
Enzyme responsible for facilitating translation of mRNA into proteins
catalyzes the peptide bond formation of the growing amino acid chain
Eukaryotic Ribosomal Subunits
60s and 40s
Forms the 80s subunit
Prokaryotic subunit
30s and 50s subunits
forms 70s ribosome
Codons
segment of an mRNA transcript that encode for 1 amino acid of for translations termination
made up of 3 RNA bases
Codon degeneracy
Multiple codons encode for the same amino acid
64 possible codons; only 20 amino acids
How many amino acids are there?
20
Start codon
AUG (Methionine)
Stop codons
UAA, UAG, UGA
Do not encode for any proteins
Signal for the end of translation
Open reading frame
Stretch of mRNA transcript in between the start and stop codon
Region of ribosome encoding
codons found in this frame will be part of translation to become proteins
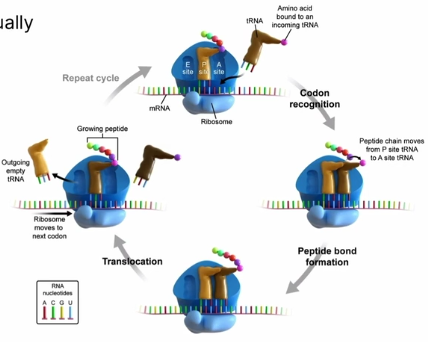
tRNA (transfer RNA)
tRNA brings amino acid to ribosome to be associated to mRNA
Links up amino acids
anticodon reads mRNA transcript; houses 3 bases that complements mRNA

A binding site
Where the tRNA first enters the ribosome
Where amino acid binds to the growing peptide chain
P binding site
houses the aminoacyl-tRNA that holds the growing polypeptide
E binding site
Exit Site
site where tRNA is is released from the ribosome; leaving the amino acid
Translocation
name for the movement of tRNA molecules through the A, P, and E binding sites
peptide chain in P site is transferred over to A site (where it will bond with the amino acid in the A site); the A site will now hold the polypeptide chain
Translation Termination
when a stop codon in reached
a release factor (with no new amino acid) will bind instead of a tRNA
Polypeptides chain is released from the last tRNA into the cytoplasm
The ribosome will dissociate into its 2 subunits
Protein folding (post translation)
structure of any protein is directly related to its function
chaperone protein assisits with folding
Chaperonin proteins
assist some newly synthesized polypeptide chains in folding to their proper shape
Ensures proper transition between primary protein structure into secondary protein structure
present in eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells
Base Substitutions (DNA Mutations)
when one nucleotide is replace by another
Silent mutations (DNA Mutations)
Single nucleotide change does not change the encoded amino acid
Relies of codon degeneracy (when codons encode for the same amino acid)
Missense (DNA Mutations)
single nucleotide change that changes the encoded amino acid
Nonesense mutation (DNA Mutation)
Conservative missense mutations
when the missense mutation does not change the polarity (polar/ non-polar) of the molecule
Frameshift mutations (DNA Mutations)
Insertion: Nucleotide addition from the DNA sequence
Deletions: Nucleotide removal from the DNA Sequence
Null mutations (DNA Mutations)
type of loss of function mutation where a null allele is produced ( a non-functional allele)
Chromosomal mutations
Affect an entire chromosome rather than just one nucleotide or a small series nucleotides
Include:
Deletion
Duplication
Inversion
Translocation
Deletion (Chromosomal Mutation)
Portion of a chromosome is deleted
Chromosomal arm shortening
